气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 469-476.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.001
大西洋经向翻转环流及其对全球气候的影响
陈显尧1( ), 毕瀚文1,2,3, 郝潇洁1,2, 马天骄1,2,3, 郭凌瑞1,2
), 毕瀚文1,2,3, 郝潇洁1,2, 马天骄1,2,3, 郭凌瑞1,2
- 1 中国海洋大学深海圈层与地球系统前沿科学中心/物理海洋教育部重点实验室,青岛 266100
2 中国海洋大学海洋与大气学院,青岛 266100
3 中国海洋大学未来海洋学院,青岛 266100
-
收稿日期:2025-01-02修回日期:2025-05-29出版日期:2025-07-30发布日期:2025-06-27 -
作者简介:陈显尧,男,教授,chenxy@ouc.edu.cn -
基金资助:自然科学基金项目(42394130);自然科学基金项目(424B2053)
Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and its impact on global climate change
CHEN Xian-Yao1( ), BI Han-Wen1,2,3, HAO Xiao-Jie1,2, MA Tian-Jiao1,2,3, GUO Ling-Rui1,2
), BI Han-Wen1,2,3, HAO Xiao-Jie1,2, MA Tian-Jiao1,2,3, GUO Ling-Rui1,2
- 1 Frontier Science Center for Deep Ocean Multispheres and Earth System/Key Laboratory of Physical Oceanography, Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
2 College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
3 Academy of the Future Ocean, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
-
Received:2025-01-02Revised:2025-05-29Online:2025-07-30Published:2025-06-27
摘要:
全球气候在温室气体强迫作用下呈现长期变暖趋势,且伴随着与大西洋经向翻转环流(AMOC)密切相关的60~70 a的准周期多年代际振荡。AMOC是全球海洋环流的核心部分,影响全球海洋热量和淡水的分布,进而影响全球气候变化。文中回顾了有器测温度、盐度和海表面高度等观测数据以来,基于直接观测阵列和代用观测指标展示的AMOC的结构与变异过程,基于器测观测数据构建的AMOC代用指标显示,AMOC多年代际变异与全球平均表面温度的多年代际变异之间存在约45°~90°的位相差,两者之间的位相关系主要受到中深层海洋的热输送对表层气候系统能量收支平衡的影响以及气候系统外部辐射强迫作用的调制。文中还讨论了研究AMOC变异及其对全球气候变化影响过程面临的挑战:尽管观测数据显示AMOC并没有明显的趋势变化,但稀缺的观测不足以支撑数值模式模拟的AMOC减缓的现象;气候系统的外部辐射强迫作用会影响气候的内部变率,改变AMOC多年代际变异与全球表面平均温度的关系。未来需要进行持续且高质量的观测以增强对AMOC多年代际变异及其气候效应的认识,为气候模式改进和气候变化政策制定提供科学依据。
引用本文
陈显尧, 毕瀚文, 郝潇洁, 马天骄, 郭凌瑞. 大西洋经向翻转环流及其对全球气候的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 469-476.
CHEN Xian-Yao, BI Han-Wen, HAO Xiao-Jie, MA Tian-Jiao, GUO Ling-Rui. Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and its impact on global climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 469-476.

图1 基于1925—1927年德国大西洋探险队数据的西大西洋经向盐度断面分布图 注:本图根据文献[11]重新绘制,等值线单位是盐度(psu)。
Fig. 1 Meridional cross section of salinity in the western Atlantic Ocean constructed from the measurements during the German Atlantic expeditions from 1925 to 1927

图2 (a)大洋传送带示意图[12],(b)更为精细的“大洋传送带”示意图 注:(b)图根据文献[13]重新绘制。
Fig. 2 (a) Schematic of the Great Ocean Conveyor Belt[12], (b) a more detailed schematic of the Great Ocean Conveyor Belt
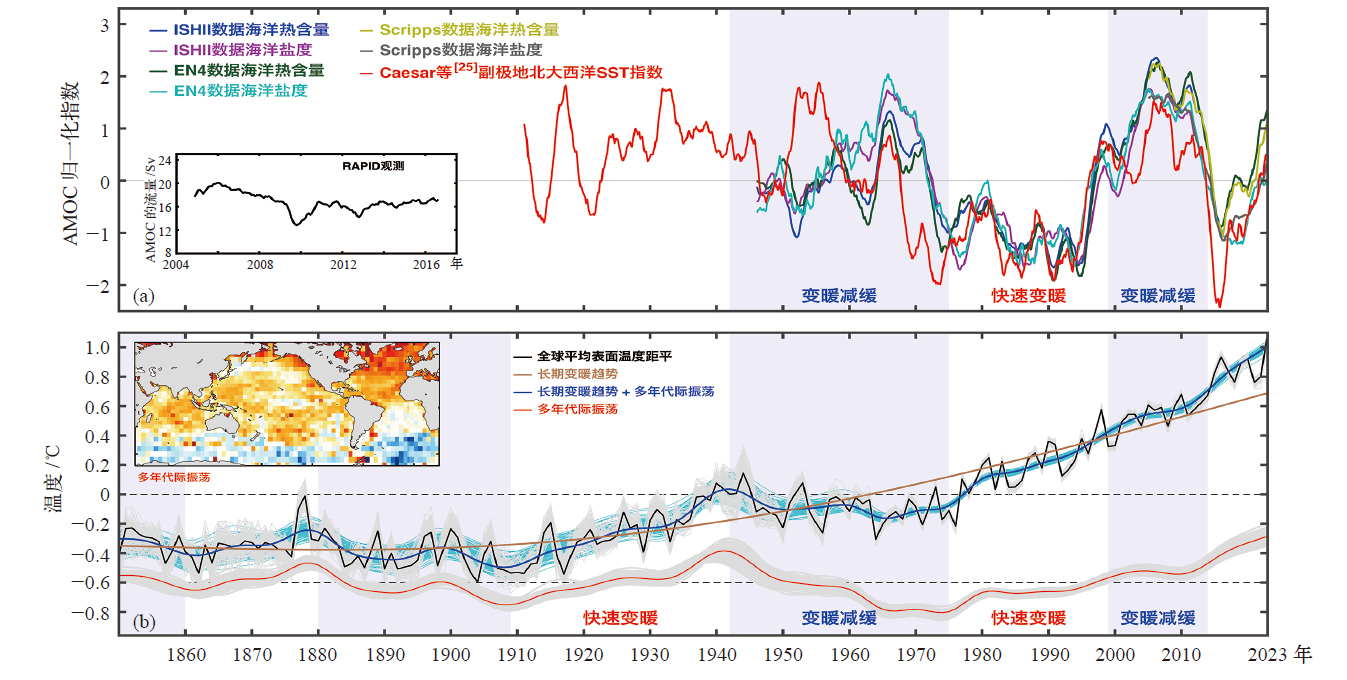
图3 (a) AMOC代用指标[24-26],(b) HadCRUT4.6数据计算的全球表面平均温度距平(GSTA)[24] 注:(b)图周围的浅色线条表示来自HadCRUT4.6的100个集合成员结果,小图是将SST回归到多年代际变率(MDV)的空间分布。
Fig. 3 AMOC and GSTA variations. (a) The AMOC fingerprint[24-26], (b) GSTA variations[24] (The inset shows the SST spatial pattern associated with MDV obtained by regressing SST onto its time series. The blue curve is the smoothed version of GSTA obtained as the sum of the secular trend and MDV. The faint lines around the solid lines are from 100 ensemble members of the HadCRUT4.6, which assess the range of uncertainty of the data used in the solid lines)
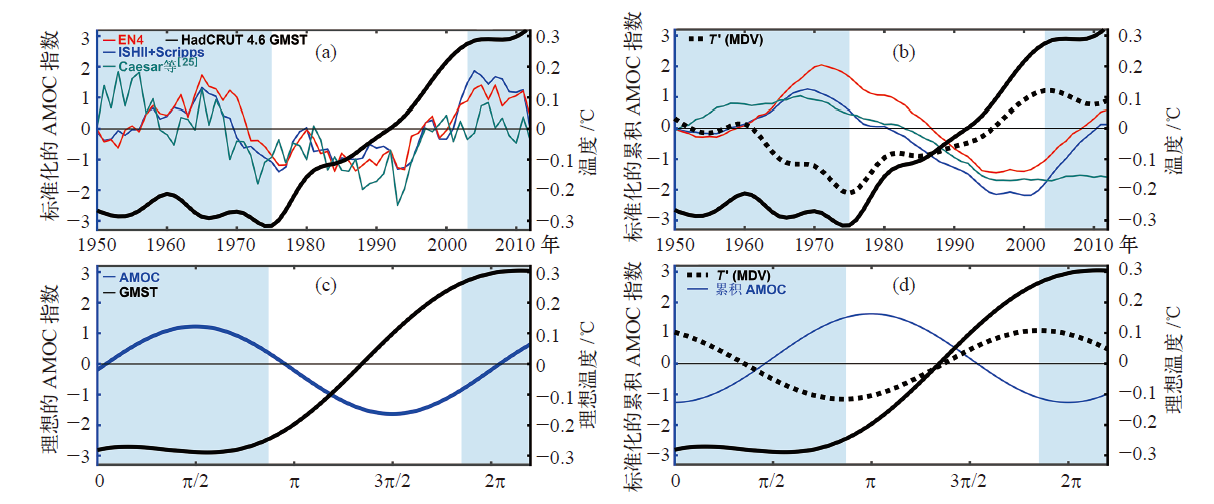
图4 观测与理论解的全球平均表面温度距平(GMST)和标准化的AMOC指数[38]及其积分时间序列(a)观测的GMST和标准化的AMOC指数,(b)观测的GMST和标准化的AMOC指数的积分, (c), (d)分别与(a),(b)一致,但为式(1)的理论解 注:黑色实线为GMST,红线、蓝线为AMOC副极地上层海洋盐度指数[24],绿线为AMOC的SST指数[25],黑色虚线T′(MDV)是GMST多年代际振荡;阴影区域表示变暖放缓的时期,无阴影区域表示加速变暖的时期 [38]。
Fig. 4 Observed and theoretical solution of anomalous global mean surface temperature (GMST). (a) Observed GMST plotted with various normalized AMOC indices [38], (b) observed GMST plotted with the integral of various AMOC indices, normalized, (c), (d) Same as (a), (b) but for the theoretical solution of Equation (1). (The black solid line is the GMST, and the red and blue lines represent the subpolar upper-ocean salinity indices [24]. The green line denotes the SST-based AMOC fingerprint [25]. Black dash line T′ (MDV) is the multidecadal variability of GMST. The shade areas denote periods of warming slowdown and the unshaded area the period of accelerated warming [38])
| [1] | Wu Z, Huang N E, Wallace J M, et al. On the time-varying trend in global-mean surface temperature[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2011, 37: 759-773 |
| [2] | Jeong D, Yoo C, Yeh S W, et al. Contributions of external forcing and internal variability to the multidecadal warming rate of East Asia in the present and future climate[J]. NPJ Climate Atmospheric Science, 2024, 7: 22 |
| [3] | Qian C, Yu J Y, Chen G. Decadal summer drought frequency in China: the increasing influence of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2014, 9: 124004 |
| [4] | Miles M W, Divine D V, Furevik T, et al. A signal of persistent Atlantic multidecadal variability in Arctic sea ice[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41 (2): 463-469 |
| [5] | Li X, Holland D, Gerber E, et al. Impacts of the north and tropical Atlantic Ocean on the Antarctic Peninsula and sea ice[J]. Nature, 2014, 505: 538-542 |
| [6] | Gao M, Yang J, Gong D, et al. Footprints of Atlantic multidecadal oscillation in the low-frequency variation of extreme high temperature in the Northern Hemisphere[J]. Journal of Climate, 2019, 32: 791-802 |
| [7] |
Goldenberg S B, Landsea C W, Mestas-Nuñez A M, et al. The recent increase in Atlantic hurricane activity: causes and implications[J]. Science, 2001, 293 (5529): 474-479
pmid: 11463911 |
| [8] | Kosaka Y, Xie S P. Recent global-warming hiatus tied to equatorial Pacific surface cooling[J]. Nature, 2013, 501: 403-407 |
| [9] | Stommel Henry M. Evolution of physical oceanography: scientific surveys in honor of Henry Stommel[M]. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press, 1981: 61-64 |
| [10] | Rumford B. The propagation of heat in fluids[J]. Essays, Political, Economical, and Philosophical, 1800: 197-386 |
| [11] |
Lozier M S. Overturning in the North Atlantic[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2012, 4: 291-315
pmid: 22457977 |
| [12] | Broecker W S. The great ocean conveyor[J]. Oceanography, 1991, 4 (2): 79-89 |
| [13] | Kuhlbrodt T, Griesel A, Montoya M, et al. On the driving processes of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2007, 45: RG2001 |
| [14] | Bryan K. Measurements of meridional heat transport by ocean currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1962, 67 (9): 3403-3414 |
| [15] | Ganachaud A, Wunsch C. Improved estimates of global ocean circulation, heat transport and mixing from hydrographic data[J]. Nature, 2000, 408 (6811): 453-457 |
| [16] | Hastenrath S. On meridional heat transports in the world ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1982, 12 (8): 922-927 |
| [17] | Hastenrath S. Heat budget of tropical ocean and atmosphere[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1980, 10 (2): 159-170 |
| [18] | Sverdrup H U. Oceanography[M]. Handbuch der Physik, 1957, 48: 608-670 |
| [19] | Talley L D. Shallow, intermediate, and deep overturning components of the global heat budget[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2003, 33 (3): 530-560 |
| [20] | Toggweiler J R, Samuels B. On the ocean’s large-scale circulation near the limit of no vertical mixing[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1998, 28 (9): 1832-1852 |
| [21] | Munk W, Wunsch C. Abyssal recipes II: energetics of tidal and wind mixing[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1998, 45 (12): 1977-2010 |
| [22] | McCarthy G, Frajka-Williams E, Johns W E, et al. Observed interannual variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at 26.5°N[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L19609 |
| [23] |
Lozier M S, Li F, Bacon S, et al. A sea change in our view of overturning in the subpolar North Atlantic[J]. Science, 2019, 363: 516-521
doi: 10.1126/science.aau6592 pmid: 30705189 |
| [24] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Global surface warming enhanced by weak Atlantic overturning circulation[J]. Nature, 2018, 559: 387-391 |
| [25] | Caesar L, Rahmstorf S, Robinson A, et al. Observed fingerprint of a weakening Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation[J]. Nature, 2018, 556: 191-196 |
| [26] | Zhang R. Coherent surface-subsurface fingerprint of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35: L20705 |
| [27] |
Moat B I, Smeed D A, Frajka-Williams E, et al. Pending recovery in the strength of the meridional overturning circulation at 26 degrees N[J]. Ocean Science, 2020, 16: 863-874
doi: 10.5194/os-16-863-2020 |
| [28] | Wunsch C, Heimbach P. Estimated decadal changes in the North Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and heat flux 1993-2004[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2006, 36: 2012-2024 |
| [29] | Balmaseda M A, Smith G C, Haines K, et al. Historical reconstruction of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation from the ECMWF operational ocean reanalysis[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34: L23615 |
| [30] | Bakker P, Schmittner A, Lenaerts J T M, et al. Fate of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: strong decline under continued warming and Greenland melting[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 12252-12260 |
| [31] | Weijer W, Cheng W, Garuba O A, et al. CMIP6 models predict significant 21st century decline of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47: e2019GL086075 |
| [32] | Jungclaus J H, Fischer N, Haak H, et al. Characteristics of the ocean simulations in the Max Planck Institute Ocean Model (MPIOM) the ocean component of the MPI-Earth system model[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2013, 5: 422-446 |
| [33] |
Renssen H, Mairesse A, Goosse H, et al. Multiple causes of the Younger Dryas cold period[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8: 946-949
doi: 10.1038/NGEO2557 |
| [34] | Stolpe M, Medhaug I, Sedláček J, et al. Multidecadal variability in global surface temperatures related to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31: 2889-2906 |
| [35] | Trenberth K E, Fasullo J T. Atlantic meridional heat transports computed from balancing Earth’s energy locally[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44: 1919-1927 |
| [36] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Varying planetary heat sink led to global-warming slowdown and acceleration[J]. Science, 2014, 345: 897-903 |
| [37] | Caesar L, Rahmstorf S, Feulner G. On the relationship between Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation slowdown and global surface warming[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2020, 15: 024003 |
| [38] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Comment on ‘On the relationship between Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation slowdown and global surface warming’[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16: 038001 |
| [39] | Zhang L P, Wang C Z. Multidecadal North Atlantic sea surface temperature and Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation variability in CMIP5 historical simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118: 5772-5791 |
| [40] | Buckley M W, Marshall J. Observations, inferences, and mechanisms of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a review[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2015, 54: 5-63 |
| [41] | McCarthy G D, Brown P J, Flagg C N, et al. Sustainable observations of the AMOC: methodology and technology[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2020, 58: e2019RG000654 |
| [42] | Johnson H L, Cessi P, Marshall D P, et al. Recent contributions of theory to our understanding of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124: 5376-5399 |
| [43] |
Lynch-Stieglitz J. The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and abrupt climate change[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2017, 9: 83-104
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060415 pmid: 27814029 |
| [44] | Zhang R, Sutton R, Danabasoglu G, et al. A review of the role of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in Atlantic Multidecadal Variability and associated climate impacts[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2019, 57: 316-375 |
| [45] | Weijer W, Cheng W, Drijfhout S S, et al. Stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124: 5336-5375 |
| [46] | Manabe S, Stouffer R J. Two stable equilibria of a coupled ocean-atmosphere model[J]. Journal of Climate, 1988, 1: 841-866 |
| [47] | Weaver A, Sedláček J, Edy M, et al. Stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a model intercomparison[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L20709 |
| [48] | Weijer W, Maltrud M E, Hecht M W, et al. Response of the Atlantic Ocean circulation to Greenland Ice Sheet melting in a strongly-eddying ocean model[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L09606 |
| [49] | Menary M B, Robson J, Allan R P, et al. Aerosol-forced AMOC changes in CMIP6 historical simulations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47: e88166 |
| [50] | Bellomo K, Angeloni M, Corti S, et al. Future climate change shaped by inter-model differences in Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation response[J]. Nature Communication, 2021, 12: 3659 |
| [51] | Rahmstorf S. On the freshwater forcing and transport of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation[J]. Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12 (12): 799-811 |
| [52] | Vellinga M, Wood R A. Global climatic impacts of a collapse of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation[J]. Climatic Change, 2002, 54: 251-267 |
| [53] | van Westen R M, Michael K, Henk A D, et al. Physics-based early warning signal shows that AMOC is on tipping course[J]. Science Advance, 2024, 10: eadk1189 |
| [54] | Boers N. Observation-based early-warning signals for a collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 680-688 |
| [55] | Ditlevsen P, Ditlevsen S. Warning of a forthcoming collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Communication, 2023, 14: 4254 |
| [56] | Fu Y, Li F, Karstensen J, et al. A stable Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in a changing North Atlantic Ocean since the 1990s[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6: eabc8736 |
| [57] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Evidence lacking for a pending collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2023, 14: 1 |
| [1] | 樊星, 梁启迪, 吴承霖, 高翔. 巴库气候大会成果盘点及全球气候治理形势展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 583-592. |
| [2] | 孙若水, 梁媚聪. 从巴黎到贝伦——《巴黎协定》十周年进展与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 574-582. |
| [3] | 谭显春, 程永龙, 闫洪硕, 幸绣程, 朱开伟, 王晨旭. IPCC第七次评估报告第三工作组减缓气候变化概要解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 494-501. |
| [4] | 朱松丽. 联合国气候公约体系下的国家分类演变[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 565-573. |
| [5] | 丁杰, 曹左男, 胡国铮, 干珠扎布, 赵芬, 王海锋, 高清竹. IPCC第七次评估报告第二工作组气候变化影响、适应与脆弱性大纲解读及启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 484-493. |
| [6] | 王博文, 贺一, 滕飞. 我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 502-518. |
| [7] | 崔鹏, 王岩, 张国涛, 张正涛, 雷雨, 王昊, 王姣, 郝建盛, 朱宏. 气候变化灾害风险防范:现状、挑战与科学问题[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 449-460. |
| [8] | 姜克隽. 综合评估模型在全球应对气候变化中的角色和未来研究转型[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 461-468. |
| [9] | 陈思达, 刘凯, 李博浩, 汪明. 中国脱贫县破纪录极端天气事件研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 327-339. |
| [10] | 张琴, 张利平, 李意, 刘丽娜, 佘敦先, 周芷菱, 袁喆. 气候水文预估不确定性量化及约束方法研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 317-326. |
| [11] | 李慧慧, 齐明, 孙仁金. 气候转型金融标准的国际实践及中国路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 428-439. |
| [12] | 石英, 徐影, 巢清尘, 张梦然, 韩振宇, 王荣. 基于CMIP6多模式的南水北调西线工程区未来气候变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 340-352. |
| [13] | 曲洋, 王铭铭, 周方卓, 黄俊灵, 常世彦. 基于气候因子框架的气候变化对能源系统的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(3): 353-363. |
| [14] | 王英珊, 孙维君, 丁明虎, 刘伟刚, 杜文涛, 秦翔, 张东启. 青藏高原冰川物质平衡变化特征及其对气候变化响应的研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(2): 208-220. |
| [15] | 孙颖, 王东阡, 张学斌. 中国气候变化检测归因研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(2): 153-168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||