气候变化研究进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (2): 191-202.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.218
双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望
- 1 清华大学低碳能源实验室,北京 100084
2 清华-力拓资源能源与可持续发展联合研究中心,北京 100084
3 清华大学气候变化与可持续发展研究院,北京 100084
-
收稿日期:2022-09-21修回日期:2022-11-21出版日期:2023-03-30发布日期:2023-02-15 -
通讯作者:杨秀,女,副研究员,yangxiuthu@tsinghua.edu.cn -
作者简介:杨姗姗,女,高级工程师,yangss@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金专项项目“碳达峰碳中和路径与对策综合研究”(72140005);研究阐释党的十九届五中全会精神国家社科基金重大项目“中国2030年前碳排放达峰行动方案研究”(21ZDA085)
Consideration and prospect of total carbon emission control system under the double carbon target
YANG Shan-Shan1,2( ), GUO Hao1,3, YANG Xiu3(
), GUO Hao1,3, YANG Xiu3( ), LI Zheng1,3
), LI Zheng1,3
- 1 Low Carbon Energy Laboratory, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 Tsinghua-Rio Tinto Joint Research Centre for Resources, Energy and Sustainable Development, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
3 Institute of Climate Change and Sustainable Development, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2022-09-21Revised:2022-11-21Online:2023-03-30Published:2023-02-15
摘要:
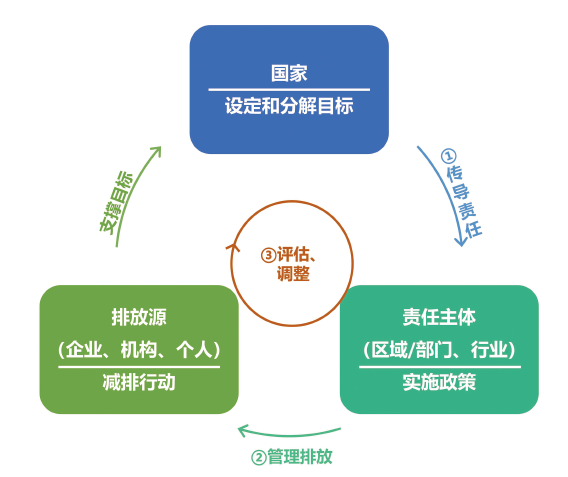
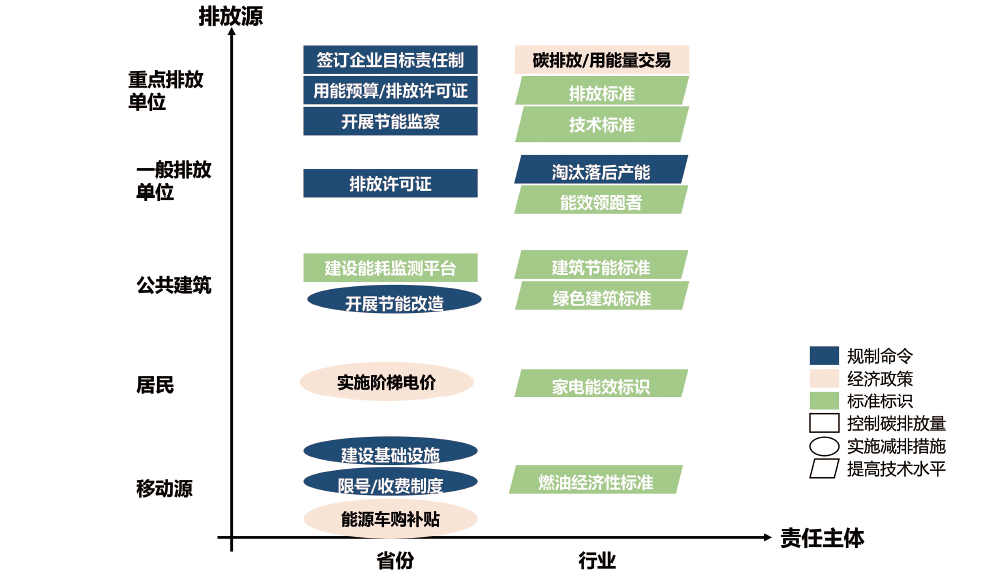
中国在碳达峰碳中和的“1+N”政策体系中提出要将能耗双控过渡到碳排放双控,建立碳排放总量控制制度。已有研究大多关注目标制定、碳排放分配的方法学,或以制度体系设计为对象进行分析,缺乏对分解模式、不同责任主体协同、责任主体与排放源匹配等制度关键问题的讨论。文中从制度实施角度着眼,梳理国内外控制碳排放的相关制度实践,提出构建碳排放总量控制制度的“目标分解→出台政策→实施行动→评估调整”全流程管理和要素,并提出各个环节的具体建议:(1)目标分解采用“区域和行业分解相结合”的模式,将发电等纳入碳市场行业的重点排放单位按行业分解和管控,其他排放源(包括一般排放企业、建筑、交通等)按区域分解和管控;(2)政策工具要匹配责任主体的管理模式和排放源的减排重点,发挥不同责任主体间的协同作用,避免重复管理;(3)要建设相应的数据核算和支撑体系,并形成评估反馈和调整机制。
引用本文
杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 李政. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 191-202.
YANG Shan-Shan, GUO Hao, YANG Xiu, LI Zheng. Consideration and prospect of total carbon emission control system under the double carbon target[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(2): 191-202.
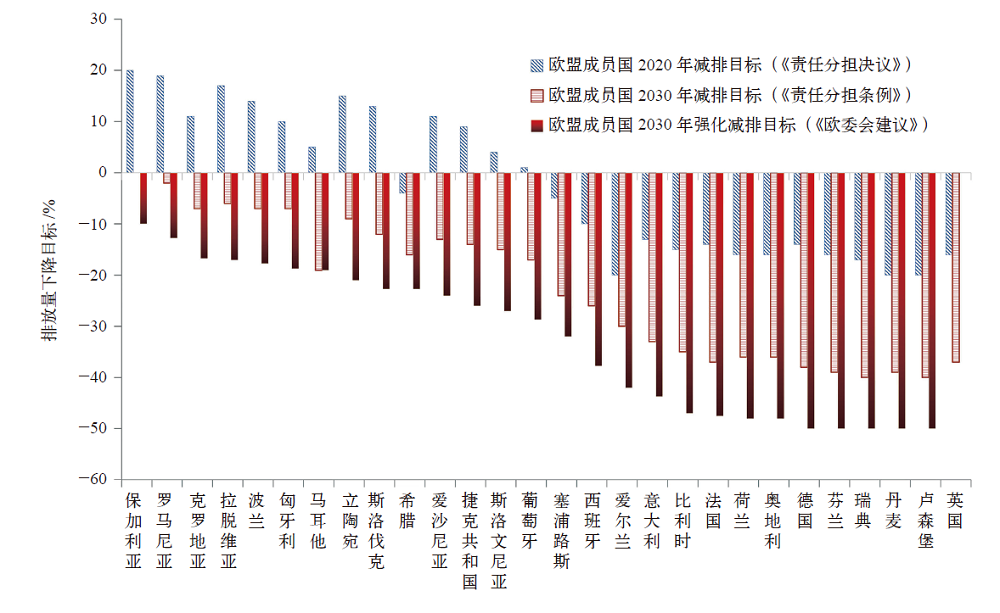
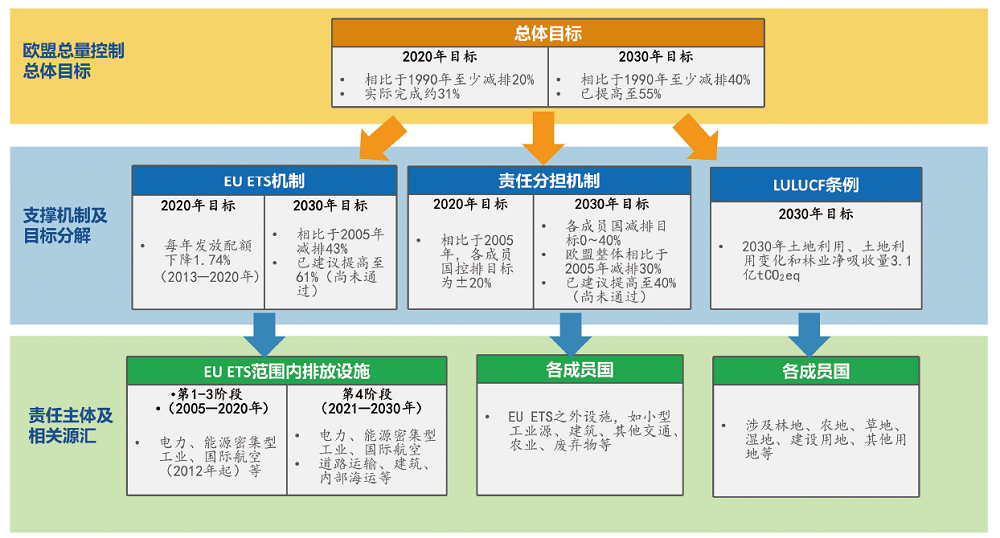
图2 成员国在减排责任分担机制下的减排目标 注:根据欧盟能源与气候变化有关政策整理;正值表示增排,负值表示减排。
Fig. 2 Emission reduction targets of member states under the emission reduction responsibility sharing mechanism
| [1] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 顾佰和. 中国碳总量控制新进展: 省域碳配额分配研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (1): 63-73. |
| Tan X C, Cheng Y L, Gu B H. New progress in controlling the total volume of carbon emissions in China: a review on the allocation of provincial carbon emission allowances[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (1): 63-73 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 谭显春, 牛苗苗, 顾佰和, 等. 基于高质量发展视角的中国碳配额省级分配方案评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (1): 74-83. |
| Tan X C, Niu M M, Gu B H, et al. Evaluation of China’s provincial carbon quota allocation scheme from the perspective of high-quality development[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (1): 74-83 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 项目综合报告编写组. 《中国长期低碳发展战略与转型路径研究》综合报告[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2020, 30 (11): 1-25. |
| Project Comprehensive Report Preparation Group. Comprehensive report on China’s long-term low-carbon development strategy and transformation path[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2020, 30 (11): 1-25 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 中国青年报客户端. 中国工程院: 我国有望2027年实现碳达峰, 2060年前实现碳中和[EB/OL]. 2022 [2022-08-12]. https://m.gmw.cn/baijia/2022-04/01/1302876708.html. |
| China Youth Daily Client. Chinese academy of engineering: China is expected to achieve carbon peaking in 2027 and carbon neutralization by 2060[EB/OL]. 2022 [2022-08-12]. https://m.gmw.cn/baijia/2022-04/01/1302876708.html (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 张希良, 黄晓丹, 张达, 等. 碳中和目标下的能源经济转型路径与政策研究[J]. 管理世界, 2022, 38 (1): 35-66. |
| Zhang X L, Huang X D, Zhang D, et al. Research on the path and policy of energy economy transformation under the goal of carbon neutrality[J]. Management World, 2022, 38 (1): 35-66 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 熊小平, 康艳兵, 冯升波, 等. 碳排放总量控制目标区域分解方法研究[J]. 中国能源, 2015, 37 (11): 15-19. |
| Xiong X P, Kang Y B, Feng S B, et al. Research on regional decomposition method of total carbon emission control target[J]. Energy of China, 2015, 37 (11): 15-19 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 裴晨雯, 屈卓然, 刘若彬. 中国省际碳排放权的初始分配[J]. 科学技术创新, 2021 (22): 25-27. |
| Pei C W, Qu Z R, Liu R B. Initial allocation of inter-provincial carbon emission rights in China[J]. Ke Xue Ji Shu Chuang Xin, 2021 (22): 25-27 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 王金南, 蔡博峰, 曹东, 等. 中国CO2排放总量控制区域分解方案研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2011, 31 (4): 680-685. |
| Wang J N, Cai B F, Cao D, et al. Scenario study on regional allocation of CO2 emissions allowance in China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2011, 31 (4): 680-685 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
田云, 林子娟. 巴黎协定下中国碳排放权省域分配及减排潜力评估研究[J]. 自然资源学报, 2021, 36 (4): 921-933.
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20210409 |
|
Tian Y, Lin Z J. Provincial distribution of China’s carbon emission rights and assessment of its emission reduction potential under the Paris Agreement[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2021, 36 (4): 921-933 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20210409 URL |
|
| [10] |
Cheng Y L, Gu B H, Tan X C, et al. Allocation of provincial carbon emission allowances under China’s 2030 carbon peak target: a dynamic multi-criteria decision analysis method[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 837: 155798
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155798 URL |
| [11] | 吴军, 李曼, 徐广姝, 等. 碳排放总量控制下行业间碳配额分配的博弈机制研究[J]. 北京化工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 47 (6): 115-120. |
| Wu J, Li M, Xu G S, et al. Carbon quota allocation among industries with carbon emission control by using game model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology: Natural Science, 2020, 47 (6): 115-120 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 刘海英, 王钰. 基于历史法和零和DEA方法的用能权与碳排放权初始分配研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2020, 28 (9): 209-220. |
| Liu H Y, Wang Y. Research on initial allocation of energy-consuming right and CO2-emission right based on historical method and ZSG-DEA method[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2020, 28 (9): 209-220 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 宣晓伟. “能耗双控”到“碳双控”: 挑战与对策[J]. 城市与环境研究, 2022 (3): 42-55. |
| Xuan X W. From “the amount and intensity control of energy consumption” to “the amount and intensity control of carbon emission”: challenge and strategy[J]. Urban and Environmental Studies, 2022 (3): 42-55 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 杨艳, 谷树忠, 李维明, 等. 从战略到行动: 德国经济绿色低碳转型历程及启示[J]. 发展研究, 2021, 38 (4): 58-63. |
| Yang Y, Gu S Z, Li W M, et al. From strategy to action: the green and low-carbon transformation process of German economy and its enlightenment[J]. Development Research, 2021, 38 (4): 58-63 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 邢佰英. 美国碳交易经验及启示: 基于加州总量控制与交易体系[J]. 宏观经济管理, 2012 (9): 84-86. |
| Xing B Y. American carbon trading experience and enlightenment: based on California’s total amount control and trading system[J]. Macroeconomic Management, 2012 (9): 84-86 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 杨慧. 日本碳排放交易体系的构建及对我国的启示[J]. 农村经济与科技, 2018, 29 (4): 18-19. |
| Yang H. Construction of Japan’s carbon emissions trading system and its enlightenment to China[J]. Rural Economy and Science, 2018, 29 (4): 18-19 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | European Union. European green deal[EB/OL]. 2019 [2022-07-12]. https://ec.europa.eu/clima/policies/eu-climate-action_en |
| [18] | European Union. European climate law[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-07-12]. https://climate.ec.europa.eu/eu-action/european-green-deal/european-climate-law_en |
| [19] | Official Journal of The European Union. Decision No 406/2009/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April 2009 on the effort of Member States to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions to meet the Community’s greenhouse gas emission reduction commitments up to 2020[EB/OL]. 2009 [2022-07-12]. http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec/2009/406/oj |
| [20] | Official Journal of The European Union. Regulation (EU) 2018/842 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 May 2018 on binding annual greenhouse gas emission reductions by Member States from 2021 to 2030 contributing to climate action to meet commitments under the Paris Agreement and amending regulation (EU) No 525/2013[EB/OL]. 2018 [2022-07-12]. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2018/842/oj |
| [21] | European Commission. Proposal for a regulation of the European parliament and of the council amending regulation EU 2018/842 on binding annual greenhouse gas emission reductions by member states from 2021 to 2030 contributing to climate action to meet commitments under the Paris Agreement[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-07-12]. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52021PC0555 |
| [22] | European Commission. Proposal for a Directive of the European parliament and of the council amending Directive 2003/87/EC establishing a system for greenhouse gas emission allowance trading within the Union Decision (EU) 2015/1814 concerning the establishment and operation of a market stability reserve for the Union greenhouse gas emission trading scheme and Regulation (EU) 2015/757[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-07-12]. tps://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52021PC0551&qid=1657601568403 |
| [23] | European Commission. Proposal for a regulation of the European parliament and of the council amending Regulations EU 2018/841 as regards the scope, simplifying the compliance rules, setting out the targets of the Member States for 2030 and committing to the collective achievement of climate neutrality by 2035 in the land use, forestry and agriculture sector, and (EU) 2018/1999 as regards improvement in monitoring, reporting, tracking of progress and review[EB/OL]. 2021 [2022-07-12]. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52021PC0554 |
| [24] | Official Journal of The European Union. Regulation (EU) 2018/1999 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11 December 2018 on the Governance of the Energy Union and Climate Action, amending Regulations (EC) No 663/2009 and (EC) No 715/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council, Directives 94/22/EC, 98/70/EC, 2009/31/EC, 2009/73/EC, 2010/31/EU, 2012/27/EU and 2013/30/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council, Council Directives 2009/119/EC and (EU) 2015/652 and repealing Regulation (EU) No 525/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council[EB/OL]. 2018 [2022-07-12]. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2018/1999/oj |
| [25] | Official Journal of the European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2018/2066 of 19 December 2018 on the monitoring and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions pursuant to Directive 2003/87/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and amending Commission Regulation (EU) No 601/2012[EB/OL]. 2018 [2022-07-12]. http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2018/2066/oj |
| [26] | UK Parliament. Climate change act 2008[EB/OL]. 2008 [2022-07-12]. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2008/27/contents |
| [27] | Climate Change Committee. The sixth carbon budget the UK’s path to net zero[R/OL]. 2020 [2022-07-12]. https://www.theccc.org.uk/publication/sixth-carbon-budget |
| [28] | Climate Change Committee. 2022 progress report to parliament[R/OL]. 2022 [2022-07-12]. https://www.theccc.org.uk/publication/2022-progress-report-to-parliament/ |
| [29] | UK Government. Net zero strategy: build back greener[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-07-12]. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/net-zero-strategy |
| [30] | Federal Ministry for The Environment, Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer Protection. Federal climate change act (Bundes-Klimaschutzgesetz)[R/OL]. 2019 [2022-07-12]. https://www.bmuv.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Gesetze/ksg_aendg_en_bf.pdf |
| [31] | 田丹宇, 徐华清. 德国气候保护法立法动因、特征及对我国立法的启示[J]. 环境资源法论丛, 2020, 12 (1): 141-153. |
| Tian D Y, Xu H Q. The legislative motivation and characteristics of German climate protection law and its enlightenment to China’s legislation[J]. Environmental and Resources Law Review, 2020, 12 (1): 141-153 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 刘然, 王旭明, 岳高, 等. “十三五”能源消耗总量和强度“双控”机制研究[J]. 能源与环境, 2017 (6): 2-4, 7. |
| Liu R, Wang X M, Yue G, et al. Research on the “double control” mechanism of total energy consumption and intensity in the “13th Five-Year Plan”[J]. Energy and Environment, 2017 (6): 2-4, 7 (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 马丽, 李惠民, 齐晔. 中央―地方互动与“十一五”节能目标责任考核政策的制定过程分析[J]. 公共管理学报, 2012, 9 (1): 1-8, 121. |
| Ma L, Li H M, Qi Y. Analysis on policy-making process of China’s energy-saving performance assessment institution: taking a perspective of central-local interaction[J]. Journal of Public Management, 2012, 9 (1): 1-8, 121 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 张焕波, 马丽, 李惠民, 等. 中国地方政府应对气候变化的行为及机制分析[J]. 公共管理评论, 2009, 8 (1): 80-97. |
| Zhang H B, Ma L, Li H M, et al. Analysis of the development and mechanisms for actions in climate change by China’s local governments[J]. China Public Administration Review, 2009, 8 (1): 80-97 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 杜莉, 张云. 我国碳排放总量控制交易的分配机制设计: 基于欧盟排放交易体系的经验[J]. 国际金融研究, 2013 (7): 51-58. |
| Du L, Zhang Y. The allocation mechanism design of China’s total carbon emission control transaction: based on the experience of the EU emission trading system[J]. Global Finance, 2013 (7): 51-58 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 解瑞丽, 郑彦强, 苏旭东. 关于实施碳排放总量控制制度的思考[J]. 中国环保产业, 2020 (7): 13-17. |
| Xie R L, Zheng Y Q, Su X D. Reflections on the implementation of total carbon emission control system[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2020 (7): 13-17 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | 卞勇, 刘宇. 建立碳排放总量控制制度[J]. 开放导报, 2021 (5): 14-20. |
| Bian Y, Liu Y. Establish total carbon emission control system[J]. China Opening Journal, 2021 (5): 14-20 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | 田丹宇, 郑文茹, 高诗颖. 加快构建碳排放总量控制的长效机制[J]. 环境保护, 2020, 48 (12): 55-57. |
| Tian D Y, Zheng W R, Gao S Y. Accelerating the construction of a long-term mechanism for total carbon emission control[J]. Environmental Protection, 2020, 48 (12): 55-57 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 姜华, 李艳萍, 高健, 等. 关于统筹建立二氧化碳排放总量控制制度的思考[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2022, 12 (1): 1-5. |
| Jiang H, Li Y P, Gao J, et al. Thoughts on the overall establishment of total carbon dioxide emission control system[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2022, 12 (1): 1-5 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 朱松丽, 朱磊, 赵小凡, 等. “十二五”以来中国应对气候变化政策和行动评述[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2020, 30 (4): 1-8. |
| Zhu S L, Zhu L, Zhao X F, et al. A review of China’s climate policies and actions since the launch of the 12th Five Year Plan[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2020, 30 (4): 1-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] |
付琳, 张东雨, 闫昊本, 等. 基于政策文本分析的中国碳减排政策工具研究[J]. 科学学研究, 2022. DOI: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.20220627.001.
doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.20220627.001 |
|
Fu L, Zhang D Y, Yan H B, et al. Research on China’s policy instruments of carbon emission mitigation through policy content analysis method[J]. Studies in Science of Science, 2022. DOI: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.20220627.001 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.20220627.001 |
| [1] | 谭显春, 高瑾昕, 曾桉, 幸绣程. 绿色金融改革创新试验区政策对碳排放的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [2] | 李晓易, 吴睿. 交通运输温室气体核算边界和测算方法研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 84-90. |
| [3] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 顾佰和. 中国碳总量控制新进展:省域碳配额分配研究综述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 63-73. |
| [4] | 李品, 谢晓敏, 黄震. 德国能源转型进程及对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 116-126. |
| [5] | 刘季熠, 张旖尘, 张东雨, 付琳, 曹颖. 欧盟减排《责任分担条例》修正案分析与启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(6): 756-763. |
| [6] | 宝哲, 周小亮. 数字赋能与城市碳排放——基于下一代互联网示范城市的准自然试验[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 503-508. |
| [7] | 徐一剑, 李潭峰, 徐丽丽. 国土空间总体规划温室气体核算模型[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 355-365. |
| [8] | 冯国会, 崔航, 常莎莎, 黄凯良, 王茜如. 近零能耗建筑碳排放及影响因素分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 205-214. |
| [9] | 陈燕, 惠品宏, 周学东, 杨杰. 气候变化对城市年径流总量控制率分区的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 525-536. |
| [10] | 张海军, 段茂盛. 中国试点ETS的碳减排效果评估——基于分省高耗能工业子行业数据的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 579-589. |
| [11] | 王敏, 冯相昭, 安祺, 卓岳, 赵梦雪, 杜晓林, 王鹏. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的青海省绿色低碳发展策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(5): 598-607. |
| [12] | 王利宁, 陈文颖, 戴家权, 向征艰, 龚金双. 智能互联重塑中国能源体系[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(2): 204-211. |
| [13] | 原嫄, 孙欣彤. 城市化、产业结构、能源消费、经济增长与碳排放的关联性分析——基于中国省际收入水平异质性的实证研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6): 738-747. |
| [14] | 陈怡, 田川, 曹颖, 刘强, 郑晓奇. 中国电力行业碳排放达峰及减排潜力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(5): 632-640. |
| [15] | 魏琦,周红伟,李林静. 不同监管强度下碳排放权交易违约行为的实验研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3): 345-354. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||