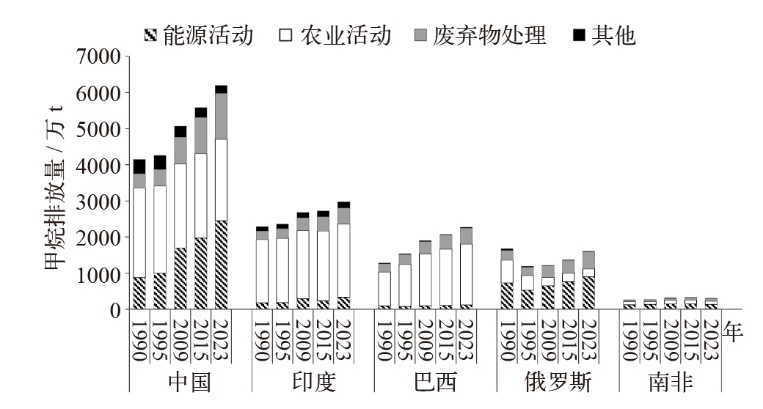
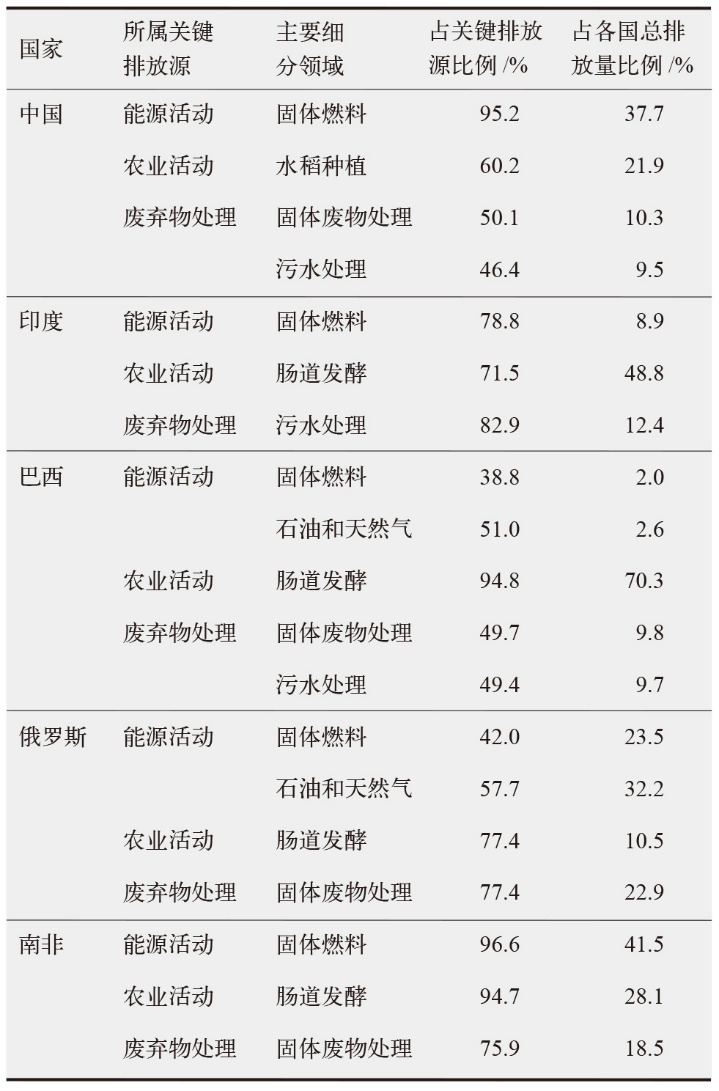
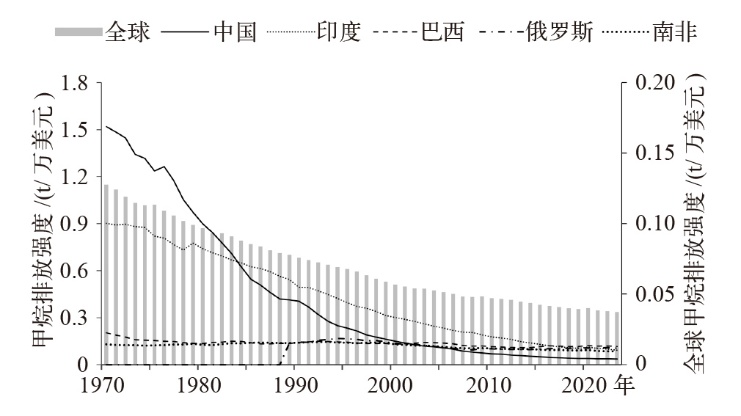
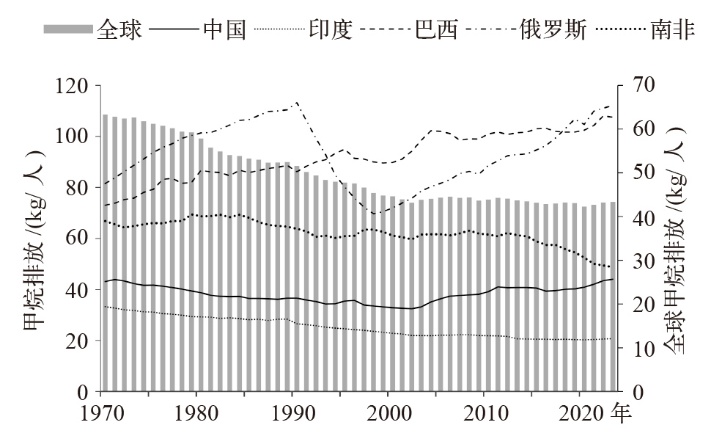
| [1] |
International Energy Agency (IEA). Global methane tracker 2024[R/OL]. 2025 [2025-03-26]. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-methane-tracker-2024
|
| [2] |
UNFCCC. 1/CMA.5-outcome of the first global stocktake[R/OL]. 2023 [2025-04-01]. https://unfccc.int/decisions
|
| [3] |
IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021
|
| [4] |
IPCC. Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation and vulnerability[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022
|
| [5] |
IPCC. Climate change 2022: mitigation of climate change[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022
|
| [6] |
王敏, 杨儒浦, 李丽平. 甲烷排放对近地面臭氧污染的影响: 研究进展及启示[J]. 环境科学研究, 2025, 38 (3): 561-568.
|
|
Wang M, Yang R P, Li L P. The impact of methane on ground-level ozone pollution: research progress and policy implications[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2025, 38 (3): 561-568 (in Chinese)
|
| [7] |
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC). Global methane assessment: 2030 baseline report summary for policy makers[R/OL]. 2022 [2025-03-26]. https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/41108/methane_2030_SPM.pdf?sequence=l&isAllowed=y
|
| [8] |
IEA. Methane tracker[R/OL]. 2024 [2025-04-01]https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/methane-tracker
|
| [9] |
Saunois M, Stavert A R, Poulter B, et al. The global methane budget 2000-2017[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2020, 12 (3): 1561-1623
doi: 10.5194/essd-12-1561-2020
URL
|
| [10] |
IEA. Global methane tracker 2025[R/OL]. 2025 [2025-06-04]. https://www.iea.org/reports/global-methane-tracker-2025
|
| [11] |
Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC). Factsheet: 2024 global methane pledge ministerial[R/OL]. 2024 [2025-04-01]. https://www.ccacoalition.org/news/factsheet-2024-global-methane-pledge-ministerial
|
| [12] |
惠婧璇, 朱松丽. 全球甲烷控排政策措施评述及其对中国的启示和建议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (6): 683-692.
|
|
Hui J X, Zhu S L. Overview on global policies and measures to control methane emissions and its implications for China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (6): 683-692 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
高文康, 胡杰, 马占云, 等. 全球发达国家CH4排放现状及特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (6): 693-703.
|
|
Gao W K, Hu J, Ma Z Y, et al. Global methane emission status and characteristics based on greenhouse gas inventory in UNFCCC Annex I countries[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (6): 693-703 (in Chinese)
|
| [14] |
王杰, 李治国, 谷继建. 金砖国家碳排放与经济增长脱钩弹性及驱动因素: 基于Tapio脱钩和LMDI模型的分析[J]. 世界地理研究, 2021, 30 (3): 501-508.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.03.2019470
|
|
Wang J, Li Z G, Gu J J. Decoupling analysis between energy consumption and economic growth in BRICS countries: based on Tapio decoupling and LMDI model analysis[J]. World Regional Studies, 2021, 30 (3): 501-508 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9479.2021.03.2019470
|
| [15] |
杨儒浦, 冯相昭, 王敏, 等. G7 国家固体废弃物处理领域甲烷排放驱动力分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (5): 573-581.
|
|
Yang R P, Feng X Z, Wang M, et al. Analysis on the driving forces of methane emissions from solid waste treatment in G7 countries[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (5): 573-581 (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
马占云, 李照濛, 刘舒乐, 等. 全球甲烷控排对中国的启示[J]. 中国能源, 2023 (1-2): 20-30.
|
|
Ma Z Y, Li Z M, Liu S L, et al. Global experiences in mitigating methane emissions and its implication for China[J]. Energy of China, 2023 (1-2): 20-30 (in Chinese)
|
| [17] |
张建宇, 秦虎, 汪维. 中国开展甲烷排放控制关键问题与建议[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2019, 44 (5): 4.
|
|
Zhang J Y, Qin H, Wang W. Key issues and suggestions on methane emission control in China[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2019, 44 (5): 4 (in Chinese)
|
| [18] |
冯相昭. 英国重点领域甲烷排放控制经验及对我国的启示与建议[J]. 环境影响评价, 2023, 45 (3): 17-21.
|
|
Feng X Z. UK’s policy practices in reducing methane emission in key sectors and its implications for China[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2023, 45 (3): 17-21 (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
龙凤, 董战峰, 连超, 等. 甲烷排放控制的国际经验及对我国的启示[J]. 环境保护, 2023, 51 (1): 68-71.
|
|
Long F, Dong Z F, Lian C, et al. International experience of methane emission control and its inspiration to China[J]. Environmental Protection, 2023, 51 (1): 68-71 (in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
Tapio P. Towards a theory of decoupling: degrees of decoupling in the EU and the case of road traffic in Finland between 1970 and 2001[J]. Transport Policy, 2005, 12 (2): 137-151
doi: 10.1016/j.tranpol.2005.01.001
URL
|
| [21] |
王敏, 冯相昭, 安祺, 等. 基于脱钩指数和LMDI的青海省绿色低碳发展策略研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607.
|
|
Wang M, Feng X Z, An Q, et al. Study on green and low-carbon development in Qinghai province based on decoupling index and LMDI[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (5): 598-607 (in Chinese)
|
| [22] |
丁利杰, 朱泳丽. 中国交通运输业碳排放区域差异及脱钩效应[J]. 东南学术, 2023 (4): 162-174.
|
|
Ding L J, Zhu Y L. Regional differences in carbon emissions and decoupling effects of China’s transportation industry[J]. Southeast Academic, 2023 (4): 162-174 (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
Crippa M, Guizzardi D, Pagani F, et al. GHG emissions of all world countries: JRC/IEA 2024 report[R/OL]. 2024 [2025-04-01]. https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2760/4002897, JRC138862
|
| [24] |
World Bank Group. GDP (constant 2015 US$)[DB/OL]. 2025 [2025-03-21]. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD?view=chart
|
| [25] |
UNFCCC. Documents and decisions-submissions-reports[R/OL]. 2005 [2025-04-23]. https://unfccc.int/reports?f%5B0%5D=document_type%3A4233
|
 ), YANG Ru-Pu(
), YANG Ru-Pu( ), LI Li-Ping, WANG Min
), LI Li-Ping, WANG Min