气候变化研究进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 231-241.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.148
中国四大城市群碳排放驱动因素时空分解研究
刘元欣1, 贺铄1, 江雅婧1, 罗旭1, 袁家海1,2( )
)
- 1 华北电力大学经济与管理学院,北京 102206
2 新能源电力与低碳发展研究北京市重点实验室,北京 102206
-
收稿日期:2023-07-07修回日期:2023-10-17出版日期:2024-03-30发布日期:2024-01-08 -
通讯作者:袁家海,男,教授,yuanjh126@126.com -
作者简介:刘元欣,女,副教授 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目“碳中和下煤电退出路径、影响评估及公正转型机制设计”(72173043)
Spatial-temporal decomposition of carbon emissions in China’s four major urban agglomerations
LIU Yuan-Xin1, HE Shuo1, JIANG Ya-Jing1, LUO Xu1, YUAN Jia-Hai1,2( )
)
- 1 School of Economics and Management, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China
2 Beijing Key Laboratory of New Energy and Low-Carbon Development, Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2023-07-07Revised:2023-10-17Online:2024-03-30Published:2024-01-08
摘要:
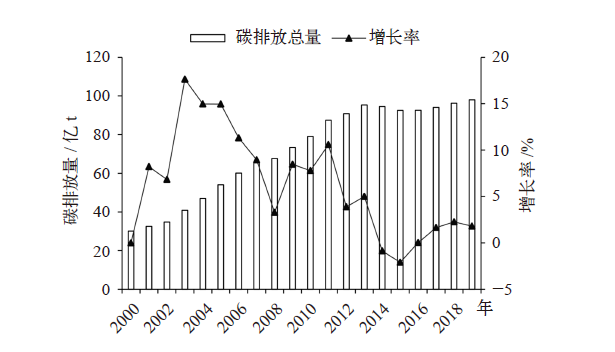
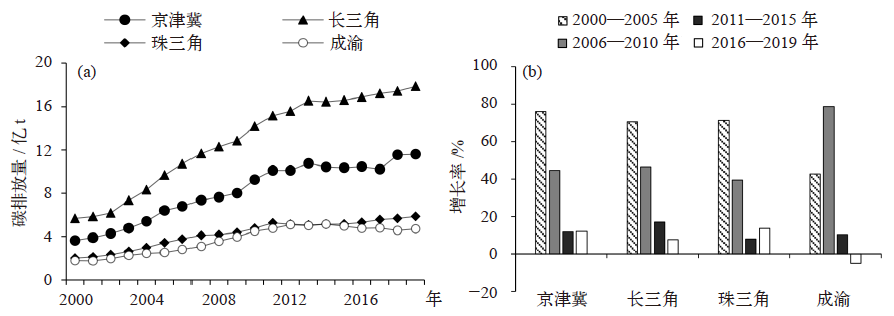
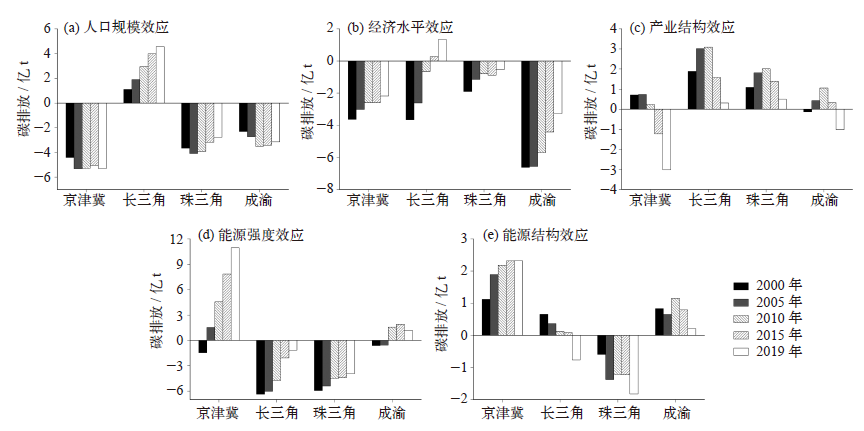
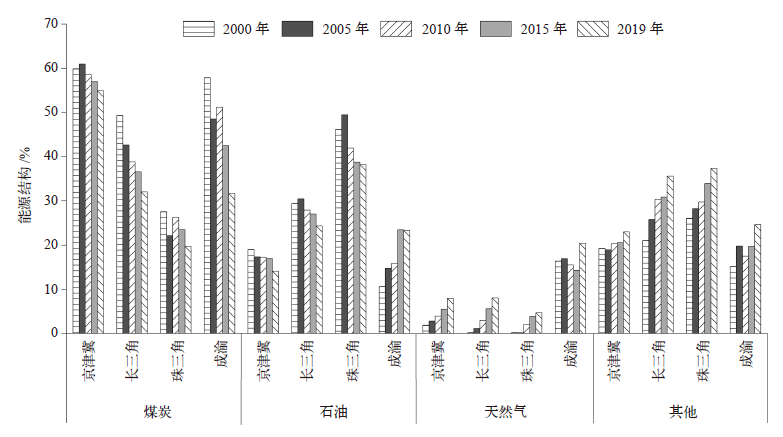
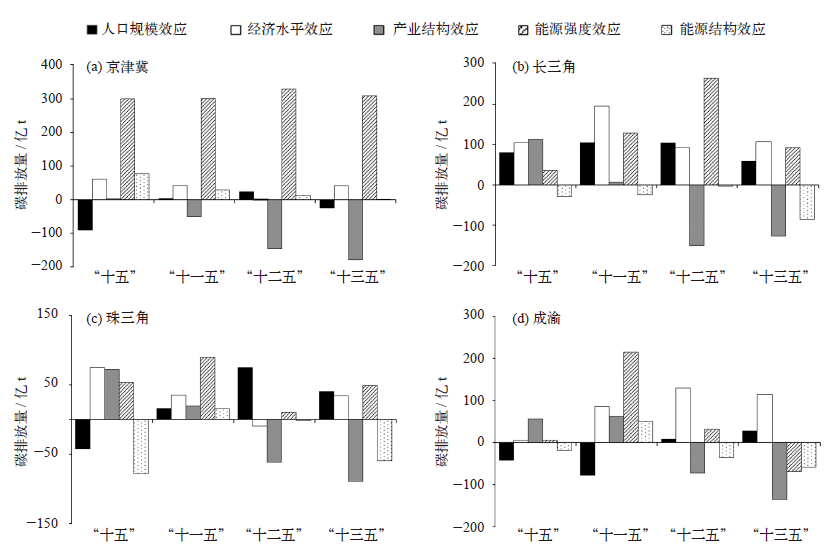
城市群是中国经济发展和能源消耗的集聚区域,也是碳排放的主要来源。研究中国典型城市群碳排放的时空演变特征及其影响因素对实现“双碳”目标具有重要意义。文中应用ST-IDA模型(时空指数分解分析法)和LMDI(对数平均迪氏指数法)分解法,分析2000—2019年京津冀、长三角、珠三角和成渝城市群的碳排放驱动因素(人口规模、经济水平、产业结构、能源强度和能源结构)。研究发现:2000—2019年间,四大城市群能源活动碳排放总体趋势均由高速增长阶段步入平稳增长阶段,其中成渝城市群已基本实现碳达峰;能源强度效应是影响碳排放空间差异的主要因素;人口规模扩张、经济发展水平提高和能源强度上升是促进碳排放增长的主要因素,产业结构和能源消费结构优化起到抑制作用;四大城市群碳排放的时空演变主要取决于工业部门。鉴于四大城市群呈现出不同的碳排放特征,未来应探索差异化、多元化的城市群减排路径,促进城市群碳减排。
引用本文
刘元欣, 贺铄, 江雅婧, 罗旭, 袁家海. 中国四大城市群碳排放驱动因素时空分解研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 231-241.
LIU Yuan-Xin, HE Shuo, JIANG Ya-Jing, LUO Xu, YUAN Jia-Hai. Spatial-temporal decomposition of carbon emissions in China’s four major urban agglomerations[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 231-241.
| [1] | 冯宗宪, 高赢. 中国区域碳排放驱动因素、减排贡献及潜力探究[J]. 北京理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2019, 21 (4): 13-20. |
| Feng Z X, Gao Y. Study on China’s regional driving factors of carbon emission, emission reduction contribution and potential[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2019, 21 (4): 13-20 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] |
Guan D B, Hubacek K, Weber C L, et al. The drivers of Chinese CO2emissions from 1980 to 2030[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2008, 18 (4): 626-634
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2008.08.001 URL |
| [3] |
Ye B, Jiang J J, Li C S, et al. Quantification and driving force analysis of provincial-level carbon emissions in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 198: 223-238
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.04.063 URL |
| [4] | 王勇, 许子易, 张亚新. 中国超大城市碳排放达峰的影响因素及组合情景预测: 基于门限-STIRPAT模型的研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39 (12): 4284-4292. |
| Wang Y, Xu Z Y, Zhang Y X. Influencing factors and combined scenario prediction of carbon emission peaks in megacities in China: based on Threshold-STIRPAT model[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39 (12): 4284-4292 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 落基山研究所. 中国城市群碳排放达峰之路: 机遇与探索[R]. 北京, 2019. |
| Rocky Mountain Institute. Carbon emission peaking path of China’s city clusters: exploring the opportunities[R]. Beijing, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 廖明球, 许雷鸣. 二氧化碳排放的IO-SDA模型及其实证研究[J]. 统计研究, 2017, 34 (7): 62-70. |
| Liao M Q, Xu L M. IO-SDA model of CO2 emissions and its empirical research[J]. Statistical Research, 2017, 34 (7): 62-70 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 马峥, 崔豫泓. 基于SDA模型的中国碳排放驱动因素分解研究[J]. 煤炭经济研究, 2020, 40 (7): 32-36. |
| Ma Z, Cui Y H. Research on decomposition of driving factors of China’s carbon emission based on SDA model[J]. Coal Economic Research, 2020, 40 (7): 32-36 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 胡雷. 我国城镇化对二氧化碳排放的影响机理研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12 (4): 341-347. |
| Hu L. Research on the mechanism of how urbanization effect on carbon emissions in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12 (4): 341-347 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 曹俊文, 姜雯昱. 基于LMDI的电力行业碳排放影响因素分解研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2018, 34 (14): 128-131. |
| Cao J W, Jiang W Y. Research on decomposition of influencing factors of power industry carbon emission based on LMDI[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2018, 34 (14): 128-131 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 王敏, 冯相昭, 安祺, 等. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的青海省绿色低碳发展策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607. |
| Wang M, Feng X Z, An Q, et al. Study on green and low-carbon development in Qinghai province based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] |
Ang B W. Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method?[J]. Energy Policy, 2004, 32: 1131-1139
doi: 10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4 URL |
| [12] |
Ma C. A multi-fuel, multi-sector and multi-region approach to index decomposition: an application to China’s energy consumption 1995-2010[J]. Energy Economics, 2014, 42: 9-16
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2013.11.009 URL |
| [13] | 马晓明, 包金梅, 熊思琴. 基于LMDI分解的中国多区域碳排放驱动因素分析[J]. 现代管理科学, 2017 (8): 63-65. |
| Ma X M, Bao J M, Xiong S Q. Analysis of driving factors of multi-regional carbon emissions in China based on LMDI decomposition[J]. Modern Management Science, 2017 (8): 63-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 刘小丽, 王永利. 基于LMDI分解的中国制造业碳排放驱动因素分析[J]. 统计与决策, 2022, 38 (12): 60-63. |
| Liu X L, Wang Y L. Based on LMDI decomposition of China’s manufacturing carbon driving factors analysis[J]. Journal of Statistics and Decision, 2022, 38 (12): 60-63 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 陈锋, 张晶, 任娇, 等. 基于LMDI模型的黄河流域碳排放时空差异及影响因素研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 2022, 13 (4): 418-427. |
| Chen F, Zhang J, Ren J, et al. Spatial and temporal differences and influencing factors of carbon emissions in the Yellow River basin based on LMDI model[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 2022, 13 (4): 418-427 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
Ang B W, Zhang F Q. Inter-regional comparisons of energy-related CO2 emissions using the decomposition technique[J]. Energy, 1999, 24 (4): 297-305
doi: 10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00092-9 URL |
| [17] |
Ang B W, Xu X Y, Su B. Multi-country comparisons of energy performance: the index decomposition analysis approach[J]. Energy Economics, 2015, 47: 68-76
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2014.10.011 URL |
| [18] |
Ang B W, Su B, Wang H. A spatial-temporal decomposition approach to performance assessment in energy and emissions[J]. Energy Economics, 2016, 60: 112-121
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2016.08.024 URL |
| [19] |
Song C, Zhao T, Wang J. Spatial-temporal analysis of China’s regional carbon intensity based on ST-IDA from 2000 to 2015[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 238: 117874
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117874 URL |
| [20] |
Ang B W, Su B. Carbon emission intensity in electricity production: a global analysis[J]. Energy Policy, 2016, 94: 56-63
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2016.03.038 URL |
| [21] |
Ang B W, Goh T. Carbon intensity of electricity in ASEAN: drivers, performance and outlook[J]. Energy Policy, 2016, 98: 170-179
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2016.08.027 URL |
| [22] |
Wang J F, He S T, Qiu Y, et al. Investigating driving forces of aggregate carbon intensity of electricity generation in China[J]. Energy Policy, 2018, 113: 249-257
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2017.11.009 URL |
| [23] |
Xu X Y, Ang B W. Multilevel index decomposition analysis: approaches and application[J]. Energy Economics, 2014, 44: 375-382
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2014.05.002 URL |
| [24] |
Ang B W, Choi K H. Decomposition of aggregate energy and gas emission intensities for industry: a refined divisia index method[J]. Energy Journal, 1997, 18 (3): 59-73
doi: 10.5547/ISSN0195-6574-EJ-Vol18-No3-3 URL |
| [25] | 张黎. 基于LMDI的中国能源消费的影响因素分解分析[J]. 中国能源, 2013, 35 (10): 21-24. |
| Zhang L. Decomposition analysis of influencing factors of energy consumption in China based on LMDI[J]. Energy of China, 2013, 35 (10): 21-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
顾阿伦, 何崇恺, 吕志强. 基于LMDI方法分析中国产业结构变动对碳排放的影响[J]. 资源科学, 2016, 38 (10): 1861-1870.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2016.10.04 |
|
Gu A L, He C K, Lv Z Q. Industrial structure changes impacts on carbon emissions in China based on LMDI method[J]. Resources Science, 2016, 38 (10): 1861-1870 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.18402/resci.2016.10.04 |
|
| [27] |
Ang B W. LMDI decomposition approach: a guide for implementation[J]. Energy Policy, 2015, 86: 233-238
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2015.07.007 URL |
| [28] | Zhang M, Ang B W. A survey of index decomposition analysis in energy and environmental studies[J]. Energy, 2017, 44 (1): 590-597 |
| [29] | Ang B W, Zhang F Q. Survey of decomposition analysis in energy studies[J]. Energy, 2018, 54 (1): 10-18 |
| [30] | Fotheringham A S, Brunsdon C, Charlton M. Quantitative geography: perspectives on spatial data analysis[M]. London: SAGE Publications, 2000 |
| [31] | Martin D. Area, scale and weighting in census data analysis[J]. Journal of Geographical Systems, 2003, 5 (2): 157-174 |
| [32] | Charlton M, Fotheringham S, Brunsdon C. Geographically weighted regression: the analysis of spatially varying relationships[J]. Geographical Analysis, 2003. DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-4632.2003.tb01114.x |
| [33] | 周春山. 发挥人口集聚效应建设现代化的城市群和都市圈[J]. 国家治理, 2021 (31): 19-24. |
| Zhou C S. Use population agglomeration effect to build modern city agglomeration and metropolitan area[J]. Governance, 2021 (31): 19-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] |
Li H, Zhao Y H, Qiao X Y, et al. Identifying the driving forces of national and regional CO2 emissions in China: based on temporal and spatial decomposition analysis models[J]. Energy Economics, 2017, 68: 522-538
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2017.10.024 URL |
| [1] | 罗晓予, 曹星煜, 宋志茜. 中日建筑全生命周期碳排放比较[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 220-230. |
| [2] | 曹翔, 姜璐, 于洋. 外资进入的碳排放效应及其对碳达峰的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 205-219. |
| [3] | 田佩宁, 梁肖, 官雨捷, 赵义馨, 毛保华, 薛婷. 中国电网全生命周期碳排放及发电结构转型路径规划研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(1): 97-106. |
| [4] | 杨子艺, 胡姗, 徐天昊, 燕达, 江亿. 面向碳中和的各国建筑运行能耗与碳排放对比研究方法及应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 749-760. |
| [5] | 王文治, 唐帼. 增加值驱动视角下省域中间品贸易的碳减排效应[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 771-785. |
| [6] | 丁丽媛, 王艳华, 王克. 碳排放权交易的减污降碳协同效应及影响机制[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 786-798. |
| [7] | 杨红雄, 杨光. 基于现代化的中国省级碳排放时空演变及影响因素研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 457-471. |
| [8] | 吴筱雯, 何洁琳, 李妍君, 宋洁慧, 秦川. 广西北部湾沿海城市群气候承载力分析与评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 446-456. |
| [9] | 陈俣秀, 王超彬, 于剑. 基于实物期权法的航空公司减排投资策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 483-495. |
| [10] | 田利军, 秦文, 黎杰. “双碳”目标下ETS与航空公司绿色全要素生产率[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 320-333. |
| [11] | 戈秋虞, 徐艺诺, 邱荣祖, 胡喜生, 张园园, 刘娜翠, 张兰怡. 基于系统动力学的城市客运交通减碳情景模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 357-370. |
| [12] | 田佩宁, 毛保华, 童瑞咏, 张皓翔, 周琪. 我国交通运输行业及不同运输方式的碳排放水平和强度分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 347-356. |
| [13] | 杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 李政. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 191-202. |
| [14] | 谭显春, 高瑾昕, 曾桉, 幸绣程. 绿色金融改革创新试验区政策对碳排放的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [15] | 李晓易, 吴睿. 交通运输温室气体核算边界和测算方法研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 84-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||