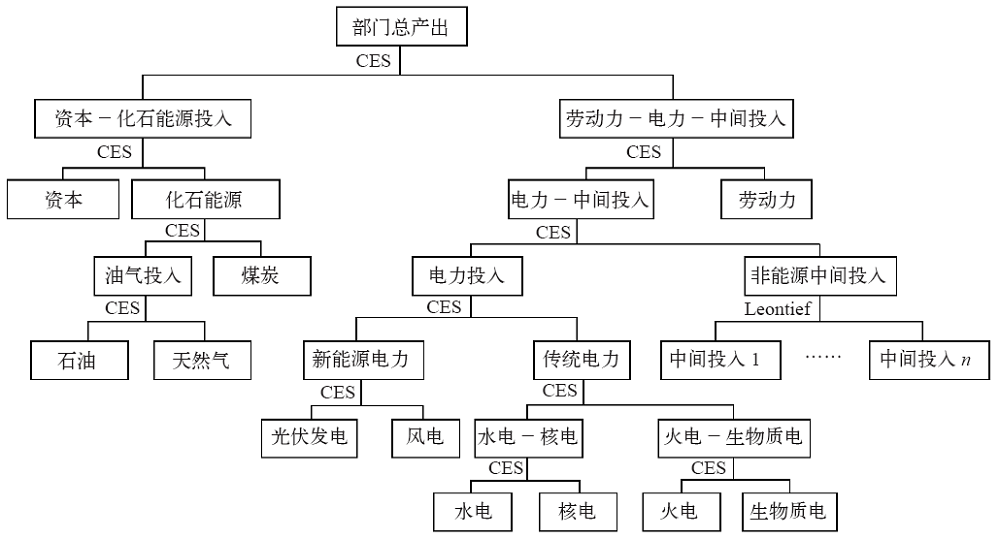
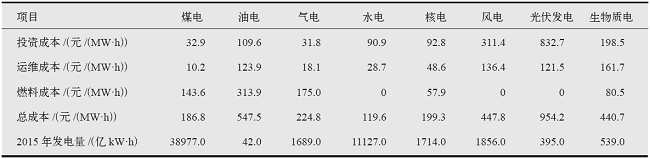
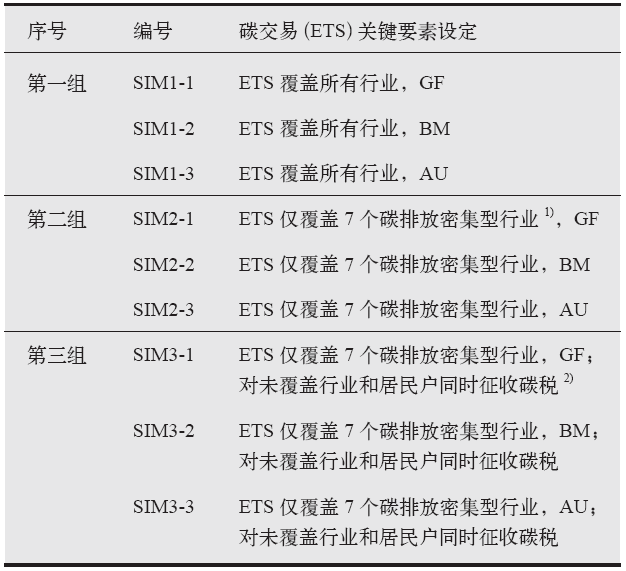
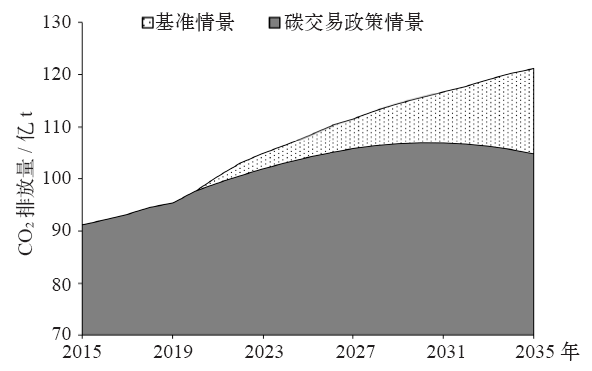
气候变化研究进展 ›› 2020, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (5): 617-631.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.069
实现国家自主贡献目标背景下我国碳交易机制研究
- 1 南方电网能源发展研究院有限责任公司,广州 510080
2 中国人民大学环境学院,北京 100872
-
收稿日期:2020-04-09修回日期:2020-05-22出版日期:2020-09-30发布日期:2020-09-30 -
通讯作者:庞军 -
作者简介:肖谦,男,高级工程师,xiaoqian1@csg.cn -
基金资助:南方电网公司科技项目(ZBKJXM20180375);国家自然科学基金(71701087)
Research on carbon trading mechanism of China at the background of achieving the NDC targets
XIAO Qian1( ), PANG Jun2(
), PANG Jun2( ), Xu Yun2, CHEN Hui1, Zeng Wen-Wan2
), Xu Yun2, CHEN Hui1, Zeng Wen-Wan2
- 1 Energy Development Research Institute, China Southern Power Grid, Guangzhou 510080, China
2 School of Environment and Natural Resources, Renmin University of China, Beijing 100872, China
-
Received:2020-04-09Revised:2020-05-22Online:2020-09-30Published:2020-09-30 -
Contact:PANG Jun
摘要:
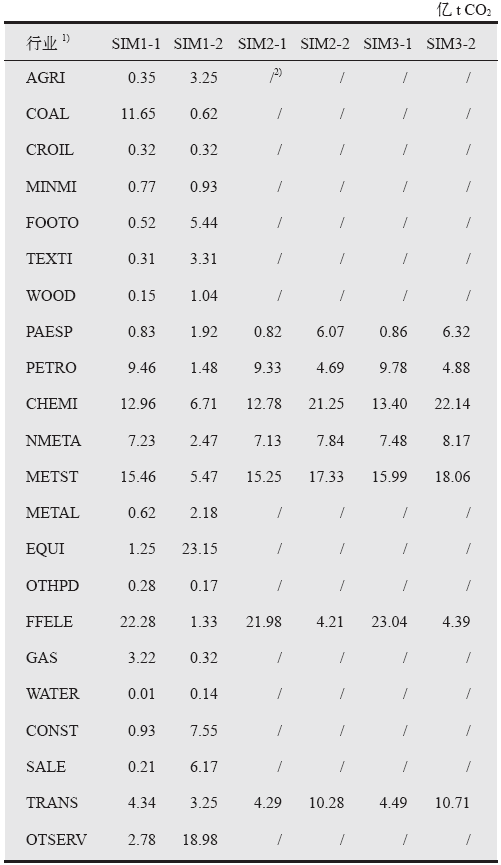
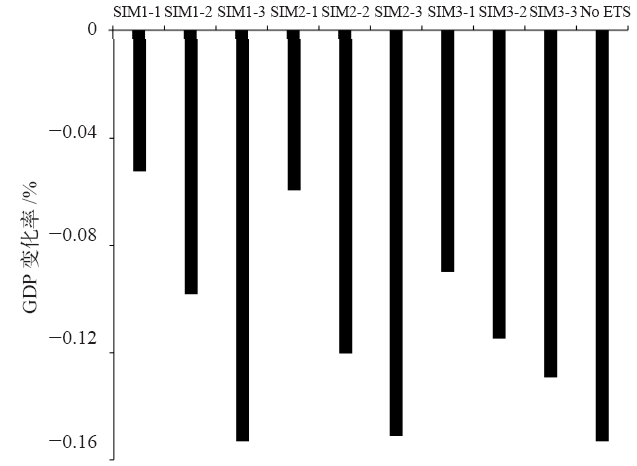
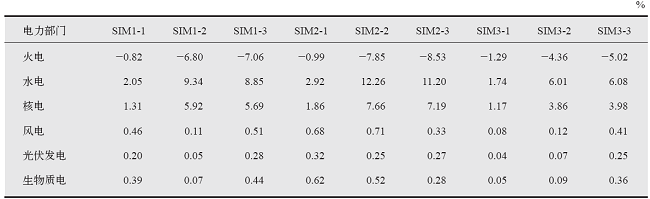
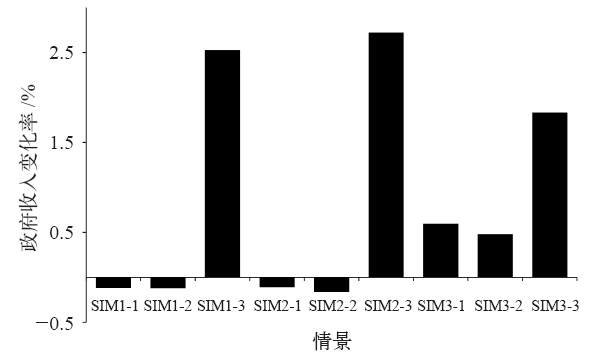
以实现国家自主贡献目标为背景,运用电力行业细分的递推动态可计算一般均衡(CGE)模型,模拟我国统一碳市场下不同碳交易机制的实施效果及其经济影响。研究表明,全国统一碳市场有助于我国实现国家自主贡献目标,并且可以缓解碳减排对经济增长造成的负面影响;相比基于碳排放量免费分配初始碳配额的“祖父法则”,基于碳强度基准免费分配初始碳配额的“标杆法则”可以降低碳交易价格、增加碳配额交易量并扩大碳市场规模;采取拍卖方式有偿分配初始碳配额时碳市场中各行业面临更大的减排成本,但有利于增加政府收入;对碳市场未覆盖的行业和居民户征收碳税能有效控制其碳排放、增加政府财政收入、降低碳交易价格并促进我国国家自主贡献目标的实现;全国统一碳市场在抑制火电行业发展的同时将不同程度地促进清洁能源发电部门的发展。
引用本文
肖谦, 庞军, 许昀, 陈晖, 曾文婉. 实现国家自主贡献目标背景下我国碳交易机制研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(5): 617-631.
XIAO Qian, PANG Jun, Xu Yun, CHEN Hui, Zeng Wen-Wan. Research on carbon trading mechanism of China at the background of achieving the NDC targets[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(5): 617-631.
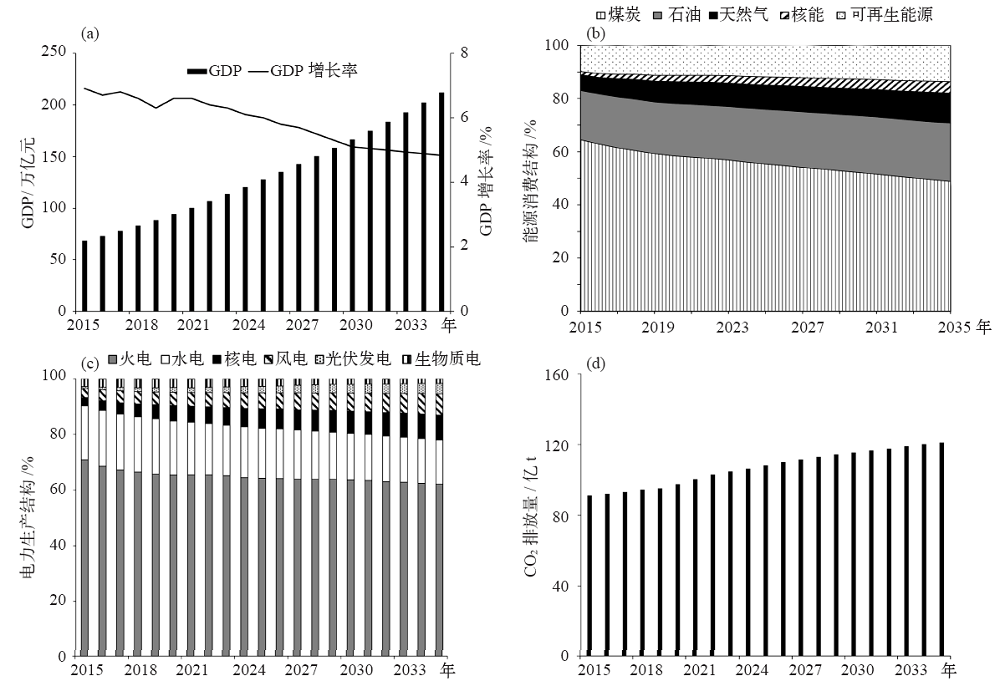
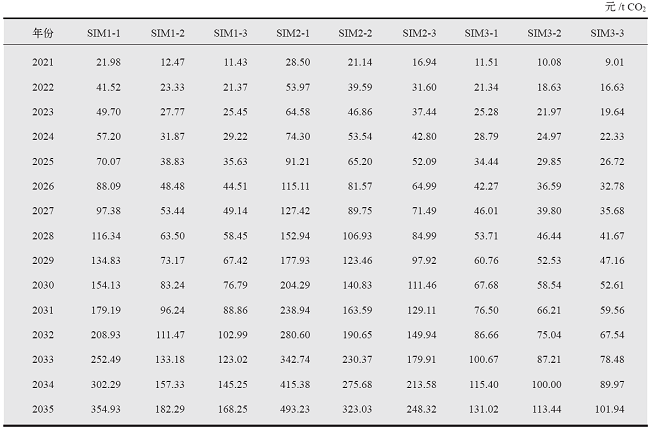
图3 动态基准情景下中国GDP和GDP增长率(a)、能源消费结构(b)、电力生产结构(c)以及CO2排放量(d)
Fig. 3 China’s GDP and its growth rate, consumption, electric power consumption structure and CO2 emissions under baseline
| [1] |
Sam M, Mahinda S, Judith M, et al. The impact of an ETS on the Australian energy sector: an integrated CGE and electricity modelling approach[J]. Energy Economics, 2018,69:213-224
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2017.11.017 URL |
| [2] |
Wu R, Dai H C, Geng Y, et al. Achieving China’s INDC through carbon cap-and-trade: insights from Shanghai[J]. Applied Energy, 2016,184:1114-1122
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.06.011 URL |
| [3] |
Liu Z Q, Geng Y, Dai H C, et al. Regional impacts of launching national carbon emissions trading market: a case study of Shanghai[J]. Applied Energy, 2018,230:232-240
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.08.117 URL |
| [4] |
Liu Y, Tan X J, Yu Y, et al. Assessment of impacts of Hubei pilot emission trading schemes in China: a CGE-analysis using TermCO2 model[J]. Applied Energy, 2017,189:762-769
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.05.085 URL |
| [5] |
Lin B Q, Jia Z J. The impact of emission trading scheme (ETS) and the choice of coverage industry in ETS: a case study in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2017,205:1512-1527
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.098 URL |
| [6] |
Mu Y Q, Evans S, Wang C, et al. How will sectoral coverage affect the efficiency of an emissions trading system? A CGE-based case study of China[J]. Applied Energy, 2018,227:403-414
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.072 URL |
| [7] |
Lin B Q, Jia Z J. Does the different sectoral coverage matter? An analysis of China’s carbon trading market[J]. Energy Policy, 2020,137:111164
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2019.111164 URL |
| [8] |
Tang L, Shi J, Bao Q. Designing an emissions trading scheme for China with a dynamic computable general equilibrium model[J]. Energy Policy, 2016,97:507-520
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2016.07.039 URL |
| [9] | Wu J, Fan Y, Xia Y. The economic effects of initial quota allocations on carbon emissions trading in China[J]. Energy Journal, 2016,37(1):129-151 |
| [10] |
Hübler M, Voigt S, Löschel A. Designing an emissions trading scheme for China: an up-to-date climate policy assessment[J]. Energy Policy, 2014,75:57-72
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2014.02.019 URL |
| [11] |
Li W, Jia Z J. The impact of emission trading scheme and the ratio of free quota: a dynamic recursive CGE model in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2016,174:1-14
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.04.086 URL |
| [12] |
Lin B, Jia Z J. Impact of quota decline scheme of emission trading in China: a dynamic recursive CGE model[J]. Energy, 2018,149:190-203
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.02.039 URL |
| [13] | 孙亚男. 碳交易市场中的碳税策略研究[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2014,24(3):32-40. |
| Sun Y N. Carbon tax policy in the carbon market[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2014,24(3):32-40 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 石敏俊, 袁永娜, 周晟吕, 等. 碳减排政策: 碳税、碳交易还是两者兼之?[J]. 管理科学学报, 2013,16(9):9-19. |
| Shi M J, Yuan Y N, Zhou S L, et al. Carbon tax, cap-and-trade or mixed policy: which is better for carbon mitigation?[J]. Journal of Management Sciences in China, 2013,16(9):9-19 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 刘磊, 张永强. 基于碳排放权交易市场的碳税制度研究[J]. 税务研究, 2019,409(2):48-54. |
| Liu L, Zhang Y Q. Study on carbon tax at the background of carbon market[J]. Taxation Research, 2019,409(2):48-54 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
Cao J, Ho M S, Jorgenson D W, et al. China’s emissions trading system and an ETS-carbon tax hybrid[J]. Energy Economics, 2019,81:741-753
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2019.04.029 URL |
| [17] |
Wing I S. The synjournal of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technologies and the cost of limiting US CO2 emissions[J]. Energy Policy, 2006,34(18):3847-3869
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2005.08.027 URL |
| [18] |
Wing I S. The synjournal of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technology detail in a social accounting framework[J]. Energy Economics, 2008,30(2):547-573
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2006.06.004 URL |
| [19] |
Cai Y Y, Arora V. Disaggregating electricity generation technologies in CGE models: a revised technology bundle approach with an application to the US clean power plan[J]. Applied Energy, 2015,154:543-555
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.05.041 URL |
| [20] |
Peters J. The GTAP-Power data base: disaggregating the electricity sector in the GTAP data base[J]. Journal of Global Economic Analysis, 2016,1(1):209-250
doi: 10.21642/JGEA URL |
| [21] |
Dai H, Xie X, Xie Y, et al. Green growth: the economic impacts of large-scale renewable energy development in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2016,162:435-449
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.049 URL |
| [22] |
Mittal S, Dai H, Fujimori S, et al. Bridging greenhouse gas emissions and renewable energy deployment target: comparative assessment of China and India[J]. Applied Energy, 2016,166:301-313
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.12.124 URL |
| [23] | Cao J, Mun H, Govinda R T. Impacts of carbon pricing in reducing the carbon intensity of China’s GDP [R/OL]. 2016 [2020-01-01]. https://ideas.repec.org/p/wbk/wbrwps/7735.html |
| [24] |
Wu J, Fan Y, Xia Y. How can China achieve its nationally determined contribution targets combining emissions trading scheme and renewable energy policies?[J]. Energies, 2017,10(8):1166-1185
doi: 10.3390/en10081166 URL |
| [25] |
Dai H C, Xie Y, Liu J Y, et al. Aligning renewable energy targets with carbon emissions trading to achieve China’s INDCs: a general equilibrium assessment[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018,82:4121-4131
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.10.061 URL |
| [26] |
Mu Y Q, Wang C, Cai W J. The economic impact of China’s INDC: distinguishing the roles of the renewable energy quota and the carbon market[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018,81:2955-2966
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.06.105 URL |
| [27] |
Lin B Q, Jia Z J. Is emission trading scheme an opportunity for renewable energy in China? A perspective of ETS revenue redistributions[J]. Applied Energy, 2020,263:114605
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.114605 URL |
| [28] |
Bao Q, Tang L, Zhang Z X, et al. Impacts of border carbon adjustments on China’s sectoral emissions: simulations with a dynamic computable general equilibrium model[J]. China Economic Review, 2013,24(1):77-94
doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2012.11.002 URL |
| [29] | 贺菊煌, 沈可挺, 徐嵩龄. 碳税与CO2减排的CGE模型[J]. 数量经济与技术经济, 2002 (10):39-47. |
| He J H, Shen K T, Xu S L. Carbon taxation and CGE model of carbon dioxide mitigation[J]. The Journal of Quantitative and Technical Economics, 2002 (10):39-47 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | Zhai F, Hertel T W. Impacts of the DDA on China: the role of labor markets and complementary education reforms [R]. Poverty and the WTO: Impact of the Doha Development Agenda, Washington DC: World Bank, 2006 |
| [31] | Chen Y H, Paltsev S, Reilly J M, et al. The MIT EPPA6 model: economic growth, energy use, and food consumption. MIT Joint Program Report Series Report 278 [R/OL]. 2015 [2020-03-10]. http://globalchange.mit.edu/publication/16262 |
| [32] | IEA. CO2 emissions from fuel combustion highlights 2015 [R/OL]. 2015 [2020-03-10]. http://www.iea.org/co2highlights/CO2highlights.pdf |
| [33] | NEA, IEA, OECD. Projected costs of generating electricity 2015 [R/OL]. 2015 [2020-03-10]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/cost_electricity-2015-en |
| [34] | Åsa J, Guillemette Y, Murtin F, et al. Long-term growth scenarios[J]. OECD Economics Department Working Papers, 2013 |
| [35] | 国际能源署. 世界能源展望2017中国特别报告[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2017: 12. |
| IEA. World energy outlook 2017 special report [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2017: 12(in Chinese) | |
| [36] | Bloomberg New Energy Finance. China power market outlook to 2030 [R/OL]. 2013 [2020-03-12]. http://news.nost.org.cn/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/BNEF_the_future_of_chinas_power_sector.pdf |
| [37] | 何建坤. CO2排放峰值分析:中国的减排目标与对策[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2013,23(12):1-9. |
| He J K. CO2 emission peak analysis: China’s emission reduction goals and countermeasures[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2013,23(12):1-9 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 周迪, 蔡晓婷, 张达泉, 张雨帆. 基于CGE模型的碳税政策模拟——以广东省为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(4): 516-525. |
| [2] | 李继峰,顾阿伦,张成龙,孙振清. “十四五”中国分省经济发展、能源需求与碳排放展望——基于CMRCGE模型的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6): 649-659. |
| [3] | 洪祎君, 崔惠娟, 王芳, 葛全胜. 基于发展中国家自主贡献文件的资金需求评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(6): 621-631. |
| [4] | 刘俊伶,孙一赫,王克,邹骥,孔英. 中国交通部门中长期低碳发展路径研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 513-521. |
| [5] | 林洁,祁悦,蔡闻佳,王灿. 公平实现《巴黎协定》目标的碳减排贡献分担研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 529-539. |
| [6] | 刘宇, 温丹辉, 王毅, 孙振清. 天津碳交易试点的经济环境影响评估研究——基于中国多区域一般均衡模型TermCO2[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(6): 561-570. |
| [7] | 马晓哲, 王铮, 唐钦能, 朱永彬. 全球实施碳税政策对碳减排及世界经济的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(3): 217-229. |
| [8] | 刘 宇, 胡晓虹. 提高火电行业排放标准对中国经济和污染物排放的影响——基于环境CGE模型的测算[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(2): 154-161. |
| [9] | 王文军, 谢鹏程, 胡际莲, 王乐, 赵黛青. 碳税和碳交易机制的行业减排成本比较优势研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(1): 53-60. |
| [10] | 裴惠娟, 曾静静, 曲建升. 国际碳税格局及其对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015, 11(6): 412-419. |
| [11] | 周晟吕. 基于CGE模型的上海市碳排放交易的环境经济影响分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015, 11(2): 144-152. |
| [12] | 庞军 石媛昌 冯相昭 刘嘉 孙文龙. 实施低碳水泥标准的影响及协同减排效果分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(4): 275-283. |
| [13] | 曾静静 曲建升. 欧盟航空碳税及其国际影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(4): 292-296. |
| [14] | 袁永娜 石敏俊 李娜 周晟吕. 碳排放许可的强度分配标准与中国区域经济协调发展——基于30省区CGE模型的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(1): 60-67. |
| [15] | 魏一鸣;范英;王毅;刘兰翠;梁巧梅;吴刚;曹明奎;黄耀;王绍强. 关于我国碳排放问题的若干对策与建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2006, 02(01): 15-20. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||