Climate Change Research ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 789-806.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.105
• Mitigation to Climate Change • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analyzing drivers of embodied carbon in renewable energy sector within global industry chains
GUO Chen-Yu1, CHEN Cong1( ), ZHAO Shu-Yuan1, DONG Cong2
), ZHAO Shu-Yuan1, DONG Cong2
- 1 School of Economics and Management, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing 100083, China
2 School of Management, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510520, China
-
Received:2025-05-14Revised:2025-07-14Online:2025-11-30Published:2025-11-11
Cite this article
GUO Chen-Yu, CHEN Cong, ZHAO Shu-Yuan, DONG Cong. Analyzing drivers of embodied carbon in renewable energy sector within global industry chains[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 789-806.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.105
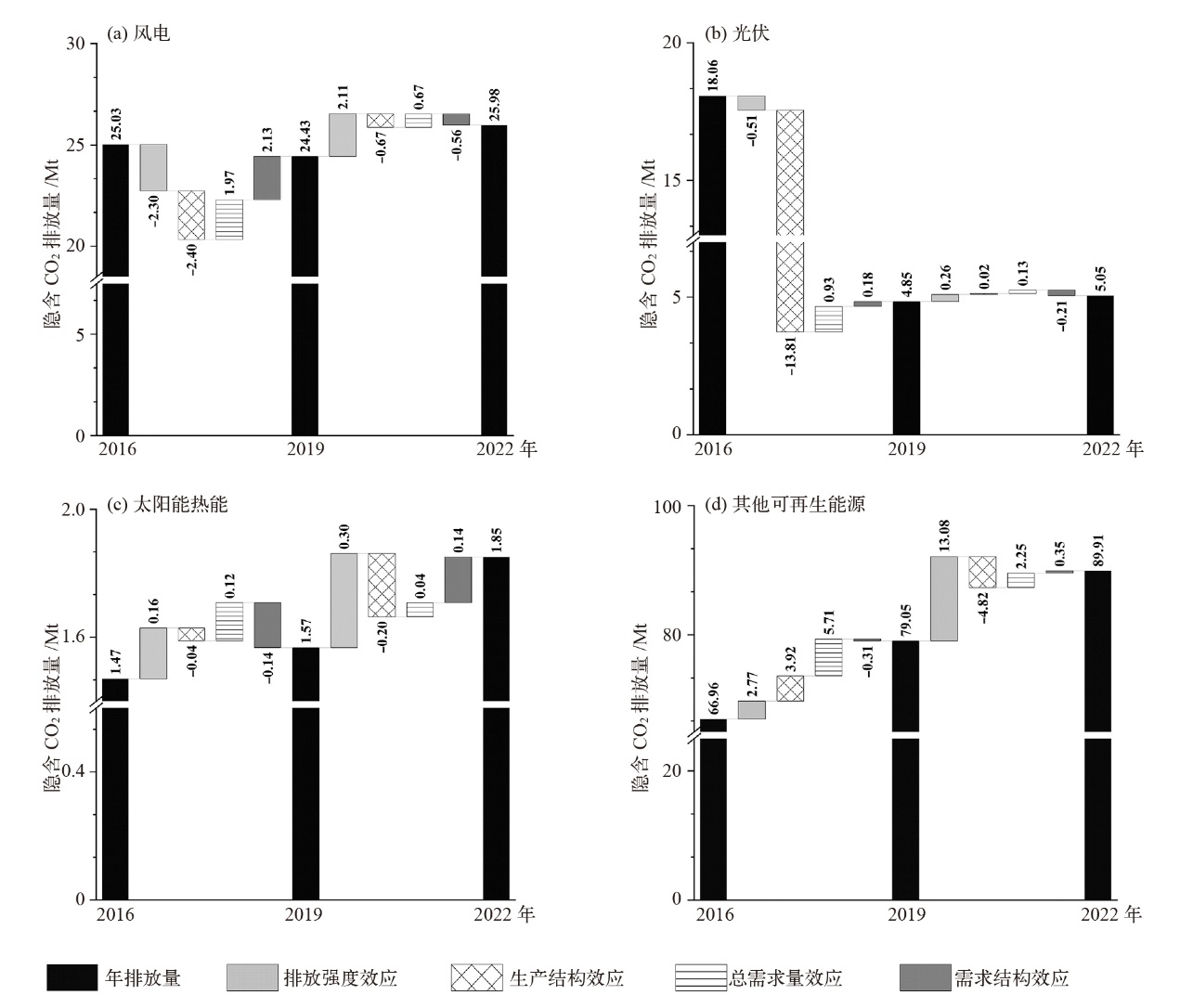
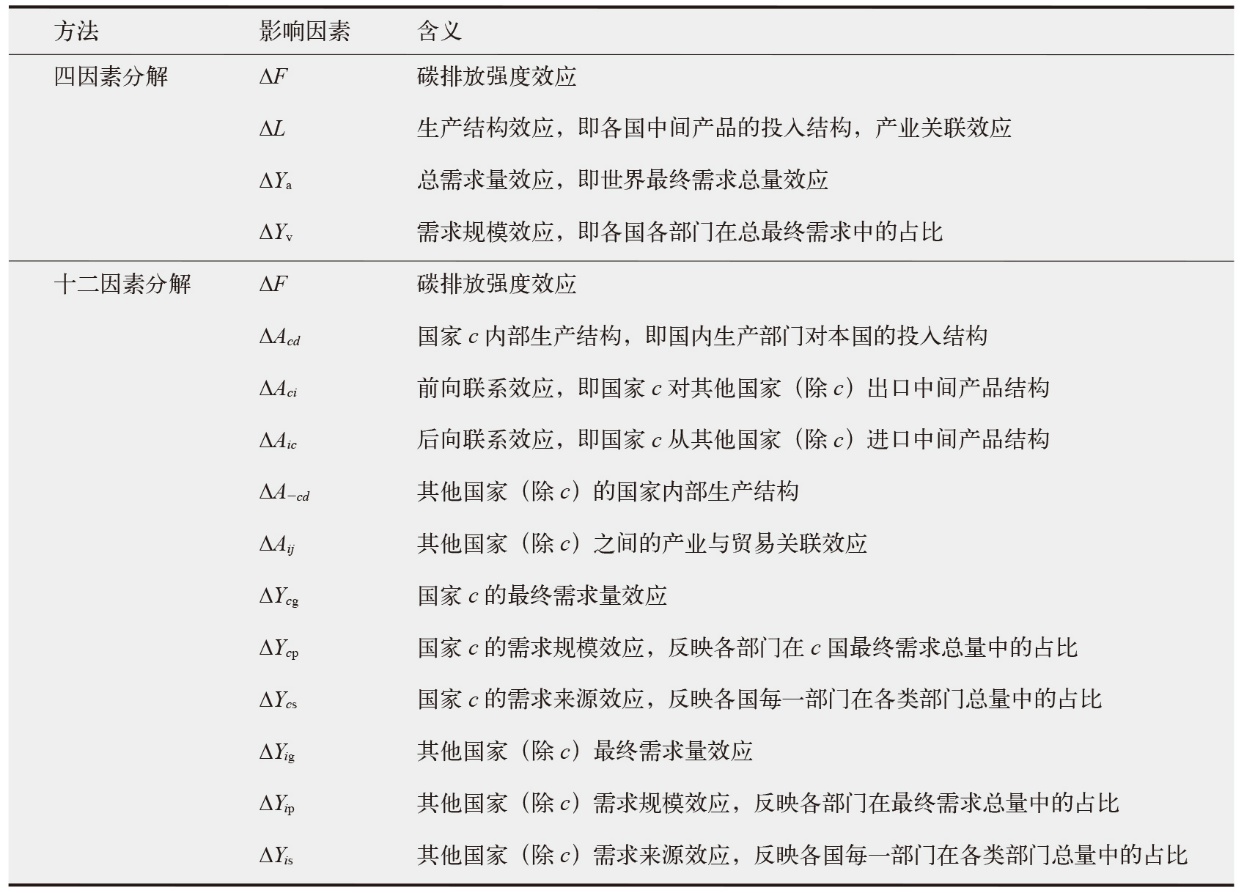
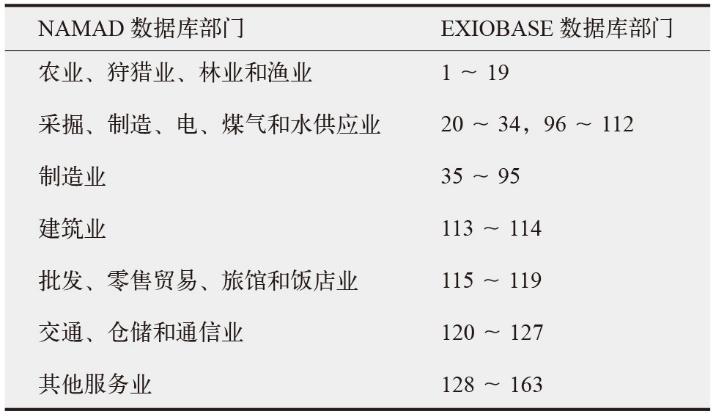
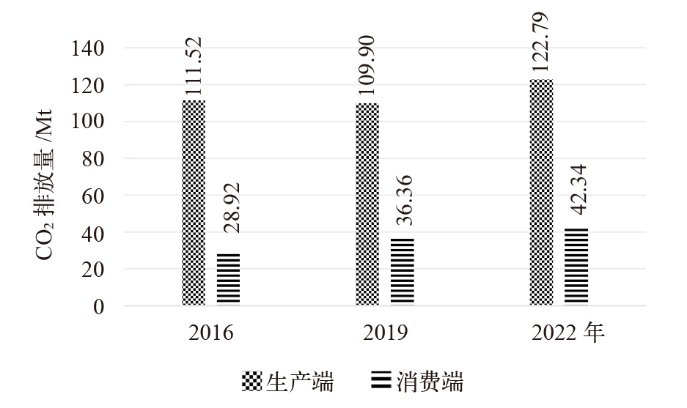
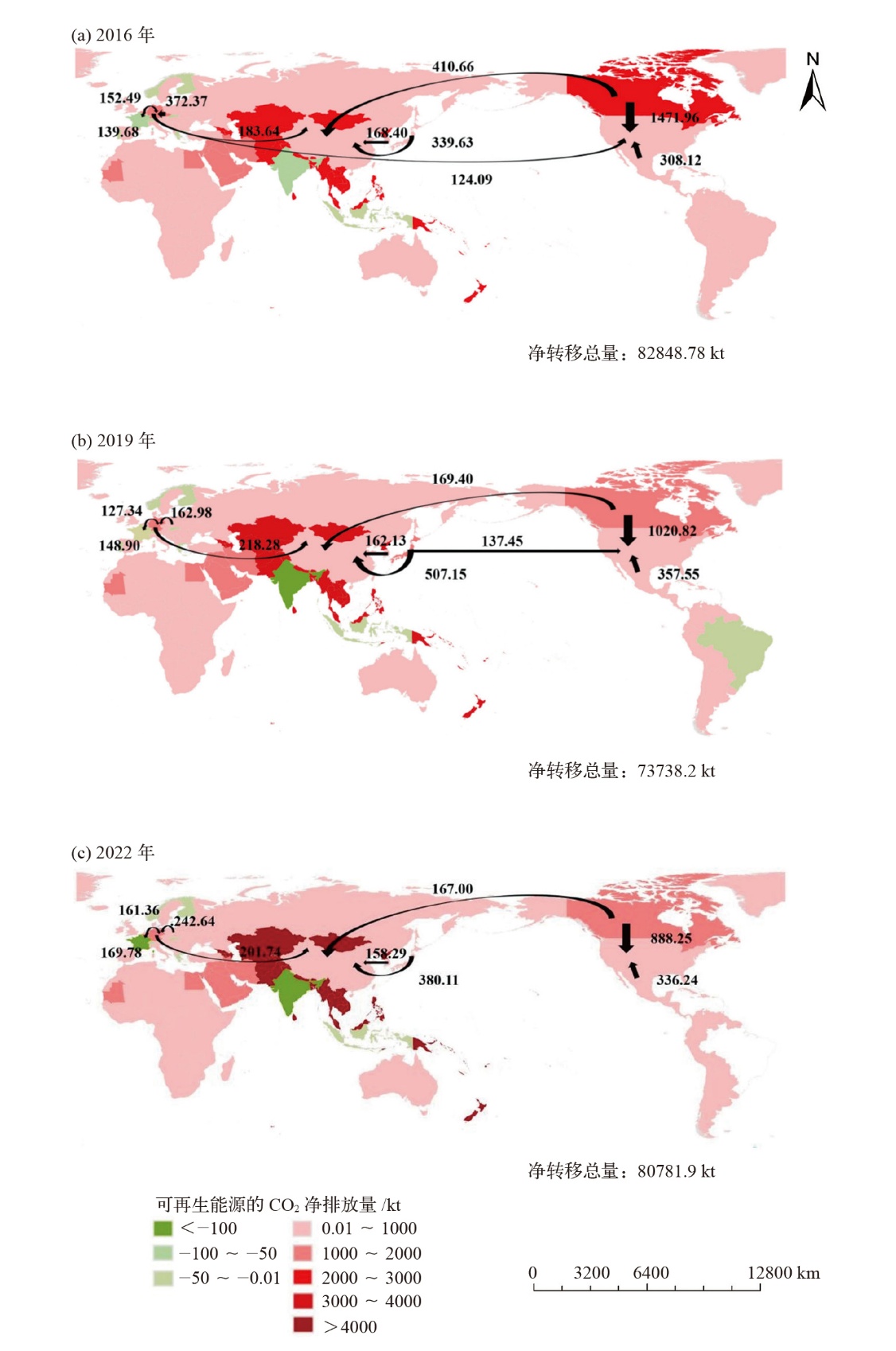
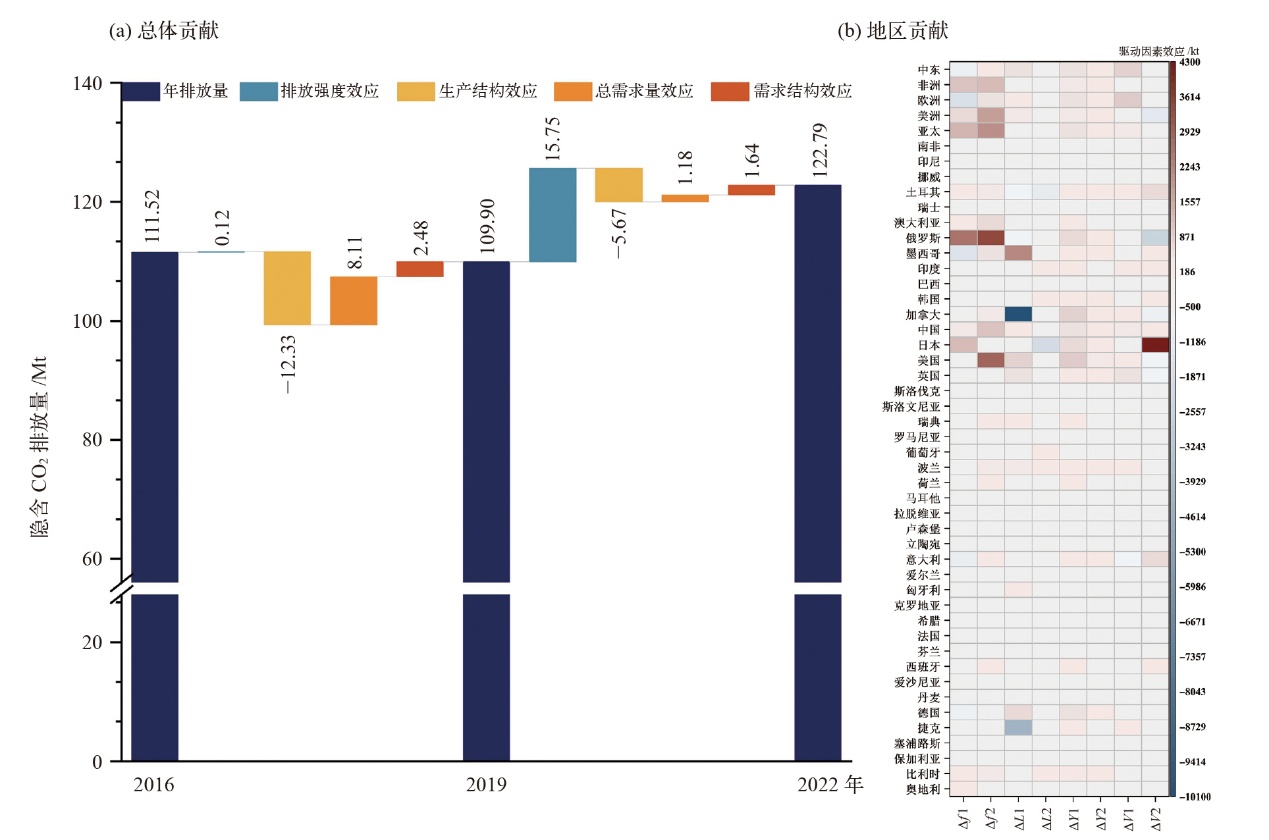
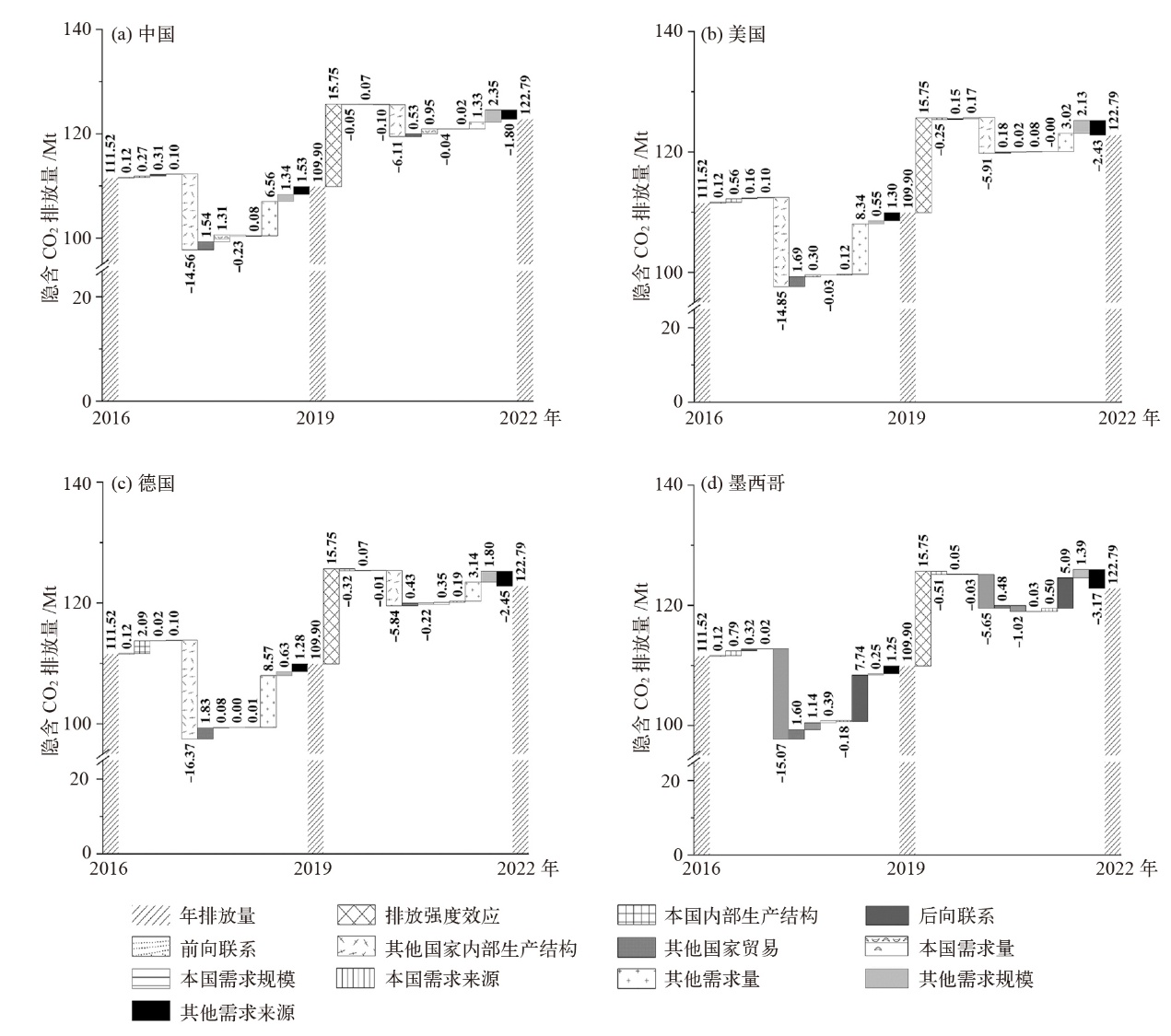
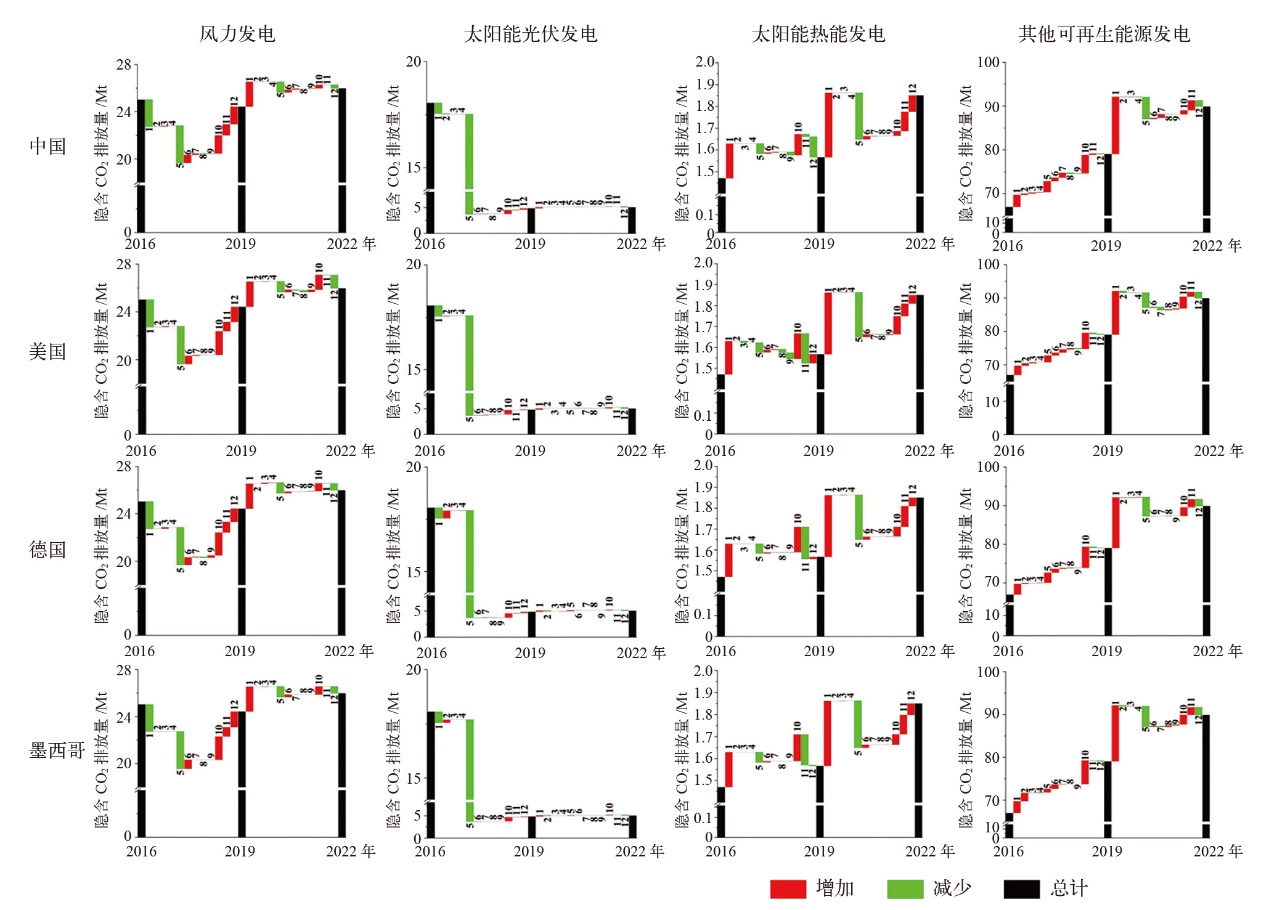
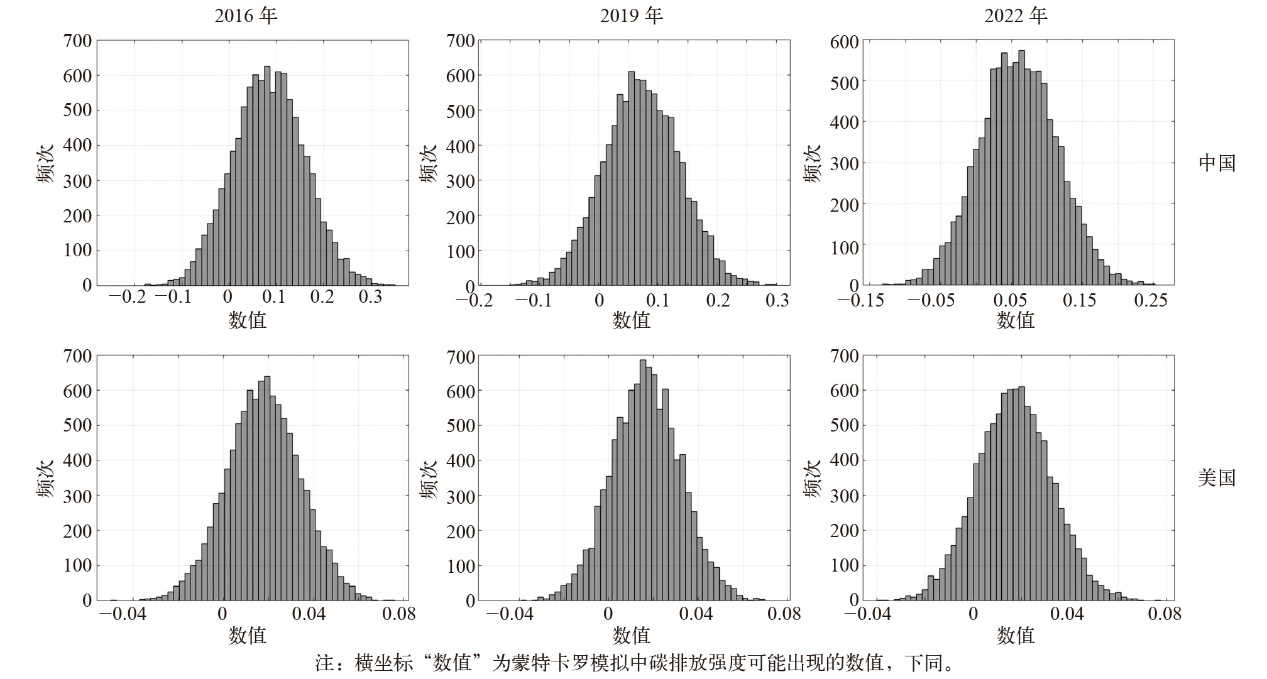
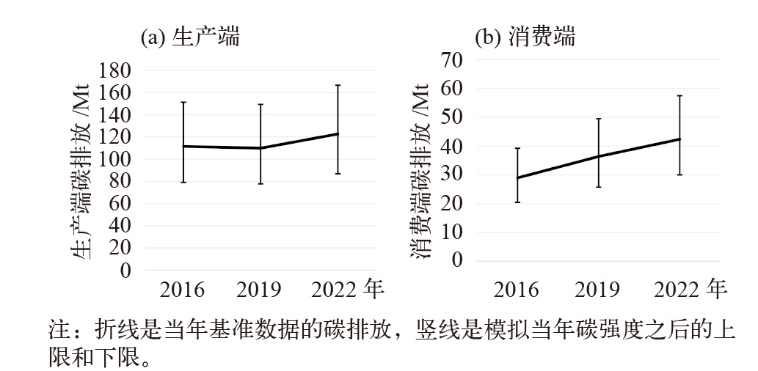
Fig. 5 Analysis of four driving factors in different power generation sectors. (a) Wind power, (b) solar photovoltaic, (c) solar thermal, (d) other renewable energy
| [1] | UNFCCC. 2024 NDC synthesis report[R/OL]. 2024 [2025-05-14]. https://unfccc.int/process-and-meetings/the-paris-agreement/nationally-determined-contributions-ndcs/2024-ndc-synthesis-report |
| [2] | British Petroleum (BP). BP energy outlook[R/OL]. 2023 [2025-05-14]. https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/energy-outlook/bp-energy-outlook-2023.pdf |
| [3] |
Fu R, Peng K, Wang P, et al. Tracing metal footprints via global renewable power value chains[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14 (1): 3703
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39356-x pmid: 37349289 |
| [4] |
Wang Z, Peng H, Meng J, et al. Enormous inter-country inequality of embodied carbon emissions and its driving forces in South America[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2024, 89: 102944
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2024.102944 URL |
| [5] |
邢贞成, 王济干, 冯奎双, 等. 国际贸易中碳排放与增加值的虚拟转移及其不公平性研究[J]. 世界地理研究, 2023, 32 (8): 16-24, 138.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2023.08.2021735 |
|
Xing Z C, Wang J G, Feng K S, et al. Study on virtual transfer of carbon emissions and value added in international trade and its inequality[J]. World Regional Studies, 2023, 32 (8): 16-24, 138 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2023.08.2021735 |
|
| [6] |
史江兰, 凌昕怡, 范梦涵, 等. 生产和消费双重视角下中国省域隐含碳转移研究[J]. 地域研究与开发, 2024, 43 (6): 165-170.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2363.2024.06.024 |
| Shi J L, Ling X Y, Fan M H, et al. Inter-regional transfer of China’s embodied carbon from production-and consumption-based perspectives[J]. Areal Research and Development, 2024, 43 (6): 165-170 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
宋文明, 汤淑娟, 邹嘉龄, 等. 中国南北差距扩大背景下区域间隐含碳和增加值流动[J]. 资源科学, 2024, 46 (11): 2163-2177.
doi: 10.18402/resci.2024.11.06 |
|
Song W M, Tang S J, Zou J L, et al. Interregional flows of embodied carbon and value-added in the context of widening north-south disparities in China[J]. Resources Science, 2024, 46 (11): 2163-2177 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.18402/resci.2024.11.06 |
|
| [8] |
Mi Z, Zheng J, Meng J, et al. Carbon emissions of cities from a consumption-based perspective[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 235: 509-518
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.10.137 |
| [9] |
杨子涵, 彭宝玉, 孙君. 京津冀地区产业链空间网络及其隐含碳排放研究[J]. 地理科学进展, 2024, 43 (2): 215-230.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2024.02.002 |
|
Yang Z H, Peng B Y, Sun J. Spatial network of industrial chains and their embodied carbon emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Progress in Geography, 2024, 43 (2): 215-230 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2024.02.002 |
|
| [10] | 戴奇乐, 牛仕成, 牛亮. 中国产业部门隐含碳排放测算与关联效应研究[J]. 价格理论与实践, 2024 (7): 77-83. |
| Dai Q L, Niu S C, Niu L. Study on calculation and correlation effect of industrial embodied carbon emission created by China’s industrial sector[J]. Price: Theory & Practice, 2024 (7): 77-83 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 王敏, 吴映梅, 王洋, 等. 中国行业碳排放动态变化特征及网络结构演化[J]. 环境科学, 2024, 45 (10): 5591-5600. |
| Wang M, Wu Y M, Wang Y, et al. Characterization of industrial carbon emission dynamics and network structure evolution in China[J]. Environmental Science, 2024, 45 (10): 5591-5600 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] |
Lu C, Du Q, Li J T, et al. Trade embodied CO2 transfers from transportation sector: a nested multi-scale input-output perspective[J]. Transportation Research Part D, 2023, 119: 103727
doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2023.103727 URL |
| [13] |
Coester A, Hofkes W M, Papyrakis E. Cross-border electricity transfers in the case of differentiated renewable energy sources: a simulation analysis for Germany and Spain[J]. Energy Reports, 2024, 11: 3792-3814
doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2024.02.045 URL |
| [14] | Vicent A, Emilio P, Pablo R D. The driving factors of CO2 emissions from electricity generation in Spain: a decomposition analysis[J]. Energy Sources, Part B: Economics, Planning, and Policy, 2022, 17 (1): 1-14 |
| [15] |
Wang J, Li Z M, Wu T, et al. The decoupling analysis of CO2emissions from power generation in Chinese provincial power sector[J]. Energy, 2022, 255: 124488
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.124488 URL |
| [16] |
Rodrigues F J, Wang J, Behrens P, et al. Drivers of CO2 emissions from electricity generation in the European Union 2000-2015[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2020, 133: 110104
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110104 URL |
| [17] |
Su B, Ang W B. Structural decomposition analysis applied to energy and emissions: aggregation issues[J]. Economic Systems Research, 2012, 24 (3): 299-317
doi: 10.1080/09535314.2012.677997 URL |
| [18] |
Luo F, Guo Y, Yao M, et al. Carbon emissions and driving forces of China’s power sector: input-output model based on the disaggregated power sector[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 268: 121925
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121925 URL |
| [19] |
Ma J, Du G, Xie B. CO2 emission changes of China’s power generation system: input-output subsystem analysis[J]. Energy Policy, 2019, 124: 1-12
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2018.09.030 URL |
| [20] | Wang S G, Zhu X J, Song D, et al. Drivers of CO2 emissions from power generation in China based on modified structural decomposition analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 20: 1143-1155 |
| [21] |
Jiang T Y, Yu Y, Jahanger A, et al. Structural emissions reduction of China’s power and heating industry under the goal of “Double Carbon”: a perspective from input-output analysis[J]. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 2022, 31: 346-356
doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2022.03.003 URL |
| [22] |
Yousaf M R, Liao B Q. Analysis of Pakistan’s electricity generation and CO2 emissions: based on decomposition and decoupling approach[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 359: 132074
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132074 URL |
| [23] |
Yu B L, Fang D B, Xiao K, et al. Drivers of renewable energy penetration and its role in power sector’s deep decarbonization towards carbon peak[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 178: 113247
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113247 URL |
| [24] |
Zhao L, Wang K, Yi H, et al. Carbon emission drivers of China’s power sector and its transformation for global decarbonization contribution[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 376: 124258
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.124258 URL |
| [25] | Leontief W W, Ford D. Air pollution and the economic structure: empirical results of input-output comparisons[M]. Cambridge: Harvard University, 1972 |
| [26] |
Chen W M, Zhang Z J, Chen K Y. Inter-regional economic-environmental correlation effects of power sector in China[J]. Energy, 2023, 278: 127764
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.127764 URL |
| [27] | 王火根, 汪钰婷, 肖丽香. 基于IO-SDA法的2020—2060年中国行业CO2排放预测与分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2024, 44 (3): 1743-1755. |
| Wang H G, Wang Y T, Xiao L X. Forecast and analysis of China’s industrial CO2 emissions from 2020 to 2060 based on the IO-SDA method[J]. China Environmental Science, 2024, 44 (3): 1743-1755 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 闫辉, 何晓晴, 张磊. 基于结构分解分析的中国建筑业碳增长影响因素识别[J]. 工程管理学报, 2024, 38 (1): 42-47. |
| Yang H, He X Q, Zhang L. Identification of influencing factors for the carbon growth in China’s construction industry based on structural decomposition analysis[J]. Journal of Engineering Management, 2024, 38 (1): 42-47 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | Wang J, Yang S, Dong K, et al. Assessing embodied carbon emission and its drivers in China’s ICT sector: multi-regional input-output and structural decomposition analysis[J]. Energy Policy, 2024, 186: 114008. DOI:10.1016/J.ENPOL.2024.114008 |
| [30] |
Zhou Z, Wang X K, Lu L, et al. Air pollution leakage embodied in international trade: Foreign-investment-contribution-based accounting and structural decomposition analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2025, 504: 145407
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145407 URL |
| [31] | 陆轩慧, 金轩怡, 房德琳. 省际贸易含大气污染物转移特征及驱动力分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2025, 45 (2): 1148-1161. |
| Lu X H, Jin X Y, Fang D L. Analysis of implicit air pollutant transfer and drivers of interprovincial trade in China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2025, 45 (2): 1148-1161 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 兰静, 司含华. 中国能源消费及碳排放变化的驱动因素分析[J]. 价值工程, 2023, 42 (34): 163-165. |
| Lan J, Si H H. Drivers of change in energy consumption and carbon emission in China[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42 (34): 163-165 (in Chinese) | |
| [33] |
Yuan Q, Wang Q, Zhang M. Tracing changes in manufacturing-related carbon emissions: a structural decomposition analysis from the perspective of China[J]. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 2024, 71: 568-581
doi: 10.1016/j.strueco.2024.09.003 URL |
| [34] | 彭水军, 张文城, 孙传旺. 中国生产侧和消费侧碳排放量测算及影响因素研究[J]. 经济研究, 2015, 50 (1): 168-182. |
| Peng S J, Zhang W C, Sun C W. China production-based and consumption-based carbon emissions and their determinants[J]. Economic Research Journal, 2015, 50 (1): 168-182 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | Konstantin S, Richard W, Tatyana B, et al. EXIOBASE 3 (3.8.2)[DB/OL]. 2021 [2025-03-02]. https://zenodo.org/records/5589597 |
| [36] | Meng J, Mi Z, Guan D, et al. The rise of south-south trade and its effect on global CO2 emissions[J]. Nature Communations, 2018, 9: 1871 |
| [37] | The United Nations Statistics Division. National accounts:analysis of Main Aggregates (AMA)[EB/OL]. 2024 [2025-02-10]. https://unstats.un.org/unsd/snaama/ |
| [38] |
Guo C Y, Chen C, Dong C, et al. Carbon footprints and decarbonization potential in the global renewable power sector[J]. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 2025, 58: 100-122
doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2025.06.012 URL |
| [39] |
Yang Y, Cui Q, Wang H. Assessing the socioeconomic and environmental impacts of China’s power sector changes in 2010-2020[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 364: 123159
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123159 URL |
| [1] | LIU Yuan-Xin, HE Shuo, JIANG Ya-Jing, LUO Xu, YUAN Jia-Hai. Spatial-temporal decomposition of carbon emissions in China’s four major urban agglomerations [J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(2): 231-241. |
| [2] | GAO Yun-Xiang, LI Ke-Ke, ZHANG Wen-Ting, WANG Tian-Wei, LI Shan. Spatio-temporal evolution and projection of urban heat island in China under the shared socioeconomic pathways [J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(4): 431-445. |
| [3] | TAN Xian-Chun, DAI Han-Cheng, GU Bai-He, HUANG Chen, ZHU Kai-Wei, MA Xiao-Tian, YAN Hong-Shuo, LIU Xin-Yuan, ZHU Yan-Lei. Analysis on the key findings related to emission trends and drivers from the IPCC AR6 report [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(5): 538-545. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||