| [1] |
National Academy of Sciences. Climate intervention: reflecting sunlight to cool Earth [M]. Washington DC: National Academies Press, 2015
|
| [2] |
Irvine P J, Kravitz B, Lawrence M G, et al. An overview of the Earth system science of solar geoengineering[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Climate Change, 2016,7:815-833. DOI: 10.1002/wcc.423
|
| [3] |
Crutzen P J. Albedo enhancement by stratospheric sulfur injections: a contribution to resolve a policy dilemma?[J]. Climatic Change, 2006,77:211-219
|
| [4] |
Latham J. Control of global warming?[J]. Nature, 1990,347:339-340
doi: 10.1038/347339a0
URL
pmid: 2215647
|
| [5] |
Kravitz B, Robock A, Tilmes S, et al. The Geoengineering Model Intercomparison Project phase 6 (GeoMIP6): simulation design and preliminary results[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2015,8. DOI: 10.5194/gmd-8-3379-2015
|
| [6] |
Yu X, Moore J C, Cui X, et al. Impacts, effectiveness and regional inequalities of the GeoMIP G1 to G4 solar radiation management scenarios[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2015,129. DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2015.02.010
|
| [7] |
Moore J C, Grinsted A, Guo X, et al. Atlantic hurricane surge response to geoengineering[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2015,112:13794-13799
|
| [8] |
Cao L, Duan L, Bala G, et al. Simultaneous stabilization of global temperature and precipitation through cocktail geoengineering[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017,44. DOI: 10.1002/2017GL074281
doi: 10.1002/2016GL071661
URL
pmid: 29200536
|
| [9] |
陈迎. 地球工程的国际争论与治理问题[J]. 国外理论动态, 2016 (3):57-66.
|
|
Chen Y. International debate and governance of geoengineering[J]. Foreign Theoretical Trends, 2016 (3):57-66 (in Chinese)
|
| [10] |
陈迎, 辛源. 1.5℃温控目标下地球工程问题剖析和应对政策建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(4):337-345.
|
|
Chen Y, Xin Y. Implications of geoengineering under 1.5℃target: analysis and policy recommendations[J]. Climate Change Research, 2017,13(4):337-345 (in Chinese)
|
| [11] |
Lenton T M, Rockström J, Gaffney O, et al. Climate tipping points: too risky to bet against[J]. Nature, 2019,575:592-595
URL
pmid: 31776487
|
| [12] |
Moore J C, Gladstone R, Zwinger T, et al. Geoengineer polar glaciers to slow sea-level rise[J]. Nature, 2018,555:303-305
URL
pmid: 32094708
|
| [13] |
Jevrejeva S, Jackson L P, Riva R E M, et al. Coastal sea level rise with warming above 2℃[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2016,113(47):201605312
|
| [14] |
DeConto R M, Pollard D. Contribution of Antarctica to past and future sea-level rise[J]. Nature, 2016,531:591-597
doi: 10.1038/nature17145
URL
pmid: 27029274
|
| [15] |
IPCC. Special report on global warming of 1.5℃ [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2018
|
| [16] |
Hinkel J, Lincke D, Vafeidis A T, et al. Coastal flood damage and adaptation costs under 21st century sea-level rise[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2014,111:3292-3297
|
| [17] |
IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013
|
| [18] |
van den Broeke M, Bamber J, Ettema J, et al. Partitioning recent Greenland mass loss[J]. Science, 2009,326(5955):984-986
doi: 10.1126/science.1178176
URL
pmid: 19965509
|
| [19] |
Pattyn F, Ritz C, Hanna E, et al. The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets under 1.5℃ global warming[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2018,8:1053-1061
|
| [20] |
Rignot E. Changes in West Antarctic ice stream dynamics observed with ALOS PALSAR data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008,35:L12505
|
| [21] |
Joughin I, Smith B E, Medley B. Marine ice sheet collapse potentially under way for the Thwaites glacier basin, West Antarctica[J]. Science, 2014,344(6185):735-738
doi: 10.1126/science.1249055
URL
pmid: 24821948
|
| [22] |
Favier L, Durand G, Cornford S L, et al. Retreat of Pine Island glacier controlled by marine ice-sheet instability[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2014,4:117-121
|
| [23] |
IPCC. Special report on the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate [M/OL]. 2019 [2019-12-10]. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/
|
| [24] |
Sun S, Cornford S, Gladstone R, et al. Ice shelf fracture parameterization in an ice sheet model[J]. The Cryosphere, 2017,11:2543-2554
|
| [25] |
Guo X, Zhao L, Gladstone R, et al. Simulated retreat of Jakobshavn Isbræ during the 21st century[J]. The Cryosphere, 2019,13:3139-3153
|
| [26] |
Favier L, Jourdain N C, Jenkins A, et al. Assessment of sub-shelf melting parameterisations using the ocean-ice-sheet coupled model NEMO (v3.6)-Elmer/Ice (v8.3)[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019,12:2255-2283
|
| [27] |
Cornford S L, Martin D F, Payne A J, et al. Century-scale simulations of the response of the West Antarctic ice sheet to a warming climate[J]. The Cryosphere, 2015,9:1579-1600
|
| [28] |
Gladstone R M, Warner R C, Galton-Fenzi B K, et al. Marine ice sheet model performance depends on basal sliding physics and sub-shelf melting[J]. The Cryosphere, 2017,11:319-329
|
| [29] |
Seroussi H, Nowicki S, Simo E, et al. InitMIP-Antarctica: an ice sheet model initialization experiment of ISMIP6[J]. The Cryosphere, 2019,13:1441-1471
|
| [30] |
Pritchard H D, Arthern R J, Vaughan D G, et al. Extensive dynamic thinning on the margins of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets[J]. Nature, 2009,461:971-975
doi: 10.1038/nature08471
URL
pmid: 19776741
|
| [31] |
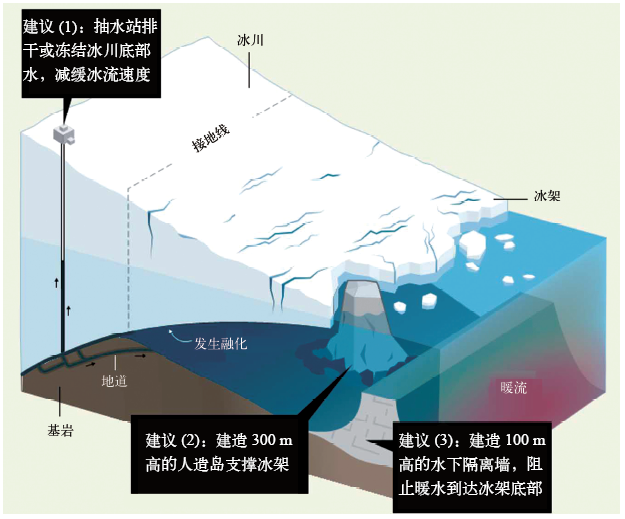
Wolovick M, Moore J C. Stopping the flood: could we use targeted geoengineering to mitigate sea level rise?[J]. The Cryosphere, 2018,12:2955-2967
|
| [32] |
Gürses ?, Kolatschek V, Wang Q, et al. Brief communication: a submarine wall protecting the Amundsen Sea intensifies melting of neighboring ice shelves[J]. The Cryosphere, 2019,13:2317-2324
|
| [33] |
Hunt J D, Byer E. Reducing sea level rise with submerged barriers and dams in Greenland[J]. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2019,24(5):779-794
|
| [34] |
Moore J C, Wolovick M, Jaiman R, et al. Stopping the flood: continued progress in targeted glacial geoengineering [R/OL]. 2019 [2019-12-02]. https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm19/webprogrampreliminary/Paper572152.html
|
 ), John C. MOORE1,3, Mike WOLOVICK1
), John C. MOORE1,3, Mike WOLOVICK1
 ), John C. MOORE1,3, Mike WOLOVICK1
), John C. MOORE1,3, Mike WOLOVICK1