Climate Change Research ›› 2024, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 129-145.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.067
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Comparative study on regional temperature simulation in China by different resolution CWRF models
DONG Li-Li1, ZHANG Han2, LI Qing-Quan1,3( ), WANG Fang1, ZHAO Chong-Bo1, XIE Bing1
), WANG Fang1, ZHAO Chong-Bo1, XIE Bing1
- 1 China Meteorological Administration Key Laboratory for Climate Prediction Studies, National Climate Centre, Beijing 100081, China
2 School of Atmospheric Science, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai 519082, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2023-04-04Revised:2023-08-15Online:2024-03-30Published:2024-01-15
Cite this article
DONG Li-Li, ZHANG Han, LI Qing-Quan, WANG Fang, ZHAO Chong-Bo, XIE Bing. Comparative study on regional temperature simulation in China by different resolution CWRF models[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 129-145.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.067

Fig. 1 Terrain height (HGT) of CWRF-R30 (a) and CWRF-R15 (b) models. (Eleven subregions include Northeast China (NE), North China (NC), Central China (CC), South China (SC), Inner Mongolia (IM), Southwest China (SW), Eastern Plateau (ET), Western Plateau (WT), Southern Plateau (ST), Southern Xinjiang (SX) and Northern Xinjiang (NX))

Fig. 4 Observation temperature at 2 m in spring, summer, autumn and winter, and differences between simulations of CWRF-R30, CWRF-R30 S, CWRF-R15 and observations, respectively
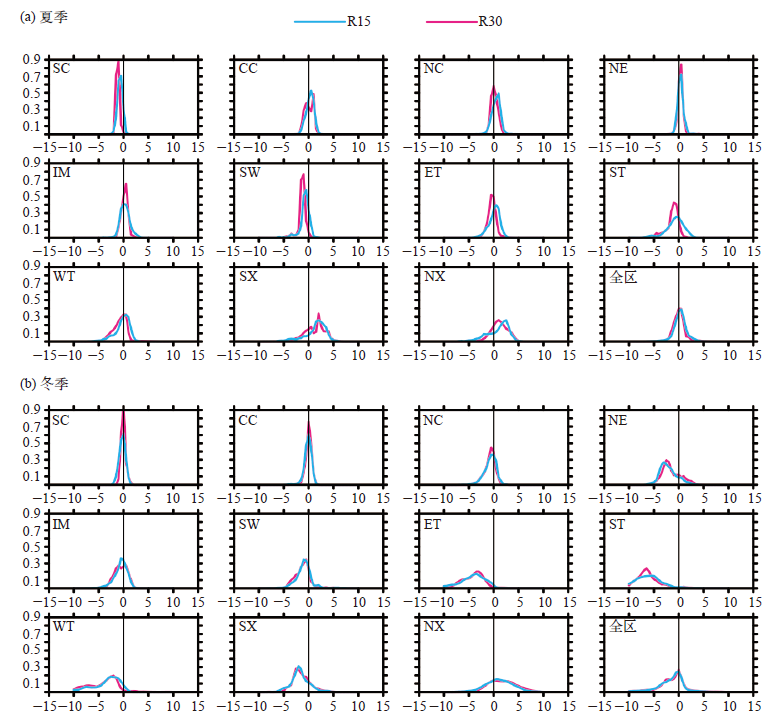
Fig. 5 Deviation density function between 2 m temperature simulated by CWRF-R30 and CWRF-R15 and observation in each sub-region and the whole region in summer (a) and winter (b) season
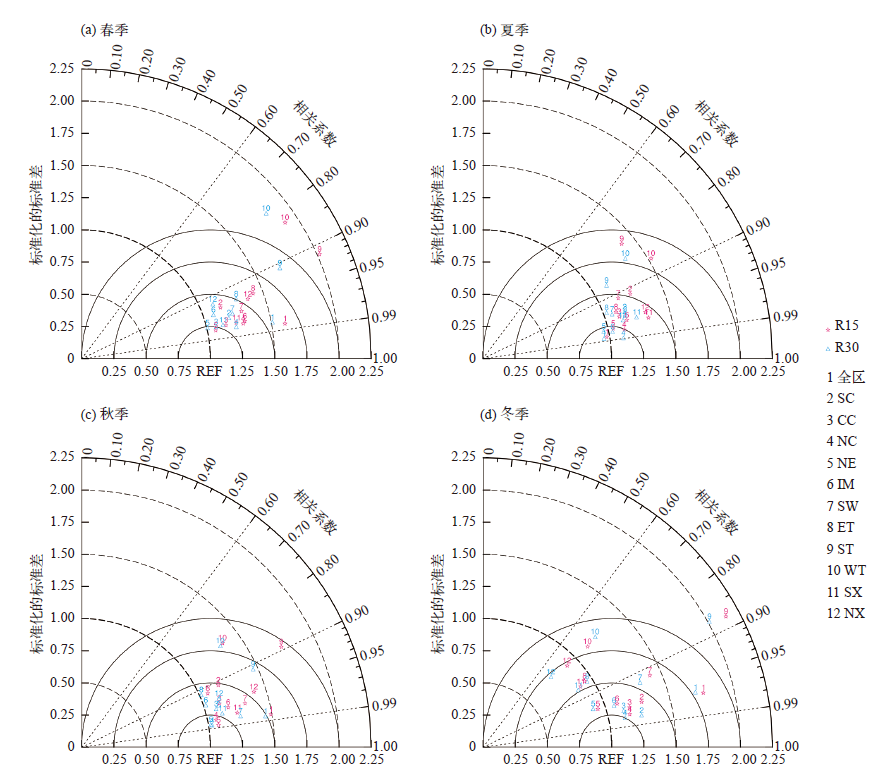
Fig. 6 Taylor charts of 2 m temperature simulated by CWRF-R30 and CWRF-R15 in spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), and winter (d) in each sub-region and the whole region

Fig. 7 The spatial distribution of correlation coefficients between 2 m temperature simulated by CWRF-R30 and CWRF-R15 and observation in spring, summer, autumn and winter, and the correlation coefficient difference distribution of CWRF-R15 minus CWRF-R30

Fig. 8 Inter-annual variation and 9-point smooth curve of observed and CWRF-R30 and CWRF-R15 simulated 2 m temperature in sub-regions and whole region by observations and simulations in summer and winter
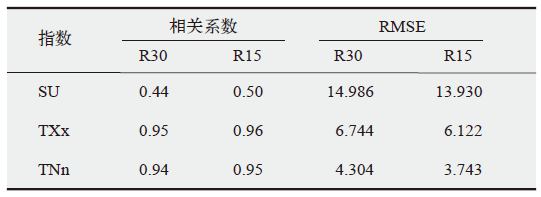 |
Table 2 Spatial correlation coefficient and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) for 2 m temperature extremes between observation and simulation by CWRF-R30 and CWRF-R15
 |
| [1] |
Zhou T J, Yu R C. Twentieth century surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by coupled climate models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006, 19: 5843-5858
doi: 10.1175/JCLI3952.1 URL |
| [2] |
Gao Y, Xu J, Chen D. Evaluation of WRF mesoscale climate simulations over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2011[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015, 28: 2823-2841
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00300.1 URL |
| [3] | Shi Y, Wang G, Gao X J. Role of resolution in regional climate change projections over China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 5: 2375-2396 |
| [4] |
Jiang D B, Wang H J, Lang X M. Evaluation of East Asian climatology as simulated by seven coupled models[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2005, 22: 479-495
doi: 10.1007/BF02918482 URL |
| [5] |
Yu E T, Wang H J, Sun J Q. A quick report on a dynamical downscaling simulation over China using the nested model[J]. Atmospheric Oceanic Science Letters, 2011, 3: 325-329
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2010.11446886 URL |
| [6] |
Chen L, Liang X Z, DeWitt D, et al. Simulation of seasonal US precipitation and temperature by the nested CWRF-ECHAM system[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 46 (3-4): 879-896
doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2619-9 URL |
| [7] | Yuan X, Liang X Z. Improving cold season precipitation prediction by the nested CWRF-CFS system[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2011, 38 (2): 1-5 |
| [8] | Li Q Q, Wang T, Wang F, et al. Dynamical downscaling simulation of the East Asian summer monsoon in a regional Climate-Weather Research and Forecasting model[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2021, 41: 1700-1716 |
| [9] |
Warner T R, Peterson R A, Treason R E. A tutorial on lateral boundary conditions as basic and potentially serious limitations to regional numerical weather prediction[J]. Bulletin of American Meteorological Society, 1997, 78 (11): 2599-2617
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<2599:ATOLBC>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [10] |
Luo Y, Zhao Z C, Ding Y H. Ability of NCAR RegCM2 in reproducing the dominant physical processes during the anomalous rainfall episodes in the summer of 1991 over the Yangtze-Huaihe valley[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2002, 19: 236-254
doi: 10.1007/s00376-002-0019-7 URL |
| [11] |
Park J H, Oh S G, Suh M S. Impacts of boundary conditions on the precipitation simulation of RegCM4 in the CORDEX East Asia domain[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2013, 118: 1652-1667
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v118.4 URL |
| [12] |
Zou L, Qian Y, Zhou T, et al. Parameter tuning and calibration of RegCM3 with MIT-Emanuel cumulus parameterization scheme over CORDEX East Asia domain[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27: 7687-7701
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00229.1 URL |
| [13] |
Wang J, Wang H J, Hong Y. Comparison of satellite-estimated and model-forecasted rainfall data during a deadly debris-flow event in Zhouqu, Northwest China[J]. Atmospheric Oceanic Science Letters, 2016, 9 (2): 139-145
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2016.1142825 URL |
| [14] |
Gao X J, Xu Y, Zhao Z C, et al. On the role of resolution and topography in the simulation of East Asia precipitation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2006, 86: 173-185
doi: 10.1007/s00704-005-0214-4 URL |
| [15] |
Gao X J, Shi Y, Song R Y, et al. Reduction of future monsoon precipitation over China: comparison between a high resolution RCM simulation and the driving GCM[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2008, 100: 73-86
doi: 10.1007/s00703-008-0296-5 URL |
| [16] |
Rojas M. Multiply nested regional climate simulation for southern South America: sensitivity to model resolution[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 2006, 134: 2208-2223
doi: 10.1175/MWR3167.1 URL |
| [17] | 邓莲堂, 史学丽, 闫之辉. 不同分辨率对淮河流域连续暴雨过程影响的中尺度模拟试验[J]. 热带气象学报, 2012, 28 (2): 167-176. |
| Deng L T, Shi X L, Yan Z H. Mesoscale simulation of a heavy rainfall in the Huaihe River valley in July 2003: effects of different horizontal resolutions[J]. Journal of Tropical Meteorology, 2012, 28 (2): 167-176 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 史金丽, 苏立娟, 郑旭程, 等. WRF模式不同分辨率模拟分析[J]. 内蒙古气象, 2012 (5): 19-26. |
| Shi J L, Su L J, Zheng X C, et al. Simulation research of different resolution ratio on WRF model[J]. Meteorology Journal of Inner Mongolia, 2012 (5): 19-26 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] |
黄子立, 吴小飞, 毛江玉. CMIP6 模式水平分辨率对模拟我国西南地区夏季极端降水的影响评估[J]. 高原气象, 2021, 40 (6): 1470-1483.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.zk010 |
|
Huang Z L, Wu X F, Mao J Y. An evaluation for impacts of the horizontal resolution of CMIP6 models on simulating extreme summer rainfall over Southwest China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2021, 40 (6): 1470-1483 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2021.zk010 |
|
| [20] | 钟琦, 孙卓, 陈昊明, 等. 京津冀强降水日变化的多模式预报偏差及成因分析[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2022, 52 (9): 1831-1848. |
| Zhong Q, Sun Z, Chen H M, et al. Multi-model forecast biases of the diurnal variations of intense rainfall in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2022, 52 (9): 1831-1848 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] |
Torma C, Coppola E, Giorgi F, et al. Validation of a high-resolution version of the regional climate model RegCM3 over the Carpathian basin[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2010, 12: 84-100
doi: 10.1175/2010JHM1234.1 URL |
| [22] |
Kendon E J, Roberts N M, Senior C A, et al. Realism of rainfall in a very high-resolution regional climate model[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012, 25: 5791-5806
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00562.1 URL |
| [23] |
Giorgi F, Torma C, Coppola E, et al. Enhanced summer convective rainfall at Alpine high elevations in response to climate warming[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2016, 9 (8): 584
doi: 10.1038/ngeo2761 |
| [24] |
Ji Z M, Kang S C. Double-nested dynamical downscaling experiments over the Tibetan Plateau and their projection of climate change under two RCP scenarios[J]. Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2013, 70: 1278-1290
doi: 10.1175/JAS-D-12-0155.1 URL |
| [25] | 孙晨, 汪方, 周月华, 等. CWRF 模式对长江流域极端降水气候事件的模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18 (1): 44-57. |
| Sun C, Wang F, Zhou Y H, et al. An assessment on extreme precipitation events in Yangtze River basin as simulated by CWRF regional climate model[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18 (1): 44-57 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Dong G T, Jang Z Y, Wang Y, et al. Evaluation of extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River delta region of China using a 1.5 km mesh convection-permitting regional climate model[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2022, 59: 2257-2273
doi: 10.1007/s00382-022-06208-1 |
| [27] | Liang X Z, Choi H I, Kunkel K E, et al. Surface boundary conditions for mesoscale regional climate models[J]. Earth Interactions, 2005, 9 (12): 305-319 |
| [28] |
Liang X Z, Xu M, Yuan X, et al. Regional climate-weather research and forecasting model[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2012, 93 (9): 1363-1387
doi: 10.1175/BAMS-D-11-00180.1 URL |
| [29] |
Liang X Z, Sun C, Zheng X, et al. CWRF performance at downscaling China climate characteristics[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 52 (3): 2159-2184
doi: 10.1007/s00382-018-4257-5 |
| [30] |
Yuan X, Liang X Z. Evaluation of a Conjunctive Surface-Subsurface Process Model (CSSP) over the contiguous United States at regional-local scales[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2011, 12 (4): 579-599
doi: 10.1175/2010JHM1302.1 URL |
| [31] |
Sun C, Liang X Z. Improving US extreme precipitation simulation: dependence on cumulus parameterization and underlying mechanism[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 55: 1325-1352
doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05328-w |
| [32] |
Sun C, Liang X Z. Improving US extreme precipitation simulation: sensitivity to physics parameterizations[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2020, 54: 4891-4918
doi: 10.1007/s00382-020-05267-6 |
| [33] |
Qiao F, Liang X Z. Effects of cumulus parameterization closures on summer precipitation simulation over the United States coastal oceans[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2016, 8 (2): 1-23
doi: 10.1002/jame.v8.1 URL |
| [34] |
Qiao F, Liang X Z. Effects of cumulus parameterization closures on simulations of summer precipitation over the continental United States[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2017, 49 (1/2): 225-247
doi: 10.1007/s00382-016-3338-6 URL |
| [35] |
Bretherton C S, Park S. A new moist turbulence parameterization in the community atmosphere model[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22: 3422-3448
doi: 10.1175/2008JCLI2556.1 URL |
| [36] |
Tao W K, Simpson J, Baker D, et al. Microphysics, radiation and surface processes in the Goddard Cumulus Ensemble (GCE) model[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2003, 82: 97-137
doi: 10.1007/s00703-001-0594-7 URL |
| [37] |
Xu K M, Randall D A. A semiempirical cloudiness parameterization for use in climate models[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1996, 53: 3084-3102
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1996)053<3084:ASCPFU>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [38] | Kahn R A, Gaitley B J, Martonchik J V, et al. Multiangle Imaging Spectro Radiometer (MISR) global aerosol optical depth validation based on 2 years of coincident Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2005, 110D10S04 |
| [39] | Kahn R A, Garay M J, Nelson D L, et al. Satellite derived aerosol optical depth over dark water from MISR and MODIS: comparisons with AERONET and implications for climatological studies[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2007, 112, D18205 |
| [40] | Zhao G, Girolamo L D, Dey S, et al. Examination of direct cumulus contamination on MIS Retrieved aerosol optical depth and angstrom coefficient over ocean[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 36, 2009, L13811 |
| [41] | Chou M D, Suarez M J. A solar radiation parameterization (CLIRAD-SW) for atmospheric studies[R/OL]. 1999 [2023-04-04]. http://geos5.org/svn/branches/Ganymed-2_1_p3-Benchmark/src/GEOSgcs_GridComp/GEOSgcm_GridComp/GEOSagcm_GridComp/GEOSphysics_GridComp/GEOSradiation_GridComp/GEOSsolar_GridComp/SolarDoc.pdf |
| [42] | Chou M D, Suarez M J, Liang X Z, et al. A thermal infrared radiation parameterization for atmospheric studies[R/OL]. 2001 [2023-04-04]. http://geos5.org/svn/branches/Fortuna-2_5_p1-RRTMG/src/GEOSgcs_GridComp/GEOSgcm_GridComp/GEOSagcm_GridComp/GEOSphysics_GridComp/GEOSradiation_GridComp/GEOSirrad_GridComp/IrradDoc03.pdf |
| [43] |
Holtslag A M, Boville B A. Local versus nonlocal boundary layer diffusion in a global climate model[J]. Journal of Climate, 1993, 6: 1825-1842
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006<1825:LVNBLD>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [44] |
Ling T, Xu M, Liang X Z et al. A multilevel ocean mixed layer model resolving the diurnal cycle: development and validation[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2015, 7: 1680-1692
doi: 10.1002/jame.v7.4 URL |
| [45] |
Ganguly S, Samanta A, Schull M A, et al. Generating vegetation leaf area index Earth system data record from multiple sensors. Part 2: Implementation, analysis and validation[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2008, 112 (12): 4318-4332
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.07.013 URL |
| [46] | Liu Y, Liu R, Chen J M. Retrospective retrieval of long-term consistent global leaf area index (1981-2011) from combined AVHRR and MODIS data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2012, 117, G04003 |
| [47] |
Dee D, Uppala S M, Simmons A J, et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: configuration and performance of the data assimilation system[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2011, 137 (656): 553-597
doi: 10.1002/qj.v137.656 URL |
| [48] |
Richard W. Reynolds impact of Mount Pinatubo aerosols on satellite-derived sea surface temperatures[J]. Journal of Climate, 1993, 6: 768-774
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006<0768:IOMPAO>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [49] | 吴佳, 高学杰. 一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56 (4): 1102-1111. |
| Wu J, Gao X J. A gridded daily observation dataset over China region and comparison with the other datasets[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013, 56 (4): 1102-1111 (in Chinese) | |
| [50] |
Xu Y, Gao X J, Shen Y, et al. A daily temperature dataset over China and its application in validating a RCM simulation[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2009, 26 (4): 763-772
doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9029-z URL |
| [51] |
Taylor K E. Summarizing multiple aspects of model performance in a single diagram[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2006, 106 (D7): 7183-7192
doi: 10.1029/2000JD900719 URL |
| [52] | World Meteorological Organization (WMO). Standardised Verification System (SVS) for long-range forecasts (LRF):new attachment II-8 to the manual on the GDPFS (WMO-No. 485)[R]. Geneva: WMO, 2006 |
| [53] | Karl T R, Nicholls N, Ghazi A. CLIVAR/GCOS/WMO workshop on indices and indicators for climate extremes: workshop summary[J]. Climate Change, 1999, 42: 3-7 |
| [54] |
Frich P, Alexander L V, Della-Marta P, et al. Observed coherent changes in climatic extremes during the second half of the twentieth century[J]. Climate Research, 2002, 19: 193-212
doi: 10.3354/cr019193 URL |
| [55] |
Zhang X B, Alexander L, Hegerl G C, et al. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 2011, 2: 851-870
doi: 10.1002/wcc.v2.6 URL |
| [56] | 徐蓉蓉, 梁信忠, 段明铿. CWRF对青藏高原气温和降水模拟效果的综合评估[J]. 大气科学学报, 2021, 44 (1): 104-117. |
| Xu R R, Liang X Z, Duan M K. Evaluation of CWRF’s simulation of temperature and precipitation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 44 (1): 104-117 (in Chinese) | |
| [57] |
Zha J L, Zhao D M, Wu J, et al. Numerical simulation of the effects of land use and cover change on the near-surface wind speed over Eastern China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 53 (3-4): 1783-1803
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-04737-w |
| [58] |
Stieglitz M, Smerdon J E. Characterizing land-atmosphere coupling and the implications for subsurface thermodynamics[J]. Journal of Climate, 2007, 20: 21-37
doi: 10.1175/JCLI3982.1 URL |
| [59] |
Diro G T, Sushama L, Huziy O. Snow-atmosphere coupling and its impact on temperature variability and extremes over North America[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018, 50: 2993-3007
doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3788-5 URL |
| [60] |
Almudena G G, Francisco J C V, Hugo B, et al. Land surface model influence on the simulated climatologies of temperature and precipitation extremes in the WRF v3.9 model over North America[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2020, 13: 5345-5366
doi: 10.5194/gmd-13-5345-2020 URL |
| [61] |
Seneviratne S I, Corti T, Davin E L, et al. Investigating soil moisture-climate interactions in a changing climate: a review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2010, 99: 125-161
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.02.004 URL |
| [62] | Xu M, Liang X Z, Samel A, et al. MODIS consistent vegetation parameter specifications and their impacts on regional climate simulations[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27 (22): 8596-8678 |
| [63] |
Donat M G, King A D, Overpeck J T, et al. Extraordinary heat during the 1930s US Dust Bowl and associated large-scale conditions[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 46: 413-426
doi: 10.1007/s00382-015-2590-5 URL |
| [64] |
Almudena G G, Francisco J C V, Hugo B, et al. Characterization of air and ground temperature relationships within the CMIP5 historical and future climate simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124: 3903-3929
doi: 10.1029/2018JD030117 URL |
| [65] |
Hirschi M, Seneviratne S I, Alexandrov V, et al. Observational evidence for soil-moisture impact on hot extremes in southeastern Europe[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4: 17-21
doi: 10.1038/ngeo1032 |
| [66] | Miralles D G, den Berg M J, Teuling A J, et al. Soil moisture-temperature coupling: a multiscale observational analysis[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39 (21): 6 |
| [67] |
Hauser M, Orth R, Seneviratne S I. Role of soil moisture versus recent climate change for the 2010 heat wave in western Russia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 2819-2826
doi: 10.1002/grl.v43.6 URL |
| [68] |
Lorenz R, Argüeso D, Donat M G, et al. Influence of land-atmosphere feedbacks on temperature and precipitation extremes in the GLACECMIP5 ensemble[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121: 607-623
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v121.2 URL |
| [69] |
Vogel M M, Orth R, Cheruy F, et al. Regional amplification of projected changes in extreme temperatures strongly controlled by soil moisture-temperature feedbacks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44: 1511-1519
doi: 10.1002/grl.v44.3 URL |
| [70] |
Leung L R, Qian Y. The sensitivity of precipitation and snow pack simulations to model resolution via nesting in regions of complex terrain[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2003, 4: 1025-1043
doi: 10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004<1025:TSOPAS>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [71] | 王乐. 陆面过程及地表覆盖对中国地区区域气候变化模拟的影响评估[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018. |
| Wang L. Evaluation of the climate change with 5 LUCCs and 3 LSMs using WRF in China land area[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [72] | 姜燕敏, 黄安宁, 吴昊旻. 不同水平分辨率BCC_CSM 模式对中亚地面气温模拟能力评估[J]. 大气科学, 2015, 39 (3): 535-547. |
| Jiang Y M, Huang A N, Wu H M. Evaluation of the performance of Beijing climate center climate system model with different horizontal resolution in simulating the annual surface temperature over Central Asia[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2015, 39 (3): 535-547 (in Chinese) | |
| [73] | Zhao M C, Yang X Q, Tao L F. Quantifying the processes of accelerated wintertime Tibetan Plateau warming: outside forcing versus local feedbacks[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2023. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-023-06741-7 |
| [74] | 鲍艳, 吕世华, 左洪超, 等. RegCM3模式在西北地区的应用研究II: 区域选择及参数化方案的敏感性[J]. 冰川冻土, 2006, 28 (2): 175-182. |
| Bao Y, Lv S H, Zuo H C, et al. Application of Regional Climate Model (RegCM3) in Northwest China II: sentivity experiment for domain choice and cumulus convection patameterization[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocetlolgy, 2006, 28 (2): 175-182 (in Chinese) | |
| [75] | 高学杰, 石英, 张冬峰, 等. RegCM3对21世纪中国区域气候变化的高分辨率模拟[J]. 科学通报, 2012, 57 (5): 374-381. |
| Gao X J, Shi Y, Zhang D F, et al. Climate change in China in the 21st century as simulated by a high resolution regional climate model[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57 (5): 374-381 (in Chinese) | |
| [76] | 赵宗慈, 罗勇. 区域气候模式在东亚地区的应用研究: 垂直分辨率与侧边界对夏季季风降水影响研究[J]. 大气科学, 1999, 23 (5): 522-532. |
| Zhao Z C, Luo Y. Application of regional climate models in East Asia: effects of vertical resolution and lateral boundary on summer monsoon precipitation[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Science, 1999, 23 (5): 522-532 (in Chinese) | |
| [77] | Singh G P, Jai H O, Jin Y K, et al. Sensitivity of summer monsoon precipitation over East Asia to convective parameterization schemes in RegCM3[J]. The Meteorological Society of Japan, 2006, 2: 29-32 |
| [78] |
Francisco J T, Carlos F A, Nicolas V, et al. On the suitability of regional climate models for reconstructing climatologies[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2011, 101 (3): 739-751
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.05.001 URL |
| [79] | 周天军, 钱永甫. 模式水平分辨率影响积云对流参数化效果的数值试验[J]. 高原气象, 1996, 15 (2): 204-211. |
| Zhou T J, Qian Y F. Numerical experiments of effect of model horizonal resolution on cumulus parameterization[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 1996, 15 (2): 204-211 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | LIU Wei, YANG Yu-Da, ZHANG Sen. Reconstruction of the 1632 rainstorm and flooding event in North China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 146-157. |
| [2] | MA Li-Juan, YUAN Jia-Shuang, HUANG Lei. Prospect of climate risks management in China under the framework of UN Early Warning for All Initiative [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 48-61. |
| [3] | HU Jia-Yi, ZHAO Lin, WANG Chong, HU Guo-Jie, ZOU De-Fu, XING Zan-Pin, JIAO Meng-Di, QIAO Yong-Ping, LIU Guang-Yue, Du Er-Ji. Applicability evaluation and correction of CLDAS surface temperature products in permafrost region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 10-25. |
| [4] | ZHANG Fan, DING Jian-Fang, YANG Min, PENG Chong. Snowfall identification and response of snowfall to temperature and precipitation under climate change in Henan province [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 714-722. |
| [5] | WANG Wei, WANG Huan, ZUO Zhi-Yan. Characteristics of the widespread extreme cold and warm days over China in winter [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(4): 418-430. |
| [6] | LIU Hai-Yan, ZHENG Shuang, SUN Yi-Jia, YU Sheng-Min. Development problems and countermeasures of forestry carbon sink market based on Saihanba CCER projects [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(3): 381-388. |
| [7] | NIE Xin-Yu, TAN Hong-Jian, CAI Rong-Shuo, GAO Xue-Jie. Projection of the tropical cyclones landing in China in the future based on regional climate model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(1): 23-37. |
| [8] | QIN Zheng, ZHAO Jing-Feng, CHENG Wu-Xue, WANG Jie, SU Hua-Li, HE Ya-Ling. Change of subtropical northern boundary in Qinling−Huaihe region in the context of climate change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(1): 38-48. |
| [9] | TU Kai, YAN Zhong-Wei, FAN Li-Jun, LI Zhen. Study of evaluation method on the climate of extreme high temperatures based on dynamic return periods [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(1): 11-22. |
| [10] | ZHAN Yun-Jian, CHEN Dong-Hui, LIAO Jie, JU Xiao-Hui, ZHAO Yu-Fei, REN Guo-Yu. Construction of a daily precipitation dataset of 60 city stations in China for the period 1901-2019 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 670-682. |
| [11] | ZHANG Shi-Yan, HU Yong-Yun, LI Zhi-Bo. Recent changes and future projection of precipitation in Northwest China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 683-694. |
| [12] | MIAO Wen-Fei, LIU Shi-Yin, ZHU Yu, DUAN Shi-Mei, HAN Feng-Ze. Spatio-temporal differentiation and altitude dependence of temperature and precipitation in Meili Snow Mountains [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(3): 328-342. |
| [13] | LI Tao, TAO Hui, CHEN Jin-Yu. Risk assessment of extreme low temperature events over the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(3): 343-354. |
| [14] | WANG Xia, WANG Ying, LIN Qi-Gen, LI Ning, ZHANG Xin-Ren, ZHOU Xiao-Ying. Projection of China landslide disasters population risk under climate change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(2): 166-176. |
| [15] | WANG Qian-Zhi, LIU Kai, WANG Ming. Evaluation of extreme precipitation indices performance based on NEX-GDDP downscaling data over China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(1): 31-43. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||