| [1] |
Net Zero Tracker. Data explorer[EB/OL]. 2025 [2025-01-19]. https://zerotracker.net/
|
| [2] |
杨儒浦, 李丽平. 实施碳预算的国际经验借鉴[J]. 中国能源, 2023, 45 (11): 73-81.
|
|
Yang R P, Li L P. International experience in implementing carbon budgets[J]. Energy of China, 2023, 45 (11): 73-81 (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
IPCC. IPCC_AR6_WGI_FAQ_chapter_05 frequently asked questions[EB/OL]. 2023 [2025-03-19]. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/downloads/faqs/IPCC_AR6_WGI_FAQ_Chapter_05.pdf
|
| [4] |
Lahn B. A history of the global carbon budget[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Climate Change, 2020, 11 (3): e636
|
| [5] |
van den Berg N J, van Soest H L, Hof A F, et al. Implications of various effort-sharing approaches for national carbon budgets and emission pathways[J]. Climatic Change, 2020, 162 (4): 1805-1822
|
| [6] |
Kuriakose J, Jones C, Anderson K, et al. What does the Paris Climate Change Agreement mean for local policy? Downscaling the remaining global carbon budget to sub-national areas[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Transition, 2022, 2: 100030
|
| [7] |
Bendig D, Schulz C, Erbar F, et al. Apples to apples: accurately assessing corporate carbon performance[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2025, 486: 144338
|
| [8] |
Matthews H D, Tokarska K B, Nicholls Z R J, et al. Opportunities and challenges in using remaining carbon budgets to guide climate policy[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2020, 13 (12): 769-779
|
| [9] |
潘家华, 陈迎. 碳预算方案: 一个公平、可持续的国际气候制度框架[J]. 中国社会科学, 2009 (5): 83-98, 206.
|
|
Pan J H, Chen Y. Carbon budget proposal: a framework for an equitable and sustainable international climate regime[J]. Social Sciences in China, 2009 (5): 83-98, 206 (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
陈晓婷, 陈迎. 从科学和政策视角看碳预算对全球气候治理的作用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14 (6): 632-639.
|
|
Chen X T, Chen Y. The scientific and political views of carbon budget for global climate governance[J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14 (6): 632-639 (in Chinese)
|
| [11] |
杨儒浦, 冯相昭. 英国碳预算对我国实施碳排放总量控制制度的启示[J]. 可持续发展经济导刊, 2023 (Z1): 36-41.
|
|
Yang R P, Feng X Z. The enlightenment of the British carbon budget on the policy development of capping carbon emission in China[J]. China Sustainability Tribune, 2023 (Z1): 36-41 (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
杨姗姗, 郭豪, 杨秀, 等. 双碳目标下建立碳排放总量控制制度的思考与展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (2): 191-202.
|
|
Yang S S, Guo H, Yang X, et al. Consideration and prospect of total carbon emission control system under the double carbon target[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (2): 191-202 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
潘晓滨. 碳中和背景下国家碳预算的理论同构与立法路径[J]. 湖南大学学报(社会科学版), 2024, 38 (1): 112-118.
|
|
Pan X B. Theoretical isomorphisms and legislative pathways for national carbon budgets in the context of carbon neutrality[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Social Sciences), 2024, 38 (1): 112-118 (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
Yuan W P, Liang M Q, Gao Y Y, et al. China’s greenhouse gas budget during 2000-2023 [J] National Science Review, 2025. DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwaf069
|
| [15] |
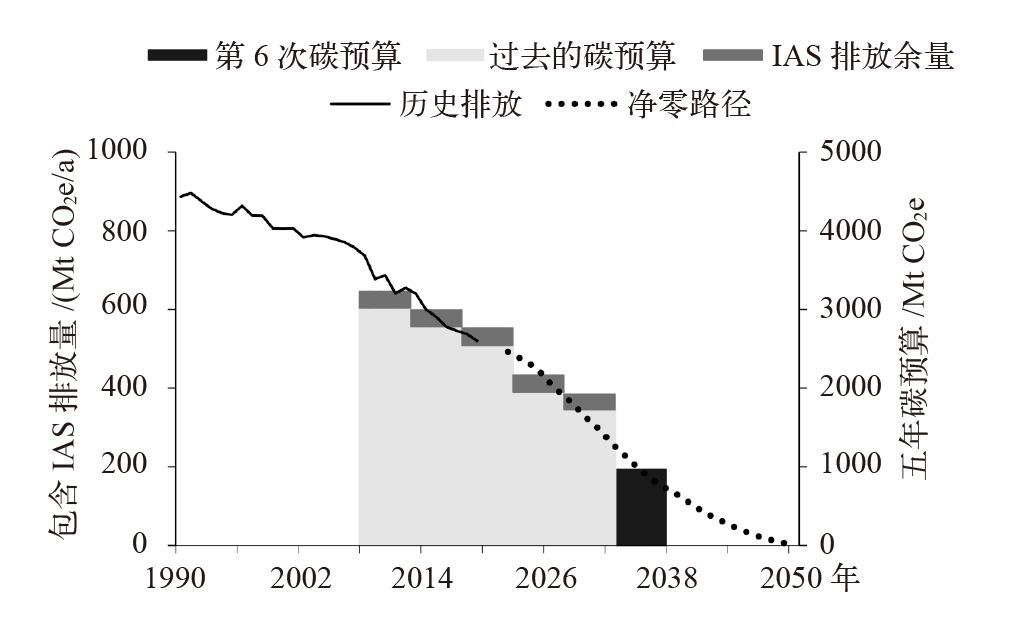
Climate Change Committee (CCC). CCC advises 81% reduction in emissions by 2035v[EB/OL]. 2024 [2025-01-03]. https://www.theccc.org.uk/2024/10/26/ccc-advises-81-reduction-in-emissions-by-2035/
|
| [16] |
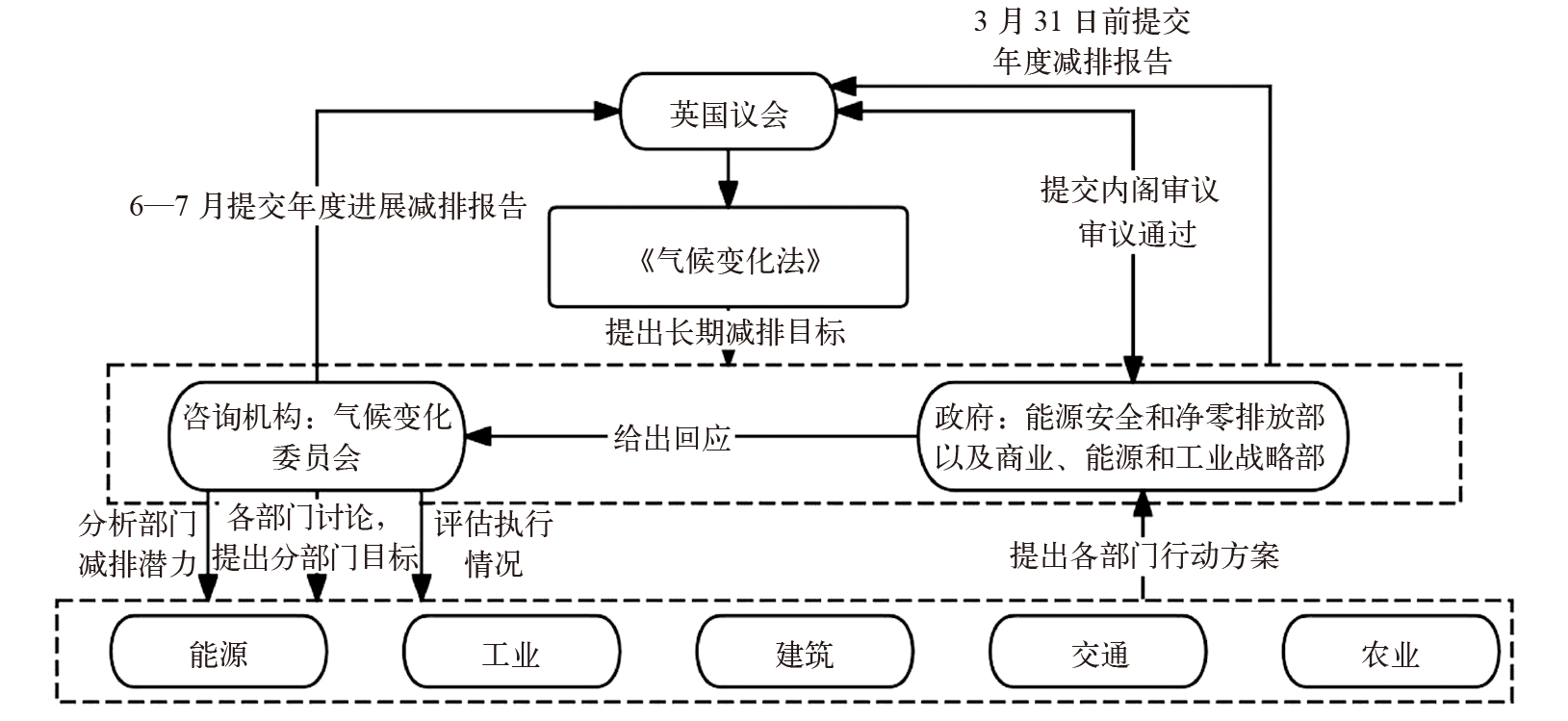
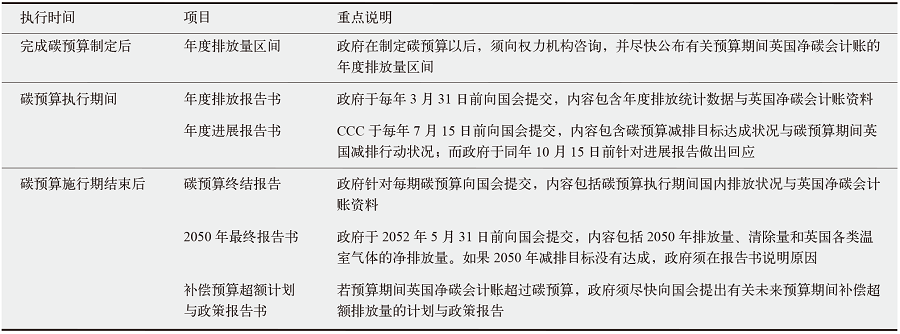
CCC. CCC insights briefing 1. The UK climate change act[EB/OL]. 2020 [2025-01-03]. https://www.theccc.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/CCC-Insights-Briefing-1-The-UK-Climate-Change-Act.pdf
|
| [17] |
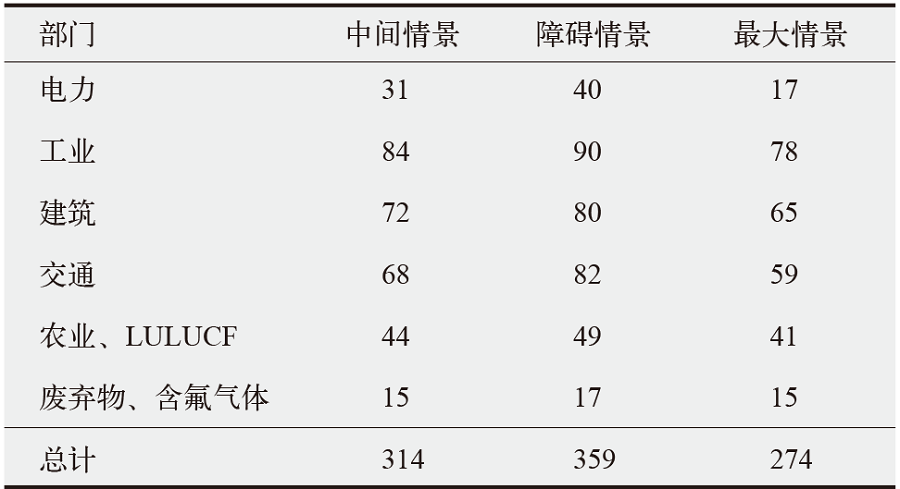
CCC. Sectoral scenarios for the fifth carbon budget[EB/OL]. 2015 [2025-03-17]. https://www.theccc.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/11/Sectoral-scenarios-for-the-fifth-carbon-budget-Committee-on-Climate-Change.pdf
|
| [18] |
UK Parliament. Climate change act 2008 [EB/OL]. 2008 [2025-03-12]. https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2008/27/contents
|
| [19] |
German Government. Lesefassung des Bundes-Klimaschutzgesetzes 2021 mit markierten Änderungen zur Fassung von 2019 [EB/OL]. 2021 [2025-03-15]. https://www.bmu.de/fileadmin/Daten_BMU/Download_PDF/Klimaschutz/ksg_aendg_2021_3_bf.pdf
|
| [20] |
田丹宇. 德国碳减排目标管理制度研究[J]. 世界环境, 2023 (2): 76-79.
|
|
Tian D Y. Research on Germany’s carbon emission reduction target management system[J]. World Environment, 2023 (2): 76-79 (in Chinese)
|
| [21] |
田丹宇, 徐华清. 德国气候保护法立法动因、特征及对我国立法的启示[J]. 环境资源法论丛, 2020, 12 (1): 141-153.
|
|
Tian D Y, Xu H Q. German climate protection law legislation motivation, characteristics and implications for China’s legislation[J]. Environmental and Resources Law Review, 2020, 12 (1): 141-153 (in Chinese)
|
| [22] |
Ministre de L’écologie. Stratégie nationale bas-carbone[EB/OL]. 2020 [2025-03-15]. https://www.ecologie.gouv.fr/sites/default/files/documents/2020-03-25_MTES_SNBC2.pdf
|
| [23] |
Ministère de la Transition écologique. National low carbon strategy[EB/OL]. 2018 [2025-03-15]. https://www.ecologie.gouv.fr/sites/default/files/documents/Projet%20SNBC%20EN.pdf
|
 ), GU Bai-He1,2(
), GU Bai-He1,2( ), YU Dong-Hui1,2
), YU Dong-Hui1,2