气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 733-741.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.083
风云三号D星气温观测气候变化应用稳定性评估
- 1 中国气象局国家气候中心,北京 100081
2 独立作者,马里兰州劳雷尔市 20723,美国
-
收稿日期:2025-04-15修回日期:2025-06-10出版日期:2025-11-30发布日期:2025-10-22 -
作者简介:郭艳君,女,研究员,gyj@cma.gov.cn -
基金资助:国家重点基础研究发展计划973项目(2024YFF1306104);国家气候中心重点创新团队“第三极气候变化监测预估”(NCCCXTD007);风云卫星应用先行计划(2023);气候应用专项(FY-APP-ZX-2023.02)
Evaluation of temporal stability in atmospheric temperature observations from FengYun-3D satellite for climate change research
GUO Yan-Jun1( ), ZOU Cheng-Zhi2
), ZOU Cheng-Zhi2
- 1 National Climate Centre, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
2 Independent Researcher, Laurel, Maryland 20723, USA
-
Received:2025-04-15Revised:2025-06-10Online:2025-11-30Published:2025-10-22
摘要:
为推进风云三号气象卫星气温观测在气候变化研究中的应用,依照全球气候观测系统(GCOS)基本气候变量观测要求,以NOAA卫星均一化气温为参照,定量评估了风云三号D星微波温度计-II型(FY-3D MWTS-II)业务观测全球高空气温资料稳定性,结论如下:对流层中层通道4海洋上空、对流层上层通道6和平流层下层通道9观测稳定性达到气候变化应用要求;通道4陆地上空气温和平流层中上层10~13通道气温存在由轨道漂移引发的日变化误差,对流层上层通道7和平流层下层通道8气温存在定标误差漂移,气候变化应用前需要均一化处理。稳定性评估可为气候变化研究筛选高信度卫星观测资料,为构建风云卫星均一化气温气候数据集奠定科学基础,进而显著提高风云卫星气温观测气候应用水平。
引用本文
郭艳君, 邹成智. 风云三号D星气温观测气候变化应用稳定性评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 733-741.
GUO Yan-Jun, ZOU Cheng-Zhi. Evaluation of temporal stability in atmospheric temperature observations from FengYun-3D satellite for climate change research[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 733-741.
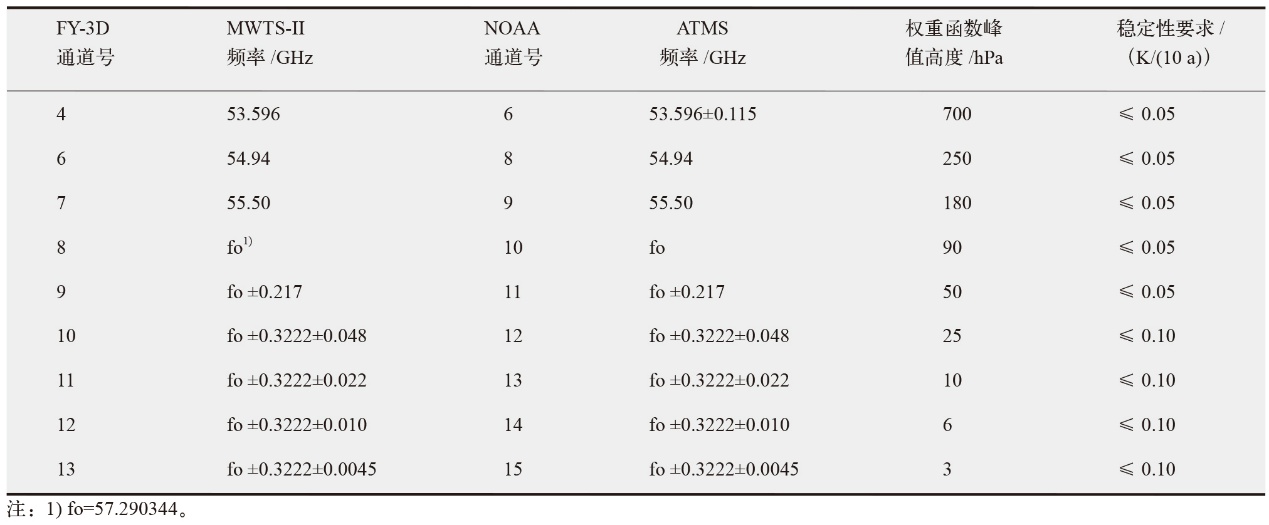 |
表1 FY-3D和NOAA卫星微波气温探测通道参数对比和气候变化应用稳定性需求
Table 1 Comparison of microwave temperature sounding channels between FY-3D and NOAA, and the temporal stability requirements for climate change
 |
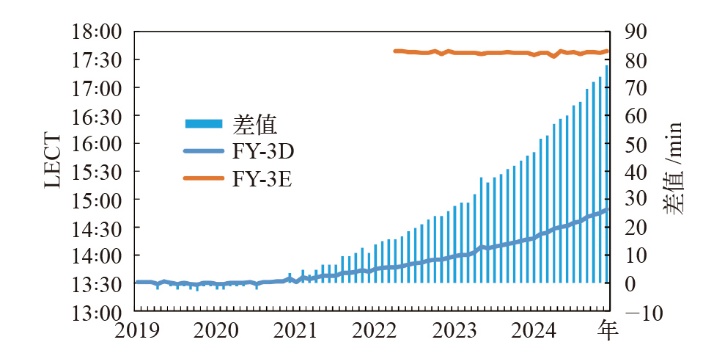
图1 FY-3D 和 FY-3E抬升轨道月均过赤道时刻(LECT)及FY-3D LECT与2019年1月LECT逐月差值
Fig. 1 Monthly mean Ascending Local Equator Crossing Time (LECT) for the FY-3D and FY-3E satellites from 2019 to 2024, along with the FY-3D LECT differences relative to its January 2019
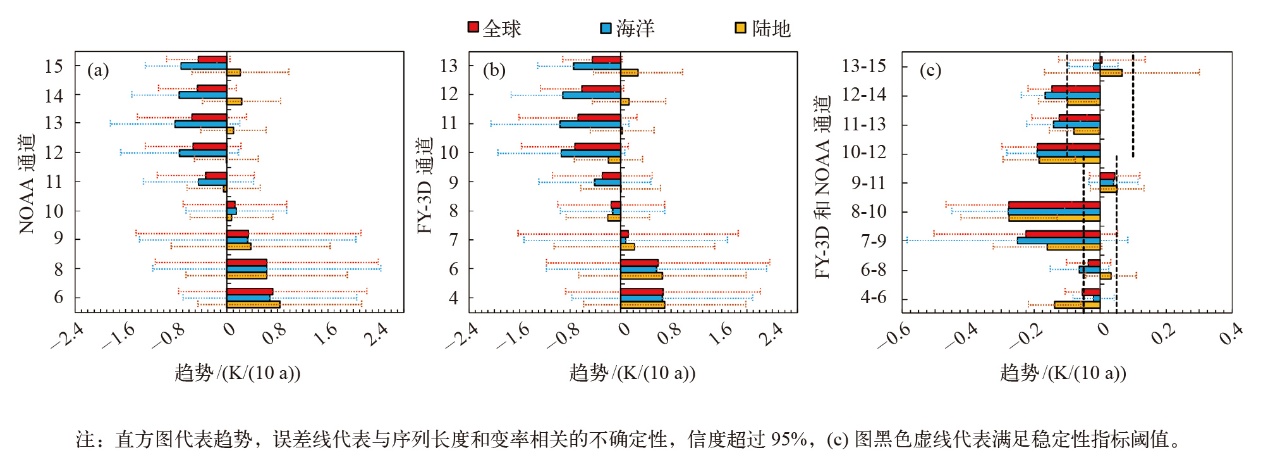
图2 2019—2024年NOAA (a)和FY-3D (b) 9个通道全球、海洋和陆地气温变化趋势对比及两者差值变化趋势(c) 注:直方图代表趋势,误差线代表与序列长度和变率相关的不确定性,信度超过95%,(c)图黑色虚线代表满足稳定性指标阈值。
Fig. 2 Trends of mean-layer temperature anomalies during 2019-2024 for the 9 channels analyzed in this study, averaged over the globe, ocean, and land for NOAA (a), FY-3D (b), and their differences (c). (The bars represent trends with error bars superimposed on them. The trend uncertainty represents 95% confidence intervals with autocorrelation adjustments, which account for time length limitations and temporal variability. The black dashed lines in (c) represent the stability thresholds for the 9 channels)

图3 2019—2024年FY-3D和NOAA 9个通道月平均全球海洋(a)和陆地(b)气温距平和差值序列 注:图例中的数字代表通道,例如(a1)图中FY-3D_4代表FY-3D通道4气温距平,NOAA_6代表NOAA通道6气温距平,Diff_4-6代表FY-3D通道4与NOAA通道6的气温距平差值;距平为月平均气温与2019—2023年平均气温的差值;图里数字标注自左至右分别为变化趋势、标准差和相关系数,其中蓝色为NOAA值,红色为FY-3D值,黑色为两者之差或相关值。
Fig. 3 Monthly temperature anomaly time series from 2019 to 2024 for FY-3D and NOAA, and their differences, averaged over the ocean (a) and land (b). (Anomalies are calculated as departures from the 2019-2024 base period. The labels in each panel from left to right represent linear trend and uncertainty, standard deviation, and correlation coefficient, respectively. Blue represents NOAA, red represents FY-3D, and black represents their difference or correlation)
| [1] |
Hurrell J, Trenberth K. Spurious trends in satellite MSU temperatures from merging different satellite records[J]. Nature, 1997, 386: 164-167
doi: 10.1038/386164a0 |
| [2] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007: 265-271 |
| [3] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 194-201 |
| [4] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 327-329 |
| [5] | Zou C Z, Goldberg M, Cheng Z, et al. Recalibration of microwave sounding unit for climate studies using simultaneous nadir overpasses[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 2006, 111: 1-24 |
| [6] | Zou C Z, Xu H, Hao X, et al. Mid-tropospheric layer temperature record derived from satellite microwave sounder observations with backward merging approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2023, 128: e2022JD037472 |
| [7] |
Mears C A, Schabel M C, Wentz F J. A reanalysis of the MSU channel 2 tropospheric temperature record[J]. Journal of Climate, 2003, 16: 3650-3664
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3650:AROTMC>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [8] |
Mears C A, Wentz F J. Sensitivity of satellite-derived tropospheric temperature trends to the diurnal cycle adjustment[J]. Journal of Climate, 2016, 29: 3629-3646
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0744.1 URL |
| [9] |
Spencer R W, Christy J R. Precision and radiosonde validation of satellite grid point temperature anomalies. Part I: MSU channel 2[J]. Journal of Climate, 1992, 5: 847-857
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1992)005<0847:PARVOS>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [10] |
Spencer R W, Christy J R, Braswell W D. UAH version 6 global satellite temperature products: methodology and results[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 53: 121-130
doi: 10.1007/s13143-017-0010-y URL |
| [11] |
Steiner A K, Ladst?dter F, Randel W, et al. Observed temperature changes in the troposphere and stratosphere from 1979 to 2018[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33: 8165-8194
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0998.1 |
| [12] |
Guo Y, Weng F, Wang G, et al. The long-term trend of upper-air temperature in China derived from microwave sounding data and its comparison with radiosonde observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33: 7875-7895
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0742.1 URL |
| [13] |
Santer B D, Solomon S, Pallotta G, et al. Comparing tropospheric warming in climate models and satellite data[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30: 373-392
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0333.1 URL |
| [14] |
Zou X. Studies of FY-3 observations over the past 10 years: a review[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13: 673
doi: 10.3390/rs13040673 URL |
| [15] |
Xian D, Zhang P, Gao L, et al. Fengyun meteorological satellite products for Earth system science applications[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Science, 2021, 38: 1267-1284
doi: 10.1007/s00376-021-0425-3 |
| [16] | 谷松岩, 郭杨, 谢鑫新, 等. 风云三号卫星微波载荷历史数据再定标[J]. 遥感学报, 2023, 27 (10): 2252-2269. |
|
Gu S Y, Gou Y, Xie X X, et al. Recalibration of the FY-3 microwave payload historical data records[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2023, 27 (10): 2252-2269 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11834/jrs.20221436 URL |
|
| [17] | 曹皓东, 张鹏, 廖蜜, 等. 风云三号微波温度计长序列再定标历史数据集质量评估[J]. 大气科学学报, 2024, 47 (4): 669-680. |
| Cao H D, Zhang P, Liao M, et al. Quality assessment of the long-term recalibration history dataset of the FY-3 microwave temperature sounder[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2024, 47 (4): 669-680 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | GCOS (Global Climate Observing Systems)-245. The 2022 GCOS ECVs requirements[R]. Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2022: 1-244 |
| [19] |
Carminati F, Atkinson N, Candy B, et al. Insights into the microwave instruments onboard the Fengyun 3D satellite: data quality and assimilation in the Met Office NWP system[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Science, 2021, 38 (8): 1379-1396
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0010-1 |
| [20] | 陆其峰. 风云三号A星大气探测资料数据在欧洲中期天气预报中心的初步评价与同化研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41 (7): 890-894. |
| Lu Q F. Initial evaluation and assimilation of FY-3A atmospheric sounding data in the ECMWF System[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 41 (7): 890-894 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王祥, 任义方, 吴彬. 用GPS资料对风云三号微波温度计资料进行绝对校准[J]. 大气科学学报, 2017, 40 (1): 81-89. |
| Wang X, Ren Y F, Wu B. Absolute calibration of MWTS sounding channels using GPS RO data[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 40 (1): 81-89 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | GCOS-107. Systematic observation requirements for satellite-based products for climate[R]. Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2006: 1-103 |
| [23] | Zou C Z, Goldberg M, Hao X. New generation of U.S. satellite microwave sounder achieves high radiometric stability performance for reliable climate change detection[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4 (10): eaau0049 |
| [24] | Zou C Z, Xu H, Hao X, et al. Post-millennium atmospheric temperature trends observed by satellites on stable orbits[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48 (13): e2021GL093291 |
| [25] | Zou C Z, Wang W. Inter-satellite calibration of AMSU-A observations for weather and climate applications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 2011, 116: D23113 |
| [26] |
Christy J R, Spencer R W, Braswell W D, et al. Examination of space-based bulk atmospheric temperatures used in climate research[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 39 (11): 3580-3607
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1444293 URL |
| [27] |
Dee D P, Uppala S. Variational bias correction of satellite radiance data in the ERA-Interim reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2009, 135: 1830-1841
doi: 10.1002/qj.v135:644 URL |
| [28] | Fu Y, Zou C Z, Zhang P, et al. A climate data record of atmospheric moisture and sea surface temperature from satellite observations[J]. Earth System Science Data Discuss, 2025, 17: 4651-4670. DOI: 10.5194/essd-17-4651-2025 |
| [1] | 曾颖婷, 唐振飞, 吴滨, 周明珠. 中国近海光伏发电潜力预估及驱动因子分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 830-838. |
| [2] | 肖雪, 黄萌田, 周佰铨, 王晨鹏, 翟盘茂. 2022年青藏高原复合高温干旱事件对区域植被的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 777-788. |
| [3] | 王胜, 陈健, 周宇, 孙佳丽, 翟振芳, 谢五三, 戴娟, 丁小俊, 吴蓉. 基于CMIP6和MaxEnt模型的江淮一季稻适生区分布预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 766-776. |
| [4] | 韩池, 温洪启, 张书林, 张俊龙, 李伟, 陈明帅, 尤立. 气候变化多情景下缺水流域跨行业水权交易的水管理效应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 753-765. |
| [5] | 何昊, 李曼, 刘淼, 陈铭杰, 李琪, 胡正华. 气候变化对水稻病害影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 641-658. |
| [6] | 胡金鹏, 何研, 史培军. 复合干热事件对小麦产量影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 625-640. |
| [7] | 张馨月, 李阔, 赵明月, 许吟隆. 中国农业适应气候变化能力建设进展回顾与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 613-624. |
| [8] | 樊星, 梁启迪, 吴承霖, 高翔. 巴库气候大会成果盘点及全球气候治理形势展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 583-592. |
| [9] | 孙若水, 梁媚聪. 从巴黎到贝伦——《巴黎协定》十周年进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 574-582. |
| [10] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 闫洪硕, 幸绣程, 朱开伟, 王晨旭. IPCC第七次评估报告第三工作组减缓气候变化概要解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 494-501. |
| [11] | 陈显尧, 毕瀚文, 郝潇洁, 马天骄, 郭凌瑞. 大西洋经向翻转环流及其对全球气候的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 469-476. |
| [12] | 朱松丽. 联合国气候公约体系下的国家分类演变[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 565-573. |
| [13] | 丁杰, 曹左男, 胡国铮, 干珠扎布, 赵芬, 王海锋, 高清竹. IPCC第七次评估报告第二工作组气候变化影响、适应与脆弱性大纲解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 484-493. |
| [14] | 王博文, 贺一, 滕飞. 我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 502-518. |
| [15] | 周天军, 陈晓龙, 张文霞, 江洁, 胡帅. IPCC第七次评估报告第一工作组“气候变化科学基础”大纲解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 477-483. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||