气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (5): 641-658.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.072
气候变化对水稻病害影响的研究进展与展望
南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心/生态与应用气象学院 南京 210044
-
收稿日期:2025-04-02修回日期:2025-06-16出版日期:2025-09-30发布日期:2025-09-05 -
通讯作者:胡正华,男,教授,zhhu@nuist.edu.cn -
作者简介:何昊,男,博士研究生,202311080003@nuist.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(42071023);国家自然科学基金面上项目(42375114)
Impact of climate change on rice diseases: research progress and future prospects
HE Hao( ), LI Man, LIU Miao, CHEN Ming-Jie, LI Qi, HU Zheng-Hua(
), LI Man, LIU Miao, CHEN Ming-Jie, LI Qi, HU Zheng-Hua( )
)
Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters / School of Ecology and Applied Meteorology ,Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2025-04-02Revised:2025-06-16Online:2025-09-30Published:2025-09-05
摘要:
气候变化对水稻病害的影响日益显著,已成为影响全球水稻生产和粮食安全的重要因素。文中综述了气候变化影响水稻病害的主要机制及相关研究进展,主要包括:气温升高加速病原体生命周期,提高其孢子萌发、侵染和扩散能力,同时抑制水稻防御激素信号通路,削弱其免疫能力;降水模式的变化不仅影响田间湿度和病原体传播,还通过改变水稻冠层结构和根际环境,调控微气候与土壤微生物群落,间接影响病害的发生与流行;大气CO2浓度升高改变水稻碳氮代谢,降低抗病次生代谢物含量,而O3浓度升高则通过氧化胁迫破坏水稻的物理防御屏障,干扰病害信号传导网络;极端天气事件如台风、干旱增加水稻的生理胁迫和易感性,并助推病害远距离扩散。当前研究虽揭示了部分关键机制,但在跨区域、长时间尺度的监测和系统性解析方面仍存在局限,尤其是病原体的适应性进化及其与水稻生理防御的动态关系仍需深入探讨。未来建议开展跨尺度、跨区域的系统研究,以揭示水稻病害在不同气候情景下的传播规律与动态响应。此外,应加快抗病品种选育、优化农艺管理、构建智能监测预警系统,实现从基因到田间、从预警到干预的全链条、多层次协同防控体系,为气候变化背景下的水稻病害防控提供科学支撑。
引用本文
何昊, 李曼, 刘淼, 陈铭杰, 李琪, 胡正华. 气候变化对水稻病害影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 641-658.
HE Hao, LI Man, LIU Miao, CHEN Ming-Jie, LI Qi, HU Zheng-Hua. Impact of climate change on rice diseases: research progress and future prospects[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(5): 641-658.
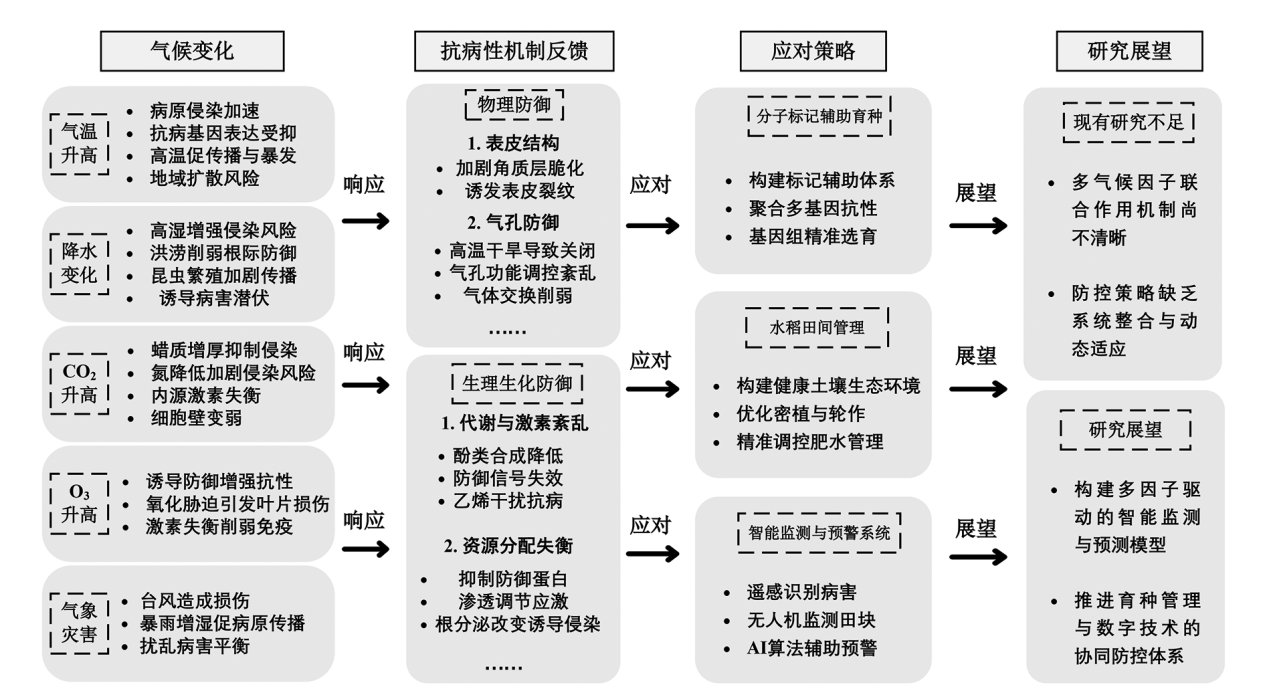
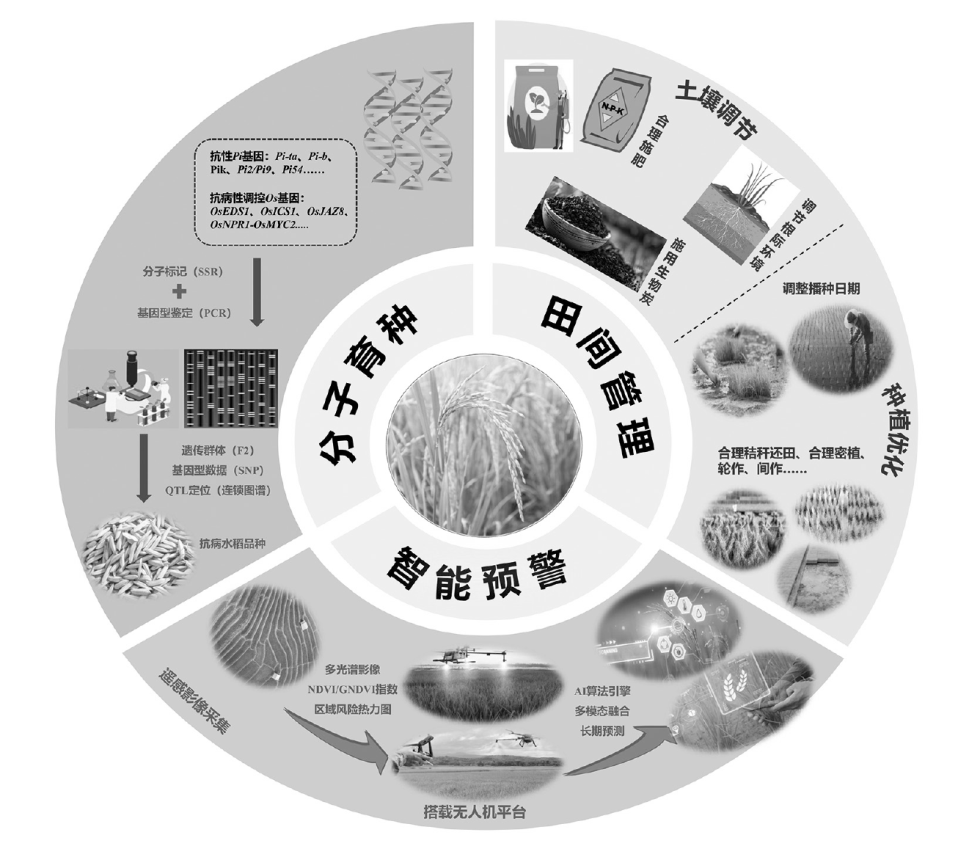
图1 气候变化对水稻病害影响、抗病性机制反馈、应对策略以及研究展望流程图
Fig. 1 Flowchart of the climate change on rice diseases, feedback mechanisms of disease resistance, response strategies, and future research directions
| [1] | Ortiz-Bobea A, Ault T R, Carrillo C M, et al. Anthropogenic climate change has slowed global agricultural productivity growth[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11 (4): 306-312 |
| [2] | 周泽宇, 王君华, 曹颖. 全球适应气候变化行动进展评估及相关工作建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20 (6): 764-772. |
| Zhou Z Y, Wang J H, Cao Y. Assessment of global climate change adaptation progress and related recommendations[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20 (6): 764-772 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | Cai S, Zhao X, Pittelkow C M, et al. Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China[J]. Nature, 2023, 615 (7950): 73-79 |
| [4] | Cassman K G, Grassini P. A global perspective on sustainable intensification research[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2020, 3 (4): 262-268 |
| [5] | Jing L, Zhou N, Lai S, et al. Interactions between elevated atmospheric CO2 and temperature on rice yield are highly dependent on growth season temperature[J]. Field Crops Research, 2024, 307: 109270 |
| [6] | Zhang J, Li Y, Yu Z, et al. Elevated atmospheric CO2 and warming enhance the acquisition of soil-derived nitrogen rather than urea fertilizer by rice cultivars[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2022, 324: 109117 |
| [7] | Yuan M, Cai C, Wang X, et al. Warm air temperatures increase photosynthetic acclimation to elevated CO2 concentrations in rice under field conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2021, 262: 108036 |
| [8] | Wang W, Yu Z, Zhang W, et al. Responses of rice yield, irrigation water requirement and water use efficiency to climate change in China: historical simulation and future projections[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2014, 146: 249-261 |
| [9] | Eseola A B, Ryder L S, Osés-Ruiz M, et al. Investigating the cell and developmental biology of plant infection by the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Fungal Genetics and Biology, 2021, 154: 103562 |
| [10] | Savary S, Willocquet L, Pethybridge S J, et al. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops[J]. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2019, 3 (3): 430-439 |
| [11] | Hunjan M S, Kamboj I, Lore J S, et al. Expression of defense related enzymes in rice near isogenic lines IRBB4 and IRBB7 challenged with Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae at elevated temperature[J]. Indian Phytopathology, 2021, 74 (1): 33-43 |
| [12] | Lee M, Lee S, Park J W, et al. Prevalence of rice stripe virus can be altered by temperature and the virus-mediated development of insect vector, Laodelphax striatellus, in Korea[J]. Journal of Asia-Pacific Entomology, 2017, 20 (4): 1145-1149 |
| [13] | Li C, Yang W, Zhang Y, et al. Investigation and characterization of rice dwarfing epidemic caused by southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus in Jiangsu in 2023[J]. Virology, 2024, 593: 110027 |
| [14] | 姚彦坡, 朱永官, 褚海燕. 加强气候变化背景下植物病原真菌控制技术的创新和突破[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43 (3): 473-475. |
| Yao Y P, Zhu Y G, Chu H Y. Strengthen the innovation and breakthrough of plant pathogenic fungi control technology in the context of climate change[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43 (3): 473-475 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | Pugliese M, Gilardi G, Garibaldi A, et al. The impact of climate change on vegetable crop diseases and their management: the value of phytotron studies for the agricultural industry and associated stakeholders[J]. Phytopathology, 2024, 114 (5): 843-854 |
| [16] | Richard B, Qi A, Fitt B D L. Control of crop diseases through integrated crop management to deliver climate-smart farming systems for low- and high-input crop production[J]. Plant Pathology, 2022, 71 (1): 187-206 |
| [17] | Waheed A, Haxim Y, Islam W, et al. Climate change reshaping plant-fungal interaction[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 238: 117282 |
| [18] |
Azizi P, Rafii M Y, Abdullah S N A, et al. Toward understanding of rice innate immunity against magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 2016, 36 (1): 165-174
doi: 10.3109/07388551.2014.946883 pmid: 25198435 |
| [19] | 张荣胜, 陈志谊, 刘永锋. 水稻细菌性条斑病菌遗传多样性和致病型分化研究[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2011, 25 (5): 523-528. |
| Zhang R S, Chen Z Y, Liu Y F. Genetic diversity and pathotype variability of xanthomans oryzae pv. oryzicola strains[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2011, 25 (5): 523-528 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | Feng Z, Ding X, Zhang H, et al. Spectroscopic detection of wheat yellow mosaic virus infection based on invariant shape spectral processing and machine learning[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2023, 154: 110750 |
| [21] | Abraham A. Synergistic crop virus disease complexes in Sub-Saharan Africa: causes, consequences and control[J]. Phytoparasitica, 2024, 52 (1): 27 |
| [22] | Pitt W J, Kairy L R, Mora V, et al. Landscapes with higher crop diversity have lower aphid species richness but higher plant virus prevalence[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 61 (7): 1573-1586 |
| [23] |
Fengmin Z, Zhenzhen C, Xin Z, et al. Interaction between ustilaginoidea virens and rice and its sustainable control[J]. Rice Science, 2024, 31 (3): 269-284
doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2023.11.012 |
| [24] |
Dean R, van Kan J A L, Pretorius Z A, et al. The top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2012, 13 (4): 414-30
doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x pmid: 22471698 |
| [25] | Ansari M M, Bisht N, Singh T, et al. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens modulate autophagy pathways to control Rhizoctonia solani infection in rice[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2025, 218: 109317 |
| [26] |
Sunani S K, Koti P S, Sunitha N C, et al. Ustilaginoidea virens, an emerging pathogen of rice: the dynamic interplay between the pathogen virulence strategies and host defense[J]. Planta, 2024, 260 (4): 92
doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04523-x pmid: 39261328 |
| [27] | Chinnaiah S, Gautam S, Workneh F, et al. First report of Sw-5 resistance-breaking strain of tomato spotted wilt virus (Orthotospovirus tomatomaculae) infecting tomato in Texas[J]. Plant Disease, 2023, 107 (8): 2569 |
| [28] | Yan H, Mi Y, Man Z, et al. First report of leaf spot disease caused by Fusarium asiaticum on Lonicera caerulea L. in Heilongjiang province, China[J]. Plant Disease, 2024 |
| [29] |
Mishra R, Zheng W, Joshi R K, et al. Genome editing strategies towards enhancement of rice disease resistance[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28 (2): 133-145
doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.01.003 |
| [30] | 张蕾. 气候变化背景下农作物病虫害的变化及区域动态预警研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2013. |
| Zhang L. Variation and regional dynamic warning of crop disease and pestsunder climate change[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, 2013 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 王丽, 霍治国, 张蕾, 等. 气候变化对中国农作物病害发生的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31 (7): 1673-1684. |
| Wang L, Huo Z G, Zhang L, et al. Effects of climate change on the occurrence of crop diseases in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31 (7): 1673-1684 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 戚海迪, 张定海, 单立山, 等. 昆虫病原真菌感染昆虫宿主的机制和宿主昆虫的防御策略研究进展[J]. 生物多样性, 2023, 31 (11): 226-239. |
| Qi H D, Zhang D H, Shan L S, et al. Advances in the mechanisms of entomopathogenic fungi infecting insect hosts and the defense strategies of insects[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2023, 31 (11): 226-239 (in Chinese) | |
| [33] |
Singh B K, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Egidi E, et al. Climate change impacts on plant pathogens, food security and paths forward[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2023, 21 (10): 640-656
doi: 10.1038/s41579-023-00900-7 pmid: 37131070 |
| [34] | Joshi M, Hawkins E, Sutton R, et al. Projections of when temperature change will exceed 2℃ above pre-industrial levels[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2011, 1 (8): 407-412 |
| [35] | Agnew D C. A global timekeeping problem postponed by global warming[J]. Nature, 2024, 628 (8007): 333-336 |
| [36] | Matić S, Garibaldi A, Gullino M L. Combined and single effects of elevated CO2 and temperatures on rice bakanae disease under controlled conditions in phytotrons[J]. Plant Pathology, 2021, 70 (4): 815-826 |
| [37] | Du Y, Qi Z, Yu J, et al. Effects of panicle development stage and temperature on rice panicle blast infection by Magnaporthe oryzae and visualization of its infection process[J]. Plant Pathology, 2021, 70 (6): 1436-1444 |
| [38] |
Chen Q, Huang X, Chen X, et al. Reversible activation of XA21-mediated resistance by temperature[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2019, 153 (4): 1177-1184
doi: 10.1007/s10658-018-01634-6 |
| [39] | 黄乾龙, 李贤勇, 欧阳杰, 等. 高温胁迫对抽穗扬花期水稻丙二醛含量和抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 杂交水稻, 2025, 40 (1): 21-26. |
| Huang Q L, Li X Y, Ouyang J, et al. Effects of high temperature stress on the MDA content and antioxidant enzyme activity of rice at heading and flowering stage[J]. Hybrid Rice, 2025, 40 (1): 21-26 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] |
汪胜勇, 陈宇航, 陈会丽, 等. 水稻减数分裂期高温对苯丙烷类代谢及下游分支代谢途径的影响[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2023, 37 (4): 368-378.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221112 |
|
Wang S Y, Chen Y H, Chen H L, et al. Effects of high temperature on phenylpropane metabolism and downstream branch metabolic pathways in rice meiosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2023, 37 (4): 368-378 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2023.221112 |
|
| [41] | Qiu J, Xie J, Chen Y, et al. Warm temperature compromises JA-regulated basal resistance to enhance Magnaporthe oryzae infection in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2022, 15 (4): 723-739 |
| [42] | Eastburn D M, McElrone A J, Bilgin D D. Influence of atmospheric and climatic change on plant-pathogen interactions[J]. Plant Pathology, 2011, 60 (1): 54-69 |
| [43] | 江陵杰, 范鹏, 郭柯凡, 等. 水稻冠层温度研究进展[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2020, 36 (1): 234-242. |
| Jiang L J, Fan P, Guo K F, et al. Research progress on the factors affecting canopy temperature of rice[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 36 (1): 234-242 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | Chakraborty S, Newton A C. Climate change, plant diseases and food security: an overview[J]. Plant Pathology, 2011, 60 (1): 2-14 |
| [45] | He D C, Zhan J, Cheng Z B, et al. Viruliferous rate of small brown planthopper is a good indicator of rice stripe disease epidemics[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6 (1): 21376 |
| [46] | Hwang S, Kim D. Effect of temperature on rice stripe virus infection, transmission efficiency, and the development period in laodelphax striatellus[J]. Entomological Research, 2025, 55 (2): e70021 |
| [47] | Jia Q, Lv B, Guo M, et al. Effect of rice growth stage, temperature, relative humidity and wetness duration on infection of rice panicles by Villosiclava virens[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 141 (1): 15-25 |
| [48] | Song J H, Wang Y, Chen L Y, et al. Higher relative humidity and more moderate temperatures increase the severity of rice false smut disease in the rice-crayfish coculture system[J]. Food and Energy Security, 2022, 11 (1): e323 |
| [49] | 邱虎森, 甄博, 周新国. 高温对水稻根际细菌群落及功能代谢多样性的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39 (11): 97-103. |
| Qiu H S, Zhen B, Zhou X G. The effects of thermal stress on diversity of rhizobacteria and functional genes of rice rhizosphere[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39 (11): 97-103 (in Chinese) | |
| [50] | Jones R A C. Chapter three-future scenarios for plant virus pathogens as climate change progresses[M]//Kielian M, Maramorosch K, Mettenleiter T C. Advances in virus research. Academic Press, 2016: 87-147 |
| [51] | Yamamura K, Yokozawa M. Prediction of a geographical shift in the prevalence of rice stripe virus disease transmitted by the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus (Fallén) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae), under global warming [J]. Applied Entomology and Zoology, 2002, 37 (1): 181-90 |
| [52] | 赵梦, 欧阳芳, 张永生, 等. 2000—2010年我国水稻病虫害发生与为害特征分析[J]. 生物灾害科学, 2014, 37 (4): 275-280. |
| Zhao M, Ouyang F, Zhang Y S, et al. Characteristics of occurrence and damage from diseases and insect pests in rice production in China during 2000-2010[J]. Biological Disaster Science, 2014, 37 (4): 275-280 (in Chinese) | |
| [53] | 沈建新, 董国堃, 张水妹, 等. 水稻细菌性条斑病发生流行与综防技术[J]. 植物保护, 2002 (1): 33-34. |
| Shen J X, Dong G K, Zhang S M, et al. Epidemic and comprehensive control technology of bacterial stripe spot disease in rice[J]. Plant Protection, 2002 (1): 33-34 (in Chinese) | |
| [54] | Macasero J B M, Castilla N P, Pangga I B, et al. Influence of production situation on the incidence of brown spot of rice (Oryza sativa) caused by Bipolaris oryzae in the Philippines[J]. Plant Pathology, 2024, 73 (2): 390-403 |
| [55] | 陈冰, 陈观浩, 江满桃, 等. 影响南方水稻黑条矮缩病发生流行的因子分析[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42 (2): 204-208, 24. |
| Chen B, Chen G H, Jiang M T, et al. Factor analysis of epidemic of Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus[J]. Plant Protection, 2016, 42 (2): 204-208, 24 (in Chinese) | |
| [56] | Naveenkumar R, Anandan A, Singh V, et al. Deciphering environmental factors and defense response of rice genotypes against sheath blight disease[J]. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2022, 122: 101916 |
| [57] | 张国, 朱凤, 于居龙, 等. 2020年江苏省稻飞虱虫源地及暴发成因分析[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2022, 44 (3): 658-669. |
| Zhang G, Zhu F, Yu J Y, et al. Source areas and outbreak reasons of rice planthoppers in Jiangsu province, 2020[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2022, 44 (3): 658-669 (in Chinese) | |
| [58] |
颜松毅, 陈冰, 陈蔚烨, 等. 粤西地区南方水稻黑条矮缩病的流行规律及防治[J]. 农学学报, 2017, 7 (10): 14-18.
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17050003 |
|
Yan S Y, Chen B, Chen W Y, et al. Southern rice black-streaked dwarf disease: the epidemic law and control in western Guangdong[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2017, 7 (10): 14-18 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas17050003 |
|
| [59] |
Bailey-Serres J, Fukao T, Gibbs D J, et al. Making sense of low oxygen sensing[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17 (3): 129-138
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.12.004 pmid: 22280796 |
| [60] | Li P, Tedersoo L, Crowther T W, et al. Fossil-fuel-dependent scenarios could lead to a significant decline of global plant-beneficial bacteria abundance in soils by 2100[J]. Nature Food, 2023, 4 (11): 996-1006 |
| [61] | Martínez-Arias C, Witzell J, Solla A, et al. Beneficial and pathogenic plant-microbe interactions during flooding stress[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2022, 45 (10): 2875-2897 |
| [62] | Huang X Q, Wen T, Zhang J B, et al. Control of soil-borne pathogen Fusarium oxysporum by biological soil disinfestation with incorporation of various organic matters[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 143 (2): 223-235 |
| [63] | Mohiddin F A, Majid R, Bhat A H, et al. Molecular phylogeny, pathogenic variability and phytohormone production of Fusarium species associated with bakanae disease of rice in temperate agro-ecosystems[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2021, 48 (4): 3173-3184 |
| [64] |
Mendes R, Garbeva P, Raaijmakers J M. The rhizosphere microbiome: significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 2013, 37 (5): 634-643
doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12028 pmid: 23790204 |
| [65] | Raaijmakers J M, Paulitz T C, Steinberg C, et al. The rhizosphere: a playground and battlefield for soilborne pathogens and beneficial microorganisms[J]. Plant and Soil, 2009, 321 (1): 341-361 |
| [66] |
Fang Y, Xiong L. General mechanisms of drought response and their application in drought resistance improvement in plants[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2015, 72 (4): 673-689
doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1767-0 pmid: 25336153 |
| [67] | 朱书生, 黄惠川, 刘屹湘, 等. 农业生物多样性防控作物病害的研究进展[J]. 植物保护学报, 2022, 49 (1): 42-57. |
| Zhu S S, Huang H C, Liu Y X, et al. Research advances in agrobiodiversity for crop disease management[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2022, 49 (1): 42-57 (in Chinese) | |
| [68] | Sturrock R N, Frankel S J, Brown A V, et al. Climate change and forest diseases[J]. Plant Pathology, 2011, 60 (1): 133-149 |
| [69] | Thomson L J, Macfadyen S, Hoffmann A A. Predicting the effects of climate change on natural enemies of agricultural pests[J]. Biological Control, 2010, 52 (3): 296-306 |
| [70] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021 |
| [71] | Roy S, Kapoor R, Mathur P. Revisiting changes in growth, physiology and stress responses of plants under the effect of enhanced CO2 and temperature[J]. Plant and Cell Physiology, 2024, 65 (1): 4-19 |
| [72] | Dorneles K R, Refatti J P, Pazdiora P C, et al. Biochemical defenses of rice against Bipolaris oryzae increase with high atmospheric concentration of CO2[J]. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 2020, 110: 101484 |
| [73] |
Chen X, Ma J, Wang X, et al. Functional modulation of an aquaporin to intensify photosynthesis and abrogate bacterial virulence in rice[J]. The Plant Journal, 2021, 108 (2): 330-346
doi: 10.1111/tpj.15427 pmid: 34273211 |
| [74] | Kumar U, Quick W P, Barrios M, et al. Atmospheric CO2concentration effects on rice water use and biomass production[J]. PLOS One, 2017, 12 (2): e0169706 |
| [75] | Ye Z P, He J Q, An T, et al. Influences of residual stomatal conductance on the intrinsic water use efficiency of two C3 and two C4 species[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2024, 306: 109136 |
| [76] | 崔景会, 王怡丹, 齐秀芬, 等. 水分胁迫和高浓度CO2处理下水稻幼苗光合生理响应特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2023, 42 (6): 1381-1388. |
| Cui J H, Wang Y D, Qi X F, et al. Photosynthetic physiological response of rice seedlings to waterstress and high CO2 concentration[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2023, 42 (6): 1381-1388 (in Chinese) | |
| [77] |
Kobayashi T, Ishiguro K, Nakajima T, et al. Effects of elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration on the infection of rice blast and sheath blight[J]. Phytopathology, 2006, 96 (4): 425-431
doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-96-0425 pmid: 18943425 |
| [78] | Goria M M, Ghini R, Bettiol W. Elevated atmospheric CO2concentration increases rice blast severity[J]. Tropical Plant Pathology, 2013, 38 (3): 253-257 |
| [79] | 唐美玲, 肖谋良, 袁红朝, 等. CO2倍增条件下不同生育期水稻碳氮磷含量及其计量比特征[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39 (12): 5708-5716. |
| Tang M L, Xiao M L, Yuan H C, et al. Effect of CO2 doubling and different plant growth stages on rice carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus and their stoichiometric ratios[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39 (12): 5708-5716 (in Chinese) | |
| [80] | 张立极, 潘根兴, 张旭辉, 等. 大气CO2浓度和温度升高对水稻植株碳氮吸收及分配的影响[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47 (1): 26-32. |
| Zhang L J, Pan G X, Zhang X H, et al. Effect of experimental CO2enrichment and warming on uptake and distribution of C and N in rice plant[J]. Soils, 2015, 47 (1): 26-32 (in Chinese) | |
| [81] | Dwivedi S K, Kumar S, Mishra J S, et al. Interactive effect of elevated [CO2] and temperature on the photosynthetic process, anti-oxidative properties, and grain yield of rice[J]. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 2022, 208 (3): 384-393 |
| [82] |
da Rosa Dorneles K, Martins A C, Fernando J A, et al. Increased atmospheric CO2 concentration causes modification of physiological, biochemical and histological characteristics that affects rice-Bipolaris oryzae interaction[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2020, 157 (1): 29-38
doi: 10.1007/s10658-020-01972-4 |
| [83] | Roy S, Mathur P. Delineating the mechanisms of elevated CO2mediated growth, stress tolerance and phytohormonal regulation in plants[J]. Plant Cell Reports, 2021, 40 (8): 1345-1365 |
| [84] | 卢培利, 杨涵, 丁阿强, 等. 碳源与氮源限制下细菌代谢调节研究进展[J]. 微生物学报, 2023, 63 (3): 946-962. |
| Lu P L, Yang H, Ding A Q, et al. Metabolic regulation of bacteria with limited carbon and nitrogen sources[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2023, 63 (3): 946-962 (in Chinese) | |
| [85] |
陈宏艳, 李小二, 李忠光. 糖信号及其在植物响应逆境胁迫中的作用[J]. 生物技术通报, 2022, 38 (7): 80-89.
doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-1289 |
| Chen H Y, Li X E, Li Z G. Sugar signaling and its role in plant response to environmental stress[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2022, 38 (7): 80-89 (in Chinese) | |
| [86] | Wu X, Ding C, Baerson S R, et al. The roles of jasmonate signalling in nitrogen uptake and allocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2019, 42 (2): 659-672 |
| [87] | Li X K, Huang Y H, Zhao R, et al. Membrane protein MHZ3 regulates the on-off switch of ethylene signaling in rice[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15 (1): 5987 |
| [88] | Cao S, Wang Y, Gao Y, et al. The RLCK-VND6 module coordinates secondary cell wall formation and adaptive growth in rice[J]. Molecular Plant, 2023, 16 (6): 999-1015 |
| [89] |
Ellsworth P V, Ellsworth P Z, Koteyeva N K, et al. Cell wall properties in Oryza sativa influence mesophyll CO2 conductance[J]. New Phytologist, 2018, 219 (1): 66-76
doi: 10.1111/nph.15173 pmid: 29676468 |
| [90] | 胡安琪, 谢晓栋, 龚康佳, 等. 气候变化对中国夏季臭氧影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44 (4): 1801-1810. |
| Hu A Q, Xie X D, Gong K J, et al. Impact of climate change on summer ozone in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44 (4): 1801-1810 (in Chinese) | |
| [91] |
Barnes P W, Williamson C E, Lucas R M, et al. Ozone depletion, ultraviolet radiation, climate change and prospects for a sustainable future[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2019, 2 (7): 569-579
doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0314-2 |
| [92] | Fu T M, Tian H. Climate change penalty to ozone air quality: review of current understandings and knowledge gaps[J]. Current Pollution Reports, 2019, 5 (3): 159-171 |
| [93] | 王志彬, 傅杨, 乔晓军, 等. 臭氧植保机在设施蔬菜苗期病害防治中的应用研究[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2023, 44 (7): 55-62. |
|
Wang Z B, Fu Y, Qiao X J, et al. Application of ozone sterilizer devices for controlling vegetable diseases during seeding stages in greenhouse[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2023, 44 (7): 55-62 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13733/j.jcam.issn.2095-5553.2023.07.008 |
|
| [94] | Wilkinson S, Davies W J. Drought, ozone, ABA and ethylene: new insights from cell to plant to community[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2010, 33 (4): 510-525 |
| [95] | 常浩, 姬明飞, 牟明, 等. 臭氧对水稻恶苗病菌的抑制作用[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44 (35): 157-158, 201. |
| Chang H, Ji M F, Mou M, et al. Inhibition effect of ozone on fusarium moniliforme[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44 (35): 157-158, 201 (in Chinese) | |
| [96] | 姚洪军, 于深州, 付立东, 等. 臭氧功能水对水稻病害的防治效果及产量影响[J]. 北方水稻, 2017, 47 (4): 9-11. |
| Yao H J, Yu S Z, Fu L D, et al. Effects of ozone water on rice diseases and yield[J]. Northern Rice, 2017, 47 (4): 9-11 (in Chinese) | |
| [97] | 列淦文, 叶龙华, 薛立. 臭氧胁迫对植物主要生理功能的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34 (2): 294-306. |
| Lie G W, Ye L H, Xue L. Effects of ozone stress on major plant physiological functions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34 (2): 294-306 (in Chinese) | |
| [98] |
Wedow J M, Ainsworth E A, Li S. Plant biochemistry influences tropospheric ozone formation, destruction, deposition, and response[J]. Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 2021, 46 (12): 992-1002
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.06.007 pmid: 34303585 |
| [99] | Alam M S, Maina A W, Feng Y, et al. Interactive effects of tropospheric ozone and blast disease (Magnaporthe oryzae) on different rice genotypes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29 (32): 48893-48907 |
| [100] |
Krupa S, McGrath M T, Andersen C P, et al. Ambient ozone and plant health[J]. Plant Disease, 2001, 85 (1): 4-12
doi: 10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.1.4 pmid: 30832068 |
| [101] | 何龙鑫, 徐彦森, 冯兆忠, 等. 不同水稻品种光合特性及叶绿素对臭氧浓度升高的响应差异[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2023, 42 (4): 715-723. |
| He L X, Xu Y S, Feng Z Z, et al. Different responses to elevated ozone among cultivars in the photosynthetic characteristics and chlorophyll of rice[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2023, 42 (4): 715-723 (in Chinese) | |
| [102] |
Frei M. Breeding of ozone resistant rice: relevance, approaches and challenges[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2015, 197: 144-155
doi: S0269-7491(14)00511-9 pmid: 25528448 |
| [103] |
Merilo E, Laanemets K, Hu H, et al. PYR/RCAR receptors contribute to ozone-, reduced air humidity-, darkness-, and CO2-induced stomatal regulation[J]. Plant Physiology, 2013, 162 (3): 1652-1668
doi: 10.1104/pp.113.220608 pmid: 23703845 |
| [104] | 郭洪刚, 王世藩, 戈峰. 植物激素信号调控的“植物病毒-植物-媒介昆虫”三者互作对温室气体变化的响应[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2017, 47 (9): 928-935. |
| Guo H G, Wang S P, Ge F. Effect of elevated CO2 and O3 on phytohormone-mediated plant resistance to vector insects and insect-borne plant viruses[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2017, 47 (9): 928-935 (in Chinese) | |
| [105] | 鲍歆歆, 周伟奇, 郑重, 等. 城市植物挥发性有机化合物排放与臭氧相互作用及其机制[J]. 生态学报, 2023, 43 (5): 1749-1762. |
| Bao X X, Zhou W Q, Zheng Z, et al. The interactions and mechanisms between biogenic volatile organic compounds emissions and ozone concentrations in urban areas: a review[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2023, 43 (5): 1749-1762 (in Chinese) | |
| [106] | 冯兆忠, 袁相洋. 臭氧浓度升高对植物源挥发性有机化合物 (BVOCs) 影响的研究进展[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39 (11): 5257-5265. |
| Feng Z Z, Yuan X Y. Effects of elevated ozone on Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds (BVOCs) emission: a review[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39 (11): 5257-5265 (in Chinese) | |
| [107] |
Helliwell E E, Wang Q, Yang Y. Ethylene biosynthesis and signaling is required for rice immune response and basal resistance against magnaporthe oryzae infection[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 2016, 29 (11): 831-843
pmid: 27671120 |
| [108] | 葛少彬, 刘敏, 骆世明, 等. 硅和稻瘟病菌接种对水稻植株有机酸含量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33 (11): 3002-3009. |
| Ge S B, Liu M, Luo S M, et al. Influence of silicon application and Magnaporthe oryzae infection on organic acids contents in rice plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33 (11): 3002-3009 (in Chinese) | |
| [109] | 刘明津, 汪文娟, 冯爱卿, 等. 稻瘟病综合防控技术研究进展[J]. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29 (9): 1285-1294. |
| Liu M J, Wang W J, Feng A Q, et al. Advance of integrated control technology of rice blast[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29 (9): 1285-1294 (in Chinese) | |
| [110] |
Patharkar O R, Walker J C. Connections between abscission, dehiscence, pathogen defense, drought tolerance, and senescence[J]. Plant Science, 2019, 284: 25-29
doi: S0168-9452(18)31020-3 pmid: 31084875 |
| [111] | Ye T, Wang H, An C, et al. An expanded cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase gene cluster functionally differentiates in drought, cold, heat, and pathogen stress responses in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2024, 22 (10): 2672-2674 |
| [112] | Meher J, Lenka S, Keerthana U, et al. Intermittent drought adversely impacts monogenic resistance of rice to the blast pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae and is associated with alteration in histone acetylation[J]. Plant and Soil, 2025, 509 (1): 649-669 |
| [113] |
韦还和, 马唯一, 左博源, 等. 盐、干旱及其复合胁迫对水稻产量和品质形成影响的研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38 (4): 350-363.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240205 |
|
Wei H H, Ma W Y, Zuo B Y, et al. Research progress in the effect of salinity, drought, and their combined stresses on rice yield and quality formation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38 (4): 350-363 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.240205 |
|
| [114] | 张启辉, 李晓曼, 龙希洋, 等. 植物角质蜡质代谢及抗病机制研究[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2020, 37 (6): 1207-1215. |
| Zhang Q H, Li X M, Long X Y, et al. Metabolism of the cutin and wax of plants and their diseaseresistance mechanisms[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2020, 37 (6): 1207-1215 (in Chinese) | |
| [115] | 王莎, 贺勇, 罗光宇, 等. OsWR2-RNAi对水稻角质层生物合成和耐旱性的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43 (3): 315-323. |
| Wang S, He Y, Luo G Y, et al. Influence of OsWR2-RNAi on rice cuticle biosynthesis and drought resistance[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43 (3): 315-323 (in Chinese) | |
| [116] | 周玲艳, 姜大刚, 李静, 等. 逆境处理下水稻叶角质层蜡质积累及其与蜡质合成相关基因OsGL1表达的关系[J]. 作物学报, 2012, 38 (6): 1115-1120. |
| Zhou L Y, Jiang D G, Li J, et al. Effect of stresses on leaf cuticular wax accumulation and its relationship to expression of OsGL1-homologous genes in rice[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2012, 38 (6): 1115-1120 (in Chinese) | |
| [117] |
郭展, 张运波. 水稻对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应及分子调控研究进展[J]. 中国水稻科学, 2024, 38 (4): 335-349.
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230410 |
|
Guo Z, Zhang Y B. Research progress in physiological, biochemical responses of rice to drought stress and its molecular regulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rice Science, 2024, 38 (4): 335-349 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16819/j.1001-7216.2024.230410 |
|
| [118] | Tang M, Ning Y, Shu X, et al. The Nup98 homolog APIP12 targeted by the effector avrPiz-t is involved in rice basal resistance against magnaporthe oryzae[J]. Rice, 2017, 10 (1): 5 |
| [119] | Pitaloka M K, Harrison E L, Hepworth C, et al. Rice stomatal mega-papillae restrict water loss and pathogen entry[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 677839-677839 |
| [120] | Liu J, Lefevere H, Coussement L, et al. The phenylalanine ammonia-lyase inhibitor AIP induces rice defence against the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne graminicola[J]. Molecular Plant Pathology, 2024, 25 (1): e13424 |
| [121] | Ahmad S, Jeridi M, Siddiqui S, et al. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of the chalcone synthase gene family in oryza sativa under abiotic stresses[J]. Plant Stress, 2023, 9: 100201 |
| [122] | Xu G, Zhong X, Shi Y, et al. A fungal effector targets a heat shock-dynamin protein complex to modulate mitochondrial dynamics and reduce plant immunity[J]. Science Advances, 6 (48): eabb7719 |
| [123] | Madhusudhan P, Sinha P, Rajput L S, et al. Effect of temperature on Pi54-mediated leaf blast resistance in rice[J]. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019, 35 (10): 148 |
| [124] |
姚姝, 陈涛, 张亚东, 等. 利用分子标记辅助选择聚合水稻Pi-ta、Pi-b和Wx-mq基因[J]. 作物学报, 2017, 43 (11): 1622-1631.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1006.2017.01622 |
| Yao S, Chen T, Zhang Y D, et al. Pyramiding Pi-ta, Pi-b, and Wx-mq genes by marker-assisted selection in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2017, 43 (11): 1622-1631 (in Chinese) | |
| [125] | Zhao D D, Chung H, Jang Y H, et al. Analysis of rice blast fungus genetic diversity and identification of a novel blast resistance OsDRq12 gene[J]. Phytopathology, 2024, 114 (8): 1917-1925 |
| [126] |
Balija V, Bangale U, Ponnuvel S, et al. Improvement of upland rice variety by pyramiding drought tolerance QTL with two major blast resistance genes for sustainable rice production[J]. Rice Science, 2021, 28 (5): 493-500
doi: 10.1016/j.rsci.2021.07.009 |
| [127] |
Ye H, Hou Q, Lv H, et al. D53 represses rice blast resistance by directly targeting phenylalanine ammonia lyases[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2024, 66 (9): 1827-1830
doi: 10.1111/jipb.13734 |
| [128] |
Wu Y, Xu W, Zhao G, et al. A canonical protein complex controls immune homeostasis and multipathogen resistance[J]. Science, 2024, 386 (6728): 1405-1412
doi: 10.1126/science.adr2138 pmid: 39509474 |
| [129] | Incarbone M, Bradamante G, Pruckner F, et al. Salicylic acid and RNA interference mediate antiviral immunity of plant stem cells[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2023, 120 (42): e2302069120 |
| [130] |
Ma X, Du M, Liu P, et al. Alternation of soil bacterial and fungal communities by tomato-rice rotation in Hainan Island in Southeast of China[J]. Archives of Microbiology, 2021, 203 (3): 913-925
doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-02086-5 pmid: 33078269 |
| [131] | Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini M T, et al. Microbial diversity and soil functions[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2003, 54 (4): 655-670 |
| [132] | Yang Y, Tang Z, Gao A, et al. Silicon-enriched rice straw biochar and silicon fertilizer mitigate rice straighthead disease by reducing dimethylarsinic acid accumulation[J/OL]. Plant and Soil, 2025 [2025-04-22]. DOI: 10.1007/s11104-025-07478-4 |
| [133] |
李烨锋, 周兵, 朱练峰, 等. 氮肥减量配施硅肥对水稻产量及病虫害防控的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2020, 26 (3): 76-80.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2020.03.019 |
|
Li Y F, Zhou B, Zhu L F, et al. Effects of reduce nitrogen fertilizer combined with silicon fertilizer on grain yield and pests and diseases of rice[J]. China Rice, 2020, 26 (3): 76-80 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2020.03.019 |
|
| [134] | 吴天琦, 李保同, 刘浪, 等. 氮肥运筹对江西省双季稻主要病虫害发生及产量的影响[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2020, 42 (6): 1087-1098. |
| Wu T Q, Li B T, Liu L, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer operation on occurrence of major diseases and insects in double cropping rice and its yield in Jiangxi province[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2020, 42 (6): 1087-1098 (in Chinese) | |
| [135] |
Jamali H, Sharma A, Roohi, et al. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus subtilis RH5 against sheath blight of rice caused by Rhizoctonia solani[J]. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 2020, 60 (3): 268-280
doi: 10.1002/jobm.201900347 pmid: 31851769 |
| [136] | Qi Z, Yu J, Shen L, et al. Enhanced resistance to rice blast and sheath blight in rice (oryza sativa L.) by expressing the oxalate decarboxylase protein Bacisubin from Bacillus subtilis[J]. Plant Science, 2017, 265: 51-60 |
| [137] | Mirara F, Kwadjo D D, Mwangi M. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens D203 ameliorates rice growth and resistance to rice blast disease[J]. Cogent Food & Agriculture, 2024, 10 (1): 2371943 |
| [138] | Prabhukarthikeyan S R, Yadav M K, Anandan A, et al. Bio-protection of brown spot disease of rice and insight into the molecular basis of interaction between Oryza sativa, Bipolaris oryzae and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens[J]. Biological Control, 2019, 137: 104018 |
| [139] | Zhu J L, Zhu Z R, Zhou Y, et al. Effect of rice sowing date on occurrence of small brown planthopper and epidemics of planthopper-transmitted rice stripe viral disease[J]. Agricultural Sciences in China, 2009, 8 (3): 332-341 |
| [140] | Miao Liu J, Mei Q, Yun Xue C, et al. Mutation of G-protein γ subunit DEP1 increases planting density and resistance to sheath blight disease in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2021, 19 (3): 418-420 |
| [141] | Sun Q, Li T Y, Li D D, et al. Overexpression of loose plant architecture 1 increases planting density and resistance to sheath blight disease via activation of PIN-FORMED 1 a in rice[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2019, 17 (5): 855-857 |
| [142] | 马军韬, 张国民, 王永力, 等. 翻耕深度对水稻稻瘟病和纹枯病发生程度的影响[J]. 中国植保导刊, 2024, 44 (11): 51-54, 70. |
| Ma J T, Zhang G M, Wang Y L, et al. Effect of tillage depth on the incidence of rice blast and rice sheath blight[J]. China Plant Protection, 2024, 44 (11): 51-54, 70 (in Chinese) | |
| [143] | Sekiya N, Nakajima T, Oizumi N, et al. Agronomic practices preventing local outbreaks of rice yellow mottle virus disease revealed by spatial autoregressive analysis[J]. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2022, 42 (2): 15 |
| [144] | Han Z, Zhang Y, Di C, et al. Application of rice straw inhibits clubroot disease by regulating the microbial community in soil[J]. Microorganisms, 2024, 12 (4): 717 |
| [145] | Anam I, Arafat N, Hafiz M S, et al. A systematic review of UAV and AI integration for targeted disease detection, weed management, and pest control in precision agriculture[J]. Smart Agricultural Technology, 2024, 9: 100647 |
| [146] | Bai X, Fang H, He Y, et al. Dynamic UAV phenotyping for rice disease resistance analysis based on multisource data[J]. Plant Phenomics, 2023, 5: 0019 |
| [147] |
Li G M, Zhao D X, Li J P, et al. Unmanned aerial vehicle hierarchical detection of leaf blast in rice crops based on a specific spectral vegetation index[J]. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 2025, 12 (2): 231-244
doi: 10.15302/J-FASE-2024576 |
| [148] | Gu C, Cheng T, Cai N, et al. Assessing narrow brown leaf spot severity and fungicide efficacy in rice using low altitude UAV imaging[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2023, 77: 102208 |
| [149] | 谢亚平, 仝晓刚, 王晓慧. 基于高光谱的水稻稻曲病早期监测研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2023, 54 (9): 288-296. |
| Xie Y P, Tong X G, Wang X H. Early monitoring of rice koji disease based on hyperspectroscop[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2023, 54 (9): 288-296 (in Chinese) | |
| [150] | Chakrabarty A, Ahmed S T, Islam M F U, et al. An interpretable fusion model integrating lightweight CNN and transformer architectures for rice leaf disease identification[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2024, 82: 102718 |
| [151] | Ramadan S T Y, Islam M S, Sakib T, et al. Image-based rice leaf disease detection using CNN and generative adversarial network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2025, 37 (1): 439-456 |
| [152] | Yu H, Li X, Yu Y, et al. A dual-branch multimodal model for early detection of rice sheath blight: fusing spectral and physiological signatures[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2025, 231: 110031 |
| [1] | 胡金鹏, 何研, 史培军. 复合干热事件对小麦产量影响的研究进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 625-640. |
| [2] | 张馨月, 李阔, 赵明月, 许吟隆. 中国农业适应气候变化能力建设进展回顾与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 613-624. |
| [3] | 樊星, 梁启迪, 吴承霖, 高翔. 巴库气候大会成果盘点及全球气候治理形势展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 583-592. |
| [4] | 孙若水, 梁媚聪. 从巴黎到贝伦——《巴黎协定》十周年进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 574-582. |
| [5] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 闫洪硕, 幸绣程, 朱开伟, 王晨旭. IPCC第七次评估报告第三工作组减缓气候变化概要解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 494-501. |
| [6] | 陈显尧, 毕瀚文, 郝潇洁, 马天骄, 郭凌瑞. 大西洋经向翻转环流及其对全球气候的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 469-476. |
| [7] | 朱松丽. 联合国气候公约体系下的国家分类演变[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 565-573. |
| [8] | 丁杰, 曹左男, 胡国铮, 干珠扎布, 赵芬, 王海锋, 高清竹. IPCC第七次评估报告第二工作组气候变化影响、适应与脆弱性大纲解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 484-493. |
| [9] | 王博文, 贺一, 滕飞. 我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 502-518. |
| [10] | 崔鹏, 王岩, 张国涛, 张正涛, 雷雨, 王昊, 王姣, 郝建盛, 朱宏. 气候变化灾害风险防范:现状、挑战与科学问题[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 449-460. |
| [11] | 姜克隽. 综合评估模型在全球应对气候变化中的角色和未来研究转型[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 461-468. |
| [12] | 陈思达, 刘凯, 李博浩, 汪明. 中国脱贫县破纪录极端天气事件研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 327-339. |
| [13] | 张琴, 张利平, 李意, 刘丽娜, 佘敦先, 周芷菱, 袁喆. 气候水文预估不确定性量化及约束方法研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 317-326. |
| [14] | 李慧慧, 齐明, 孙仁金. 气候转型金融标准的国际实践及中国路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 428-439. |
| [15] | 石英, 徐影, 巢清尘, 张梦然, 韩振宇, 王荣. 基于CMIP6多模式的南水北调西线工程区未来气候变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 340-352. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||