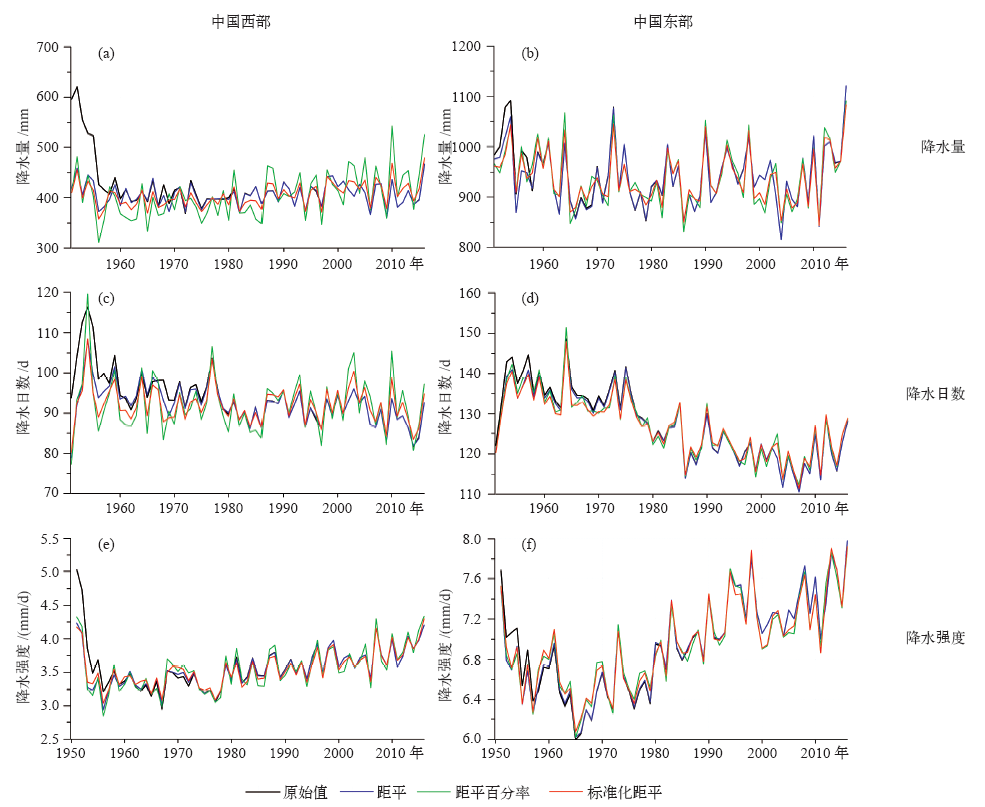
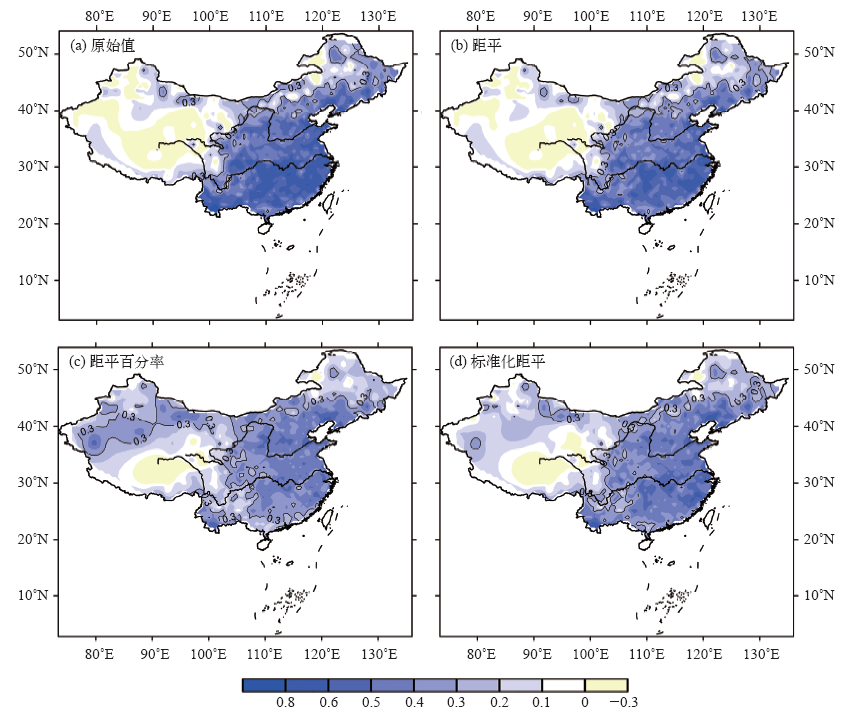
| [1] | Trenberth K E, Dai A, Rasmussen R M , et al. The changing character of precipitation[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2003,84(9):1205-1217 | | [2] | Easterling D R . Climate extremes: observations, modeling, and impacts[J]. Science, 2000,289(5487):2068-2074 | | [3] | Alexander L V, Zhang X, Peterson T C , et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006,111(D5):1042-1063 | | [4] | Donat M G, Alexander L V, Yang H , et al. Updated analyses of temperature and precipitation extreme indices since the beginning of the twentieth century: the HadEX2 dataset[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013,118(5):2098-2118 | | [5] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 | | [6] | Wan H, Zhang X, Zwiers F W , et al. Effect of data coverage on the estimation of mean and variability of precipitation at global and regional scales[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013,118(2):534-546 | | [7] | 任国玉, 战云健, 任玉玉 , 等. 中国大陆降水时空变异规律: I. 气候学特征[J]. 水科学进展, 2015,26(3):299-310. | | [7] | Ren G Y, Zhan Y J, Ren Y Y , et al. Spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation variability over mainland China: I. Climatology[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015,26(3):299-310 (in Chinese) | | [8] | Liang L, Zhao L, Gong Y , et al. Probability distribution of summer daily precipitation in the Huaihe basin of China based on Gamma distribution[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2012,26(1):72-84 | | [9] | Jamaludin S, Jemain A A . Fitting the statistical distributions to the daily rainfall amount in Peninsular Malaysia[J]. Journal Teknologi, 2007,46(1):33-48 | | [10] | Ison N T, Feyerherm A M, Bark L D . Wet period precipitation and the Gamma distribution[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 2010,10(10):658-665 | | [11] | Jones P D, Hulme M . Calculating regional climatic time series for temperature and precipitation: methods and illustrations[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 1996,16(4):361-377 | | [12] | 任国玉, 任玉玉, 战云健 , 等. 中国大陆降水时空变异规律: II.现代变化趋势[J]. 水科学进展, 2015,26(4):451-465. | | [12] | Ren G Y, Ren Y Y, Zhan Y J , et al. Spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation variability over mainland China: II. Recent trends[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015,26(4):451-465 (in Chinese) | | [13] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 中华人民共和国国家标准: 地面标准气候值统计方法(GB/T 34412—2017) [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 1-16. | | [13] | General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. National standard of the People’s Republic of China: statistical method for surface standard climate normals (GB/T 34412-2017) [S]. Beijing: Standard Press of China, 2017: 1-16(in Chinese) |
|
 ),Peng-Ling WANG2
),Peng-Ling WANG2