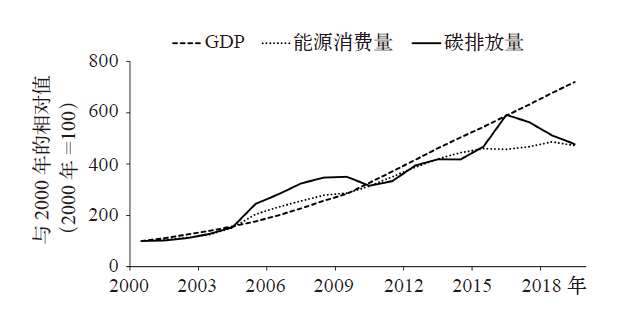
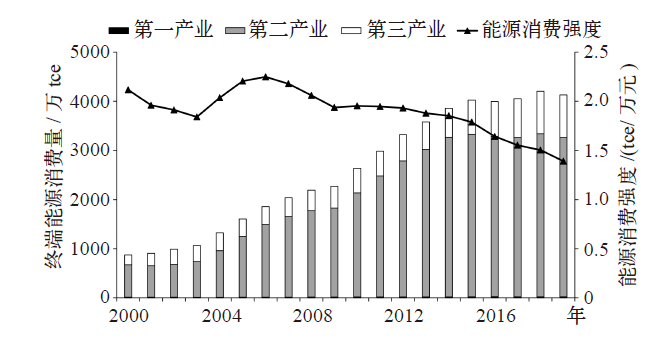
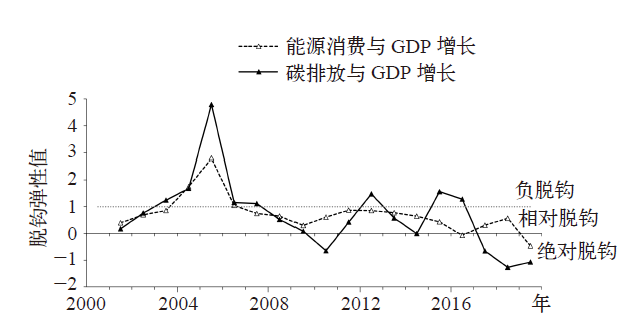
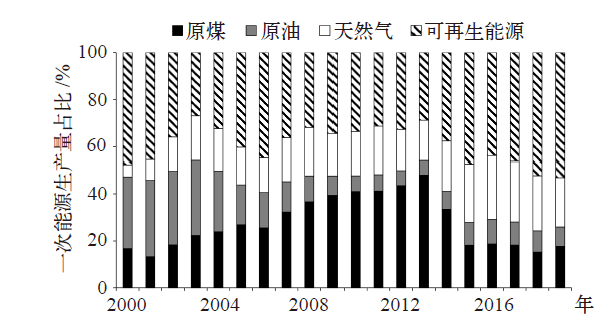
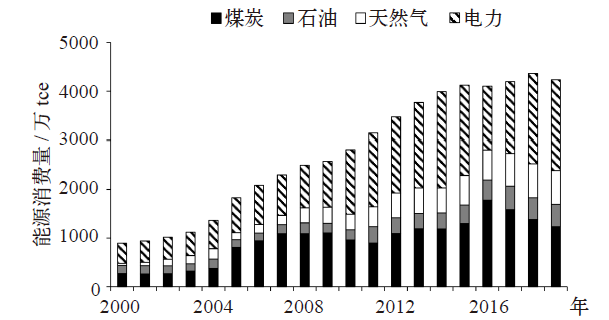
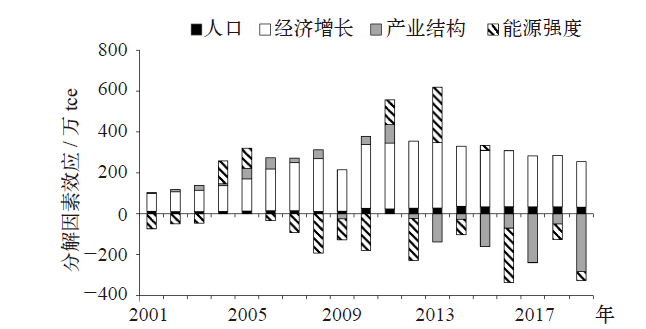
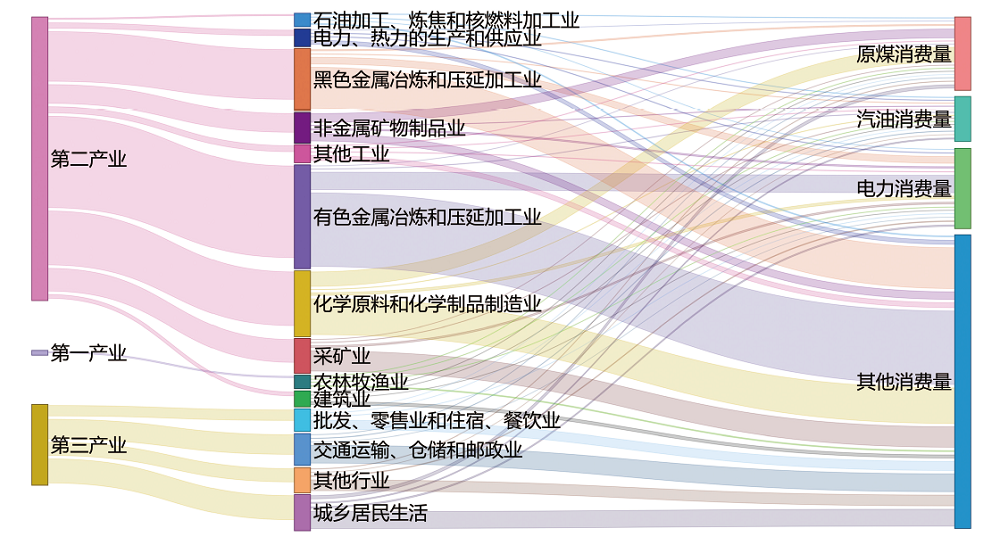
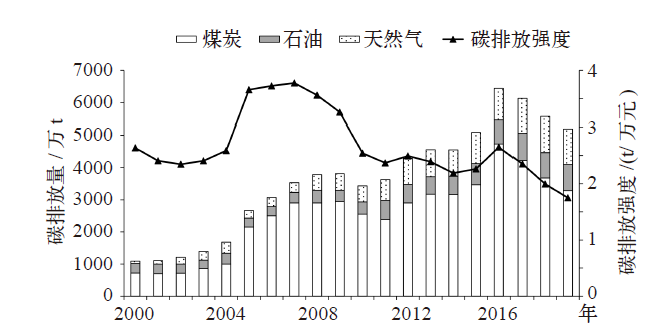
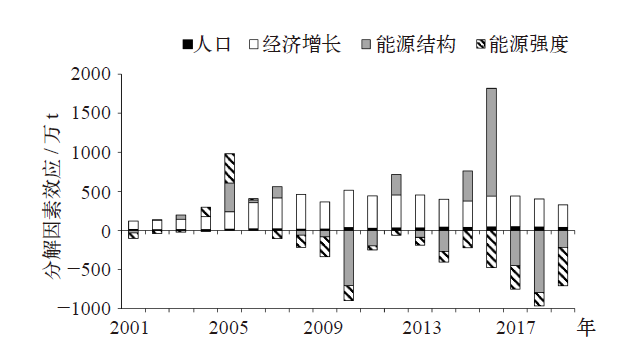
Climate Change Research ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (5): 598-607.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.216
• Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Previous Articles Next Articles
Study on green and low-carbon development in Qinghai province based on decoupling index and LMDI
WANG Min1( ), FENG Xiang-Zhao1(
), FENG Xiang-Zhao1( ), AN Qi1, ZHUO Yue2, ZHAO Meng-Xue1, DU Xiao-Lin1, WANG Peng1
), AN Qi1, ZHUO Yue2, ZHAO Meng-Xue1, DU Xiao-Lin1, WANG Peng1
- 1 Department of Energy and Environmental Policy Research, Policy Research Center for Environment and Economy, Ministry of Ecology and Environment, Beijing 100029, China
2 Beijing Zhongchuang Carbon Investment Technology Co., LTD., Beijing 100041, China
-
Received:2020-09-17Revised:2020-10-19Online:2021-09-30Published:2021-09-28 -
Contact:FENG Xiang-Zhao E-mail:wang.min@prcee.org;feng.xiangzhao@prcee.org
Cite this article
WANG Min, FENG Xiang-Zhao, AN Qi, ZHUO Yue, ZHAO Meng-Xue, DU Xiao-Lin, WANG Peng. Study on green and low-carbon development in Qinghai province based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(5): 598-607.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.216
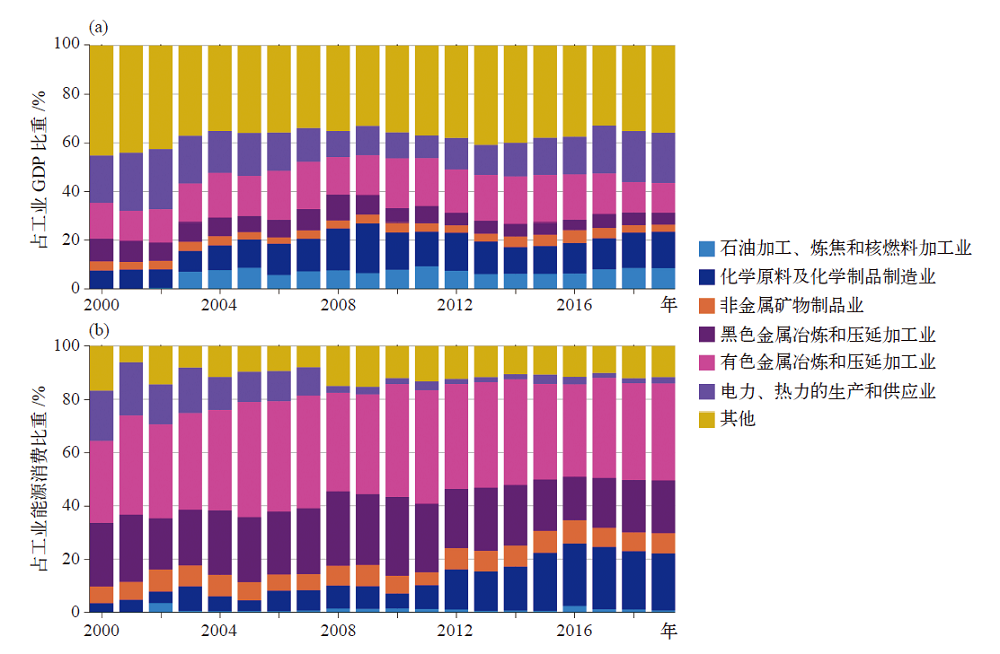
Fig. 7 The proportion of traditional energy-intensive industries accounting for industrial GDP (a) and corresponding energy consumption (b) in Qinghai province from 2000 to 2019
| [1] | 王强, 伍世代, 林羽珊. 中国东南沿海地区工业能源消费碳排放的驱动因素分析[J]. 资源科学, 2015, 37(6):1239-1248. |
| Wang Q, Wu S D, Lin Y S. Driving factors of industrial energy consumption and carbon emissions in southeast coastal regions of China: taking Fujian province as a case study[J]. Resources Science, 2015, 37(6):1239-1248 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 宋佩珊, 计军平, 马晓明. 广东省能源消费碳排放增长的结构分解分析[J]. 资源科学, 2012, 34(3):551-558. |
| Song P S, Ji J P, Ma X M. Structural decomposition analysis on the growth of carbon emission from energy consumption in Guangdong[J]. Resources Science, 2012, 34(3):551-558 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 严翔, 成长春, 贾亦真. 中国城镇化进程中产业、空间、人口对能源消费的影响分解[J]. 资源科学, 2018, 40(1):216-225. |
| Yan X, Cheng C C, Jia Y Z. Effect decomposition of industry, space and population on energy consumption during Chinese urbanization[J]. Resources Science, 2018, 40(1):216-225 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 邓吉祥, 刘晓, 王铮. 中国碳排放的区域差异及演变特征分析与因素分解[J]. 自然资源学报, 2014, 29(2):189-200. |
| Deng J X, Liu X, Wang Z. Characteristics analysis and factor decomposition based on the regional difference changes in China’s CO2 emission[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2014, 29(2):189-200 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 徐国泉, 刘则渊, 姜照华. 中国碳排放的因素分解模型及实证分析(1995—2004)[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2006, 16(6):158-161. |
| Xu G Q, Liu Z Y, Jiang Z H. Decomposition model and empirical study of carbon emissions for China, 1995-2004[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2006, 16(6):158-161 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 许士春, 习蓉, 何正霞. 中国能源消耗碳排放的影响因素分析及政策启示[J]. 资源科学, 2012, 34(1):2-12. |
| Xu S C, Xi R, He Z X. Influential factors and policy implications of carbon emissions for energy consumption in China[J]. Resources Science, 2012, 34(1):2-12 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 孙倩, 汪鹏, 蔡国田, 等. 基于LMDI的城市能源消费总量指标评价模型研究[J]. 生态经济, 2019, 35(6):98-105. |
| Sun Q, Wang P, Cai G T, et al. Research on evaluation model of urban energy consumption total indicators based on LMDI[J]. Ecological Economy, 2019, 35(6):98-105 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 武红, 谷树忠, 周洪, 等. 河北省能源消费、碳排放与经济增长的关系[J]. 资源科学, 2011, 33(10):1897-1905. |
| Wu H, Gu S Z, Zhou H, et al. Relationships between energy consumption carbon emissions and economic growth in Hebei province[J]. Resources Science, 2011, 33(10):1897-1905 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 张京玉. 影响中国能源消耗碳排放因素分析: 基于LMDI分解模型[J]. 煤炭经济研究, 2019, 39(11):23-28. |
| Zhang J Y. Analysis of factors affecting China’s energy consumption carbon emissions: based on LMDI decomposition model[J]. Coal Economic Research, 2019, 39(11):23-28 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 于明亮, 李雨莳, 陈文浩, 等. 长三角地区能源消费变化的驱动因素分解研究: 基于1995—2016年数据的分析[J]. 东南大学学报: 哲学社会科学版, 2020, 22(2):69-79. |
| Yu M L, li Y S, Chen W H, et al. Study on the driver decomposition of energy consumption change in the Yangtze River delta region: based on the analysis of 1995-2016 data[J]. Journal of Southeast University: Philosophy and Social Science, 2020, 22(2):69-79 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 邵敏, 郝晴, 闫桂焕, 等. 山东省能源消费碳排放影响因素分析[J]. 科学与管理, 2019, 39(4):64-68. |
| Shao M, Hao Q, Yan G H, et al. Influence factors of energy-related carbon emissions in Shandong province[J]. Science and Management, 2019, 39(4):64-68 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 张伟, 张金锁, 邹绍辉, 等. 基于LMDI的陕西省能源消费碳排放因素分解研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2013, 27(9):26-31. |
| Zhang W, Zhang J S, Zou S H, et al. Factor decomposition of carbon emissions from energy consumption of Shaanxi province based on LMDI[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2013, 27(9):26-31 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 顾阿伦, 何崇恺, 吕志强. 基于LMDI 方法分析中国产业结构变动对碳排放的影响[J]. 资源科学, 2016, 38(10):1861-1870. |
| Gu A L, He C K, Lv Z Q. Industrial structure changes impacts on carbon emissions in China based on LMDI method[J]. Resources Science, 2016, 38(10):1861-1870 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 范建双, 周琳. 中国建筑业碳排放时空特征及分省贡献[J]. 资源科学, 2019, 41(5):897-907. |
| Fan J S, Zhou L. Spatiotemporal distribution and provincial contribution decomposition of carbon emissions for the construction industry in China[J]. Resources Science, 2019, 41(5):897-907 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 田华征, 马丽. 中国工业碳排放强度变化的结构因素解析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(3):639-653. |
| Tian H Z, Ma L. Study on the change of China’s industrial carbon emission intensity from the perspective of sector structure[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(3):639-653 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 任勇, 安祺. 经济增长与环境退化关系的趋势分析[J]. 环境经济, 2009 (12):41-44. |
| Ren Y, An Q. Trend analysis of the relationship between economic growth and environmental degradation[J]. Journal of Environmental Economics, 2009 (12):41-44 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 王杰. 中国高耗能行业碳排放脱钩关系及影响因素研究[J]. 甘肃科学学报, 2019, 31(4):129-136. |
| Wang J. Decoupling relationship and impact of carbon emission in Chinese energy-intensive industries factor research[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences, 2019, 31(4):129-136 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 曲健莹, 李科. 工业增长与二氧化碳排放“脱钩”的测算与分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报:社会科学版, 2019, 39(5):92-104. |
| Qu J Y, li K. Measurement and analysis of “decoupling” between industrial growth and carbon dioxide emissions in China[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University: Social Sciences, 2019, 39(5):92-104 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 周彦楠, 杨宇, 程博, 等. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的中国经济增长与碳排放耦合关系的区域差异[J]. 中国科学院大学学报, 2020, 37(3):295-307. |
| Zhou Y N, Yang Y, Cheng B, et al. Regional differences in the coupling relationship between Chinese economic growth and carbon emissions based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020, 37(3):295-307 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
Tapio P. Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decopling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finaland between 1970 and 2001[J]. Transport Policy, 2005, 12(2):137-151
doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001 URL |
| [21] |
Peters G P, Weber C L, Guan D, et al. China’s growing CO2 emissions: a race between increasing consumption and efficiency gains[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(17):5939-5944
doi: 10.1021/es070108f URL |
| [22] | Ang B W. The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide[J]. Energy Policy, 2005 (33):867-871 |
| [23] | 梁启迪, 冯相昭, 杜晓林, 等. 基于LMDI的能源消费碳排放影响因素研究: 以唐山市为例[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2020, 45(1) :150-154. |
| Liang Q D, Feng X Z, Du X L, et al. Study on the influencing factors of carbon emissions from energy consumption based on LMDI method: taking Tangshan city as an example[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2020, 45(1):150-154 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 宋杰鲲. 基于LMDI的山东省能源消费碳排放因素分解[J]. 资源科学, 2012, 34(1):35-41. |
| Song J K. Factor decomposition of carbon emissions from energy consumption of Shandong province based on LMDI[J]. Resources Science, 2012, 34(1):35-41 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 胡雷. 我国城镇化对二氧化碳排放的影响机理研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(4):341-347. |
| Hu L. Research on the mechanism of how urbanization effect on carbon emissions in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4):341-347 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | TONG Rui-Yong, WEI Run-Bin, WU Jin-Yan, MAO Bao-Hua, TIAN Pei-Ning. Influence of power generation structure on carbon emission factor of high-speed railway in operation period [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(1): 116-124. |
| [2] | QIN Yu-Xiang, HUANG Rui. Carbon emission efficiency and influencing factors in Central and Eastern European countries based on Super-SBM model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(5): 581-592. |
| [3] | WEI Xi-Kai, TAN Xiao-Shi, RUAN Jia-Tong, LIN Ming, QIN Lu, SUN Guo-Li, XIANG Ke-Qi, CHU Yao-Hui. Research on carbon emission factors of regional and provincial power grids from 2005 to 2021 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(3): 337-350. |
| [4] | LIU Yuan-Xin, HE Shuo, JIANG Ya-Jing, LUO Xu, YUAN Jia-Hai. Spatial-temporal decomposition of carbon emissions in China’s four major urban agglomerations [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 231-241. |
| [5] | LUO Xiao-Yu, CAO Xing-Yu, SONG Zhi-Qian. Comparison of carbon emissions throughout the entire lifecycle of buildings between China and Japan [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 220-230. |
| [6] | CAO Xiang, JIANG Lu, YU Yang. Carbon emission effect of foreign investment and its influence on carbon peaking [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 205-219. |
| [7] | MA Guo-Song, DUAN Mao-Sheng. Potential risks of double-counting carbon emission reductions in environmental rights trading and countermeasures [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 85-96. |
| [8] | TIAN Pei-Ning, LIANG Xiao, GUAN Yu-Jie, ZHAO Yi-Xin, MAO Bao-Hua, XUE Ting. Whole life cycle carbon emission and power generation structure transformation pathway planning of China’s power [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 97-106. |
| [9] | ZHANG Gui-Chi, LI Xiao-Mei, YANG Feng, SUN Rui-Ling. Working ideas of urban reduction of pollution and carbon emissions management: based on great inventory management system [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(1): 75-84. |
| [10] | YANG Zi-Yi, HU Shan, XU Tian-Hao, YAN Da, JIANG Yi. Method and application of global building operation energy use and carbon emissions comparison in the context of carbon neutrality [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 749-760. |
| [11] | WANG Wen-Zhi, TANG Guo. Carbon emission reduction effects of provincial intermediate trade from the perspective of value-added driven [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 771-785. |
| [12] | DING Li-Yuan, WANG Yan-Hua, WANG Ke. The synergistic effect of carbon emission trading on pollution and carbon reduction and the influence mechanism [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(6): 786-798. |
| [13] | CAI Li-Ya, GUO Jian-Feng, SHI Chuan, WANG Hao-Bin, ZHU Rong-Qi, NIU Yan, XUE Zhi-Guang, BAI Ruo-Bing, JI Jun-Ping, DUAN Jing-Lin. Simulation research on the evolution pathway planning of energy supply and demand in China under the dual carbon targets [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 616-633. |
| [14] | YANG Ru-Pu, FENG Xiang-Zhao, WANG Min, LI Li-Ping. Analysis on the driving forces of methane emissions from solid waste treatment in G7 countries [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 573-581. |
| [15] | ZHANG Chun-Li. Research on setting framework of carbon emissions control industry’s benchmarks under carbon emissions trading [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 645-652. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||