气候变化研究进展 ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 541-558.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.136
稻田甲烷排放现状、减排技术和低碳生产战略路径
- 中国农业科学院农业环境与可持续发展研究所/中国农业科学院农业农村碳达峰碳中和研究中心/农业农村部农业环境重点实验室,北京 10008
-
收稿日期:2023-06-21修回日期:2023-07-13出版日期:2023-09-30发布日期:2023-09-28 -
作者简介:秦晓波,男,研究员,qinxiaobo@caas.cn -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划(2021YFD1700202-05);江西省中央引导地方科技发展资金项目(20221ZDH04057);国家自然科学基金(41775157)
Status of methane emissions from paddy fields, mitigation technologies and strategic pathways for low-carbon production
QIN Xiao-Bo( ), WANG Jin-Ming, WANG Bin, WAN Yun-Fan
), WANG Jin-Ming, WANG Bin, WAN Yun-Fan
- Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture / Agricultural and Rural Carbon Peak and Carbon Neutral Research Center, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key Laboratory for Agro-Environment, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Beijing 100081, China
-
Received:2023-06-21Revised:2023-07-13Online:2023-09-30Published:2023-09-28
摘要:
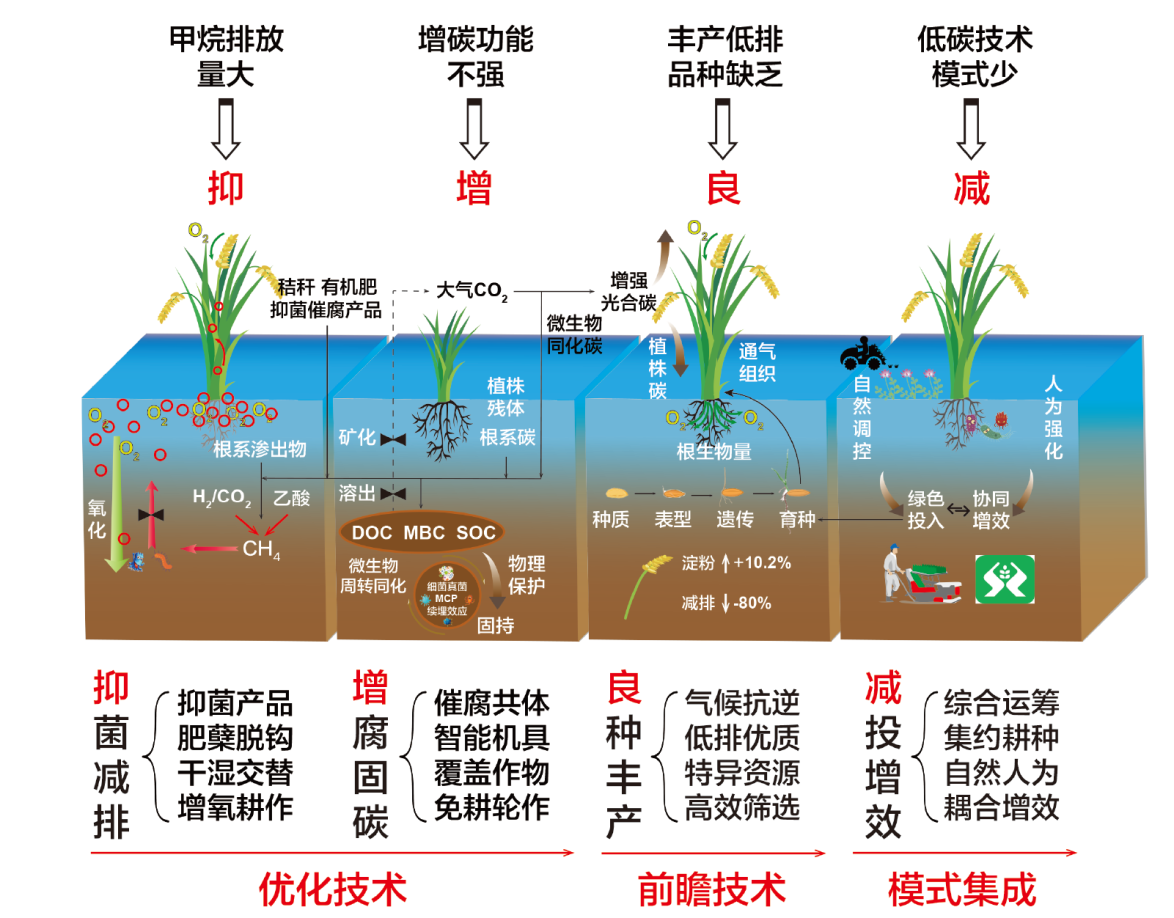
作为第一大主粮作物,水稻在我国粮食和重要农产品稳定安全供给体系中占有举足轻重的地位,其低碳生产不仅关乎国家双碳战略的推进,更对国家粮食自给率提升、国民膳食营养改善和气候外交的实施意义重大。文中从我国稻田甲烷(CH4)排放现状、减排技术和低碳生产战略等方面,系统论述了低碳可持续稻谷生产系统的实现路径。近年来,我国水稻种植面积尽管有所波动,但水稻单产持续增加,2021年平均亩产高达474.2 kg,创历史新高。与此同时,稻田也是我国CH4主要排放源(1.87 亿t CO2e),占我国农业活动CH4排放总量的40.1%。因此,面对水稻可持续生产、未来气候变化不利影响及气候外交的多重挑战,稻田CH4减排要充分考虑水分、肥料、品种、耕作和菌剂产品等的综合运筹,以人为强化措施为主,辅以基于自然的解决方案,建立主产稻区适用“抑菌减排-增腐固碳-良种丰产-减投增效”的“抑增良减”技术体系。实施覆盖作物种植、免耕轮作、高产低排品种选育、覆膜保墒、菌剂增效产品、智能机具、合理密植、肥蘖脱钩、干湿交替和增氧耕作等十大技术模式,在确保稻米有效供给的同时减排增碳,实现水稻可持续绿色高质量发展。
引用本文
秦晓波, 王金明, 王斌, 万运帆. 稻田甲烷排放现状、减排技术和低碳生产战略路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(5): 541-558.
QIN Xiao-Bo, WANG Jin-Ming, WANG Bin, WAN Yun-Fan. Status of methane emissions from paddy fields, mitigation technologies and strategic pathways for low-carbon production[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 541-558.
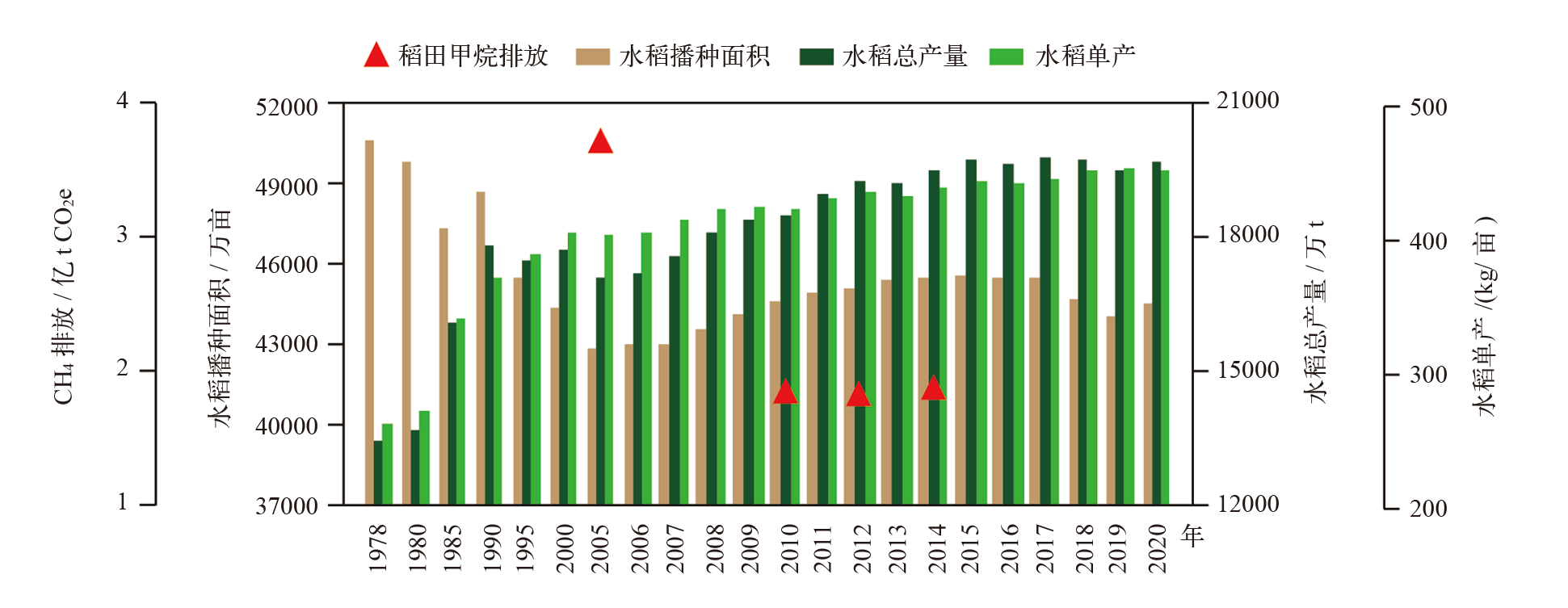
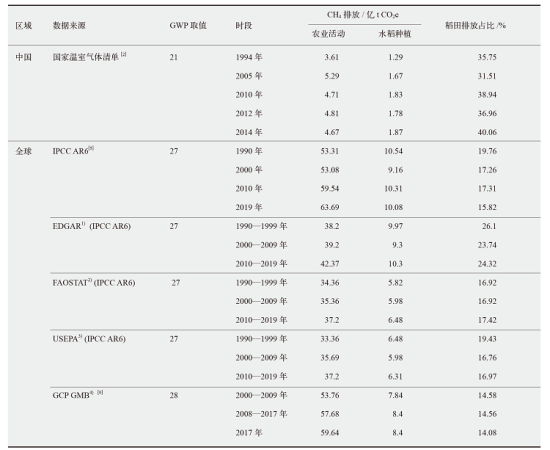
图1 我国水稻生产和稻田CH4排放现状 注:数据来源于《中国统计年鉴(1979—2021年)》和《中华人民共和国气候变化第二次两年更新报告》。
Fig. 1 Current situation of rice production and methane emission from paddy field in China
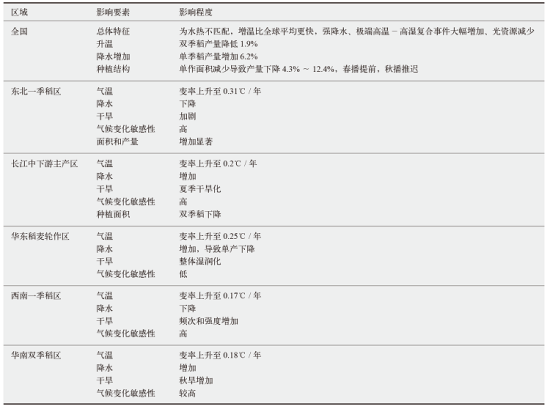 |
表2 我国气候变化特征及其对水稻产量、耕地面积和种植结构的影响[95]
Table 2 Characteristics of climate change in China and its impact on rice yield, cultivated land area and planting structure [95]
 |
图4 水稻低碳生产战略路径桑基图 注:调控方案分为人为强化和基于自然的解决方案2大类9小类,互作效应表明9个小类调控手段之间的交互,技术手段则是在9小类措施下的具体技术模式及其组合,调控途径则表示从技术手段到调控目标路径,其中也包括诸多技术的交互调控机制。
Fig. 4 Sankey diagram of rice low-carbon production strategic path
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2023: synthesis report[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023: 36 |
| [2] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 中华人民共和国气候变化第二次两年更新报告[R/OL]. 2018 [2022-10-10]. http://www.ncsc.org.cn/SY/tjkhybg/202003/t20200323_770096.shtml. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. Second biennial update report on climate change of the People’s Republic of China[R/OL]. 2018 [2022-10-10]. http://www.ncsc.org.cn/SY/tjkhybg/202003/t20200323_770096.shtml (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 王斌, 李玉娥, 蔡岸冬, 等. 碳中和视角下全球农业减排固碳政策措施及对中国的启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18 (1): 110-118. |
| Wang B, Li Y E, Cai A D, et al. Global policies in agricultural greenhouse gas reduction and carbon sequestration and their enlightenment to China in the view of carbon neutrality[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18 (1): 110-118 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 陈松文, 刘天奇, 曹凑贵, 等. 水稻生产碳中和现状及低碳稻作技术策略[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2021, 40 (3): 10. |
| Chen S W, Liu T Q, Cao C G, et al. Situation of carbon neutrality in rice production and techniques for low-carbon rice farming[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021, 40 (3): 10 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | IPCC. Climate change 2022: mitigation of climate change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022 |
| [6] | 赵立欣, 高清竹, 韩雪, 等. 中国农业农村低碳发展报告[M]. 北京: 社会科学文献出版社, 2023. |
| Zhao L X, Gao Q Z, Han X, et al. Agriculture and rural low-carbon development report in China[M]. Beijing: Social Sciences Literature Press, 2023 | |
| [7] | 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 中国水稻研究所. 2022年中国水稻产业发展报告[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2022. |
| China National Rice Research Institute. China rice industry development report 2022[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
Saunois M, Stavert A R, Poulter B, et al. The global methane budget 2000-2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12 (3): 1561-1623
doi: 10.5194/essd-12-1561-2020 URL |
| [10] |
Mer J L, Roger P. Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: a review[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2001, 37 (1): 25-50
doi: 10.1016/S1164-5563(01)01067-6 URL |
| [11] | 陈洪儒, 鲁艳红, 廖育林, 等. 等养分投入下冬种紫云英比秸秆还田更有效抑制稻田CH4的产生和排放[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28 (8): 1376-1387. |
| Chen H R, Lu Y H, Liao Y L, et al. Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) is a more effective inhibitor of methane production and emission than straw under equal nutrient condition in paddy field[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2022, 28 (8): 1376-1387 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | Qin X B, Li Y E, Wan Y F, et al. Multiple stable isotopic signatures corroborate the predominance of acetoclastic methanogenesis during CH4 formation in agricultural river networks[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2020, 296 (C): 106930 |
| [13] |
Zhou Z, Zhang C J, Liu P F, et al. Non-syntrophic methanogenic hydrocarbon degradation by an archaeal species[J]. Nature, 2021, 601 (7892): 257-262
doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04235-2 |
| [14] | 李玉娥, 林而达. 减缓稻田甲烷排放的技术研究[J]. 农业环境与发展, 1995 (2): 38-40, 50. |
| Li Y E, Lin E D. Research on technology of reducing methane emission in rice field[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 1995 (2): 38-40, 50 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] |
Cho S R, Verma P P, Das S, et al. A new approach to suppress methane emissions from rice cropping systems using ethephon[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 804: 150159
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150159 URL |
| [16] | Czatzkowska M, Harnisz M, Korzeniewska E, et al. Inhibitors of the methane fermentation process with particular emphasis on the microbiological aspect: a review[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2020, 8 (5): 1880-1897 |
| [17] |
Waghmode T R, Haque M M, Kim S Y, et al. Effective suppression of methane emission by 2-bromoethanesulfonate during rice cultivation[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10 (11): e0142569
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142569 URL |
| [18] |
Pramanik P, Kim P J. Contrasting effects of EDTA applications on the fluxes of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from straw-treated rice paddy soils[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2017, 97 (1): 278-283
doi: 10.1002/jsfa.7727 URL pmid: 27010126 |
| [19] | 苗曼倩, 朱超群, 莫天麟, 等. EM对稻田甲烷排放抑制作用的初步研究[J]. 应用气象学报, 1998 (4): 83-90. |
| Miao M Q, Zhu C Q, Mo T L, et al. Preliminary study on the suppression effect of EM on methane emissions in paddy fields[J]. Quarterly Journal of Applied Meteorology, 1998 (4): 83-90 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
王斌, 李玉娥, 万运帆, 等. 控释肥和添加剂对双季稻温室气体排放影响和减排评价[J]. 中国农业科学, 2014, 47 (2): 314-323.
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.02.011 |
|
Wang B, Li Y E, Wan Y F, et al. Effect and assessment of controlled release fertilizer and additive treatments on greenhouse gases emission from a double rice field[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2014, 47 (2): 314-323 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2014.02.011 |
|
| [21] | 王斌, 万运帆, 郭晨, 等. 控释尿素、稳定性尿素和配施菌剂尿素提高双季稻产量和氮素利用率的效应比较[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2015, 21 (5): 1104-1112. |
| Wang B, Wan Y F, Guo C, et al. A comparison of the effects of controlled release urea, stable urea and microorganisms increasing double rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2015, 21 (5): 1104-1112 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 蔡威威, 艾天成, 李然, 等. 控释肥及尿素添加剂对双季稻光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018 (3): 54-60. |
| Cai W W, Ai T C, Li R, et al. Effect of controlled release fertilizer and urea additive on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of double cropping rice[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2018 (3): 54-60 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
Shaaban M, Peng Q A, Lin S, et al. Dolomite application enhances CH4 uptake in an acidic soil[J]. Catena, 2016, 140: 9-14
doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.01.014 URL |
| [24] |
Khatun L, Ali M A, Sumon M H, et al. Mitigation rice yield scaled methane emission and soil salinity stress with feasible soil amendments[J]. Journal of Agricultural Chemistry and Environment, 2021, 10 (1): 16-36
doi: 10.4236/jacen.2021.101002 URL |
| [25] |
Zhou X, Smaill S J, Clinton P W. Methane oxidation needs less stressed plants[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2013, 18 (12): 657-659
doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2013.09.011 URL pmid: 24161402 |
| [26] | Qin X B, Li Y E, Wang H, et al. Long-term effect of biochar application on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions in a rice paddy cropping system: a four-year case study in South China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2016, 569-570: 1390-1401 |
| [27] |
Qin X B, Li Y E, Wang H, et al. Effect of rice cultivars on yield-scaled methane emissions in a double rice field in South China[J]. Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences, 2015, 12 (S1): 47-66
doi: 10.1080/1943815X.2015.1118388 URL |
| [28] | 祝贞科, 肖谋良, 魏亮, 等. 稻田土壤固碳关键过程的生物地球化学机制及其碳中和对策[J]. 中国生态农业学报 (中英文), 2022, 30 (4): 592-602. |
| Zhu Z K, Xiao M L, Wei L, et al. Key biogeochemical processes of carbon sequestration in paddy soil and its countermeasures for carbon neutrality[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30 (4): 592-602 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
Liu G, Ma J, Yang Y T, et al. Effects of straw incorporation methods on nitrous oxide and methane emissions from a wheat-rice rotation system[J]. Pedosphere, 2019, 29 (2): 204-215
doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60410-7 URL |
| [30] |
Xie Z B, Liu G, Bei Q C, et al. CO2 mitigation potential in farmland of China by altering current organic matter amendment pattern[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2010, 53 (9): 1351-1357
doi: 10.1007/s11430-010-4014-z URL |
| [31] | Yan X Y, Akiyama H, Yagi K, et al. Global estimations of the inventory and mitigation potential of methane emissions from rice cultivation conducted using the 2006 intergovernmental panel on climate change guidelines[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2009, 23 (2): GB2002-GB2002 |
| [32] | Qin X B, Lu Y H, Wan Y F, et al. Rice straw application improves yield marginally and increases carbon footprint of double cropping paddy rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Field Crops Research, 2023, 291 |
| [33] | 曹凑贵, 李成芳, 展茗, 等. 稻田管理措施对土壤碳排放的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2011, 44 (1): 93-98. |
| Cao C G, Li C F, Zhan M, et al. Effects of agricultural management practices on carbon emissions in paddy fields[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2011, 44 (1): 93-98 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] |
Hu Q Y, Liu T Q, Jiang S S, et al. Combined effects of straw returning and chemical n fertilization on greenhouse gas emissions and yield from paddy fields in northwest Hubei province, China[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2020, 20 (2): 392-406
doi: 10.1007/s42729-019-00120-0 URL |
| [35] | 刘天奇, 胡权义, 汤计超, 等. 长江中下游水稻生产固碳减排关键影响因素及技术体系[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2022, 30 (4): 603-615. |
| Liu T Q, Hu Q Y, Tang J C, et al. Key influencing factors and technical system of carbon sequestration and emission reduction in rice production in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2022, 30 (4): 603-615 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 张俊, 邓艾兴, 尚子吟, 等. 秸秆还田下水稻丰产与甲烷减排的技术模式[J]. 作物杂志, 2021 (6): 230-235. |
| Zhang J, Deng A X, Shang Z Y, et al. Innovative rice cropping for higher yield and less CH4emission under crop straw incorporation[J]. Crops, 2021 (6): 230-235 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | Balakrishnan D, Kulkarni K, Latha P C, et al. Crop improvement strategies for mitigation of methane emissions from rice[J]. Emirates Journal of Food and Agriculture, 2018, 30 (6): 451-462 |
| [38] |
Jiang Y, Wang L L, Yan X J, et al. Super rice cropping will enhance rice yield and reduce CH4 emission: a case study in Nanjing, China[J]. Rice Science, 2013, 20 (6): 427-433
doi: 10.1016/S1672-6308(13)60157-2 URL |
| [39] |
Wang B, Xu Y, Wang Z, et al. Methane emissions from ricefields as affected by organic amendment, water regime, crop establishment, and rice cultivar[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 1999, 57 (2): 213-228
doi: 10.1023/A:1006039231459 URL |
| [40] | Minami K, Mosier A, Sass R, et al. CH4 and N2O global emissions and controls from rice fields and other agriculture and industrial sources[M]. NIAES Series 2, 1994, 2: 87-104 |
| [41] |
Bhattacharyya P, Dash P K, Swain C K, et al. Mechanism of plant mediated methane emission in tropical lowland rice[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2019, 651 (1): 84-92
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.141 URL |
| [42] |
Mariko S, Harazono Y, Owa N, et al. Methane in flooded soil water and the emission through rice plants to the atmosphere[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 1991, 31 (3): 343-350
doi: 10.1016/0098-8472(91)90059-W URL |
| [43] | 徐雨昌, 王增远, 李震, 等. 不同水稻品种对稻田甲烷排放量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 1999 (1): 94-97. |
| Xu Y C, Wang Z Y, Li Z, et al. Effect of rice cultivars on methane emission from Beijing rice field[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 1999 (1): 94-97 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] |
Aulakh M S, Bodenbender J, Wassmann R, et al. Methane transport capacity of rice plants. II. Variations among different rice cultivars and relationship with morphological characteristics[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2000, 58 (1-3): 367-375
doi: 10.1023/A:1009839929441 URL |
| [45] |
Khosa M K, Sidhu B S, Benbi D K. Effect of organic materials and rice cultivars on methane emission from rice field[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 2010, 31 (3): 281-285
pmid: 21046997 |
| [46] |
Singh S, Kumar S, Jain M C. Methane emission from two Indian soils planted with different rice cultivars[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1997, 25 (3): 285-289
doi: 10.1007/s003740050316 URL |
| [47] | 江瑜, 管大海, 张卫建. 水稻植株特性对稻田甲烷排放的影响及其机制的研究进展[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26 (2): 175-181. |
| Jiang Y, Guan D H, Zhang W J. The effect of rice plant traits on methane emissions from paddy fields: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26 (2): 175-181 (in Chinese) | |
| [48] |
Adviento-Borbe M A, Pittelkow C M, Anders M, et al. Optimal fertilizer nitrogen rates and yield-scaled global warming potential in drill seeded rice[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2013, 42 (6): 1623-1634
doi: 10.2134/jeq2013.05.0167 URL pmid: 25602403 |
| [49] |
Pittelkow C M, Adviento-Borbe M A, Hill J E, et al. Yield-scaled global warming potential of annual nitrous oxide and methane emissions from continuously flooded rice in response to nitrogen input[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2013, 177: 10-20
doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2013.05.011 URL |
| [50] |
Lueke C, Bodrossy L, Lupotto E, et al. Methanotrophic bacteria associated to rice roots: the cultivar effect assessed by T-RFLP and microarray analysis[J]. Environmental Microbiology Reports, 2011, 3 (5): 518-525
doi: 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2011.00251.x URL pmid: 23761330 |
| [51] | Liechty Z, Santos-Medellin C, Edwards J, et al. Comparative analysis of root microbiomes of rice cultivars with high and low methane emissions reveals differences in abundance of methanogenic archaea and putative upstream fermenters[J]. mSystems, 2020, 5(1) |
| [52] |
Serrano-Silva N, Valenzuela-Encinas C, Marsch R, et al. Changes in methane oxidation activity and methanotrophic community composition in saline alkaline soils[J]. Extremophiles, 2014, 18 (3): 561-571
doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0641-1 URL pmid: 24638260 |
| [53] | Su J, Hu C, Yan X, et al. Expression of barley SUSIBA2 transcription factor yields high-starch low-methane rice[J]. Nature, 2015, 523 (7562) |
| [54] | Du L, Wang Y F, Shan Z, et al. Comprehensive analysis of SUSIBA2 rice: the low-methane trait and associated changes in soil carbon and microbial communities[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 764 |
| [55] |
Soremi P A S, Chirinda N, Graterol E, et al. Potential of rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars to mitigate methane emissions from irrigated systems in Latin America and the Caribbean[J]. All Earth, 2023, 35 (1): 149-157
doi: 10.1080/27669645.2023.2207941 URL |
| [56] |
Minami K. Atmospheric methane and nitrous oxide: sources, sinks and strategies for reducing agricultural emissions[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1997, 49 (1-3): 203-211
doi: 10.1023/A:1009730618454 URL |
| [57] |
Yu K W, Wang Z P, Chen G X. Nitrous oxide and methane transport through rice plants[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1997, 24 (3): 341-343
doi: 10.1007/s003740050254 URL |
| [58] |
Mosier A R, Mohanty S K, Bhadrachalam A, et al. Evolution of dinitrogen and nitrous oxide from the soil to the atmosphere through rice plants[J]. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 1990, 9 (1): 61-67
doi: 10.1007/BF00335863 URL |
| [59] |
Schütz H, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, et al. A 3-year continuous record on the influence of daytime, season, and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 1989, 94 (D13): 16405-16416
doi: 10.1029/JD094iD13p16405 URL |
| [60] |
Tyler S C, Bilek R S, Sass R L, et al. Methane oxidation and pathways of production in a Texas paddy field deduced from measurements of flux, delta δ13C, and δD of CH4[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 1997, 11 (3): 323-348
doi: 10.1029/97GB01624 URL |
| [61] |
Chen Y, Li S Y, Zhang Y J, et al. Rice root morphological and physiological traits interaction with rhizosphere soil and its effect on methane emissions in paddy fields[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2019, 129: 191-200
doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.11.015 URL |
| [62] |
Kim W J, Bui L T, Chun J B, et al. Correlation between methane (CH4) emissions and root aerenchyma of rice varieties[J]. Plant Breeding and Biotechnology, 2018, 6 (4): 381-390
doi: 10.9787/PBB.2018.6.4.381 URL |
| [63] |
Avnery S, Mauzerall D L, Fiore A M. Increasing global agricultural production by reducing ozone damages via methane emission controls and ozone-resistant cultivar selection[J]. Global Change Biology, 2013, 19 (4): 1285-1299
doi: 10.1111/gcb.12118 URL pmid: 23504903 |
| [64] |
Wang B, Neue H U, Samonte H P. Effect of cultivar difference ('IR72', 'IR65598' and 'Dular') on methane emission[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 1997, 62 (1): 31-40
doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(96)01115-2 URL |
| [65] | Setyanto P, Kartikawati R. Integrated rice crop management for low emitance of methane[J]. Indonesian Journal of Agriculture, 2011, 4 (1): 8-16 |
| [66] |
Nihayah B, Nugroho B D A, Hasanah N A I, et al. Methane (CH4) emission flux estimation in SRI (system of rice intensification) method rice cultivation using different varieties and fertilization[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 757 (1): 012001
doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/757/1/012001 URL |
| [67] |
Li T Y, Zhang W F, Cao H B, et al. Region-specific nitrogen management indexes for sustainable cereal production in China[J]. Environmental Research Communications, 2020, 2 (7): 075002
doi: 10.1088/2515-7620/aba12d URL |
| [68] |
Qin X B, Li Y E, Wang B, et al. Nonlinear dependency of N2O emissions on nitrogen input in dry farming systems may facilitate green development in China[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 2021, 317: 107456
doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2021.107456 URL |
| [69] | 秦晓波, 李玉娥, 万运帆, 等. 耕作方式和稻草还田对双季稻田CH4和N2O排放的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2014, 30 (11): 216-224. |
| Qin X B, Li Y E, Wan Y F, et al. Effect of tillage and rice residue return on CH4 and N2O emission from double rice field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2014, 30 (11): 216-224 (in Chinese) | |
| [70] | 秦晓波, 李玉娥, 万运帆, 等. 免耕条件下稻草还田方式对温室气体排放强度的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2012, 28 (6): 210-216. |
| Qin X B, Li Y E, Wan Y F, et al. Effects of straw mulching on greenhouse gas intensity under on-tillage conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2012, 28 (6): 210-216 (in Chinese) | |
| [71] | 秦晓波, 李玉娥, Wang H, 等. 生物质炭添加对华南双季稻田碳排放强度的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31 (5): 226-234. |
| Qin X B, Li Y E, Wang H, et al. Impact of biochar amendment on carbon emissions intensity in double rice field in South China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31 (5): 226-234 (in Chinese) | |
| [72] | Yamaguchi T, Minh Tuan L, Minamikawa K, et al. Compatibility of alternate wetting and drying irrigation with local agriculture in An Giang province, Mekong Delta, Vietnam[J]. Tropical Agriculture and Development, 2017, 61 (3): 117-127 |
| [73] |
Sriphirom P, Chidthaisong A, Towprayoon S. Effect of alternate wetting and drying water management on rice cultivation with low emissions and low water used during wet and dry season[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 223: 980-988
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.212 URL |
| [74] | Quynh V D, O Sander. Applying and scaling up alternate wetting and drying for paddy rice in Vietnam[R]. International Rice Research Institute and the CGIAR Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security, 2015 |
| [75] |
Dang H T, Trong N H, Tokida T, et al. Impacts of alternate wetting and drying on greenhouse gas emission from paddy field in Central Vietnam[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2018, 64 (1): 14-22
doi: 10.1080/00380768.2017.1409601 URL |
| [76] | 张志伟, 秦晓波, 樊建凌, 等. 干湿交替灌溉模式在湖南稻区适用性及其甲烷减排潜力评估[J]. 农业工程学报, 2022, 38 (S1): 232-239. |
| Zhang Z W, Qin X B, Fan J L, et al. Applicability and abatement potential assessment of alternate wet and dry CH4 mitigation technology in major rice cropping regions in Hunan province of China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38 (S1): 232-239 (in Chinese) | |
| [77] |
Carrijo D R, Lundy M E, Linquist B A. Rice yields and water use under alternate wetting and drying irrigation: a meta-analysis[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 203: 173-180
doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2016.12.002 URL |
| [78] | 蔡祖聪, 徐华, 马静. 稻田生态系统CH4和N2O排放[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009. |
| Cai Z C, Xu H, Ma J. CH4 and N2O emissions from paddy ecosystems[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009 (in Chinese) | |
| [79] |
Lampayan R M, Rejesus R M, Singleton G R, et al. Adoption and economics of alternate wetting and drying water management for irrigated lowland rice[J]. Field Crops Research, 2015, 170: 95-108
doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2014.10.013 URL |
| [80] |
Wang J Y, Zhang X L, Xiong Z Q, et al. Methane emissions from a rice agroecosystem in South China: effects of water regime, straw incorporation and nitrogen fertilizer[J]. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2012, 93 (1): 103-112
doi: 10.1007/s10705-012-9503-3 URL |
| [81] | Zou J W, Huang Y, Jiang J Y, et al. A 3-year field measurement of methane and nitrous oxide emissions from rice paddies in China: effects of water regime, crop residue, and fertilizer application[J]. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2005, 19 (2): 1-9 |
| [82] |
Yagi K, Sriphirom P, Cha-un N, et al. Potential and promisingness of technical options for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from rice cultivation in Southeast Asian countries[J]. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2020, 66 (1): 37-49
doi: 10.1080/00380768.2019.1683890 URL |
| [83] |
Hussain S, Peng S, Fahad S, et al. Rice management interventions to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions: a review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22 (5): 3342-3360
doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3760-4 URL |
| [84] |
Kritee K, Nair D, Zavala-Araiza D, et al. High nitrous oxide fluxes from rice indicate the need to manage water for both long- and short-term climate impacts[J]. Proceedings of The National Academy of Sciences of The United States of America, 2018, 115 (39): 9720-9725
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1809276115 pmid: 30201704 |
| [85] |
Yamaguchi T, Luu Minh T, Minamikawa K, et al. Assessment of the relationship between adoption of a knowledge-intensive water-saving technique and irrigation conditions in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2019, 212: 162-171
doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2018.08.041 URL |
| [86] |
Sander B O, Wassmann R, Palao L K, et al. Climate-based suitability assessment for alternate wetting and drying water management in the Philippines: a novel approach for mapping methane mitigation potential in rice production[J]. Carbon Management, 2017, 8 (4): 331-342
doi: 10.1080/17583004.2017.1362945 URL |
| [87] | Nelson A, Wassmann R, Sander B O, et al. Climate-determined suitability of the water saving technology “alternate wetting and drying” in rice systems: a scalable methodology demonstrated for a province in the Philippines[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10 (12): e0145268 |
| [88] | IPCC. 2006 IPCC guidelines for national greenhouse gas inventories[M/OL]. 2006 [2022-10-10]. https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/chinese/index.html (in Chinese) |
| [89] | Prangbang P, Yagi K, Aunario J K S, et al. Climate-based suitability assessment for methane mitigation by water saving technology in paddy fields of the central plain of Thailand[J]. Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 2020, 4 |
| [90] | Wu K, Wang S, Song W, et al. Enhanced sustainable green revolution yield via nitrogen-responsive chromatin modulation in rice[J]. Science, 2020, 367 (6478): p.eaaz2046 |
| [91] |
Bodelier P L E, Roslev P, Henckel T, et al. Stimulation by ammonium-based fertilizers of methane oxidation in soil around rice roots[J]. Nature, 2000, 403 (6768): 421-424
doi: 10.1038/35000193 URL |
| [92] |
Shrestha M, Shrestha P M, Frenzel P, et al. Effect of nitrogen fertilization on methane oxidation, abundance, community structure, and gene expression of methanotrophs in the rice rhizosphere[J]. The ISME Journal, 2010, 4 (12): 1545-1556
doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.89 URL |
| [93] |
Hou P, Yu Y, Xue L, et al. Effect of long term fertilization management strategies on methane emissions and rice yield[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 725: 138261
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138261 URL |
| [94] |
Scholz V V, Meckenstock R U, Nielsen L P, et al. Cable bacteria reduce methane emissions from rice-vegetated soils[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11 (1): 1878
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15812-w URL pmid: 32313021 |
| [95] | 李玉娥, 朱建华, 董红敏, 等. 中国气候与生态环境演变报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. |
| Li Y E, Zhu J H, Dong H M, et al. China climate and ecological environment evolution report[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 惠婧璇, 朱松丽. 全球甲烷控排政策措施评述及其对中国的启示和建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 683-692. |
| [2] | 段居琦, 袁佳双, 徐新武, 居辉. 对IPCC AR6报告中有关农业系统结论的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 422-432. |
| [3] | 黄萌田, 周佰铨, 翟盘茂. 极端天气气候事件变化对荒漠化、土地退化和粮食安全的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 17-27. |
| [4] | 吴建国,翟盘茂,武亚堂. 对基于土地应对气候变化的新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 50-69. |
| [5] | 黄磊, 王长科, 巢清尘. IPCC《气候变化与土地特别报告》解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 1-8. |
| [6] | 许吟隆,赵运成,翟盘茂. IPCC特别报告SRCCL关于气候变化与粮食安全的新认知与启示[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 37-49. |
| [7] | 高孟霜,许吟隆,殷红,李阔,李新华. 1992—2012年东北水稻生育期变化分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 495-504. |
| [8] | 刘援,孙丹妮,张建君,吴克安,郑静. 中国履行《蒙特利尔议定书(基加利修正案)》减排三氟甲烷的对策分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(4): 423-428. |
| [9] | 谢立勇 李悦 徐玉秀 赵迅 宋艳玲 姜彤 林而达. 气候变化对农业生产与粮食安全影响的新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(4): 235-239. |
| [10] | 李祎君;王春乙. 气候变化对我国农作物种植结构的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(02): 123-129. |
| [11] | 熊伟;林而达;居辉;许吟隆. 气候变化的影响阈值与中国的粮食安全[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2005, 01(02): 84-87. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||