气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (3): 328-342.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.207
梅里雪山地区气温和降水的时空分异及海拔效应
- 云南大学国际河流与生态安全研究院,昆明 650500
-
收稿日期:2021-09-13修回日期:2021-11-09出版日期:2022-05-30发布日期:2022-02-25 -
通讯作者:刘时银 -
作者简介:缪文飞,男,硕士研究生,wenfei.miao@mail.ynu.edu.cn 。 -
基金资助:云南大学引进人才科研项目(YJRC3201702);国家自然科学基金委员会重大研究计划项目(92047301);第二次青藏高原综合科学考察项目(2019QZKK0208)
Spatio-temporal differentiation and altitude dependence of temperature and precipitation in Meili Snow Mountains
MIAO Wen-Fei( ), LIU Shi-Yin(
), LIU Shi-Yin( ), ZHU Yu, DUAN Shi-Mei, HAN Feng-Ze
), ZHU Yu, DUAN Shi-Mei, HAN Feng-Ze
- Institute of International Rivers and Eco-Security, Yunnan University, Kunming 650500, China
-
Received:2021-09-13Revised:2021-11-09Online:2022-05-30Published:2022-02-25 -
Contact:LIU Shi-Yin
摘要:
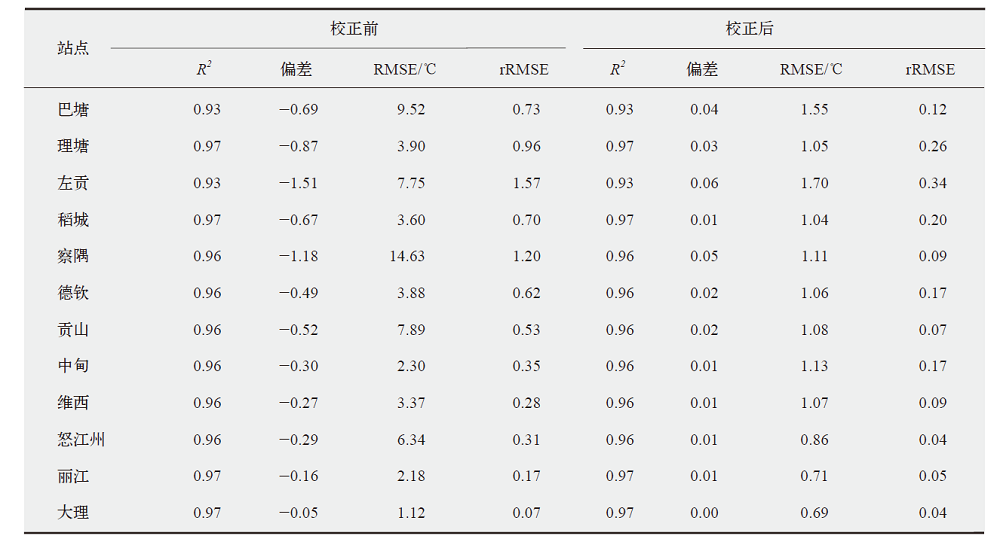
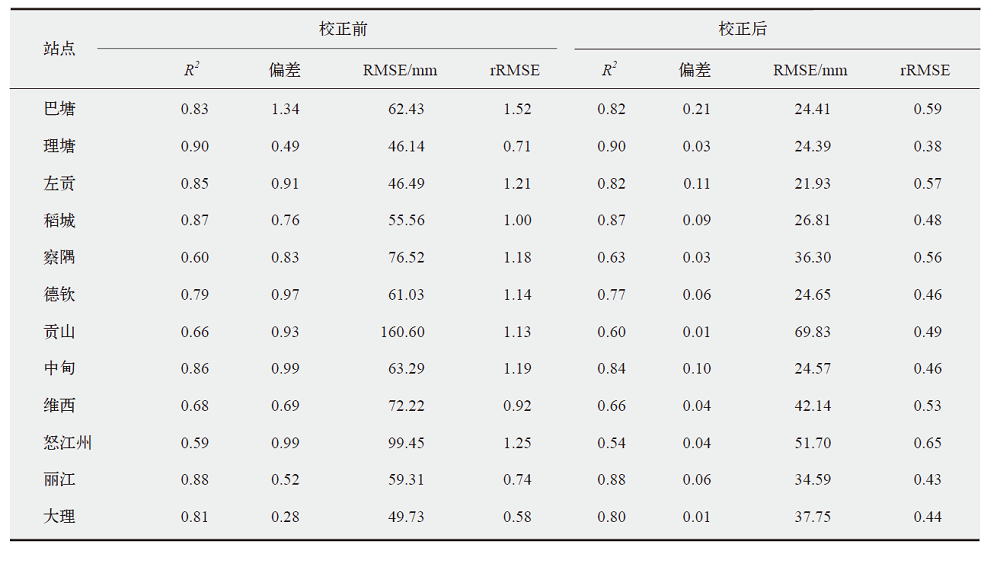
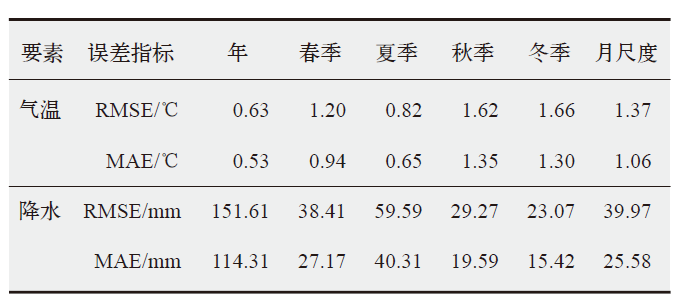
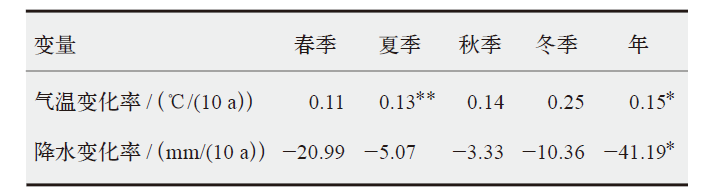
梅里雪山地区是中国地形起伏最大的地区之一,其气候环境复杂多变、空间分异特征显著,对区域气温和降水的系统分析有助于揭示区域内冰川变化的原因和水文循环过程。站点观测的缺乏和再分析资料的低空间分辨率是精细刻画该地区气象条件的主要制约因素。研究中首先基于有限站点观测,采用尺度因子法和月尺度的回归校正对ERA5-Land产品进行校准;然后,考虑气温和降水的海拔效应,采用Anusplin插值的方式对校准后的结果进行统计降尺度。最终获得了梅里雪山地区近30年(1990—2020年)1 km空间分辨率的气温、降水数据,并以此分析了这一地区降水、气温的时空异质性及其在不同海拔梯度上的表现特征。结果表明,区域气温以0.15℃/(10 a)的速率呈显著上升趋势,且各季节升温的幅度及分布范围各异;降水则以-41.19 mm/(10 a)的速率呈显著下降趋势,整个区域呈“变暖变干”的倾向。区域增温具有明显的海拔依赖性,海拔低于4000 m和>5000 m时,增温不随海拔变化而变化,当海拔处于4000~5000 m时,增温幅度随海拔升高而增加。区域降水也具有显著的海拔梯度效应,当海拔<5000 m时,西坡降水随海拔的升高而减少,当超过该海拔后降水随海拔升高而增加;东坡降水始终随海拔升高而增加。梅里雪山气候变化的时空分异特征是大气环流背景和复杂地理环境共同作用的结果。区域持续的变暖及降水的减少可能会进一步加重该区冰川水资源的流失。
引用本文
缪文飞, 刘时银, 朱钰, 段仕美, 韩丰泽. 梅里雪山地区气温和降水的时空分异及海拔效应[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 328-342.
MIAO Wen-Fei, LIU Shi-Yin, ZHU Yu, DUAN Shi-Mei, HAN Feng-Ze. Spatio-temporal differentiation and altitude dependence of temperature and precipitation in Meili Snow Mountains[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(3): 328-342.

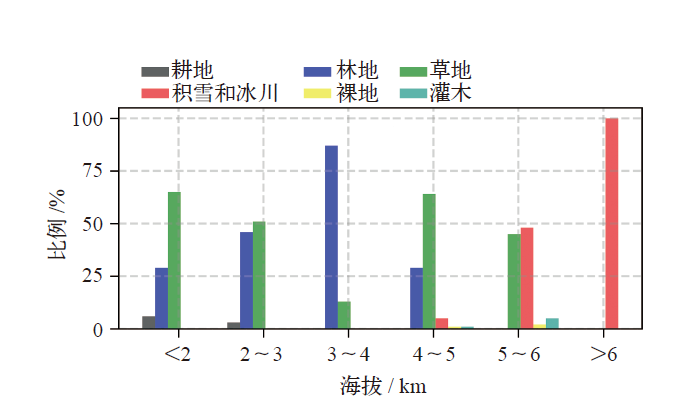
图1 研究区概况图(a)研究区周边气象站点及泰森多边形,(b)梅里雪山地形,(c)明永冰川流域雨量筒位置及降水与海拔关系 注:(c)图中红色数字1、2、3为雨量筒编号;编号后括号内数字为雨量筒高程(m)。
Fig. 1 Geographical settings of study area. (a) Weather stations and Thiessen polygon around the study area, (b) Meili Snow Mountains Region (MLSM), (c) location of rain gauge and relationship between precipitation and altitude in Mingyong Glacier basin

图2 德钦站所在ERA5-Land格点降水校正前后分量特征(a)趋势项,(b)季节项,(c)余项
Fig. 2 The component characteristics of ERA5-Land grid before and after precipitation correction at Deqin station. (a) Trend items, (b) seasonal items, (c) residual items

图3 1990—2020年梅里雪山地区春(a)、夏(b)、秋(c)、冬(d)四季及年均(e)气温变化空间分布及全区年均气温变化曲线(f) 注:(a)~(e)图横线阴影区域表示通过0.05显著性检验的地区;(f)图绿色竖线表示1998—2012年增温停滞期间。
Fig. 3 Spatial distribution of trends of seasonal and annual air temperature in MLSM during 1990-2020 spring (a), summer (b), autumn (c), winter (d), annual average (e), and variation of regional annual average air temperature (f)
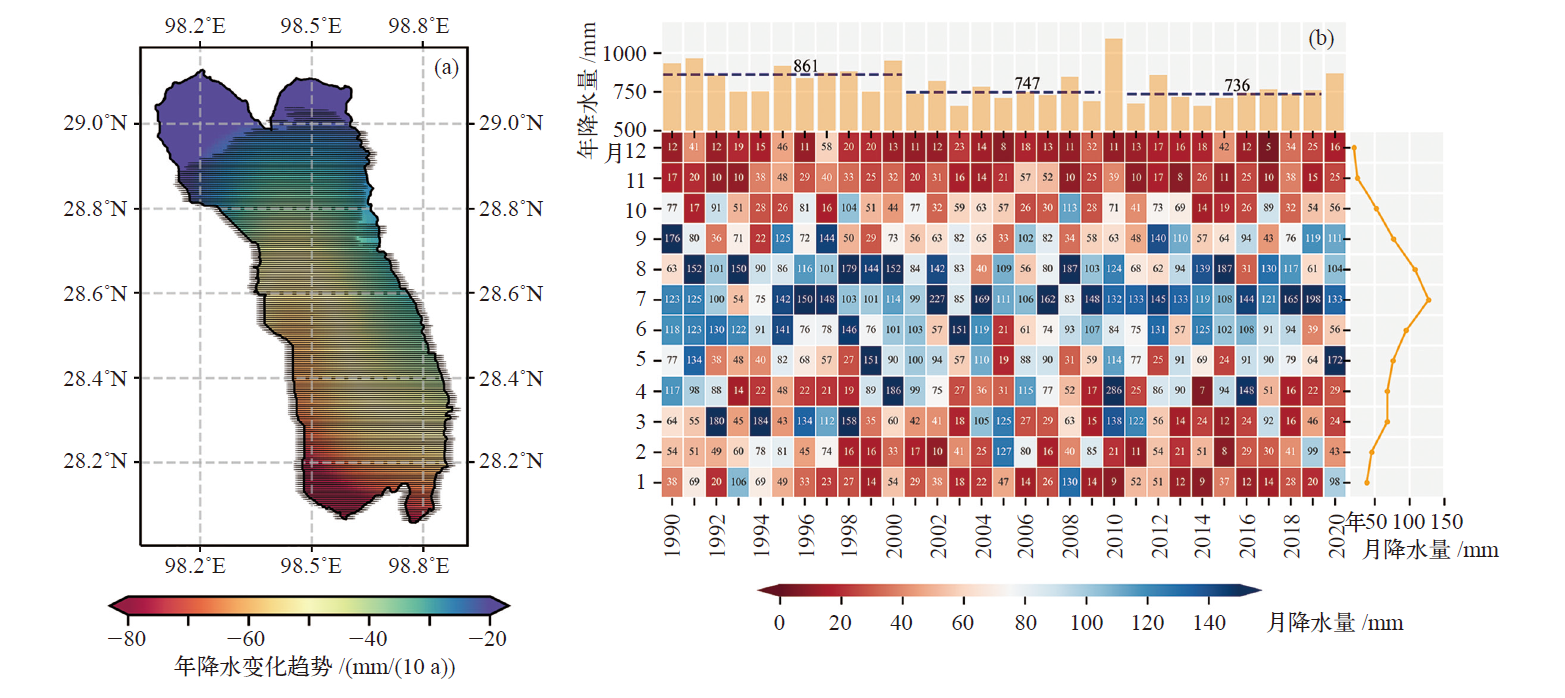
图4 1990—2020年梅里雪山地区降水变化趋势空间分布(a)及月降水分布(b) 注:(a)图中横线阴影区域表示通过0.05的显著性检验地区。
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of precipitation trends (a) and monthly precipitation distribution (b) in MLSM during 1990-2020
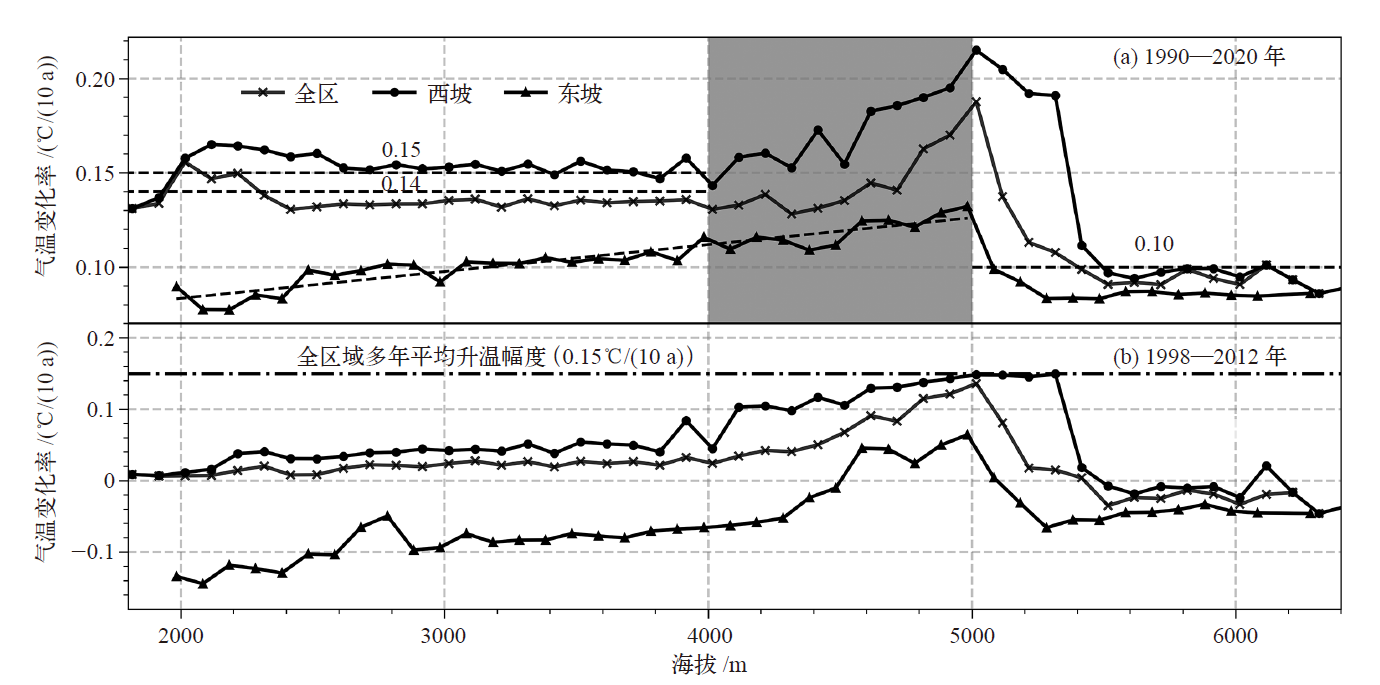
图5 梅里雪山地区不同区域在1990—2020年(a)和增温停滞期间(1998—2012年,b)气温变化率的海拔分布
Fig. 5 Altitude distribution of temperature change rates in MLSM different regions during 1990-2020 (a) and the hiatus period (1998-2012, b)
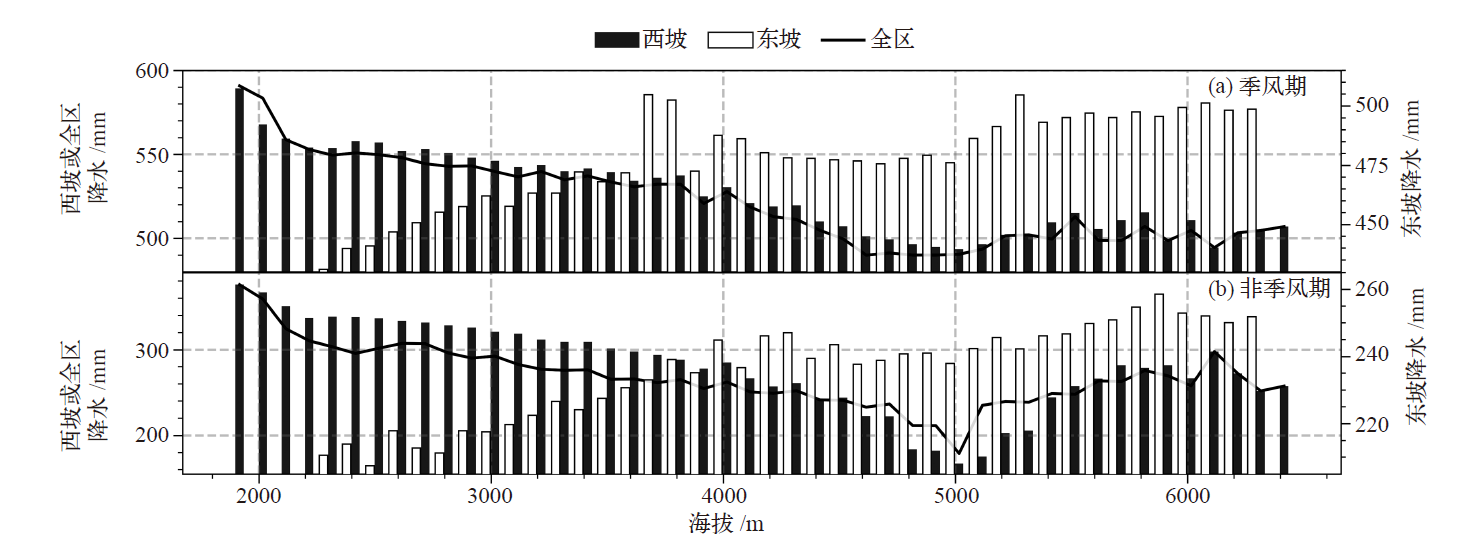
图6 梅里雪山地区季风期(a)和非季风期(b)东、西坡降水海拔梯度特征
Fig. 6 Characteristics of precipitation with elevation gradient on west and east slopes of MLSM during monsoon period (a) and non-monsoon period (b)
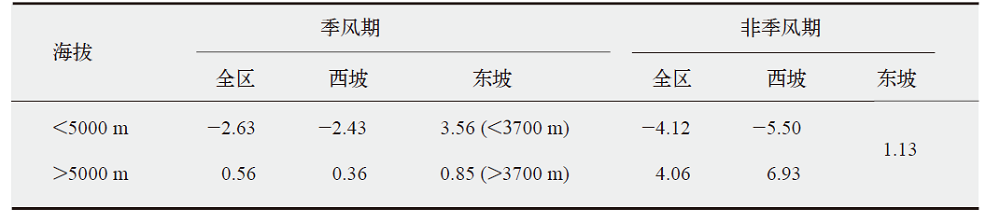 |
表5 梅里雪山地区季风期和非季风期不同区域降水的海拔梯度变率
Table 5 Elevation gradient variability of precipitation in different regions of MLSM during monsoon and non-monsoon periods mm/(100m)
 |

图7 1990—2020年大气环流变化(a) 季风期500 hPa高度场,(b) 500 hPa比湿场,(c) 850 hPa气温场,(d) 200 hPa纬向风场 注:图中黑点填充区表示通过0.05显著性检验的地区,蓝色方框为研究区所在位置。
Fig. 7 Atmospheric circulation changes during 1990-2020. (a) 500 hPa heights during monsoon period, (b) 500 hPa specific humidity, (c) 850 hPa temperature, (d) 200 hPa westward wind
| [1] | 李庆, 张春来, 王仁德, 等. 1965-2016年青藏高原关键气象因子变化特征及其对土地沙漠化的影响[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 54 (5): 659-665. |
| Li Q, Zhang C L, Wang R D, et al. Climate change and impact on desertification in Qinhai-Tibet Plateau from 1965-2016[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University: Natural Science, 2018, 54 (5): 659-665 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 李宗省, 何元庆, 辛惠娟, 等. 我国横断山区1960-2008年气温和降水时空变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65 (5): 563-579. |
| Li Z X, He Y Q, Xin H J, et al. Spatio-temporal variations of temperature and precipitation in Mts. Hengduan region during 1960-2008[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2010, 65 (5): 563-579 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 丁文荣. 横断山区干旱河谷气候变化趋势研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2013, 29 (6): 681-687. |
| Ding W R. Trend of the climate changes in dry valleys of Hengduan Mountains, China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2013, 29 (6): 681-687 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 徐飞, 贾仰文, 牛存稳, 等. 横断山区气温和降水年季月变化特征[J]. 山地学报, 2018, 36 (2): 171-183. |
| Xu F, Jia Y W, Niu C W, et al. Variation character of annual, seasonal and monthly temperature and precipitation[J]. Mountain Research, 2018, 36 (2): 171-183 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 张涛, 李宝林, 何元庆, 等. 基于TRMM订正数据的横断山区降水时空分布特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015 (2): 260-270. |
| Zhang T, Li B L, He Y Q, et al. Spatial and temporal distribution of precipitation based on corrected TRMM data in Hengduan Mountains[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2015 (2): 260-270 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
Guo D L, Yu E T, Wang H. Will the Tibetan Plateau warming depend on elevation in the future?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121 (8): 3969-3978
doi: 10.1002/2016JD024871 URL |
| [7] |
Gao Y H, Chen F, Lettenmaier D P, et al. Does elevation-dependent warming hold true above 5000 m elevation? Lessons from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. NPJ Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2018, 1 (1): 1-7
doi: 10.1038/s41612-017-0007-3 URL |
| [8] |
Guo D L, Sun J Q, Yang K, et al. Revisiting recent elevation‐dependent warming on the Tibetan Plateau using satellite based data sets[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2019, 124 (15): 8511-8521
doi: 10.1029/2019JD030666 URL |
| [9] |
Qin J, Yang K, Liang S L, et al. The altitudinal dependence of recent rapid warming over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climatic Change, 2009, 97 (1): 321-327
doi: 10.1007/s10584-009-9733-9 URL |
| [10] | 王朋岭, 唐国利, 曹丽娟, 等. 1981-2010年青藏高原地区气温变化与高程及纬度的关系[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8 (5): 313-319. |
| Wang P L, Tang G L, Cao L J, et al. Surface air temperature variability and its relationship with altitude & latitude over the Tibetan Plateau in 1981-2010[J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8 (5): 313-319 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 孙赫, 苏凤阁, 黄敬恒, 等. 第三极西风和季风主导流域源区降水呈现不同梯度特征[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65 (1): 97-110. |
| Sun H, Su F G, Huang J H, et al. Contrasting precipitation gradient characteristics between westerlies and monsoon dominated upstream river basins in the Third Pole[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2020, 65 (1): 97-110 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] |
Immerzeel W W, Pellicciotti F, Shrestha A B. Glaciers as a proxy to quantify the spatial distribution of precipitation in the Hunza basin[J]. Mountain Research and Development, 2012, 32 (1): 30-38
doi: 10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-11-00097.1 URL |
| [13] |
Zhou X, Yang K, Ouyang L, et al. Added value of kilometer-scale modeling over the Third Pole region: a CORDEX-CPTP pilot study[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2021, 57 (7): 1673-1687
doi: 10.1007/s00382-021-05653-8 URL |
| [14] | Jiang Y Z, Yang K, Shao C K, et al. A downscaling approach for constructing high-resolution precipitation dataset over the Tibetan Plateau from ERA5 reanalysis[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2021, 256: 105574 |
| [15] |
Ma J Y, Dong W J, Wei Z G, et al. Evaluating daily surface maximum temperature interpolation error by adding climate stations near border areas over China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35 (10): 2798-2808
doi: 10.1002/joc.4173 URL |
| [16] |
Rigden A J, Salvucci G D. Evapotranspiration based on equilibrated relative humidity (ETRHEQ): evaluation over the continental US[J]. Water Resources Research, 2015, 51 (4): 2951-2973
doi: 10.1002/2014WR016072 URL |
| [17] |
Persaud B D, Whitfield P H, Quinton W L, et al. Evaluating the suitability of three gridded datasets and their impacts on hydrological simulation at Scotty Creek in the southern Northwest Territories, Canada[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2020, 34 (4): 898-913
doi: 10.1002/hyp.13663 URL |
| [18] | Wen H Y, Che F J, Li J, et al. A study on spatial interpolation of temperature in Anhui province based on ANUSPLIN[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Research, 2019, 10 (2): 51-60 |
| [19] | 刘志红, 杨勤科, 李锐, 等. 基于ANUSPLIN的时间序列气象要素空间插值[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008, 36 (10): 227-234. |
| Liu Z H, Yang Q K, Li R, et al. Interpolation for time series of meteorological variables using ANUSPLIN[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University: Natural Science Edition, 2008, 36 (10): 227-234 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
贾洋, 崔鹏. 高山区多时间尺度Anusplin气温插值精度对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37 (3): 757-766.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2017.00072 |
| Jia Y, Cui P. Contrastive analysis of temperature interpolation at different time scales in the Alpine Region by Anusplin[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37 (3): 757-766 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] |
谭剑波, 李爱农, 雷光斌. 青藏高原东南缘气象要素Anusplin和Cokriging空间插值对比分析[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35 (4): 875-886.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2015.00037 |
| Tan J B, Li A N, Lei G B. Contrast on Anusplin and Cokriging meteorological spatial interpolation in Southeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2016, 35 (4): 875-886 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 乔云亭, 陈烈庭, 张庆云. 东亚季风指数的定义及其与中国气候的关系[J]. 大气科学, 2002 (1): 69-82. |
| Qiao Y T, Chen L T, Zhang Q Y. The definition of East Asian monsoon Indices and their relationship to climate in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2002 (1): 69-82 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
Yu W S, Wei F L, Ma Y M, et al. Stable isotope variations in precipitation over Deqin on the southeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau during different seasons related to various meteorological factors and moisture sources[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2016, 170: 123-130
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.11.013 URL |
| [24] | 张志明, 王文礼, 欧晓昆, 等. 梅里雪山植被空间格局与环境因子关系分析[J]. 云南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 31 (3): 311-315. |
| Zhang Z M, Wang W L, Ou X K, et al. The correlation between vegetation spatial pattern and environmental factors[J]. Journal of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2009, 31 (3): 311-315 | |
| [25] | 施雅风, 刘时银. 中国冰川对21世纪全球变暖响应的预估[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45 (4): 434-438. |
| Shi Y F, Liu S Y. Prediction of the response of Chinese glaciers to global warming in the 21st century[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45 (4): 434-438 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 何大明, 吴绍洪, 彭华, 等. 纵向岭谷区生态系统变化及西南跨境生态安全研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005, 20 (3): 338-344. |
| He D M, Wu S H, Peng H, et al. A study of ecosystem changes in longitudinal range-gorge region and transboundary eco-security in Southwest China[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2005, 20 (3): 338-344 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
阳坤, 何杰. 中国区域地面气象要素驱动数据集(1979-2018)[DB]. 国家青藏高原科学数据中心, 2019. DOI: 10.11888/AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file.
doi: 10.11888/AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file |
|
Yang K, He J. China meteorological forcing dataset (1979-2018)[DB]. National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, 2019. DOI: 10.11888/AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11888/AtmosphericPhysics.tpe.249369.file |
|
| [28] |
许尔琪. 青藏高原土地利用数据(1992、2005和2015)(V1.0)[DB]. 国家青藏高原科学数据中心, 2019. DOI: 10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270198.
doi: 10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270198 |
|
Xu E Q. Land use of the Tibet Plateau in 2015 (Version 1.0)[DB]. National Tibetan Plateau Data Center, 2019. DOI: 10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270198 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270198 |
|
| [29] | AghaKouchak A, Mehran A, Norouzi H, et al. Systematic and random error components in satellite precipitation data sets[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39 (9): 9406-9409 |
| [30] | 尹家波, 郭生练, 王俊, 等. 基于贝叶斯模式平均方法融合多源数据的水文模拟研究[J]. 水利学报, 2020, 51 (11): 1335-1346. |
| Yin J B, Guo S L, Wang J, et al. Blending multi-source data in hydrological simulations based on BMA method[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2020, 51 (11): 1335-1346 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | Yi Y, Liu S Y, Zhu Y, et al. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity of snow cover in the central and western Karakoram Mountains based on a refined MODIS product during 2002-2018[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2021, 250: 105402 |
| [32] |
Zhu Y, Liu S Y, Yi Y, et al. Spatio-temporal variations in terrestrial water storage and its controlling factors in the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Hydrology Research, 2021, 52 (1): 323-338
doi: 10.2166/nh.2020.039 URL |
| [33] | Robert C, William C, Irma T. STL: a seasonal-trend decomposition procedure based on loess[J]. Journal of Official Statistics, 1990, 6 (1): 3-73 |
| [34] | Hutchinson M F. Anusplin version 4.2 user guide[M]. Canberra: Australian National University, 2001 |
| [35] |
陆福志, 鹿化煜. 秦岭-大巴山高分辨率气温和降水格点数据集的建立及其对区域气候的指示[J]. 地理学报, 2019, 74 (5): 875-888.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201905003 |
| Lu F Z, Lu H Y. A high-resolution grid dataset of air temperature and precipitation for Qinling-Daba Mountains in central China and its implications for regional climate[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019, 74 (5): 875-888 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] |
Du Q Q, Zhang M J, Wang S J, et al. Changes in air temperature over China in response to the recent global warming hiatus[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019, 29 (4): 496-516
doi: 10.1007/s11442-019-1612-3 URL |
| [37] | Winslow L A, Leach T H, Rose K C. Global lake response to the recent warming hiatus[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2018, 13 (5): 054005 |
| [38] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 |
| [39] |
Dimri A P, Niyogi D, Barros A P, et al. Western disturbances: a review[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2015, 53 (2): 225-246
doi: 10.1002/2014RG000460 URL |
| [40] | Sun H, Su F G, Huang J H, et al. Contrasting precipitation gradient characteristics between westerlies and monsoon dominated upstream river basins in the Third Pole[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 65 (1): 91-104 |
| [41] |
Pepin N, Bradley R S, Diaz H F, et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2015, 5 (5): 424-430
doi: 10.1038/nclimate2563 URL |
| [42] |
Liu X D, Cheng Z G, Yan L B, et al. Elevation dependency of recent and future minimum surface air temperature trends in the Tibetan Plateau and its surroundings[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2009, 68: 164-174
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2009.03.017 URL |
| [43] |
Gao J, Williams M W, Fu X D, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of snow in eastern Tibet and the response to climate change[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 121: 1-9
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.01.006 URL |
| [44] |
刘时银, 姚晓军, 郭万钦, 等. 基于第二次冰川编目的中国冰川现状[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70 (1): 3-16.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb201501001 |
| Liu S Y, Yao X J, Guo W Q, et al. The contemporary glaciers in China based on the Second Chinese Glacier inventory[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70 (1): 3-16 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] |
Hulme M, Osborn T J, Johns T C. Precipitation sensitivity to global warming: comparison of observations with HadCM2 simulations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1998, 25 (17): 3379-3382
doi: 10.1029/98GL02562 URL |
| [1] | 栾澜, 翟盘茂. 基于多源数据的青藏高原雨季降水特征变化分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 173-190. |
| [2] | 秦正, 赵景峰, 程武学, 王捷, 苏华丽, 何亚玲. 气候变化背景下秦岭-淮河地区亚热带北界变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 38-48. |
| [3] | 战云健, 陈东辉, 廖捷, 鞠晓慧, 赵煜飞, 任国玉. 中国60城市站1901—2019年日降水数据集的构建[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 670-682. |
| [4] | 张诗妍, 胡永云, 李智博. 我国西北降水变化趋势和预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 683-694. |
| [5] | 王霞, 王瑛, 林齐根, 李宁, 张馨仁, 周笑影. 气候变化背景下中国滑坡灾害人口风险评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 166-176. |
| [6] | 张歆然, 陈昊明. CMIP6模式对青藏高原东坡暖季降水的模拟评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 129-141. |
| [7] | 李莹, 赵珊珊. 2001—2020年中国洪涝灾害损失与致灾危险性研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 154-165. |
| [8] | 王倩之, 刘凯, 汪明. NEX-GDDP降尺度数据对中国极端降水指数模拟能力的评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(1): 31-43. |
| [9] | 孙晨, 汪方, 周月华, 李兰. CWRF模式对长江流域极端降水气候事件的模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(1): 44-57. |
| [10] | 周天军, 陈梓明, 陈晓龙, 左萌, 江洁, 胡帅. IPCC AR6报告解读:未来的全球气候——基于情景的预估和近期信息[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(6): 652-663. |
| [11] | 胡一阳, 徐影, 李金建, 韩振宇. CMIP6不同分辨率全球气候模式对中国降水模拟能力评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(6): 730-743. |
| [12] | 何佳骏, 任国玉, 张盼峰. 资料均一化对气温变化趋势及其城市化偏差估计的影响:以北京地区为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 503-513. |
| [13] | 陈燕, 惠品宏, 周学东, 杨杰. 气候变化对城市年径流总量控制率分区的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 525-536. |
| [14] | 潘蔚娟, 吴晓绚, 何健, 吕勇平, 艾卉. 基于均一化资料的广州近百年气温变化特征研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(4): 444-454. |
| [15] | 方佳毅, 殷杰, 石先武, 方建, 杜士强, 刘敏. 沿海地区复合洪水危险性研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 317-328. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||