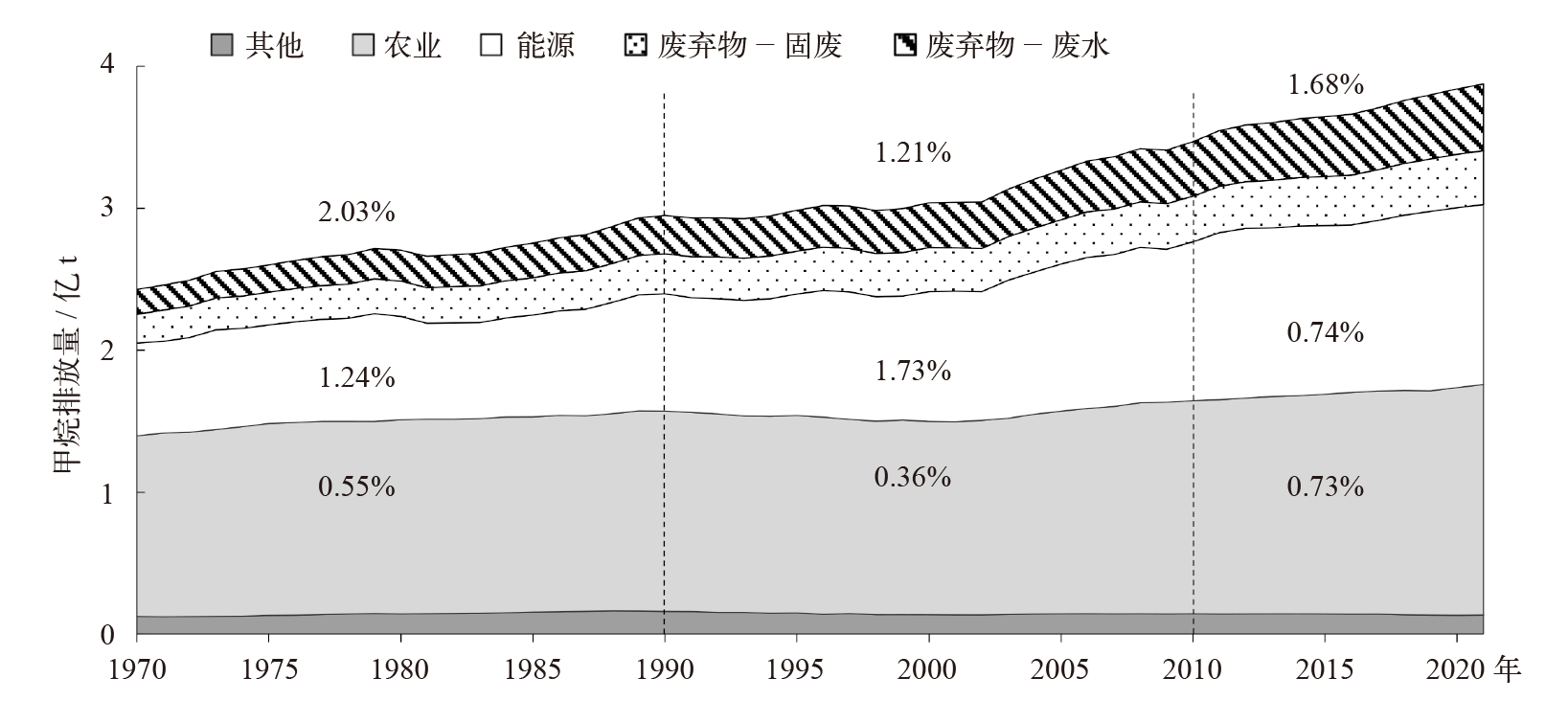
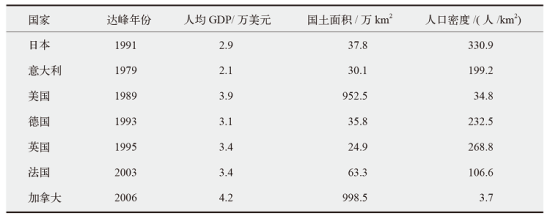
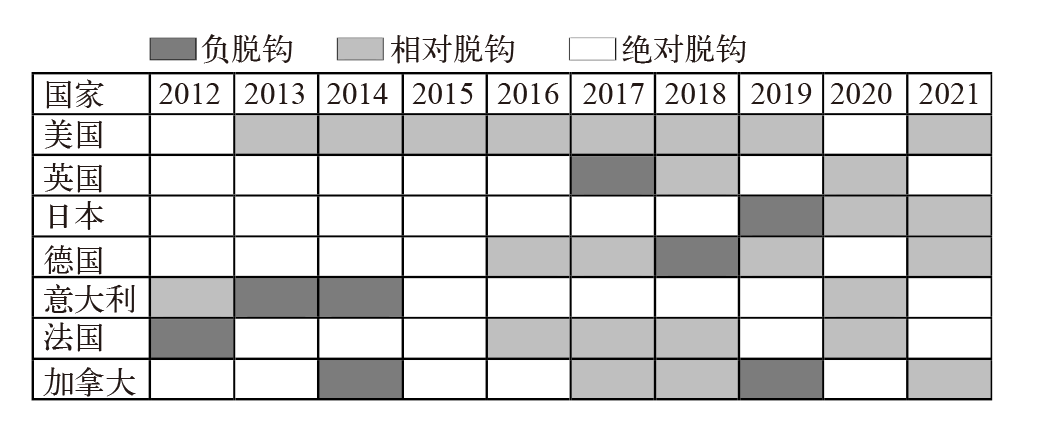
| [1] |
Shafik N. Economic development and environmental quality: an econometric analysis[J]. Oxford Economic Papers, 1994, 46: 757-773
doi: 10.1093/oep/46.Supplement_1.757
URL
|
| [2] |
Karousakis K. Waste and environmental policy[M]. Oxfordshire: Routledge, 2009: 14
|
| [3] |
Raymond L. Economic growth as environmental policy? Reconsidering the environmental Kuznets curve[J]. Public Policy, 2004, 24: 327-348
|
| [4] |
Mazzanti M, Montini A, Zoboli R. Municipal waste generation and socioeconomic drivers: evidence from comparing northern and southern Italy[J]. The Journal of Environment & Development, 2008, 17: 51-69
|
| [5] |
Ari I, Entürk H. The relationship between GDP and methane emissions from solid waste: a panel data analysis for the G7[J]. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 2020, 23: 282-290
doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2020.06.004
URL
|
| [6] |
Crippa M, Guizzardi D, Solazzo E, et al. GHG emissions of all world countries 2021[R/OL]. 2022 [2023-01-10]. https://edgar.jrc.ec.europa.eu/report_2022
|
| [7] |
The United Nations Environment Programme UNEP. Global methane assessment: benefits and costs of mitigation methane emissions[R/OL]. 2021 [2022-05-18]. https://www.unep.org/resources/report/global-methane-assessment-benefits-and-costs-mitigating-methane-emissions
|
| [8] |
庄国泰, 高培勇, 陈迎, 等.应对气候变化报告(2022): 落实“双碳”目标的政策和实践[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2022: 90-93.
|
|
Zhuang G T, Gao P Y, Chen Y, et al. Annual report on actions to address climate change (2022): policies and practices to implement the dual carbon goals[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Academic Press, 2022: 90-93 (in Chinese)
|
| [9] |
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA), Inventory of U.S. Greenhouse gas emissions and sinks 1990-2021[R/OL]. 2023 [2023-04-21]. https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2023-04/US-GHG-Inventory-2023-Main-Text.pdf
|
| [10] |
冯相昭. 英国重点领域甲烷排放控制经验及对我国的启示与建议[J]. 环境影响评价, 2023, 45 (3): 17-21.
|
|
Feng X Z. UK’s policy practices in reducing methane emission in key sectors and its implications for China[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2023, 45 (3): 17-21 (in Chinese)
|
| [11] |
王杰, 李治国, 谷继建. 金砖国家碳排放与经济增长脱钩弹性及驱动因素: 基于Tapio脱钩和LMDI模型的分析[J]. 世界地理研究, 2021, 30 (3): 501-508.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.03.2019470
|
|
Wang J, Li Z G, Gu J J. Decoupling analysis between energy consumption and economic growth in BRICS countries: based on Tapio decoupling and LMDI model analysis[J]. World Regional Studies, 2021, 30 (3): 501-508 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.03.2019470
|
| [12] |
王敏, 冯相昭, 安祺, 等. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的青海省绿色低碳发展策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607.
|
|
Wang M, Feng X Z, An Q, et al. Study on green and low-carbon development in Qinghai province based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
Tapio P. Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001[J]. Transport Policy, 2005, 12 (2): 137-151
doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
URL
|
| [14] |
Ang B W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide[J]. Energy Policy, 2005, 33 (7): 867-871
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2003.10.010
URL
|
| [15] |
Zhao X, Liu H S, Ding L L. Decomposition analysis of the decoupling and driving factors of municipal solid waste: taking China as an example[J]. Waste Management, 2022, 137: 200-209
doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.11.003
URL
|
| [16] |
宋杰鲲. 基于LMDI的山东省能源消费碳排放因素分解[J]. 资源科学, 2012, 34 (1): 35-41.
|
|
Song J K. Factor decomposition of carbon emissions from energy consumption of Shandong province based on LMDI[J]. Resources Science, 2012, 34 (1): 35-41 (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
胡雷. 我国城镇化对二氧化碳排放的影响机理研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12 (4): 341-347.
|
|
Hu L. Research on the mechanism of how urbanization effect on carbon emissions in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12 (4): 341-347 (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
Kang Y, Yang Q, Wang L, et al. China’s changing city-level greenhouse gas emissions from municipal solid waste treatment and driving factors[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2022 (180): 106168
|
| [19] |
Xiao S, Dong H, Geng Y, et al. Greenhouse gas emission mitigation potential from municipal solid waste treatment: a combined SD-LMDI model[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 120: 725-733
doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.10.040
URL
pmid: 33223250
|
| [20] |
刘晓. 德国生活垃圾管理及垃圾分类经验借鉴[J]. 世界环境, 2019 (5): 23-27.
|
|
Liu X. Draw lessons from Germany’s experience in municipal solid waste management and garbage classification[J]. World Environment, 2019 (5): 23-27 (in Chinese)
|
 ), FENG Xiang-Zhao2, WANG Min1, LI Li-Ping1(
), FENG Xiang-Zhao2, WANG Min1, LI Li-Ping1( )
)