气候变化研究进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (6): 749-760.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.128
面向碳中和的各国建筑运行能耗与碳排放对比研究方法及应用
- 清华大学建筑学院建筑节能研究中心,北京 100086
-
收稿日期:2023-06-12修回日期:2023-07-25出版日期:2023-11-30发布日期:2023-10-30 -
通讯作者:胡姗,女,助理研究员,hushan@tsinghua.edu.cn -
作者简介:杨子艺,女,博士研究生 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金国际(地区)合作与交流项目“向净零排放的公平过渡模式”(7221101340);清华大学自主科研计划“双碳目标下的碳排放责任核算体系和政策机制研究”(2022THZWYY06)
Method and application of global building operation energy use and carbon emissions comparison in the context of carbon neutrality
YANG Zi-Yi, HU Shan( ), XU Tian-Hao, YAN Da, JIANG Yi
), XU Tian-Hao, YAN Da, JIANG Yi
- Building Energy Research Center, School of Architecture, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100086, China
-
Received:2023-06-12Revised:2023-07-25Online:2023-11-30Published:2023-10-30
摘要:
在我国“双碳”目标的背景下,建筑领域亟需明确实现碳达峰碳中和的路径。为应对全球气候变化,多国均已提出碳达峰碳中和目标和建筑领域减碳路径。开展各国建筑能耗和碳排放对比研究是认识我国建筑领域现状水平、分析未来发展趋势并设计碳中和路径的重要手段,也可以为其他发展中国家提供参考。文中提出了采用电力当量法折算建筑运行总能耗的方法,应用于各国建筑运行能耗的对比研究,并提出了各国建筑运行碳排放的对比研究方法。对各国建筑运行能耗和碳排放开展横向对比,剖析各国建筑运行能耗和碳排放的主导因素和实现碳中和的关键措施。结果表明,我国建筑运行的人均和单位面积能耗以及碳排放强度相较发达国家均处于较低水平,但建筑运行人均碳排放和单位当量用电碳排放已高于全球平均值。我国建筑领域碳中和路径,一方面要维持绿色低碳生活方式,另一方面应继续推进建筑用能电气化,助力新型零碳电力系统建设,通过电力系统的低碳来实现建筑运行的低碳。
引用本文
杨子艺, 胡姗, 徐天昊, 燕达, 江亿. 面向碳中和的各国建筑运行能耗与碳排放对比研究方法及应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 749-760.
YANG Zi-Yi, HU Shan, XU Tian-Hao, YAN Da, JIANG Yi. Method and application of global building operation energy use and carbon emissions comparison in the context of carbon neutrality[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 749-760.
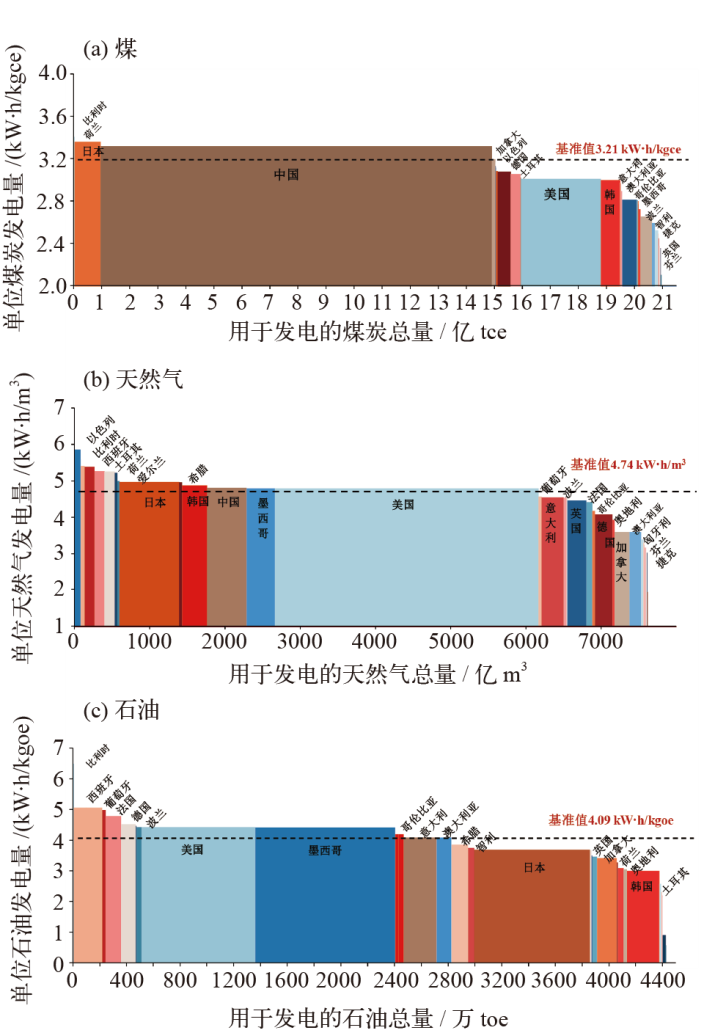
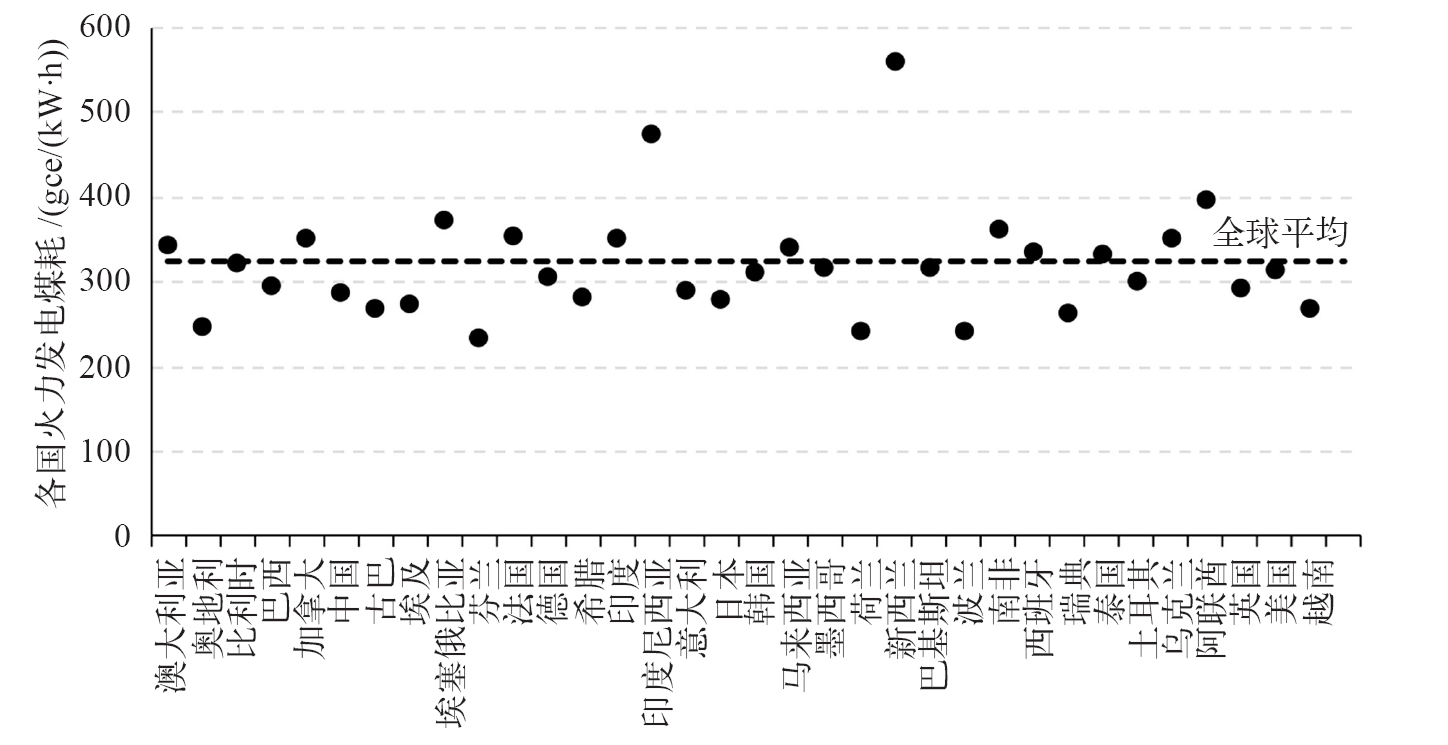
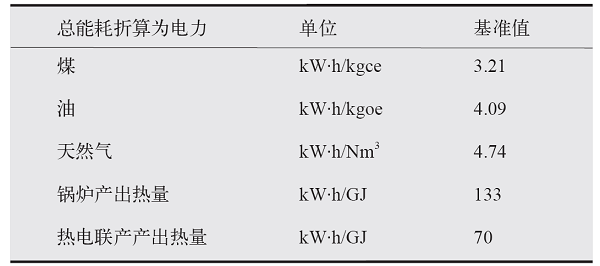
图3 2020年中国和OECD国家能源转换系数和全球基准值(a)煤,(b)石油,(c)天然气
Fig. 3 Energy conversion factors in China and OECD countries and the global benchmark in 2020. (a) Coal, (b) oil, and (c) gas

图4 2020年各国建筑运行能耗对比(建筑当量用电法) 注:圆圈面积表示建筑运行碳排放总量。
Fig. 4 Comparison of building operation energy use in different countries in 2020 (electricity-equivalent method)
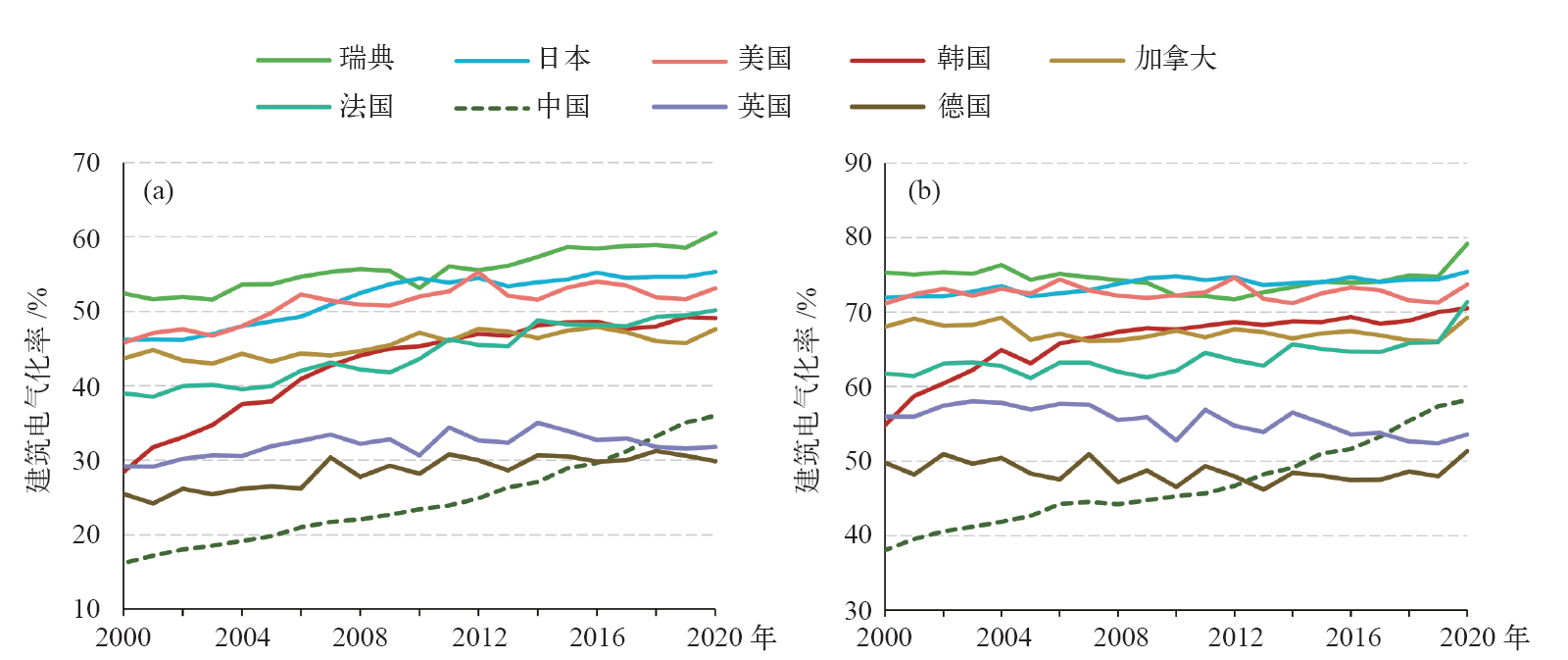
图5 2000—2020年各国建筑领域用能电气化率(a)电热当量法,(b)发电煤耗法
Fig. 5 Electrification rate of building sector in different countries in 2000-2020. (a) Electro-thermal equivalent method, (b) gross coal consumption rate for fossil-fired plant method

图7 2000和2020年典型国家建筑运行碳排放变化趋势对比 注:圆圈面积表示建筑运行碳排放总量。
Fig. 7 Comparison of building operation carbon emissions trend in different countries in 2000 and 2020

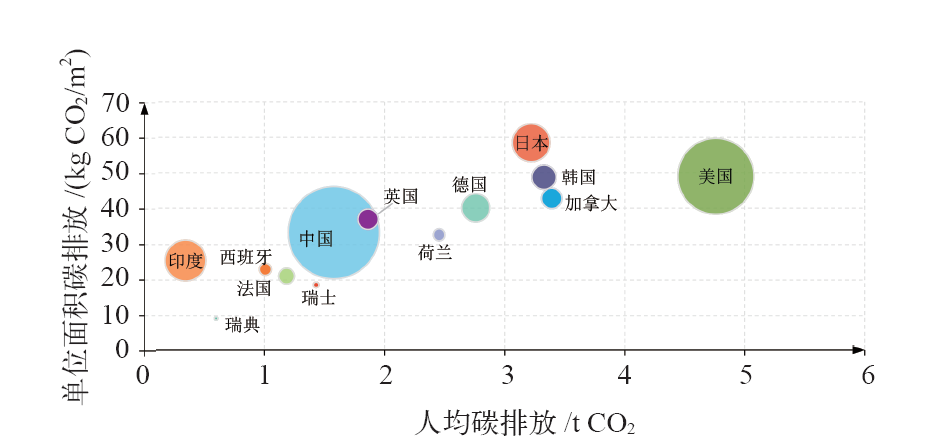
图8 2020年全球建筑运行能耗强度与碳排放强度对比 注:圆圈面积表示建筑运行碳排放总量。
Fig. 8 Global comparison of building operation energy use intensity and carbon emission intensity in 2020
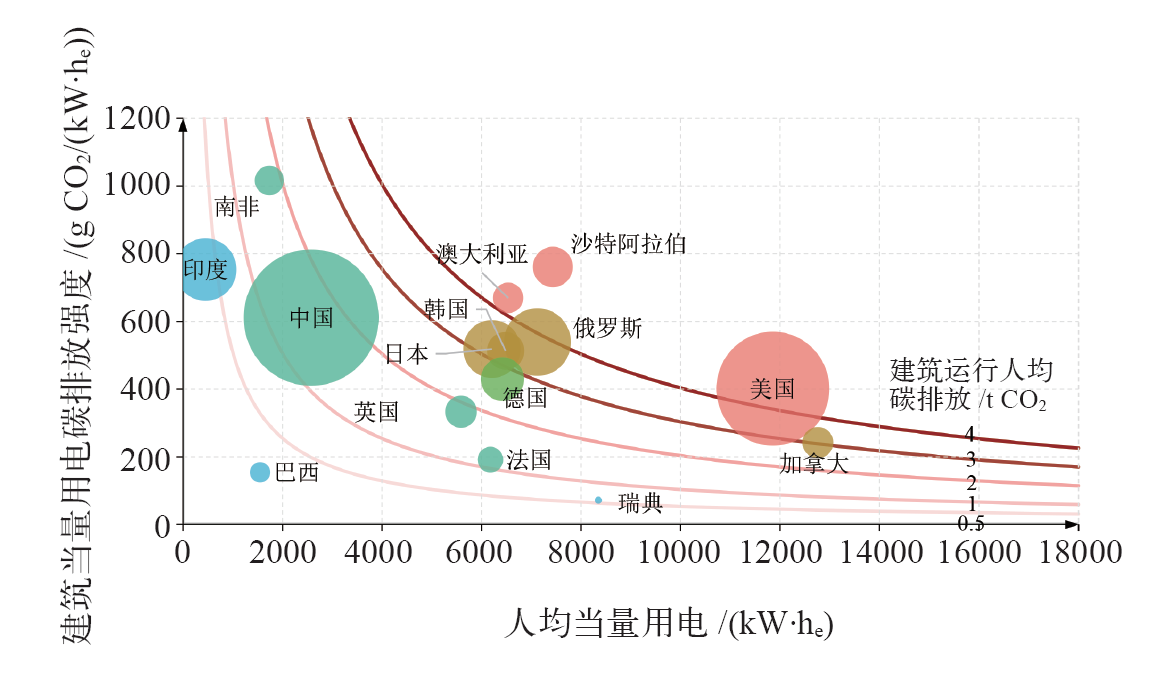
图9 2020年典型国家建筑运行能耗强度与碳排放强度对比 注:圆圈面积表示建筑运行碳排放总量。
Fig. 9 Comparison of building operation energy use intensity and carbon emission intensity in different countries in 2020
| [1] | Energy & Climate Intelligence Unit ECIU. Net zero emission race[EB/OL]. 2023 [2023-01-12]. https://eciu.net/netzerotracker |
| [2] | International Energy Agency IEA. Buildings[R/OL]. 2022 [2023-01-12]. https://www.iea.org/reports/buildings |
| [3] | IPCC. Climate change 2022: mitigation of climate change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022 |
| [4] | International Energy Agency IEA. Net zero by 2050 a roadmap for the global energy sector[R/OL]. 2022 [2023-02-15]. www.iea.org/t&c/ |
| [5] | International Energy Agency IEA, United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). Global alliance for buildings and construction: 2019 global status report for buildings and construction[R]. United Nations Environment Programme, 2019: 224 |
| [6] | 白泉, 胡姗, 谷立静. 对IPCC AR6报告建筑章节的介绍和解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18 (5): 557-566. |
| Bai Q, Hu S, Gu L J. Interpretation of IPCC AR6 on buildings[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18 (5): 557-566 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 人民日报. 习近平在第七十五届联合国大会一般性辩论上发表重要讲话[N/OL]. 2020 [2023-02-16]. http://paper.people.com.cn/rmrb/html/2020-09/22/nbs.D110000renmrb_01.htm. |
| People’s Daily. Statement by H.E. Xi Jinping president of the People’s Republic of China at the general debate of the 76th session of the United Nations general assembly[N/OL]. 2020 [2023-02-16]. http://paper.people.com.cn/rmrb/html/2020-09/22/nbs.D110000renmrb_01.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 清华大学建筑节能研究中心.中国建筑节能年度发展研究报告 2023(城市能源系统专题)[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2023. |
| Building Energy Research Center of Tsinghua University. Annual development research report on building energy efficiency in China in 2023[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 住房和城乡建设部,国家发展改革委. 城乡建设领域碳达峰实施方案[R/OL]. 2020 [2023-02-16]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-07/13/content_5700752.htm. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, National Development and Reform Commission. The action for peaking carbon dioxide emissions in urban-rural development area[R/OL]. 2020 [2023-02-16]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2022-07/13/content_5700752.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 胡姗. 中国城镇住宅建筑能耗及与发达国家的对比研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2013. |
| Hu S. Research on residential building energy consumption of China’s urban area and comparison with developed countries[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2013 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 江亿, 胡姗. 中国建筑部门实现碳中和的路径[J]. 暖通空调, 2021, 51 (5): 1-13. |
| Jiang Y, Hu S. Paths to carbon neutrality in China’s building sector[J]. Journal of HV&AC, 2021, 51 (5): 1-13 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] |
Guo S, Yan D, Hu S, et al. Global comparison of building energy use data within the context of climate change[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2020, 226: 110362
doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2020.110362 URL |
| [13] | 江亿. 在能源分析中采用等效电方法[J]. 中国能源, 2011, 32 (5): 5-11. |
| Jiang Y. The electricity equivalent method in energy analysis[J]. Energy of China, 2011, 32 (5): 5-11 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Cabeza L F, Rincón L, Vilariño V, et al. Life cycle assessment (LCA) and life cycle energy analysis (LCEA) of buildings and the building sector: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014, 29: 394-416 |
| [15] |
Ramesh T, Prakash R, Shukla K K. Life cycle energy analysis of buildings: an overview[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2010, 42 (10): 1592-1600
doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2010.05.007 URL |
| [16] |
Sharma A, Saxena A, Sethi M, et al. Life cycle assessment of buildings: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15 (1): 871-875
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2010.09.008 URL |
| [17] | Jiang Y, Hu S, Liu X, et al. Decarbonize public and commercial buildings: China building energy and emission yearbook 2022[M]. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022 |
| [18] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部.民用建筑能耗标准: GB/T51161—2016 [S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社出版, 2016. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China.Standard for energy consumption of building: GB/T51161-2016 [S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Commission E, For Energy D G, Kranzl L, et al. Renewable space heating under the revised renewable energy directive: ENER/C1/2018-494: final report[M]. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 2022 |
| [20] | European Commission D G for E, Bacquet A, Galindo Fernández M, et al. Overview of district heating and cooling markets and regulatory frameworks under the revised renewable energy directive[M]. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 2021 |
| [21] | 中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. |
| National Bureau of Statistics of China. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 国家统计局工业交通统计司. 中国能源统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. |
| Department of Industrial and Transportation Statistics, National Bureau of Statistics. China energy statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | International Energy Agency IEA. World energy balances 2022 edition database documentation database documentation[M]. Paris: IEA Publications, 2022 |
| [24] | European Union EU. Eurostat database[EB/OL]. 2018 [2023-02-12]. https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/main/data/database |
| [25] | United Nations Statistical Division. International recommendations for energy statistics (IRES)[M]. New York: United Nations Publication, 2015 |
| [26] | 江亿, 刘兰斌, 杨秀. 能源统计中不同类型能源核算方法的探讨[J]. 中国能源, 2006, 28 (6): 5-8. |
| Jiang Y, Liu L B, Yang X. Exploration of accounting methods for different types of energy in energy statistics[J]. Energy of China, 2006, 28 (6): 5-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | International Energy Agency IEA. World energy oultlook 2022[R]. Paris: OECD Publishing, 2022 |
| [28] | Bourdaire J M, Paffenbarger J. Nuclear power and sustainable development[J]. Energy and Environment, 1998, 9 (2): 125-139 |
| [29] | 国家市场监督管理总局.综合能耗计算通则: GB/T 2589—2020 [S]. 北京: 国家标准化管理委员会, 2020. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation.General rules for calculation of the comprehensive energy consumption: GB/T 2589—2020 [S]. Beijing: Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). International energy outlook 2021[R/OL]. 2021 [2023-02-16]. www.eia.gov/outlooks |
| [31] | 中华人民共和国生态环境部. 中华人民共和国气候变化第三次国家信息通报[R/OL]. 2018 [2023-02-16]. https://tnc.ccchina.org.cn/Detail.aspx?newsId=73250&TId=203. |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Third national communication on climate change of the People’s Republic of China[R/OL]. 2018 [2023-02-16]. https://tnc.ccchina.org.cn/Detail.aspx?newsId=73250&TId=203 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | IPCC. 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories[R]. Japan: IGES, 2006 |
| [33] | 国家标准化管理委员会.民用建筑能耗分类及表示方法: GB/T34913—2017 [S]. 北京: 国家标准化管理委员会, 2017. |
| Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China.Classification and presentation of civil building energy use: GB/T34913—2017 [S]. Beijing: Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 中国电力企业联合会. 中国电力行业发展统计2021[R/OL]. 2021 [2023-02-25]. https://www.cec.org.cn/menu/index.html?688. |
| China Electricity Council. Statistics on the development of China’s electric power industry 2021[R/OL]. 2021 [2023-02-25]. https://www.cec.org.cn/menu/index.html?688 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | International Energy Agency IEA. Statistics database[EB/OL]. 2019 [2023-02-25]. http://www.iea.org/statistics/ |
| [36] | 国家能源局石油天然气司, 国务院发展研究中心资源与环境政策研究所,自然资源部油气资源战略研究中心. 中国天然气发展报告(2021)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2021. |
| Oil and Gas Department, National Energy Administration, Institute of Resources and Environment Policies, Development Research Center of the State Council, Oil and Gas Resources Strategy Research Center, Ministry of Natural Resources. China natural gas development report (2021)[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] |
Hu S, Zhang Y, Yang Z, et al. Challenges and opportunities for carbon neutrality in China’s building sector: modelling and data[J]. Building Simulation, 2022, 15 (11): 1899-1921
doi: 10.1007/s12273-022-0912-1 |
| [38] | World Bank. Statistics database[EB/OL]. 2019 [2023-02-25]. http://data.worldbank.org/ |
| [39] | The National Sample Survey Office NSSO. Key indicators of drinking water, sanitation, hygiene and housing condition in India[R]. New Delhi, 2018 |
| [40] |
Kumar S, Yadav N, Singh M, et al. Estimating India’s commercial building stock to address the energy data challenge[J]. Building Research and Information, 2019, 47 (1): 24-37
doi: 10.1080/09613218.2018.1515304 URL |
| [41] | International Energy Agency (IEA), Tsinghua University. The future of cooling in China[R/OL]. 2019 [2023-05-12]. https://www.iea.org/reports/the-future-of-cooling-in-china |
| [42] |
Hu S, Yan D, Guo S, et al. A survey on energy consumption and energy usage behavior of households and residential building in urban China[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2017, 148 (1): 366-378
doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.03.064 URL |
| [43] | 徐天昊, 胡姗, 杨子艺, 等. 中国瑞典建筑碳排放对比及对中国建筑碳中和路径的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (3): 305-319. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.193. |
| Xu T H, Hu S, Yang Z Y, et al. Carbon emission comparisons of the building sector between China and Sweden and its implication for achieving carbon neutrality in the building sector of China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (3): 305-319. DOI: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.193 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | The Swedish Energy Agency. Energy in Sweden 2019[R/OL]. 2022 [2023-02-12]. https://energimyndigheten.a-w2m.se/Home.mvc?ResourceId=208766 |
| [45] | International Energy Agency IEA. India energy outlook 2021[R/OL]. 2021 [2023-02-13]. http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/content/469683/india-energy-outlook-2021/ |
| [46] | Ratshomo K. The South African energy sector report 2021[M]. Pretoria: Department of Mineral Resources & Energy, 2021 |
| [47] | Eskom. Eskom integrated report 2021[J/OL]. 2021 [2023-02-16]. https://www.eskom.co.za/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/2021IntegratedReport.pdf |
| [1] | 田佩宁, 梁肖, 官雨捷, 赵义馨, 毛保华, 薛婷. 中国电网全生命周期碳排放及发电结构转型路径规划研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(1): 97-106. |
| [2] | 王文治, 唐帼. 增加值驱动视角下省域中间品贸易的碳减排效应[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 771-785. |
| [3] | 丁丽媛, 王艳华, 王克. 碳排放权交易的减污降碳协同效应及影响机制[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 786-798. |
| [4] | 陈俣秀, 王超彬, 于剑. 基于实物期权法的航空公司减排投资策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 483-495. |
| [5] | 杨红雄, 杨光. 基于现代化的中国省级碳排放时空演变及影响因素研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 457-471. |
| [6] | 田利军, 秦文, 黎杰. “双碳”目标下ETS与航空公司绿色全要素生产率[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 320-333. |
| [7] | 田佩宁, 毛保华, 童瑞咏, 张皓翔, 周琪. 我国交通运输行业及不同运输方式的碳排放水平和强度分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 347-356. |
| [8] | 戈秋虞, 徐艺诺, 邱荣祖, 胡喜生, 张园园, 刘娜翠, 张兰怡. 基于系统动力学的城市客运交通减碳情景模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 357-370. |
| [9] | 谭显春, 高瑾昕, 曾桉, 幸绣程. 绿色金融改革创新试验区政策对碳排放的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [10] | 杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 李政. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 191-202. |
| [11] | 李晓易, 吴睿. 交通运输温室气体核算边界和测算方法研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 84-90. |
| [12] | 宝哲, 周小亮. 数字赋能与城市碳排放——基于下一代互联网示范城市的准自然试验[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 503-508. |
| [13] | 徐一剑, 李潭峰, 徐丽丽. 国土空间总体规划温室气体核算模型[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 355-365. |
| [14] | 冯国会, 崔航, 常莎莎, 黄凯良, 王茜如. 近零能耗建筑碳排放及影响因素分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 205-214. |
| [15] | 张海军, 段茂盛. 中国试点ETS的碳减排效果评估——基于分省高耗能工业子行业数据的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 579-589. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||