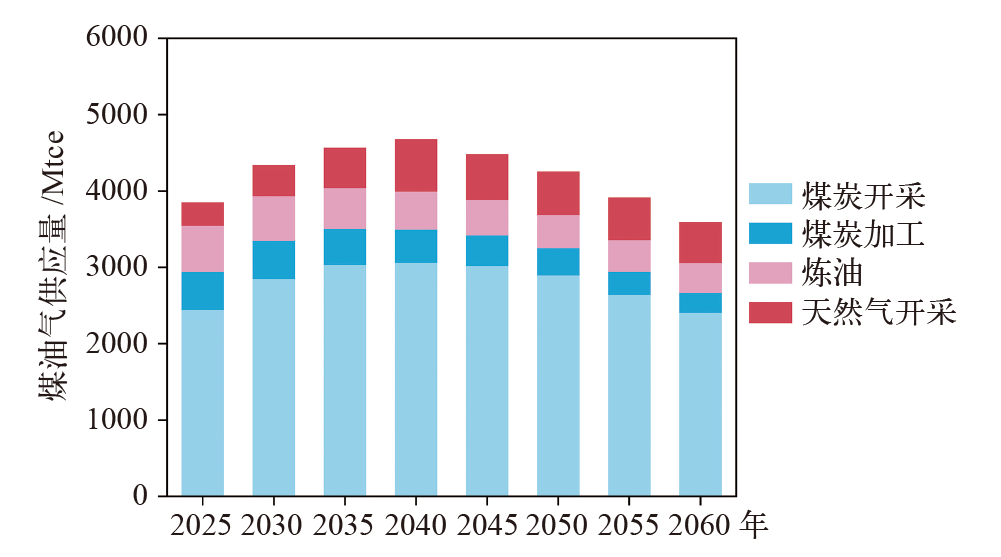
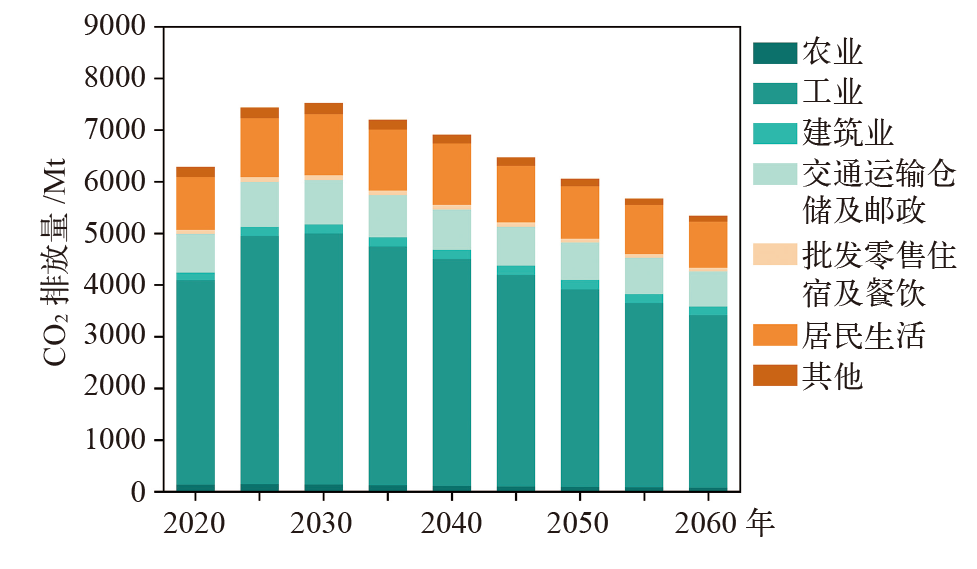
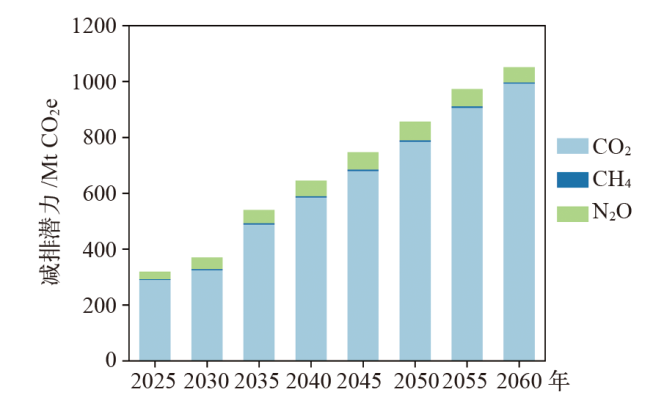
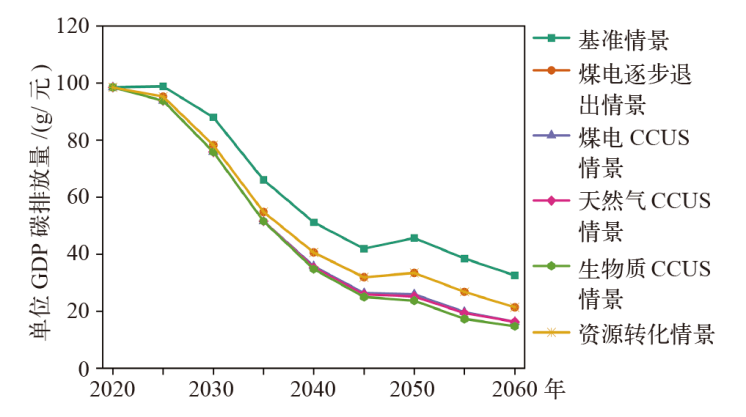
气候变化研究进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 616-633.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.286
“双碳”目标下中国能源供需演变路径规划模拟研究
蔡立亚1( ), 郭剑锋2, 石川3, 王浩彬3(
), 郭剑锋2, 石川3, 王浩彬3( ), 朱荣琦4, 牛艳5, 薛志光6, 白若冰7, 计军平8, 段婧琳1
), 朱荣琦4, 牛艳5, 薛志光6, 白若冰7, 计军平8, 段婧琳1
- 1 国家电投集团科学技术研究院有限公司,北京 102209
2 中国科学院科技战略咨询研究院,北京 100190
3 清华大学环境学院,北京 100084
4 北京航空航天大学经济管理学院,北京 100191
5 清华大学电机系,北京 100084
6 清华大学工程物理系,北京 100084
7 清华大学建设管理系,北京 100084
8 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)经济管理学院,深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2022-12-27修回日期:2023-10-23出版日期:2023-09-30发布日期:2023-07-17 -
通讯作者:王浩彬,男,博士研究生,whb19@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn -
作者简介:蔡立亚,女,高级经济师,loveparadise15@163.com -
基金资助:公司项目“企业绿色低碳领先指数研究”(C-TZH-202301)
Simulation research on the evolution pathway planning of energy supply and demand in China under the dual carbon targets
CAI Li-Ya1( ), GUO Jian-Feng2, SHI Chuan3, WANG Hao-Bin3(
), GUO Jian-Feng2, SHI Chuan3, WANG Hao-Bin3( ), ZHU Rong-Qi4, NIU Yan5, XUE Zhi-Guang6, BAI Ruo-Bing7, JI Jun-Ping8, DUAN Jing-Lin1
), ZHU Rong-Qi4, NIU Yan5, XUE Zhi-Guang6, BAI Ruo-Bing7, JI Jun-Ping8, DUAN Jing-Lin1
- 1 State Power Investment Corporation Research Institute, Beijing 102209, China
2 Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
3 School of Environment, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4 School of Economics and Management, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
5 Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
6 Department of Engineering Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
7 Department of Construction Management, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
8 School of Economics and Management, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518055, China
-
Received:2022-12-27Revised:2023-10-23Online:2023-09-30Published:2023-07-17
摘要:
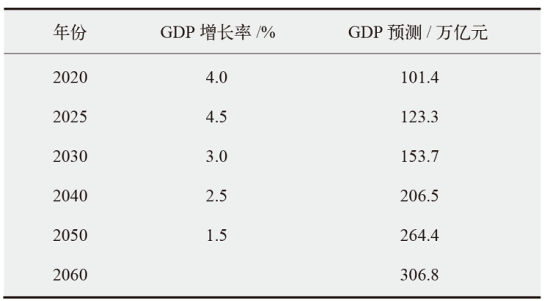
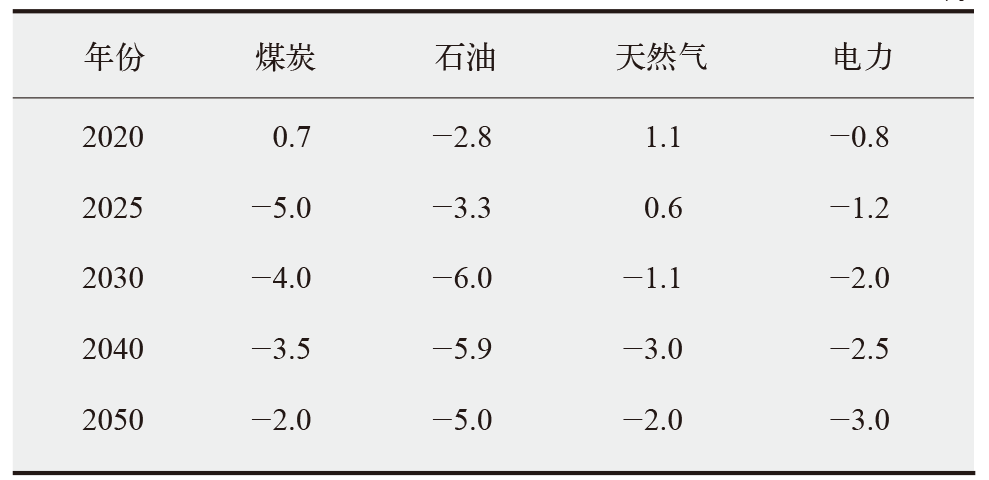
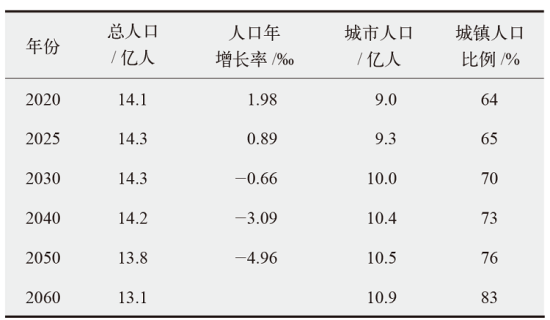
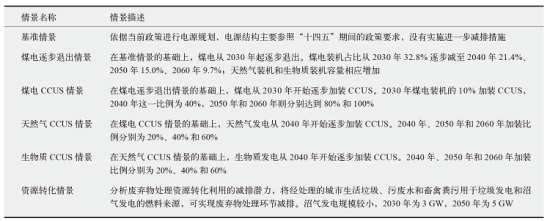
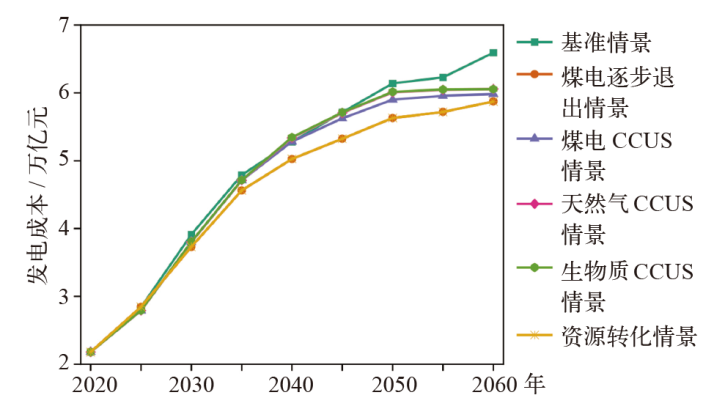
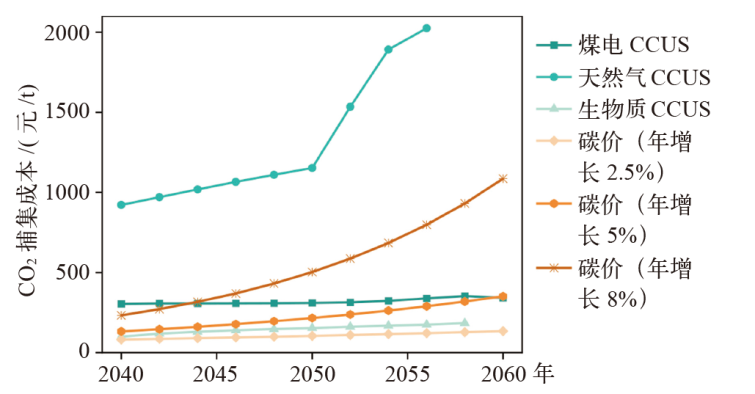
能源低碳转型是实现碳达峰、碳中和的关键,关系到我国经济社会发展全局。基于LEAP能源系统模型,以电力行业为重点减排行业,提出中国中长期“双碳”发展路径构想,模拟多情景下的能源需求、能源供给、CO2排放量和成本,分析能源配置的生态及经济影响。研究发现能源消费呈现“减煤稳油增气,电能替代加速”的局面,终端能源消费可在2040年前达峰,终端能源消费CO2排放可在2030年前达峰,碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)技术是实现CO2减排,同时保持一定火电规模以维持电网安全稳定运行的重要手段,且未来逐步具有技术优势。最后,提出了持续推进碳排放总量和强度“双控”,以技术革新促进电力系统低碳转型,以及完善全国碳市场建设促进碳排放交易等三方面实现“双碳”目标的政策建议。
引用本文
蔡立亚, 郭剑锋, 石川, 王浩彬, 朱荣琦, 牛艳, 薛志光, 白若冰, 计军平, 段婧琳. “双碳”目标下中国能源供需演变路径规划模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(5): 616-633.
CAI Li-Ya, GUO Jian-Feng, SHI Chuan, WANG Hao-Bin, ZHU Rong-Qi, NIU Yan, XUE Zhi-Guang, BAI Ruo-Bing, JI Jun-Ping, DUAN Jing-Lin. Simulation research on the evolution pathway planning of energy supply and demand in China under the dual carbon targets[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 616-633.
| [1] | 何建坤. 碳达峰碳中和目标导向下能源和经济的低碳转型[J]. 环境经济研究, 2021, 6 (1): 1-9. |
| He J K. Low carbon transformation of energy and economy aiming for the peaking of carbon emission and carbon neutrality[J]. Journal of Environmental Economics, 2021, 6 (1): 1-9 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 辛保安, 单葆国, 李琼慧, 等. “双碳”目标下“能源三要素”再思考[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42 (9): 3117-3126. |
| Xin B A, Shan B G, Li Q H, et al. Rethinking of the “three elements of energy” toward carbon peak and carbon neutrality[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42 (9): 3117-3126 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 王灿, 张雅欣. 碳中和愿景的实现路径与政策体系[J]. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12 (6): 58-64. |
| Wang C, Zhang Y X. Implementation pathway and policy system of carbon neutrality vision[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 12 (6): 58-64 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 胡鞍钢. 中国实现2030年前碳达峰目标及主要途径[J]. 北京工业大学学报 (社会科学版), 2021, 21 (3): 1-15. |
| Hu A G. China’s goal of achieving carbon peak by 2030 and its main approaches[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2021, 21 (3): 1-15 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 张希良, 黄晓丹, 张达, 等. 碳中和目标下的能源经济转型路径与政策研究[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38 (1): 35-66. |
| Zhang X L, Huang X D, Zhang D, et al. Energy economy transition pathway and policy research under carbon neutral target[J]. Management World, 2022, 38 (1): 35-66 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 项目综合报告编写组. 《中国长期低碳发展战略与转型路径研究》综合报告[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2020, 30 (11): 1-25. |
| Project General Report Writing Team. General report study on China’s long-term low carbon development strategy and transition pathway[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2020, 30 (11): 1-25 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 刘晓龙, 崔磊磊, 李彬, 等. 碳中和目标下中国能源高质量发展路径研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报 (社会科学版), 2021, 23 (3): 1-8. |
| Liu X L, Cui L L, Li B, et al. Research on the high-quality development path of China’s energy industry under the target of carbon neutralization[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2021, 23 (3): 1-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 段宏波, 汪寿阳. 中国的挑战: 全球温控目标从2℃到1.5℃的战略调整[J]. 管理世界, 2019, 35 (10): 50-63. |
| Duan H B, Wang S Y. China’s challenge: strategic adjustment of the global temperature control target from 2℃to 1.5℃[J]. Management World, 2019, 35 (10): 50-63 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 姜克隽. 实现多种目标下的能源和经济转型路径[J]. 阅江学刊, 2022, 14 (1): 34-43, 172. |
| Jiang K J. Energy and economic transformation paths to achieve multiple goals[J]. Yuejiang Academic Journal, 2022, 14 (1): 34-43, 172 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 周孝信, 赵强, 张玉琼. “双碳”目标下我国能源电力系统发展前景和关键技术[J]. 中国电力企业管理, 2021 (31): 14-17. |
| Zhou X X, Zhao Q, Zhang Y Q. Development prospect and key technologies of China’s energy and power system under the “dual carbon” target[J]. China Power Enterprise Management, 2021 (31): 14-17 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] |
Fang K, Li C, Tang Y, et al. China’s pathways to peak carbon emissions: new insights from various industrial sectors[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 306: 118039
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118039 URL |
| [12] | 刘新建, 宋中炜, 吴洁. 碳中和目标下能源经济系统转型: 碳定价与可再生能源政策作用有多大?[J/OL]. 中国管理科学, 2023 [2023-02-27]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2022.0586. |
| Liu X J, Song Z W, Wu J. Transforming the energy economic system with the carbon neutrality goal: how much can the carbon pricing and renewable energy policy contribute?[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2023 [2023-02-27]. https://doi.org/10.16381/j.cnki.issn1003-207x.2022.0586 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 李丹阳, 陈文颖. 碳中和目标下全球交通能源转型路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (2): 1-13. |
| Li D Y, Chen W Y. Global transportation energy transition pathways towards carbon neutrality targets[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (2): 1-13 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] |
Bataille C, Melton N. Energy efficiency and economic growth: a retrospective CGE analysis for Canada from 2002 to 2012[J]. Energy Economics, 2017, 64: 118-130
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2017.03.008 URL |
| [15] |
Zhou N, Fridley D, Khanna N Z, et al. China’s energy and emissions outlook to 2050: perspectives from bottom-up energy end-use model[J]. Energy Policy, 2013, 53: 51-62
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2012.09.065 URL |
| [16] | Heaps C G. LEAP: the low emissions analysis platform[M/OL]. 2020 [2022-10-25]. https://leap.sei.org |
| [17] | 黄莹, 郭洪旭, 廖翠萍, 等. 基于LEAP模型的城市交通低碳发展路径研究: 以广州市为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15 (6): 670-683. |
| Huang Y, Guo H X, Liao C P, et al. Study on low-carbon development path of urban transportation sector based on LEAP model: take Guangzhou as an example[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15 (6): 670-683 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Cai L, Luo J, Wang M, et al. Pathways for municipalities to achieve carbon emission peak and carbon neutrality: a study based on the LEAP model[J]. Energy, 2023, 262: 125435
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.125435 URL |
| [19] | Cai L, Duan J, Lu X, et al. Pathways for electric power industry to achieve carbon emissions peak and carbon neutrality based on LEAP model: a case study of state-owned power generation enterprise in China[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2022: 108334 |
| [20] | 刘俊伶, 孙一赫, 王克, 等. 中国交通部门中长期低碳发展路径研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (5): 513-521. |
| Liu J L, Sun Y H, Wang K, et al. Study on mid- and long-term low carbon development pathway for China’s transport sector[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14 (5): 513-521 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | Liu Y, Chen S, Jiang K, et al. The gaps and pathways to carbon neutrality for different type cities in China[J]. Energy, 2021: 122596 |
| [22] | 樊星, 李路, 秦圆圆, 等. 主要发达经济体从碳达峰到碳中和的路径及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (1): 102-115. |
| Fan X, Li L, Qin Y Y, et al. The pathway from carbon peak to carbon neutrality in major developed economies and its insights[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (1): 102-115 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
McDonald A, Schrattenholzer L. Learning rates for energy technologies[J]. Energy Policy, 2001, 29 (4): 255-261
doi: 10.1016/S0301-4215(00)00122-1 URL |
| [24] | 余碧莹, 赵光普, 安润颖, 等. 碳中和目标下中国碳排放路径研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报 (社会科学版), 2021, 23 (2): 17-24. |
| Yu B Y, Zhao G P, An R Y, et al. Research on China’s CO2 emission pathway under carbon neutral target[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology (Social Science Edition), 2021, 23 (2): 17-24 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 中国石油. 世界与中国能源展望[R]. 中国石油天然气集团有限公司, 2021. |
| China National Petroleum Corporation CNPC. World and China energy outlook[R]. CNPC, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 国网能源研究院有限公司. 中国能源电力发展展望[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2021: 32-35. |
| State Grid Energy Research Institure. China energy & electricity outlook 2021[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2021: 32-35 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 李国志, 刘美瑜. 中国城镇居民直接碳排放因素分解研究[J]. 环境影响评价, 2017, 39 (4): 93-96. |
| Li G Z, Liu M Y. Study on factorization of urban residents direct carbon emissions in China[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2017, 39 (4): 93-96 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 刘岱淞. 上海市居民生活用能碳排放的因素分解研究[J]. 上海经济, 2021, 2: 56-73. |
| Liu D S. Study on factor decomposition of carbon emissions from household energy use in Shanghai[J]. Shanghai Economy, 2021, 2: 56-73 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 张宇轩, 苏义坤. 面向可持续发展的农村居民生活用能结构转型影响因素研究[J]. 价值工程, 2020, 39 (8): 292-298. |
| Zhang Y X, Su Y K. Research on the influencing factors of the transformation of rural residents’ living energy use structure for sustainable development[J]. Value Engineering, 2020, 39 (8): 292-298 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2021[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2021. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook 2021[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家人口发展规划(2016—2030年)[R/OL]. 2016 [2022-12-27]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/201705/t20170502_1196730.html. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National population development plan (2016-2030)[R/OL]. 2016 [2022-12-27]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/201705/t20170502_1196730.html (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 欧阳慧, 李智, 李沛霖. “十四五”时期我国城镇化率变化趋势及政策含义[J]. 城市发展研究, 2021, 28 (6): 1-9. |
| Ouyang H, Li Z, Li P L. Trend and policy implication of urbanization rate in China during the 14th Five Year Plan period[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2021, 28 (6): 1-9 (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | UN. World population prospects[R]. UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs Population Division, 2019 |
| [34] | 育娲人口. 中国人口预测报告2021版[R]. 育娲人口研究, 2021. |
| Yuwa Population. China population projections report 2021[R]. Yuwa Population Research, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 张现苓, 翟振武, 陶涛. 中国人口负增长: 现状、未来与特征[J]. 人口研究, 2020, 44 (3): 3-20. |
| Zhang X L, Zhai Z W, Tao T. China’s negative population growth: present, future and characteristics[J]. Population Research, 2020, 44 (3): 3-20 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 陈霞, 肖岚. Logistic模型的改进与中国人口预测[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2020, 35 (2): 239-243. |
| Chen X, Xiao L. Improved logistic model and China population forecast[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Information Technology, 2020, 35 (2): 239-243 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | IEA International Energy Agency, NEA (Nuclear Energy Agency). Projected costs of generating electricity[R]. IEA, NEA, 2020 |
| [38] | 国家统计局能源统计司. 中国能源统计年鉴2021[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022: 94-99. |
| Office of Energy Statistics National Bureau of Statistics. China energy statistical yearbook 2021[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022: 94-99 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 国家发展改革委, 国家能源局等. “十四五”可再生能源发展规划[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-12-27]. http://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/1310611148_16541341407541n.pdf. |
| National Development and Reform Commission, National Energy Administration. “Fourteen Five” renewable energy development plan[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-12-27]. http://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/1310611148_16541341407541n.pdf (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 周孝信. 双碳目标下我国能源电力系统发展前景和关键技术[R]. 上海: SNEC第十五届全球光伏大会, 2021. |
| Zhou X X. Prospects and key technologies for the development of China’s energy and power system under the double carbon target[R]. Shanghai:SNEC 15th (2021) International Photovoltaic Power Generation Conference, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 朱立志, 刘静, 向猛. 我国农业生产能源消费变化与趋势分析[J]. 环境经济, 2010 (12): 44-47. |
| Zhu L Z, Liu J, Xiang M. Analysis of changes and trends of agricultural energy production consumption in China[J]. Evironmental Economy, 2010 (12): 44-47 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 王海林, 何建坤. 交通部门CO2排放、能源消费和交通服务量达峰规律研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2018, 28 (2): 59-65. |
| Wang H L, He J K. Peaking rule of CO2 emissions, energy consumption and transport volume in transportation sector[J]. China Population Resources and Environment, 2018, 28 (2): 59-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 张车伟, 蔡翼飞. 2021人口与劳动绿皮书: 中国人口与劳动问题报告[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2021: 79-98. |
| Zhang C W, Cai Y F. Green book of population and labor[M]. Beijing: Social Science Academic Press, 2021: 79-98 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 国务院. 2030年前碳达峰行动方案[R]. 国务院, 2021. |
| The State Council. Carbon peaking action program by 2030[R]. The State Council, 2021 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | Sun H, Wang E, Li X, et al. Potential biomethane production from crop residues in China: contributions to carbon neutrality[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021: 148 |
| [46] | Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P, et al. What a waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050[R]. World Bank Publications, 2018 |
| [47] |
Chang H N, Kim N J, Kang J, et al. Biomass-derived volatile fatty acid platform for fuels and chemicals[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2010, 15 (1): 1-10
doi: 10.1007/s12257-009-3070-8 URL |
| [48] | 张亚雷. 污水处理低碳技术的现状与评价[J]. 质量与认证, 2022 (8): 78-80. |
| Zhang Y L. Status and evaluation of low carbon technologies for wastewater treatment[J]. Quality and Certification, 2022 (8): 78-80 (in Chinese) | |
| [49] | 付鹏, 徐国平, 李兴华, 等. 我国生物质发电行业发展现状与趋势及碳减排潜力分析[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2021, 47: 48-52. |
| Fu P, Xu G P, Li X H, et al. Analysis of the development status and trends of China’s biomass power industry and carbon emission reduction potential[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 47: 48-52 | |
| [50] | 科学技术部社会发展科技司. 中国碳捕集利用与封存技术发展路线图 (2019)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 12. |
| Department of Social Development Science and Technology, Ministry of Science and Technology. Roadmap for carbon capture utilization and storage technology development in China (2019)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 12 (in Chinese) | |
| [51] | 蔡博峰, 李琦, 张贤, 等. 中国二氧化碳捕集利用与封存 (CCUS) 年度报告 (2021): 中国CCUS 路径研究[R]. 生态环境部环境规划院, 中国科学院武汉岩土力学研究所, 中国21世纪议程管理中心, 2021. |
| Cai B F, Li Q, Zhang X, et al. Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) annual report (2021) in China: China’s CCUS pathway research[R]. Chinese Academy of Environmental Planning, Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, The Administrative Center for China’s Agenda 21, 2021 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 王睿, 张赫, 张韵, 黄雅哲. 基于动态改进等比例法的省级CO2排放总量目标分解研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 238-248. |
| [2] | 杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 李政. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 191-202. |
| [3] | 樊星, 李路, 秦圆圆, 高翔. 主要发达经济体从碳达峰到碳中和的路径及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 102-115. |
| [4] | 李品, 谢晓敏, 黄震. 德国能源转型进程及对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 116-126. |
| [5] | 彭雪婷, 吕昊东, 张贤. IPCC AR6报告解读:全球碳捕集利用与封存(CCUS)技术发展评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(5): 580-590. |
| [6] | 曾桉, 谭显春, 王毅, 高瑾昕. 国际气候投融资监测、报告与核证制度及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 215-229. |
| [7] | 张海军, 段茂盛. 中国试点ETS的碳减排效果评估——基于分省高耗能工业子行业数据的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 579-589. |
| [8] | 王敏, 冯相昭, 安祺, 卓岳, 赵梦雪, 杜晓林, 王鹏. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的青海省绿色低碳发展策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 598-607. |
| [9] | 何峰, 刘峥延, 邢有凯, 高玉冰, 毛显强. 中国水泥行业节能减排措施的协同控制效应评估研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 400-409. |
| [10] | 冯相昭, 赵梦雪, 王敏, 杜晓林, 田春秀, 高霁. 中国交通部门污染物与温室气体协同控制模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 279-288. |
| [11] | 原嫄, 孙欣彤. 城市化、产业结构、能源消费、经济增长与碳排放的关联性分析——基于中国省际收入水平异质性的实证研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6): 738-747. |
| [12] | 陈怡, 田川, 曹颖, 刘强, 郑晓奇. 中国电力行业碳排放达峰及减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(5): 632-640. |
| [13] | 刘俊伶,孙一赫,王克,邹骥,孔英. 中国交通部门中长期低碳发展路径研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 513-521. |
| [14] | 崔铁宁, 鲁婷. 城市公共自行车自愿碳减排机制初探——以北京市为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(2): 112-117. |
| [15] | 许金华 范英. 中国水泥行业节能潜力和CO2减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(5): 341-349. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||