Climate Change Research ›› 2024, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 170-181.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.234
• Impacts of Climate Change • Previous Articles Next Articles
Climate response to carbon dioxide radiative forcing and physiological forcing
- Department of Atmospheric Sciences, School of Earth Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
-
Received:2023-10-26Revised:2023-12-26Online:2024-03-30Published:2024-03-11
Cite this article
WU Xing-Yi, CAO Long. Climate response to carbon dioxide radiative forcing and physiological forcing[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 170-181.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.234

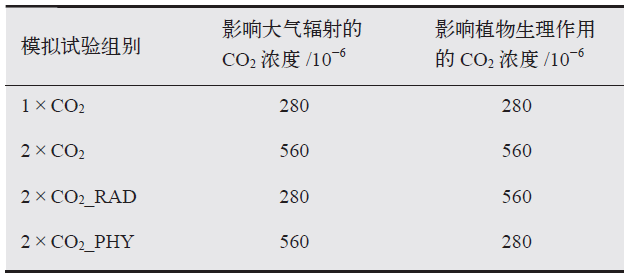
Fig. 1 Changes in surface air temperature in response to a doubling of atmospheric CO2. (Hatched areas represent regions where changes are not statistically significant at the 0.05 level using the Student t-test. The same bellow)

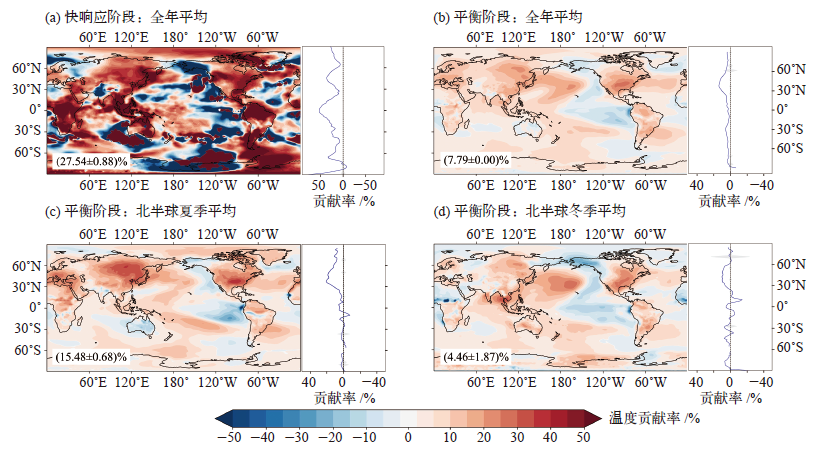
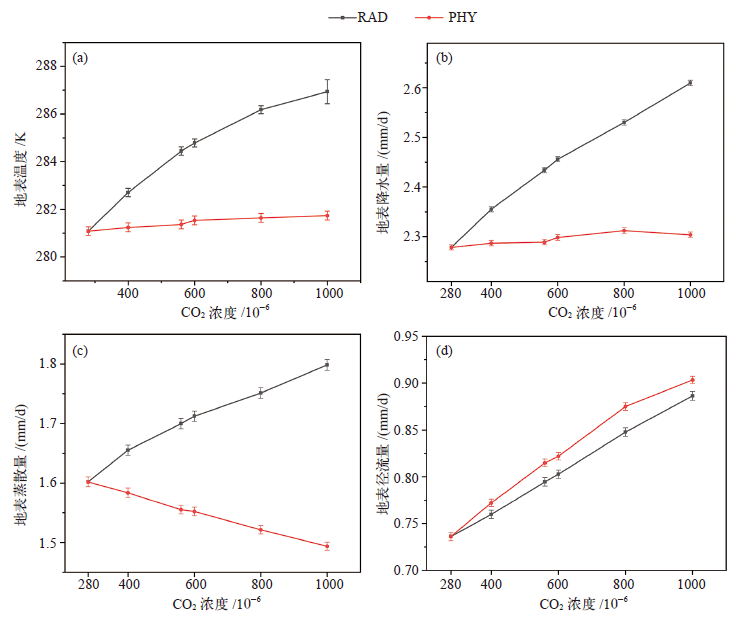
Fig. 8 Distribution of nonlinear changes in surface temperature, precipitation, and evapotranspiration at CO2 concentrations of 400×10-6 and 800×10-6 relative to CO2 concentration of 280×10-6
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023 |
| [2] |
Manabe S, Wetherald R T. Effects of doubling the CO2 concentration on the climate of a general circulation model[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1975, 32 (1): 3-15
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1975)032<0003:TEODTC>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [3] |
Hansen J, Sato M, Ruedy R. Radiative forcing and climate response[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1997, 102 (D6): 6831-6864
doi: 10.1029/96JD03436 URL |
| [4] | Gregory J M. A new method for diagnosing radiative forcing and climate sensitivity[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31 (3): L03205 |
| [5] | Hansen J. Efficacy of climate forcings[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2005, 110 (D18): D18104 |
| [6] |
Trenberth K E, Fasullo J T, Kiehl J. Earth’s global energy budget[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2009, 90 (3): 311-324
doi: 10.1175/2008BAMS2634.1 URL |
| [7] | Andrews T, Forster P M, Boucher O, et al. Precipitation, radiative forcing and global temperature change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37 (14): 783-792 |
| [8] | Zhao M, Cao L, Bala G, et al. Climate response to latitudinal and altitudinal distribution of stratospheric sulfate aerosols[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2021, 126 (24): e2021JD035379 |
| [9] |
Boucher O, Jones A, Betts R. Climate response to the physiological impact of carbon dioxide on plants in the Met Office Unified Model HadCM3[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2009, 32: 237-249
doi: 10.1007/s00382-008-0459-6 URL |
| [10] |
Cao L, Bala G, Caldeira K, et al. Importance of carbon dioxide physiological forcing to future climate change[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010, 107 (21): 9513-9518
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0913000107 URL |
| [11] |
Andrews T, Doutriaux-Boucher M, Boucher O, et al. A regional and global analysis of carbon dioxide physiological forcing and its impact on climate[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2011, 36 (3-4): 783-792
doi: 10.1007/s00382-010-0742-1 URL |
| [12] |
Field C B, Jackson R B, Mooney H A. Stomatal responses to increased CO2: implications from the plant to the global scale[J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 1995, 18 (10): 1214-1225
doi: 10.1111/pce.1995.18.issue-10 URL |
| [13] |
Ainsworth E A, Rogers A. The response of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance to rising [CO2]: mechanisms and environmental interactions: photosynthesis and stomatal conductance responses to rising [CO2][J]. Plant, Cell and Environment, 2007, 30 (3): 258-270
doi: 10.1111/pce.2007.30.issue-3 URL |
| [14] | Xu Z, Jiang Y, Jia B, et al. Elevated-CO2 response of stomata and its dependence on environmental factors[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 7: 657 |
| [15] |
Park S W, Kim J S, Kug J S. The intensification of Arctic warming as a result of CO2 physiological forcing[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 2098
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15924-3 |
| [16] | Zhao M, Cao L. Regional response of land hydrology and carbon uptake to different amounts of solar radiation modification[J]. Earth’s Future, 2022, 10 (11): e2022EF003288 |
| [17] | He M, Piao S, Huntingford C, et al. Amplified warming from physiological responses to carbon dioxide reduces the potential of vegetation for climate change mitigation[J]. Communications Earth & Environment, 2022, 3 (1): 160 |
| [18] |
Richardson T B, Forster P M, Andrews T, et al. Carbon dioxide physiological forcing dominates projected eastern Amazonian drying[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45 (6): 2815-2825
doi: 10.1002/grl.v45.6 URL |
| [19] |
Cui J, Piao S, Huntingford C, et al. Vegetation forcing modulates global land monsoon and water resources in a CO2-enriched climate[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 5184
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18992-7 |
| [20] |
Bala G, Caldeira K, Nemani R. Fast versus slow response in climate change: implications for the global hydrological cycle[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2010, 35 (2-3): 423-434
doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0583-y URL |
| [21] |
Cao L, Bala G, Caldeira K. Climate response to changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide and solar irradiance on the time scale of days to weeks[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2012, 7 (3): 034015
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/034015 URL |
| [22] | 陈晓龙, 周天军. 影响气候系统模式温室气体敏感度的反馈过程: 基于FGOALS模式的研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44 (2): 322-332. |
| Chen X L, Zhou T J. Climate sensitivities of two versions of FGOALS model to idealized radiative forcing[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 44 (2): 322-332 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
Gopalakrishnan R, Bala G, Jayaraman M, et al. Sensitivity of terrestrial water and energy budgets to CO2-physiological forcing: an investigation using an offline land model[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2011, 6 (4): 044013
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/6/4/044013 URL |
| [24] |
Powell T L, Galbraith D R, Christoffersen B O, et al. Confronting model predictions of carbon fluxes with measurements of Amazon forests subjected to experimental drought[J]. New Phytologist, 2013, 200 (2): 350-365
doi: 10.1111/nph.12390 pmid: 23844931 |
| [25] | Williams I N, Lu Y, Kueppers L M, et al. Land-atmosphere coupling and climate prediction over the U.S. Southern Great Plains[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121 (20): 12, 125-12, 144 |
| [26] |
Trugman A T, Medvigy D, Mankin J S, et al. Soil moisture stress as a major driver of carbon cycle uncertainty[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45 (13): 6495-6503
doi: 10.1029/2018GL078131 URL |
| [27] |
Lawrence D M, Fisher R A, Koven C D, et al. The Community Land Model Version 5: description of new features, benchmarking, and impact of forcing uncertainty[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2019, 11 (12): 4245-4287
doi: 10.1029/2018MS001583 |
| [28] |
Liang X, Wood E F, Lettenmaier D P, et al. The Project for intercomparison of land-surface parameterization schemes PILPS phase 2 c Red-Arkansas River basin experiment: 2. Spatial and temporal analysis of energy fluxes[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 1998, 19 (1-4): 137-159
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(98)00045-9 URL |
| [29] |
Xia Y, Mocko D, Huang M, et al. Comparison and assessment of Three Advanced Land Surface Models in simulating terrestrial water storage components over the United States[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2017, 18 (3): 625-649
doi: 10.1175/JHM-D-16-0112.1 URL |
| [30] |
Ou M, Zhang S. Evaluation and comparison of the common land model and the community land model by using in situ soil moisture observations from the soil climate analysis network[J]. Land, 2022, 11 (1): 126
doi: 10.3390/land11010126 URL |
| [31] |
Ding X, Lai X, Fan G Z. Numerical simulation and evaluation of soil temperature on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau by the CLM4.5 model[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2023, 152 (1-2): 371-384
doi: 10.1007/s00704-023-04406-3 |
| [1] | BAO Wen, DUAN An-Min, YOU Qing-Long, HU Die. Research progress on climate change and its impact on water resources over the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 158-169. |
| [2] | FAN Xing, LI Lu, GAO Xiang, CHEN Zhi-Hua. The analysis of COP28 Global Stocktake outcome and global climate governance prospects [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 253-260. |
| [3] | MA Li-Juan, YUAN Jia-Shuang, HUANG Lei. Prospect of climate risks management in China under the framework of UN Early Warning for All Initiative [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 48-61. |
| [4] | XU Yan, LU Wen-Hai, ZENG Rong, LIU Chang. Reflections on the application of “The Ocean Solutions Initiative” for climate change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 121-128. |
| [5] | ZHANG Fan, DING Jian-Fang, YANG Min, PENG Chong. Snowfall identification and response of snowfall to temperature and precipitation under climate change in Henan province [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 714-722. |
| [6] | WANG Bing-Jie, SUN Ying, HU Ting, DONG Si-Yan. Changes of extreme cold events in China over the last century based on reanalysis data [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(4): 403-417. |
| [7] | LUO Hui, LIU Jie, WANG Li, TANG Zhi-Yi. Impact assessment of climate warming and wetting on agricultural economy in Northwest China: a case study of Ningxia [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(3): 293-304. |
| [8] | TAN Xian-Chun, GAO Jin-Xin, ZENG An, XING Xiu-Cheng. Impact of the “Pilot Zones for Green Finance Reform and Innovations” policy on carbon emissions [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [9] | TIAN Dan-Yu, CHAI Qi-Min, LIU Bo-Han. The content and lessons from the European parliament’s climate-related legislations [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(2): 249-257. |
| [10] | MI Zhi-Fu, ZHANG Hao-Ran. Interpretation of IPCC AR6 report: climate change mitigation of urban systems [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(2): 139-150. |
| [11] | HOU Yi-Lei, XING Fang-Yuan, MA Li, YANG Ming, WEN Ya-Li. Addressing climate change and biodiversity conservation synergy: global practices and implications [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(1): 91-101. |
| [12] | FAN Xing, LI Lu, QIN Yuan-Yuan, GAO Xiang. The pathway from carbon peak to carbon neutrality in major developed economies and its insights [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(1): 102-115. |
| [13] | ZHANG Hua, LI Wen-Li, LI Xue-Min, DONG Lin, YANG You-Tian, ZHANG Guo-Ming, XU Ying-Jun. Analysis of urban and rural population scenarios and exposure characteristics in China in the future for the prevention of earthquake risk [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 707-719. |
| [14] | MEI Mei, HOU Wei, ZHOU Xing-Yan. The difference between new and old climate states and its impact on the assessment of climate and extreme event in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 653-669. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xi, CHEN Min-Peng. Adaptation and green recovery: synergistic responses to the COVID-19 pandemic and climate compounding risks [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 720-730. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||