Climate Change Research ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (6): 685-690.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.162
• Special Section on the Sixth Assessment Report of IPCC: WGI • Previous Articles Next Articles
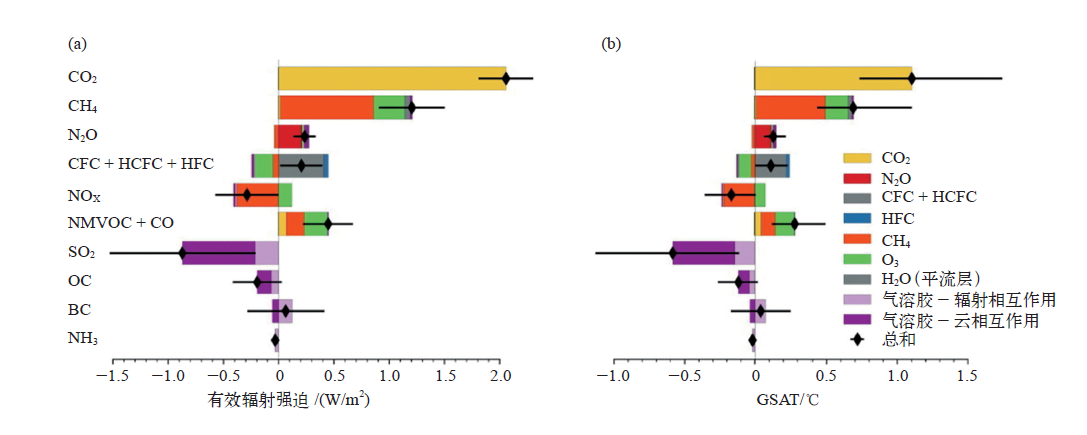
The roles of short-lived climate forcers in a changing climate
- Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Atmospheric Environment Monitoring and Pollution Control/Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center of Atmospheric Environment and Equipment Technology/School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science &Technology, Nanjing 210044, China