气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 830-838.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.043
中国近海光伏发电潜力预估及驱动因子分析
- 1 福建省气象服务中心,福州 350007
2 福建省气候中心,福州 350007
-
收稿日期:2025-02-28修回日期:2025-04-28出版日期:2025-11-30发布日期:2025-09-05 -
作者简介:曾颖婷,女,高级工程师,113236039@qq.com -
基金资助:福建省自然科学基金项目(2023J011336);华东区域气象科技协同创新基金项目(QYHZ202311)
Estimation of China’s offshore photovoltaic power generation potential and analysis of driving factors
ZENG Ying-Ting1( ), TANG Zhen-Fei2, WU Bin2, ZHOU Ming-Zhu1
), TANG Zhen-Fei2, WU Bin2, ZHOU Ming-Zhu1
- 1 Fujian Meteorological Service Center, Fuzhou 350007, China
2 Fujian Climate Center, Fuzhou 350007, China
-
Received:2025-02-28Revised:2025-04-28Online:2025-11-30Published:2025-09-05
摘要:
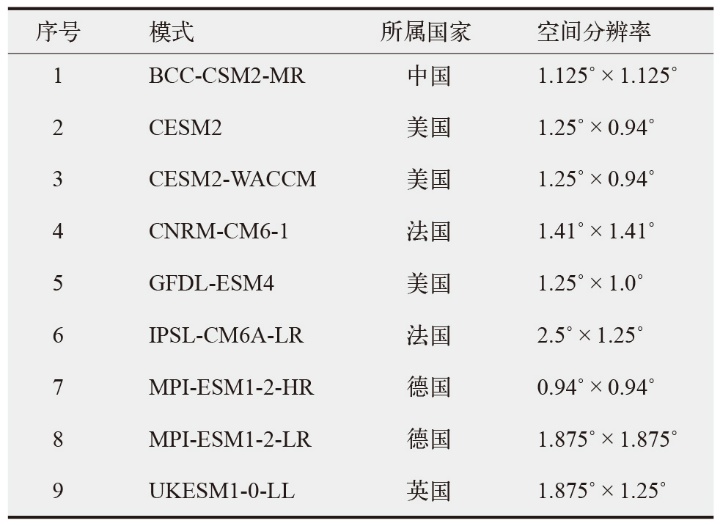
基于CMIP6资料,在SSP1-2.6和SSP5-8.5两种典型情景下,预估了近未来(2021—2060年)和远未来(2061—2100年)中国近海的光伏发电潜力相较于历史时期(1975—2014年)的变化,并分析了气候变化对未来光伏发电的潜在影响。结果表明,近未来时期,两种情景下的光伏发电潜力都呈现出在研究区北部增长、南部减少的趋势。SSP1-2.6情景下的光伏发电效率(PVP)最大增幅预估将超3%,约是SSP5-8.5情景下的1.8倍。远未来时期,SSP1-2.6情景下PVP转变为几乎整个研究区域都呈现出增长态势。从月变化来看,SSP1-2.6情景下近未来和远未来的全年PVP都将增加,最大增幅均出现在2月,分别为2.18%和4.20%。SSP5-8.5情景下两个时期PVP都在6—9月呈现出负变化,8月减少最明显。地表向下短波辐射(RSDS)对PVP变化的影响大于气温,是驱动PVP变化的主要原因。研究结果将为海上太阳能开发利用及能源规划管理提供重要参考。
引用本文
曾颖婷, 唐振飞, 吴滨, 周明珠. 中国近海光伏发电潜力预估及驱动因子分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 830-838.
ZENG Ying-Ting, TANG Zhen-Fei, WU Bin, ZHOU Ming-Zhu. Estimation of China’s offshore photovoltaic power generation potential and analysis of driving factors[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 830-838.

图1 1975—2014年中国近海多年平均辐射、气温和风速的模拟场相对于观测场(ERA5)的泰勒图(a) QM偏差订正前,(b) QM偏差订正后
Fig. 1 Taylor diagrams of the simulated fields relative to the observed fields (ERA5) for the multi-year average radiation, temperature, and wind speed over the offshore China from 1975 to 2014. (a) Before QM bias correction, (b) after QM bias correction
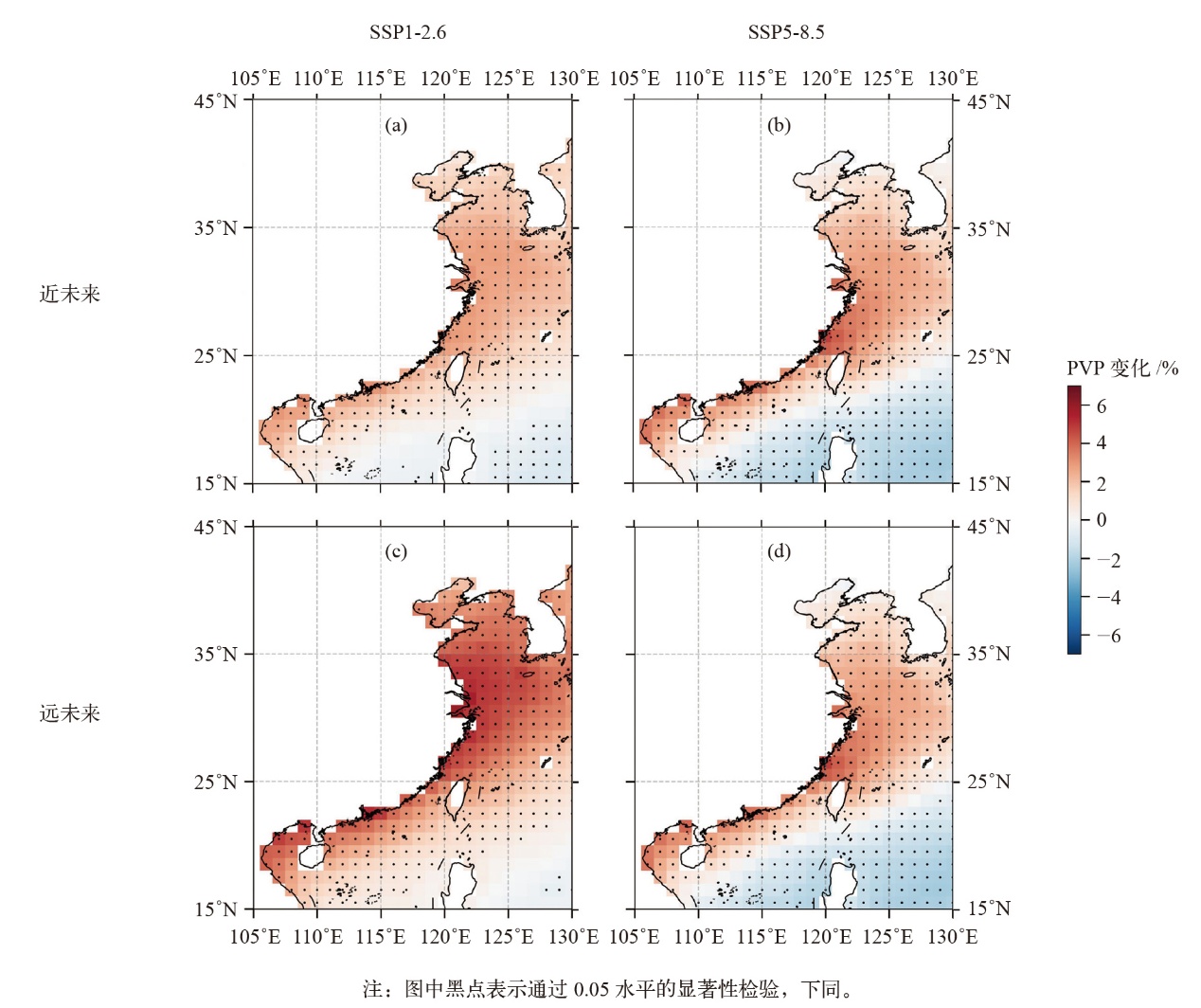
图2 SSP1-2.6和SSP5-8.5情景下近未来(a、b)和远未来(c、d)相对于历史时期的年平均光伏发电效率(PVP)的变化
Fig. 2 Changes in annual average photovoltaic power potential (PVP) in the near future (a, b) and far future (c, d) relative to the historical period under SSP1-2.6 and SSP5-8.5 scenarios. (Black dots indicate significance tests passed at the 0.05 level)
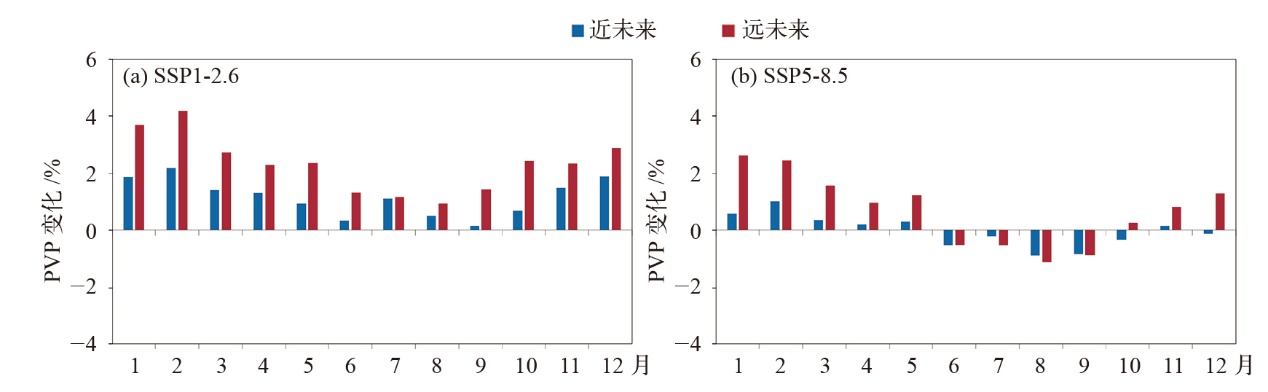
图3 SSP1-2.6 (a)和SSP5-8.5 (b)情景下未来PVP相对于历史时期的多年平均月变化
Fig. 3 Monthly change in future PVP under the SSP1-2.6 (a) and SSP5-8.5 (b) scenarios relative to the multi-year average for the historical period
图4 SSP1-2.6和SSP5-8.5情景下近未来和远未来时期地表向下短波辐射贡献的PVP变化
Fig. 4 PVP changes contributed by surface downwelling shortwave radiation in near- and far-future under SSP1-2.6 and SSP5-8.5 scenarios
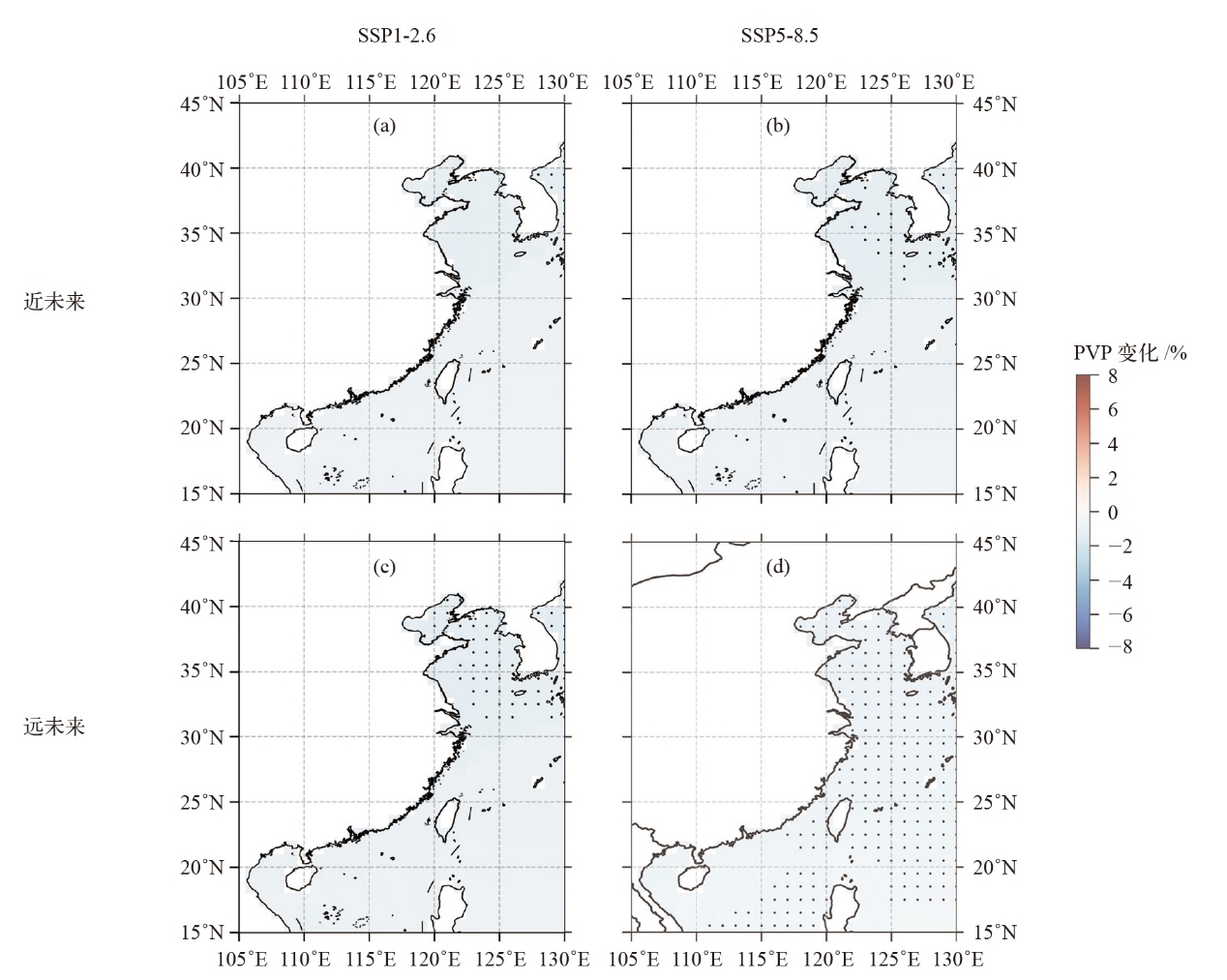
图5 SSP1-2.6和SSP5-8.5情景下近未来和远未来时期近地表气温贡献的PVP变化
Fig. 5 PVP changes contributed by near-surface air temperature in near- and far-future under SSP1-2.6 and SSP5-8.5 scenarios
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2023: synthesis report[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023 |
| [2] | Meinshausen M, Meinshausen N, Hare W, et al. Greenhouse-gas emission targets for limiting global warming to 2 degrees C[J]. Nature, 2009 (458): 1158-1162 |
| [3] | Allen M R, Frame D J, Huntingford C, et al. Warming caused by cumulative carbon emissions towards the trillionth tonne[J]. Nature, 2009 (458): 1163-1166 |
| [4] | Matthews H D, Gillett N P, Stott P A, et al. The proportionality of global warming to cumulative carbon emissions[J]. Nature, 2009 (459): 829-832 |
| [5] |
吴亚楠, 周庆伟, 武贺, 等. 中国近海太阳能资源特征分析及储量评估[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44 (12): 162-169.
doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2022-1293 |
|
Wu Y N, Zhou Q W, Wu H, et al. Characteristics analysis and reserve evaluation of offshore solar energy resources in China[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44 (12): 162-169 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.19912/j.0254-0096.tynxb.2022-1293 |
|
| [6] |
Li X, Mauzerall D L, Bergin M H. Global reduction of solar power generation efficiency due to aerosols and panel soiling[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2020, 3 (9): 1-8
doi: 10.1038/s41893-020-0471-3 |
| [7] | Gil C L T. Impact of climate change on solar irradiation and variability over the Iberian Peninsula using regional climate models[J]. International Journal of Climatology: A Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2019, 39 (3). DOI: 10.1002/joc.5916 |
| [8] | Vliet M T H V, Wiberg D, Leduc S, et al. Power-generation system vulnerability and adaptation to changes in climate and water resources[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016. DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2903 |
| [9] | Jennifer C, Gabrial A, Olivier D. Climate change impacts on the energy system: a review of trends and gaps[J]. Climatic Change, 2018: 1-15 |
| [10] | UNFCCC. Adoption of the Paris Agreement[R]. Geneva, Switzerland: United Nations Office at Geneva, 2015 |
| [11] | Kimon K, Florian F, Ana D V, et al. Global energy and climate outlook 2021: advancing towards climate neutrality[R/OL]. 2021 [2025-04-01]. https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC126767 |
| [12] | Wild M, Folini D, Henschel F, et al. Projections of long-term changes in solar radiation based on CMIP5 climate models and their influence on energy yields of photovoltaic systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2015 (116): 12-24 |
| [13] | Arvizu D, Balaya P, Cabeza L, et al. Direct solar energy. Special report on renewable energy sources and climate change mitigation[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2011 |
| [14] | Jerez S, Tobin I, Vautard R, et al. The impact of climate change on photovoltaic power generation in Europe[J]. Nature Communication, 2015 (6). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10014 |
| [15] | Costa S C, Diniz A S A, Kazmerski, L L. Dust and soiling issues and impacts relating to solar energy systems: literature review update for 2012-2015[J]. Energy, Ecology, and Business, 2016 (63): 33-61 |
| [16] | Gutiérrez C, Somot S, Nabat P, et al. Future evolution of surface solar radiation and photovoltaic potential in Europe: investigating the role of aerosols[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2020, 15: 4035 |
| [17] |
Davy R, Gnatiuk N, Pettersson L, et al. Climate change impacts on wind energy potential in the European domain with a focus on the Black Sea[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018, 81 (P2): 1652-1659
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.253 URL |
| [18] | Karnauskas K B, Lundquist J K, Zhang L. Southward shift of the global wind energy resource under high carbon dioxide emissions[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2017. DOI: 10.1038/s41561-017-0029-9 |
| [19] | Yang L, Jiang J, Liu T, et al. Projections of future changes in solar radiation in China based on CMIP5 climate models[J]. Global Energy Interconnection, 2018, 1 (4): 452-459 |
| [20] | 邓荔. 不同排放情景达到碳中和下中国区域气候变化的预估[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2023. |
| Deng L. Projection of climate change in China under carbon neutral scenarios[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 杨晨辉, 王艳君, 苏布达, 等. SSP“双碳”路径下赣江流域径流变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18 (2): 177-187. |
| Yang C H, Wang Y J, Su B D, et al. Runoff variation trend of Ganjiang River basin under SSP “Double Carbon” path[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18 (2): 177-187 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
O′Neill B C, Tebaldi C, van Vuuren D P, et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP 6[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9 (9): 3461-3482
doi: 10.5194/gmd-9-3461-2016 URL |
| [23] |
Gidden M J, Riahi K, Smith S J, et al. Global emissions pathways under different socioeconomic scenarios for use in CMIP6: a dataset of harmonized emissions trajectories through the end of the century[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019, 12 (4): 1443-1475
doi: 10.5194/gmd-12-1443-2019 URL |
| [24] |
Tebaldi C, Debeire K, Eyring V, et al. Climate model projections from the Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) of CMIP 6[J]. Earth System Dynamics, 2021, 12 (1): 253-293
doi: 10.5194/esd-12-253-2021 URL |
| [25] | Kriegler E, Bauer N, Popp A, et al. Fossil-fueled development (SSP5): an energy and resource intensive scenario for the 21st century[J]. Global Environmental Change: Human and Policy Dimensions, 2017 (42): 297-315 |
| [26] |
Mavromatakis F, Makrides G, Georghiou G, et al. Modeling the photovoltaic potential of a site[J]. Renewable Energy, 2010, 35 (7): 1387-1390
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2009.11.010 URL |
| [27] |
Chenni R, Makhlouf M, Kerbache T, et al. A detailed modeling method for photovoltaic cells[J]. Energy, 2007, 32 (9): 1724-1730
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2006.12.006 URL |
| [28] |
Boé J, Terray L, Habets f, et al. Statistical and dynamical downscaling of the Seine basin climate for hydro-meteorological studies[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2007, 27 (12): 1643-1655
doi: 10.1002/joc.v27:12 URL |
| [29] | 黄云飞, 龙银平, 马启民, 等. 基于CMIP6的2015—2100年中国气象干旱指数高分辨率数据集[J/OL]. 2025 [2025-04-01]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.6035.N.20250703.1231.002. |
| Huang Y F, Long Y P, Ma Q M, et al. A dataset of high-resolution meteorological drought indices under the CMIP6 framework in China (2015-2100)[J/OL]. 2025 [2025-04-01]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.6035.N.20250703.1231.002 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 郑衍欣, 李双林, 何源. 共享社会经济路径(SSPs)下未来30年长江流域夏季降水预估[J]. 大气科学, 2023, 47 (5): 1405-1420. |
| Zheng Y X, Li S L, He Y. Projection of summer rainfall in the Yangtze River basin in the next 30 years under different shared socioeconomic pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2023, 47 (5): 1405-1420 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | Zuluaga C F, Avila-Diaz A, Justino F B, et al. The climate change perspective of photovoltaic power potential in Brazil[J]. Renewable Energy, 2022 (193): 1019-1031 |
| [1] | 肖雪, 黄萌田, 周佰铨, 王晨鹏, 翟盘茂. 2022年青藏高原复合高温干旱事件对区域植被的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 777-788. |
| [2] | 郭艳君, 邹成智. 风云三号D星气温观测气候变化应用稳定性评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 733-741. |
| [3] | 王胜, 陈健, 周宇, 孙佳丽, 翟振芳, 谢五三, 戴娟, 丁小俊, 吴蓉. 基于CMIP6和MaxEnt模型的江淮一季稻适生区分布预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 766-776. |
| [4] | 韩池, 温洪启, 张书林, 张俊龙, 李伟, 陈明帅, 尤立. 气候变化多情景下缺水流域跨行业水权交易的水管理效应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 753-765. |
| [5] | 胡金鹏, 何研, 史培军. 复合干热事件对小麦产量影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 625-640. |
| [6] | 张馨月, 李阔, 赵明月, 许吟隆. 中国农业适应气候变化能力建设进展回顾与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 613-624. |
| [7] | 何昊, 李曼, 刘淼, 陈铭杰, 李琪, 胡正华. 气候变化对水稻病害影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 641-658. |
| [8] | 樊星, 梁启迪, 吴承霖, 高翔. 巴库气候大会成果盘点及全球气候治理形势展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 583-592. |
| [9] | 孙若水, 梁媚聪. 从巴黎到贝伦——《巴黎协定》十周年进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 574-582. |
| [10] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 闫洪硕, 幸绣程, 朱开伟, 王晨旭. IPCC第七次评估报告第三工作组减缓气候变化概要解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 494-501. |
| [11] | 陈显尧, 毕瀚文, 郝潇洁, 马天骄, 郭凌瑞. 大西洋经向翻转环流及其对全球气候的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 469-476. |
| [12] | 朱松丽. 联合国气候公约体系下的国家分类演变[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 565-573. |
| [13] | 丁杰, 曹左男, 胡国铮, 干珠扎布, 赵芬, 王海锋, 高清竹. IPCC第七次评估报告第二工作组气候变化影响、适应与脆弱性大纲解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 484-493. |
| [14] | 王博文, 贺一, 滕飞. 我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 502-518. |
| [15] | 崔鹏, 王岩, 张国涛, 张正涛, 雷雨, 王昊, 王姣, 郝建盛, 朱宏. 气候变化灾害风险防范:现状、挑战与科学问题[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 449-460. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||