气候变化研究进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (2): 158-169.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.247
青藏高原气候变化及其对水资源影响的研究进展
- 1 中国科学院科技战略咨询研究院,北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学公共政策与管理学院,北京 100049
3 厦门大学,厦门 361005
4 复旦大学,上海 200433
5 中国科学院大气物理研究所,北京 100029
-
收稿日期:2023-11-10修回日期:2023-12-04出版日期:2024-03-30发布日期:2024-02-28 -
通讯作者:段安民,男,研究员,amduan@xmu.edu.cn -
作者简介:包文,女,博士研究生 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(91937302);国家自然科学基金项目(42288101)
Research progress on climate change and its impact on water resources over the Tibetan Plateau
BAO Wen1,2, DUAN An-Min3( ), YOU Qing-Long4, HU Die5
), YOU Qing-Long4, HU Die5
- 1 Institutes of Science and Development, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
2 School of Public Policy and Management, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
4 Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
5 Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2023-11-10Revised:2023-12-04Online:2024-03-30Published:2024-02-28
摘要:
回顾总结了近20年、特别是近10年来青藏高原气候变化的特征、变化的原因及其对高原水资源的影响方面的最新研究进展。1960年以来青藏高原地区总体气温显著升高,升温趋势存在明显的海拔依赖性,温室气体、冰雪反照率反馈、云-水汽-辐射反馈、局地强迫等是影响高原气温上升具有海拔依赖性的重要因素。总体上青藏高原降水呈现增加趋势,变化的区域性和季节性差异比气温变化的时空差异更强;降水空间变化主要分为南北偶极型、东西偶极型、中部和边缘差异型和多元型;夏季降水增加最为显著。受气候变化和人为气溶胶排放等影响,青藏高原水资源特别是冰冻圈水资源发生剧烈的变化,大部分冰川加速退缩、冰川径流增加、湖泊严重扩张,导致青藏高原上水循环加强和气候偏暖湿化;青藏高原积雪的变化具有明显的年代际特征。最后提出未来需要进一步开展的研究方向和政策建议。
引用本文
包文, 段安民, 游庆龙, 胡蝶. 青藏高原气候变化及其对水资源影响的研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 158-169.
BAO Wen, DUAN An-Min, YOU Qing-Long, HU Die. Research progress on climate change and its impact on water resources over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 158-169.
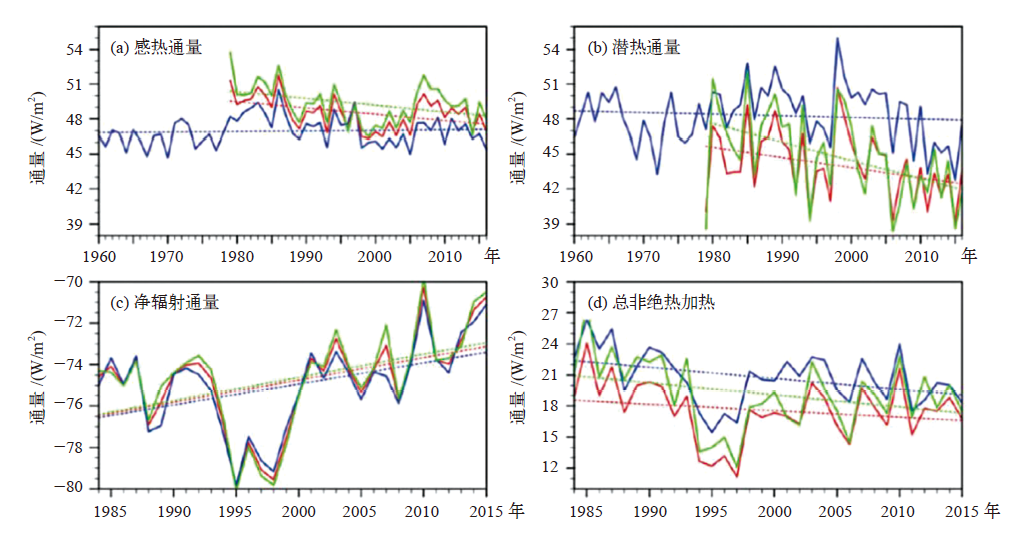
图1 青藏高原平均的感热SH (a)、潜热LH (b)、净辐射通量RC (c)、总热源E (d)的时间变化序列[43] 注:蓝线表示32个站点平均,绿线表示48个站点平均,红线表示80个站点平均。绿线站点包括了蓝线代表的32个站,红线站点包含了绿线代表的48个站。
Fig. 1 The surfaces sensible heating (a), latent release heating (b), net radiation heating (c) and total heating (d) averaged over the TP[43]
| [1] |
Qiu J. China: the third pole[J]. Nature, 2008, 454 (7203): 393-396
doi: 10.1038/454393a |
| [2] |
Yao T, Thompson L, Yang W, et al. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Tibetan Plateau and surroundings[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2012, 2 (9): 663-667
doi: 10.1038/nclimate1580 |
| [3] |
Wu G X, Duan A M, Liu Y M, et al. Tibetan Plateau climate dynamics: recent research progress and outlook[J]. National Science Review, 2015, 2: 100-116
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwu045 URL |
| [4] |
Liu Y M, Lu M M, Yang H J, et al. Land-atmosphere-ocean coupling associated with the Tibetan Plateau and its climate impacts[J]. National Science Review, 2020, 7 (3): 534-552
doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa011 pmid: 35273806 |
| [5] | Huang J P, Zhou X J, Wu G X, et al. Global climate impacts of land-surface and atmospheric processes over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2023, 61, e2022RG000771 |
| [6] | 马耀明, 姚檀栋, 王介民. 青藏高原能量和水循环试验研究: GAME/Tibet与CAMP/Tibet研究进展[J]. 高原气象, 2006, 25 (2): 344-351. |
| Ma Y M, Yao T D, Wang J M. Experimental study of energy and water cycle in Tibetan Plateau: the progress introduction on the study of GAME/Tibet and CAMP/Tibet[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2006, 25 (2): 344-351 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | Wang Y J, Xu X D, Zhao T L, et al. Structures of convection and turbulent kinetic energy in boundary layer over the southeastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2015, 58: 1198-1209. DOI: 10.1007/s11430-015-5054-1 |
| [8] |
Bian J C Yan, R C, Chen H B, et al. Formation of the summertime ozone valley over the Tibetan Plateau: the Asian summer monsoon and air column variations[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 28 (6): 1318-1325
doi: 10.1007/s00376-011-0174-9 URL |
| [9] | 陈德亮, 徐柏青, 姚檀栋, 等. 青藏高原环境变化科学评估: 过去、现在与未来[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60: 3025-3035. |
| Chen D L, Xu B Q, Yao T D, et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60: 3025-3035 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] |
Yang K, Wu H, Qin J, et al. Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: a review[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2014, 112: 79-91
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.12.001 URL |
| [11] | Li F, Gao Y Q, Wan X, et al. Earth’s “three-poles” climate change under global warming[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2021, 44: 1-11 |
| [12] |
Shen M G, Piao S L, Jeong S J, et al. Evaporative cooling over the Tibetan Plateau induced by vegetation growth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015, 112 (30): 9299-9304
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504418112 URL |
| [13] | 宋辞, 裴韬, 周成虎. 1960年以来青藏高原气温变化研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2012, 31 (11): 1503-1509. |
| Song C, Pei T, Zhou C H. Research progress on temperature changes in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau since 1960[J]. Progress in Geographic Science, 2012, 31 (11): 1503-1509 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 王朋岭, 唐国利, 曹丽娟, 等. 1981—2010年青藏高原地区气温变化与高程及纬度的关系[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8: 4-10. |
| Wang P L, Tang G L, Cao L J, et al. The relationship between temperature changes and elevation and latitude in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau region from 1981 to 2010[J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8: 4-10 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] |
Duan A M, Xiao Z X. Does the climate warming hiatus exist over the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 13711
doi: 10.1038/srep13711 pmid: 26329678 |
| [16] |
Guo D L, Sun J Q, Yang K, et al. Satellite data reveal southwestern Tibetan Plateau cooling since 2001 due to snow-albedo feedback[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2019, 40: 1644-1655
doi: 10.1002/joc.v40.3 URL |
| [17] |
许建伟, 高艳红, 彭保发, 等. 1979—2016年青藏高原降水的变化特征及成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39 (2): 234-244.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00029 |
| Xu J W, Gao Y H, Peng B F, et al. Analysis of the change characteristics and causes of precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau from 1979 to 2016[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39 (2): 234-244 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Yue S Y, Wang B, Yang K, et al. Mechanisms of the decadal variability of monsoon rainfall in the southern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2020, 16: 014011
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abcb36 |
| [19] | 游庆龙, 康世昌. 青藏高原现代气候变化特征研究[M]. 长沙: 湖南教育出版社, 2019. |
| You Q L, Kang S C. A study on the characteristics of modern climate change in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[M]. Changsha: Hunan Education Press, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | Liu X L, Liu Y M, Wu G X. Large-scale dynamics and moisture sources of the precipitation over the western Tibetan Plateau in boreal winter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2020, 125, e2019JD032133 |
| [21] |
Zhou C Y, Zhao P, Chen J M. The interdecadal change of summer water vapor over the Tibetan Plateau and associated mechanisms[J]. Journal of Climate, 2019, 32: 4103-4119
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-18-0364.1 URL |
| [22] |
Sun J, Yang K, Guo W D. Why has the Inner Tibetan Plateau become wetter since the mid-1990s?[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33: 8507-8522
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0471.1 URL |
| [23] | Jiang J, Zhou T J, Qian Y. Precipitation regime changes in High Mountain Asia driven by cleaner air[J]. Nature, 2023. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06619-y |
| [24] |
Gao Y H, Cuo L, Zhang Y X. Changes in moisture flux over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979-2011 and possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Climate, 2014, 27: 1876-1893
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00321.1 URL |
| [25] | Li L, Zhang R H, Wen M. et al. Regionally different precipitation trends over the Tibetan Plateau in the warming context: a perspective of the Tibetan Plateau vortices[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48 |
| [26] | 孙亦, 巩远发. 印度夏季风影响下的青藏高原降水及环流异常变化特征[J]. 成都信息工程大学学报, 2019, 34: 411-419. |
| Sun Y, Gong Y F. The anomalous changes in precipitation and circulation over the Tibetan Plateau under the influence of the Indian summer monsoon[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Information Technology, 2019, 34: 411-419 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
Chen B, Zhang W, Yang S. et al. Identifying and contrasting the sources of the water vapor reaching the subregions of the Tibetan Plateau during the wet season[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 53: 6891-6907
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-04963-2 |
| [28] | 刘晓东, 侯萍. 青藏高原及其邻近地区近30年气候变暖与海拔高度的关系[J]. 高原气象, 1998, 17: 245-249. |
| Liu X D, Hou P. The relationship between climate warming and altitude in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau and its adjacent areas in the past 30 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 1998, 17: 245-249 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
You Q L, Chen D L, Wu F Y, et al. Elevation dependent warming over the Tibetan Plateau: patterns, mechanisms and perspectives[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 210: 103349
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103349 URL |
| [30] |
Qin J, Yang K, Liang S L, et al. The altitudinal dependence of recent rapid warming over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climatic Change, 2019, 97: 321-327
doi: 10.1007/s10584-009-9733-9 URL |
| [31] |
You Q L, Kang S C, Pepin N. et al. Relationship between temperature trend magnitude, elevation and mean temperature in the Tibetan Plateau from homogenized surface stations and reanalysis data[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2010, 71: 124-133
doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.01.020 URL |
| [32] |
Pepin N, Bradley R, Diaz H. et al. Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2015, 5: 424-430
doi: 10.1038/nclimate2563 |
| [33] |
Duan A M, Wu G X, Zhang Q, et al. New proofs of the recent climate warming over the Tibetan Plateau as a result of the increasing greenhouse gases emissions[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51: 1396-1400
doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-1396-6 URL |
| [34] | You Q L, Cai Z Y, Pepin N. Warming amplification over the Arctic Pole and Third Pole: trends, mechanisms and consequences[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 217. DOI: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103625 |
| [35] |
游庆龙, 康世昌, 李剑东, 等. 青藏高原气候变化若干前沿科学问题[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43 (3): 885-901.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2021.0029 |
| You Q L, Kang S C, Li J D, et al. Several frontier scientific issues on climate change in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[J]. Glacier Permafrost, 2021, 43 (3): 885-901 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] |
Fang X W, Luo S Q, Lyu S H. Observed soil temperature trends associated with climate change in the Tibetan Plateau, 1960-2014 [J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2018, 135: 169-181
doi: 10.1007/s00704-017-2337-9 |
| [37] | 李栋梁, 钟海玲, 吴青柏, 等. 青藏高原地表温度的变化分析[J]. 高原气象, 2005, 24 (3). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2005.03.001. |
| Li D L, Zhong H L, Wu Q B, et al. Analysis of changes in surface temperature on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2005, 24 (3). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0534.2005.03.001 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] |
王静, 祁莉, 何金海, 等. 青藏高原春季土壤湿度与我国长江流域夏季降水的联系及其可能机理[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59: 3985-3995.
doi: 10.6038/cjg20161105 |
| Wang J, Qi L, He J H, et al. The relationship between spring soil moisture on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau and summer precipitation in the Yangtze River basin in China and its possible mechanisms[J]. Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59: 3985-3995 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] |
Meng X H, Li R, Luan L, et al. Detecting hydrological consistency between soil moisture and precipitation and changes of soil moisture in summer over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2017, 51: 4157-4168
doi: 10.1007/s00382-017-3646-5 |
| [40] |
Yang K, Ye B S, Zhou D G, et al. Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climatic Change, 2011, 109: 517-534
doi: 10.1007/s10584-011-0099-4 URL |
| [41] | Yin Y H, Wu S H, Zhao D S. Past and future spatiotemporal changes in evapotranspiration and effective moisture on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118 (10): 10850-10860 |
| [42] |
Duan A M, Wu G X. Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part I: observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 2008, 21: 3149-3164
doi: 10.1175/2007JCLI1912.1 URL |
| [43] |
Duan A M, Liu S F, Zhao Y, et al. Atmospheric heat source/sink dataset over the Tibetan Plateau based on satellite and routine meteorological observations[J]. Big Earth Data, 2018, 2: 179-189
doi: 10.1080/20964471.2018.1514143 URL |
| [44] |
Yang K, Guo X F, Wu B Y. Recent trends in surface sensible heat flux on the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54: 19-28
doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4036-6 URL |
| [45] |
Duan A M, Wu G X. Weakening trend in the atmospheric heat source over the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Part II: connection with climate warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 2009, 22: 4197-4212
doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI2699.1 URL |
| [46] |
Liu Y M, Wu G X, Hong J L, et al. Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau Forcing: II. change[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2012, 39 (5): 1183-1195
doi: 10.1007/s00382-012-1335-y URL |
| [47] | Tang W J, Yang K, Qin J, et al. Solar radiation trend across China in recent decades: a revisit with quality-controlled data[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2011, 11: 393-4067 |
| [48] | Peixoto J P, Oort A H. Physics of climate[M]. New York: American Institute of Physics, 1992: 520 |
| [49] |
Duan A M, Li F, Wang M R, et al. Persistent weakening trend in the spring sensible heat source over the Tibetan Plateau and its impact on the Asian summer monsoon[J]. Journal of Climate, 2011, 24: 5671-5682
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00052.1 URL |
| [50] | 吴国雄, 段安民, 张雪芹, 等. 青藏高原极端天气气候变化及其环境效应[J]. 自然杂志, 2013, 35: 167-171. |
| Wu G X, Duan A M, Zhang X Q, et al. Extreme weather and climate change over the Tibetan Plateau and its environmental effects[J]. Nature Magazine, 2013, 35: 167-171 (in Chinese) | |
| [51] | 吴芳营, 游庆龙, 谢文欣. 全球变暖1.5℃和2℃阈值时青藏高原气温的变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15: 130-139. |
| Wu F Y, You Q L, Xie W X. The characteristics of temperature changes over the Tibetan Plateau under global warming thresholds of 1.5℃ and 2℃[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15: 130-139 (in Chinese) | |
| [52] | 刘晓东, 程志刚, 张冉. 青藏高原未来30-50年A1B情景下气候变化预估[J]. 高原气象, 2009, 28: 475-484. |
| Liu X D, Cheng Z G, Zhang R. Prediction of climate change in the A1B scenario of the Tibetan Plateau over the next 30-50 years[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2009, 28: 475-484 (in Chinese) | |
| [53] |
You Q, Zhang Y Q, Xie X G, et al. Robust elevation dependency warming over the Tibetan Plateau under global warming of 1.5 degrees C and 2 degrees C[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2019, 53: 2047-2060
doi: 10.1007/s00382-019-04775-4 |
| [54] | Jia K, Ruan Y F, Yang Y Z, et al. Assessing the performance of CMIP5 Global Climate Models for simulating future precipitation change in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Water, 2019, 11 (9): 1771. DOI: 10.3390/w11091771 |
| [55] |
张宏文, 高艳红. 基于动力降尺度方法预估的青藏高原降水变化[J]. 高原气象, 2020, 39: 477-485.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2019.00125. |
| Zhang H W, Gao Y H. Prediction of precipitation changes over the Tibetan Plateau based on dynamic downscaling method[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2020, 39: 477-485 (in Chinese) | |
| [56] | 张人禾, 苏凤阁, 江志红, 等. 青藏高原21世纪气候和环境变化预估研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60: 3036-3047. |
| Zhang R H, Su F G, Jiang Z H, et al. Research progress in predicting climate and environmental changes on the Tibetan Plateau in the 21st century[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60: 3036-3047 (in Chinese) | |
| [57] |
You Q L, Kang S C, Ren G Y, et al. Observed changes in snow depth and number of snow days in the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climate Research, 2011, 46: 171-183
doi: 10.3354/cr00985 URL |
| [58] |
沈鎏澄, 吴涛, 游庆龙, 等. 青藏高原中东部积雪深度时空变化特征及其成因分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2019, 41: 1150-1161.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0240.2019.1100 |
| Shen L C, Wu T, You Q L, et al. Analysis of the spatiotemporal variation characteristics and causes of snow depth in the central and eastern parts of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Glacier Permafrost, 2019, 41: 1150-1161 (in Chinese) | |
| [59] |
Tang Z G, Wang J, Li H Y, et al. Spatiotemporal changes of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau based on cloud-removed moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer fractional snow cover product from 2001 to 2011[J]. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2013, 7: 073582
doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.7.073582 URL |
| [60] |
叶红, 易桂花, 张廷斌, 等. 2000—2019年青藏高原积雪时空变化[J]. 资源科学, 2020, 42: 2434-2450.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2020.12.14 |
| Ye H, Yi G H, Zhang T B, et al. The spatiotemporal variation of snow cover on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau from 2000 to 2019[J]. Resource Science, 2020, 42: 2434-2450 (in Chinese) | |
| [61] |
Yang M X, Wang X J, Pang G J, et al. The Tibetan Plateau cryosphere: observations and model simulations for current status and recent changes[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 190: 353-369
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.018 URL |
| [62] | 车涛, 郝晓华, 戴礼云, 等. 青藏高原积雪变化及其影响[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34: 1247-1253. |
| Che T, Hao X H, Dai L Y, et al. The changes and impacts of snow cover on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34: 1247-1253 (in Chinese) | |
| [63] |
Cheng W M, Zhao S M, Zhou C H, et al. Simulation of the decadal permafrost distribution on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (China) over the past 50 years[J]. Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 2012, 23: 292-300
doi: 10.1002/ppp.v23.4 URL |
| [64] |
Guo D L, Wang H J. Simulation of permafrost and seasonally frozen ground conditions on the Tibetan Plateau, 1981-2010 [J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2013, 118: 5216-5230
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v118.11 URL |
| [65] |
Jin H J, Li S X, Cheng G D, et al. Permafrost and climatic change in China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2020, 26: 387-404
doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(00)00051-5 URL |
| [66] | Wu Q B, Zhang T J. Recent permafrost warming on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 2008, 113: D131108 |
| [67] |
Wu Q, Zhang T, Liu Y. Thermal state of the active layer and permafrost along the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Railway from 2006 to 2010[J]. The Cryosphere, 2012, 6: 607-612
doi: 10.5194/tc-6-607-2012 URL |
| [68] |
Rangwala I, Miller J R, Russell GL, et al. Using a global climate model to evaluate the influences of water vapor, snow cover and atmospheric aerosol on warming in the Tibetan Plateau during the twenty-first century[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2010, 34: 859-872
doi: 10.1007/s00382-009-0564-1 URL |
| [69] |
Wu T H, Zhao L, Li R, et al. Recent ground surface warming and its effects on permafrost on the central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2013, 33: 920-930
doi: 10.1002/joc.v33.4 URL |
| [70] |
Nan Z T, Li S X, Cheng G D. Prediction of permafrost distribution on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the next 50 and 100 years[J]. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 2005, 48: 797-804
doi: 10.1360/03yd0258 URL |
| [71] |
常燕, 吕世华, 罗斯琼, 等. CMIP5 耦合模式对青藏高原冻土变化的模拟和预估[J]. 高原气象, 2016, 35 (5): 1157-1168.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2015.00090 |
| Chang Y, Lyu S H, Ross Q, et al. Simulation and estimation of permafrost changes in the Qinghai Tibet Plateau using the CMIP5 coupling model[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2016, 35 (5): 1157-1168 (in Chinese) | |
| [72] |
Guo D L, Wang H J. CMIP5 permafrost degradation projection: a comparison among different regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121: 4499-4517
doi: 10.1002/jgrd.v121.9 URL |
| [73] | 姚檀栋, 秦大河, 沈永平, 等. 青藏高原冰冻圈变化及其对区域水循环和生态条件的影响[J]. 自然杂志, 2013, 35: 179-186. |
| Yao T D, Qin D H, Shen Y P, et al. Changes in the cryosphere of the Tibetan Plateau and their impact on regional water cycle and ecological conditions[J]. Nature Magazine, 2013, 35: 179-186 (in Chinese) | |
| [74] | 姚檀栋, 邬光剑, 徐柏青, 等. “亚洲水塔”变化与影响[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34: 1203-1209. |
| Yao T D, Wu G J, Xu B Q, et al. Changes and impacts of the “Asian Water Tower”[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34: 1203-1209 (in Chinese) | |
| [75] | Yao T D, Yu W, Wu G X, et al. Glacier anomalies and relevant disaster risks on the Tibetan Plateau and surroundings[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64: 2770-2782 |
| [76] | Yasunari T, Bonasoni P, Laj P, et al. Estimated impact of black carbon deposition during pre-monsoon season from Nepal Climate observatory: pyramid data and snow albedo changes over Himalayan glaciers[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2010, 10: 6603-6615 |
| [77] | Chen X T, Kang S C, Cong Z Y, et al. Concentration, temporal variation, and sources of black carbon in the Mt. Everest region retrieved by real-time observation and simulation[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 18: 12859-12875 |
| [78] | 蒲健辰, 姚檀栋, 王宁练, 等. 近百年来青藏高原冰川的进退变化[J]. 冰川冻土, 2004, 26 (5): 517-522. |
| Pu J C, Yao T D, Wang N L, et al. The advance and retreat changes of glaciers on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau in the last century[J]. Glacier Permafrost, 2004, 26 (5): 517-522 (in Chinese) | |
| [79] |
Hewitt K. The Karakoram anomaly? Glacier expansion and the “elevation effect”, Karakoram Himalaya[J]. Mountain Research and Development, 2005, 25 (4): 332-340
doi: 10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025[0332:TKAGEA]2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [80] | 王宁练, 姚檀栋, 徐柏青, 等. 全球变暖背景下青藏高原及周边地区冰川变化的时空格局与趋势及影响[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34: 1220-1232. |
| Wang N L, Yao T D, Xu B Q, et al. The spatiotemporal pattern, trend, and impact of glacier changes in the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas under the background of global warming[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34: 1220-1232 (in Chinese) | |
| [81] | Guo Y H, Zhang Y S, Ma N. et al. Quantifying surface energy fluxes and evaporation over a significant expanding endorheic lake in the central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 2016, 94 (5): 453-465 |
| [82] |
Song C Q, Huang B, Ke L H. Heterogeneous change patterns of water level for inland lakes in High Mountain Asia derived from multi-mission satellite altimetry[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2015, 29: 2769-2781
doi: 10.1002/hyp.v29.12 URL |
| [83] |
闫立娟, 郑绵平, 魏乐军. 近40年来青藏高原湖泊变迁及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23: 310-323.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2016.04.027 |
| Yan L J, Zheng M P, Wei L J. The changes of lakes over the Tibetan Plateau in the last 40 years and their response to climate change[J]. Frontiers of Geoscience, 2016, 23: 310-323 (in Chinese) | |
| [84] |
刘田, 阳坤, 秦军, 等. 青藏高原中、东部气象站降水资料时间序列的构建与应用[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37 (6): 1449-1457.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00060 |
|
Liu T, Yang K, Qin J, et al. Construction and applications of time series of monthly precipitation at weather stations in the central and eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37 (6): 1449-1457 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00060 |
|
| [85] | 朱立平, 张国庆, 杨瑞敏, 等. 青藏高原最近40年湖泊变化的主要表现与发展趋势[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34: 1254-1263. |
| Zhu L P, Zhang G Q, Yang R M, et al. The main manifestations and development trends of lake changes in the Tibetan Plateau in the past 40 years[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34: 1254-1263 (in Chinese) | |
| [86] |
Lee Z P, Shang S, Hu C. Secchi disk depth: a new theory and mechanistic model for underwater visibility[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2015, 169: 139-149
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.08.002 URL |
| [87] |
Lei Y B, Yang K, Wang B, et al. Response of inland lake dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau to climate change[J]. Climatic Change, 2014, 125: 281-290
doi: 10.1007/s10584-014-1175-3 URL |
| [88] |
Salerno F, Thakuri S, Guyennon N, et al. Glacier melting and precipitation trends detected by surface area changes in Himalayan ponds[J]. The Cryosphere, 2016, 10: 1433-1448
doi: 10.5194/tc-10-1433-2016 URL |
| [89] | 闾利, 张廷斌, 易桂花, 等. 2000年以来青藏高原湖泊面积变化与气候要素的响应关系[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31: 573-589. |
| Lu L, Zhang T B, Yi G H, et al. Response relationship between changes in lake area and climate factors in the Tibetan Plateau since 2000[J]. Lake Science, 2019, 31: 573-589 (in Chinese) | |
| [90] | 朱立平, 彭萍, 张国庆, 等. 全球变化下青藏高原湖泊在地表水循环中的作用[J]. 湖泊科学, 2020, 32: 597-608. |
| Zhu L P, Peng P, Zhang G Q, et al. The role of Tibetan Plateau lakes in surface water cycle under global change[J]. Lake Science, 2020, 32: 597-608 (in Chinese) | |
| [91] | 《第一次全国水利普查成果丛书》编委会. 河湖基本情况普查报告[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2017. |
| Editorial Committee of the First National Water Resources Census Results Series. General survey report on the basic situation of rivers and lakes[M]. Beijing: China Water Resources and Hydropower Press, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [92] | 汤秋鸿, 兰措, 苏凤阁, 等. 青藏高原河川径流变化及其影响研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64: 2807-2821. |
| Tang Q H, Lan C, Su F G, et al. Streamflow change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its impacts[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64: 2807-2821 (in Chinese) | |
| [93] | 陈发虎, 汪亚峰, 甄晓林, 等. 全球变化下的青藏高原环境影响及应对策略研究[J]. 中国藏学, 2021, 4: 21-28. |
| Chen F H, Wang Y F, Zhen X L, et al. Research on the environmental impact and response strategies of the Qinghai Tibet Plateau under global change[J]. Chinese Tibetan Studies, 2021, 4: 21-28 (in Chinese) | |
| [94] | 张建云, 刘九夫, 金君良, 等. 青藏高原水资源演变与趋势分析[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34: 1264-1273. |
| Zhang J Y, Liu J F, Jin J L, et al. Evolution and trend analysis of water resources in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34: 1264-1273 (in Chinese) | |
| [95] |
Wang Y Y, Zhang Y Q, Chiew F H S, et al. Contrasting runoff trends between dry and wet parts of eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science Report, 2017, 7: 15458
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15678-x |
| [96] |
Lutz A, Immerzeel W, Shrestha A, et al. Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014, 4: 587-592
doi: 10.1038/nclimate2237 |
| [97] | Wu G X, Ma T T, Liu Y M, et al. PV-Q perspective of cyclogenesis and vertical velocity development downstream of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2020, 125. DOI: 10.1029/2019JD030912 |
| [98] | 吴国雄, 刘屹岷, 黄建平, 等. 青藏高原对季风和全球气候对影响[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2023: 344. |
| Wu G X, Liu Y M, Huang J P, et al. The impact of the Tibetan Plateau on monsoons and global climate[M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2023: 344 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 李现康, 韩星星, 梁洪松. 气候适应性技术采纳对农户农业收入的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 193-204. |
| [2] | 樊星, 李路, 高翔, 陈志华. COP28全球盘点成果解读及全球气候治理形势展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 253-260. |
| [3] | 吴星怡, 曹龙. CO2辐射效应与生理效应对气候系统影响异同的模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(2): 170-181. |
| [4] | 马丽娟, 袁佳双, 黄磊. 联合国全民早期预警目标下中国气候风险管理前景分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(1): 48-61. |
| [5] | 许艳, 路文海, 曾容, 刘倡. “基于海洋解决方案倡议”在应对气候变化领域的应用思考[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(1): 121-128. |
| [6] | 胡佳怡, 赵林, 王翀, 胡国杰, 邹德富, 幸赞品, 焦梦迪, 乔永平, 刘广岳, 杜二计. CLDAS地表温度产品在青藏高原多年冻土区的适用性评估与校正[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(1): 10-25. |
| [7] | 张凡, 丁建芳, 杨敏, 彭冲. 河南省降雪识别及气候变化下降雪量对气温和降水的响应[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 714-722. |
| [8] | 杨红雄, 杨光. 基于现代化的中国省级碳排放时空演变及影响因素研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 457-471. |
| [9] | 王冰杰, 孙颖, 胡婷, 董思言. 基于再分析资料的近百年中国极端冷事件的变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(4): 403-417. |
| [10] | 罗慧, 刘杰, 王丽, 唐智亿. 西北气候暖湿化的农业经济影响评估:以宁夏为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 293-304. |
| [11] | 栾澜, 翟盘茂. 基于多源数据的青藏高原雨季降水特征变化分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 173-190. |
| [12] | 谭显春, 高瑾昕, 曾桉, 幸绣程. 绿色金融改革创新试验区政策对碳排放的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [13] | 田丹宇, 柴麒敏, 刘伯翰. 欧洲议会涉气候法案的内容与经验借鉴[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 249-257. |
| [14] | 米志付, 张浩然. IPCC AR6 WGIII报告解读:城市系统减缓气候变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 139-150. |
| [15] | 侯一蕾, 邢方圆, 马丽, 杨鸣, 温亚利. 应对气候变化与保护生物多样性协同:全球实践与启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(1): 91-101. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||