气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 839-852.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.063
绿色电力证书对城市屋顶光伏经济性及地方可再生能源消纳目标的影响
- 1 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)经济管理学院,深圳 518055
2 深圳市人文社会科学重点研究基地哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)碳达峰碳中和技术、政策与管理研究中心,深圳 518055
-
收稿日期:2025-03-16修回日期:2025-06-04出版日期:2025-11-30发布日期:2025-11-11 -
通讯作者:刘俊伶,女,副教授,liujunling@hit.edu.cn -
作者简介:段舒扬,女,本科生,210710113@stu.hit.edu.cn -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年基金“1.5℃目标约束下中国能源技术系统高精度与双向能流反馈建模研究”(72004043);深圳市基础研究专项面上项目“双碳目标下深圳市分布式光伏发展模式比较研究”(JCYJ20220531095408018);政策与管理研究中心资助项目
Impact of Green Electricity Certificate on the economic viability of urban rooftop photovoltaics and local renewable energy consumption targets
DUAN Shu-Yang1( ), WU Jia-Qi1, LIU Jun-Ling1,2(
), WU Jia-Qi1, LIU Jun-Ling1,2( )
)
- 1 School of Economics and Management, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518055, China
2 Shenzhen Humanities & Social Sciences Key Research Base for Carbon Emission Peaking and Carbon Neutral Technology, Policy, and Management, Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), Shenzhen 518055, China
-
Received:2025-03-16Revised:2025-06-04Online:2025-11-30Published:2025-11-11
摘要:
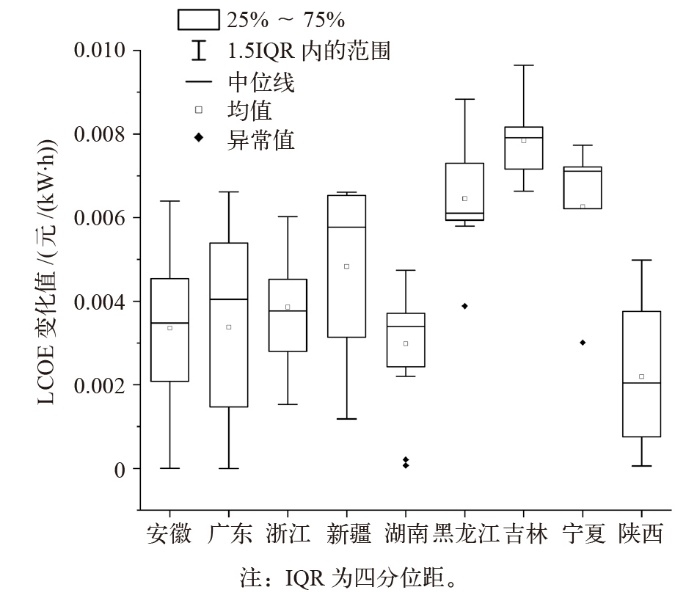
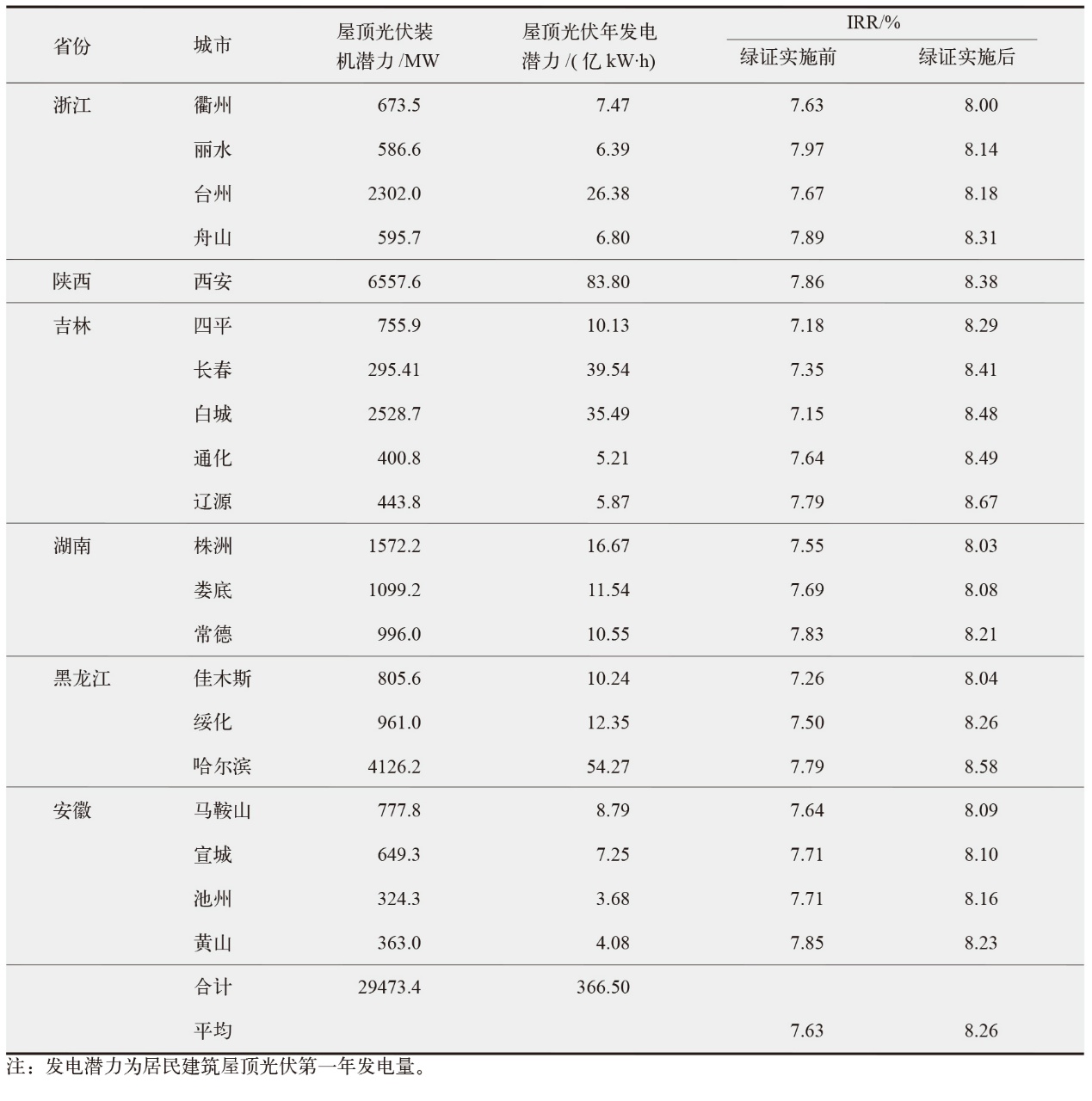
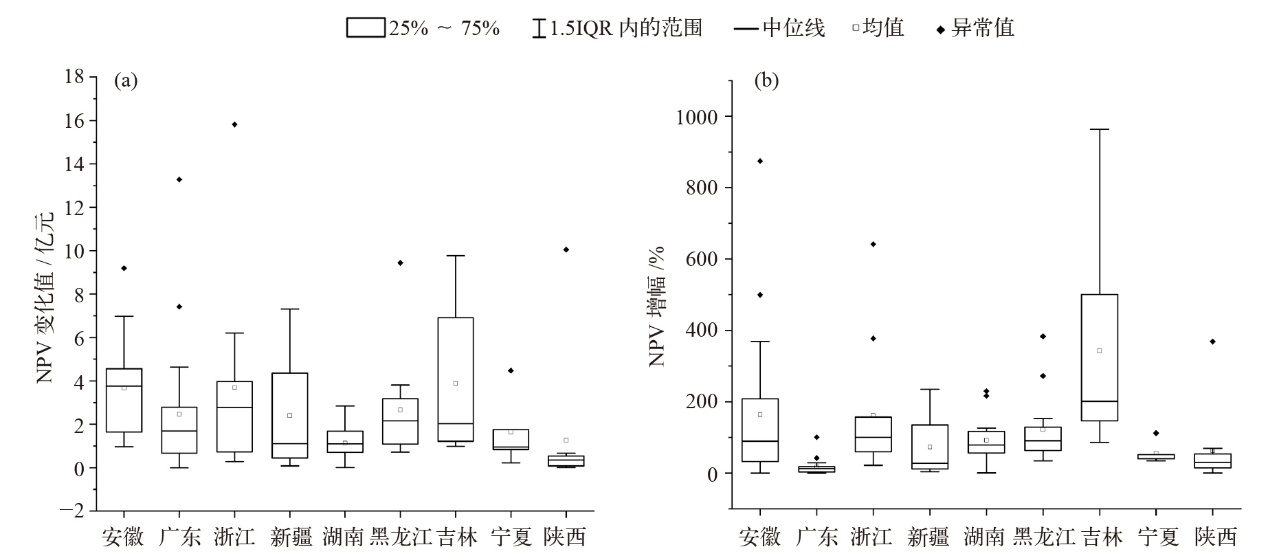
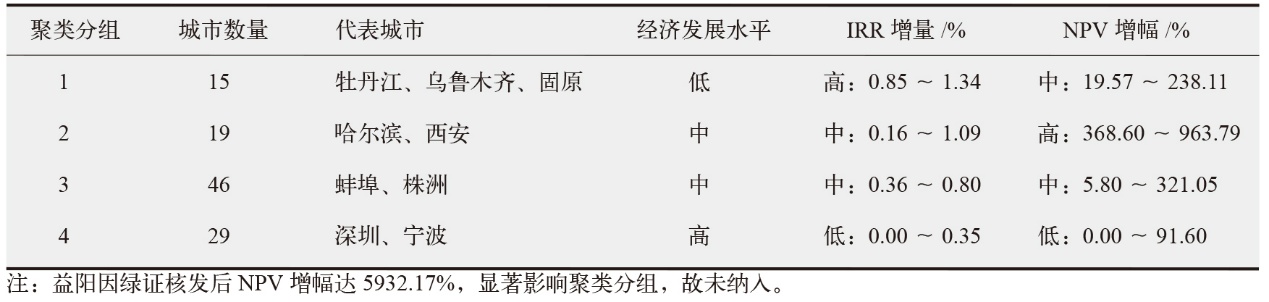
绿色电力证书(绿证)为屋顶光伏提供了经济激励,显著提升了投资吸引力,并通过纳入节能评价考核,为地方政府推动可再生能源开发提供了动力。文中选取了9个省份的100个城市,结合当地气象条件、屋顶面积、用电负荷与光伏政策,对工商业与居民建筑开展仿真建模与成本收益测算。结果表明,绿证显著提升了屋顶光伏项目的经济性,20%的城市由非经济性转为经济性,所有城市的净现值平均增加2.15亿元,内部收益率和动态回收期也有所改善。其中,居民建筑因自耗率较低,更多上网电量参与绿证交易,因此收益提升更显著。从地区影响来看,经济欠发达地区由于自耗率较低,绿证收益更高,表明绿证有助于缩小城市间屋顶光伏经济性差异,推动区域可再生能源的平衡发展。从节能评价考核视角看,屋顶光伏本地消纳对消纳责任权重的贡献率中位数达到58.75%(1.25%~264.23%),显示出屋顶光伏在实现地方可再生能源消纳目标中的重要作用。此外,敏感性分析表明,绿证价格波动对光伏自耗率较低城市的项目收益影响更大。研究为各省优化分布式光伏部署及落实可再生能源电力消纳责任权重目标提供了科学依据。
引用本文
段舒扬, 吴佳琪, 刘俊伶. 绿色电力证书对城市屋顶光伏经济性及地方可再生能源消纳目标的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(6): 839-852.
DUAN Shu-Yang, WU Jia-Qi, LIU Jun-Ling. Impact of Green Electricity Certificate on the economic viability of urban rooftop photovoltaics and local renewable energy consumption targets[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 839-852.
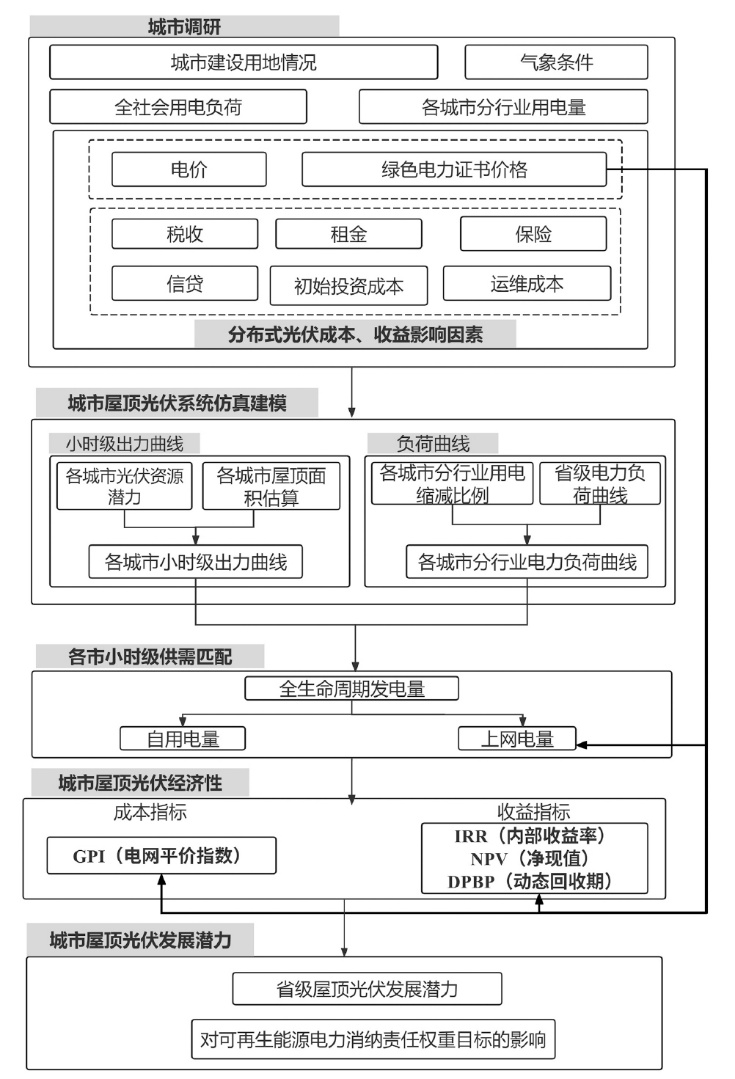
图1 绿证对城市屋顶光伏经济性及可再生能源消纳的影响分析框架
Fig. 1 Analysis framework for the impact of Green Electricity Certificate (GEC) on the economic viability and renewable energy consumption of urban rooftop photovoltaics
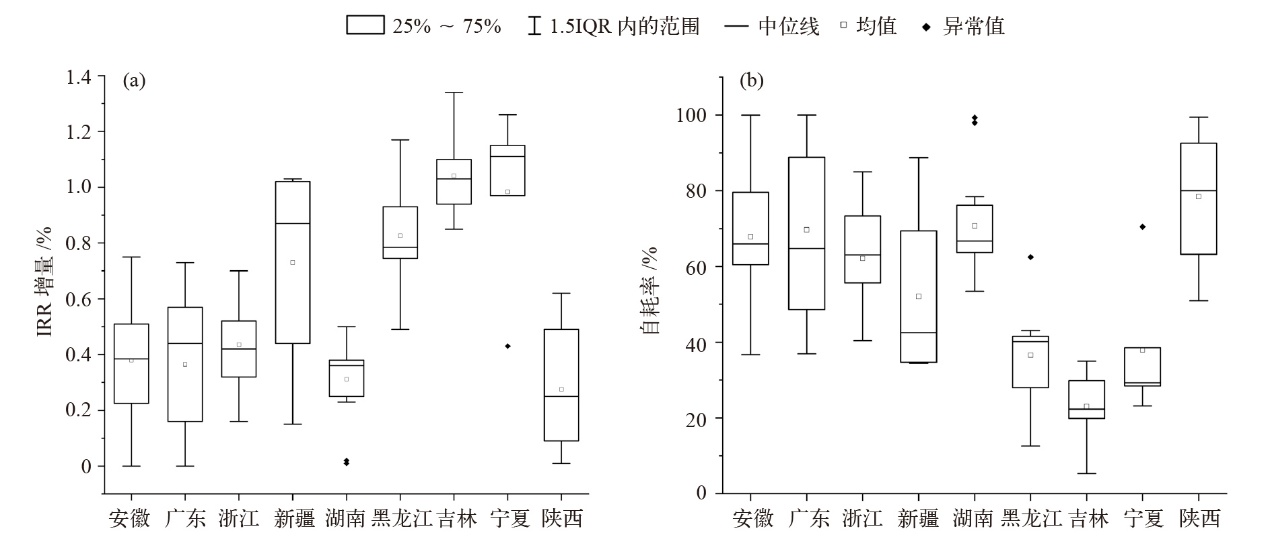
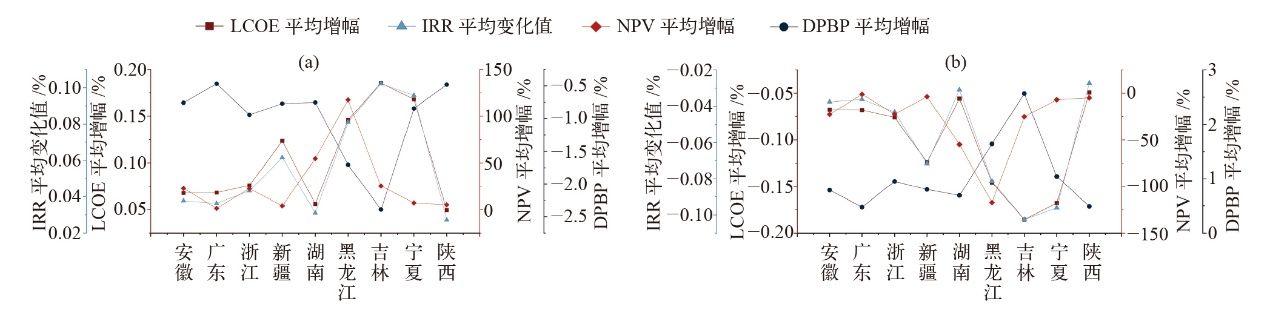
图3 绿证实施后居民建筑IRR增量(a)及与自耗率关系(b)
Fig. 3 Incremental change of the IRR of residential buildings (a) after the implementation of GEC and their self-consumption rates (b)
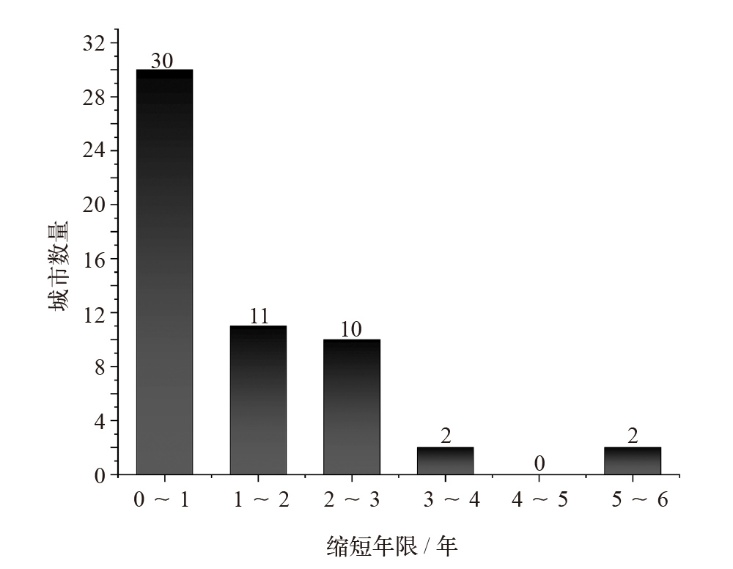
图5 绿证实施前后居民建筑的DPBP变化情况 注:图为绿证核发前DPBP<25年的城市(共55个城市)的缩短年限分布。
Fig. 5 Changes in the Dynamic Investment Pay-back Period (DPBP) of residential buildings after the implementation of GEC
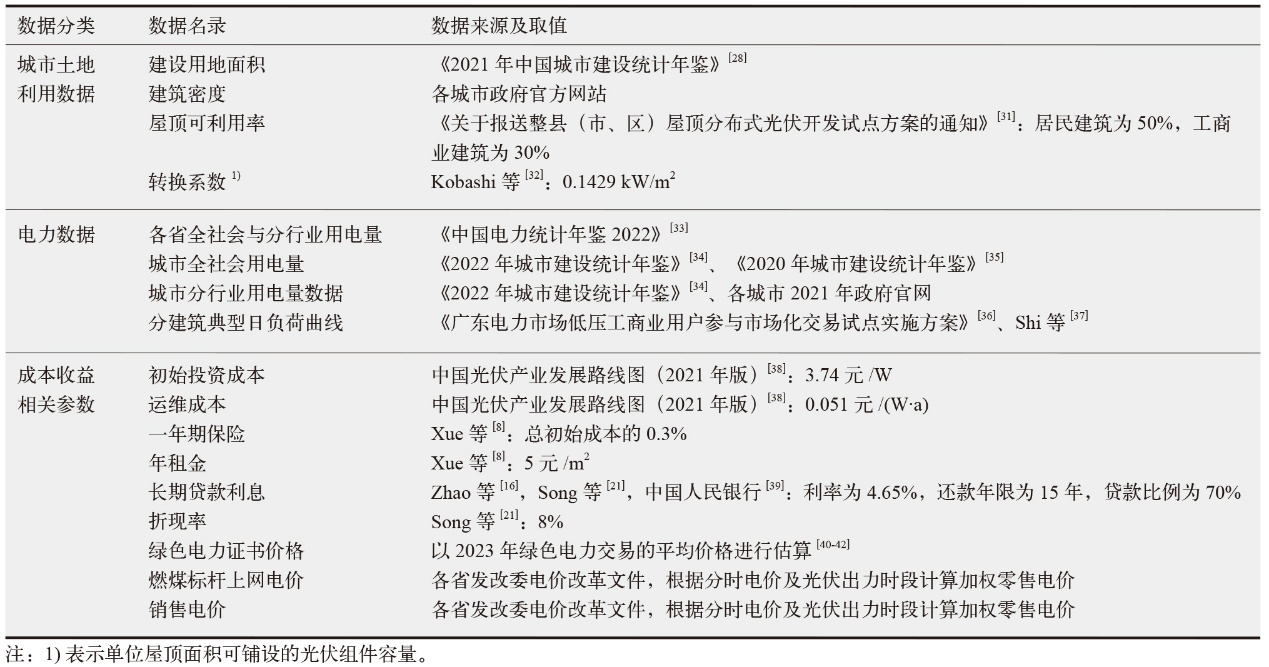
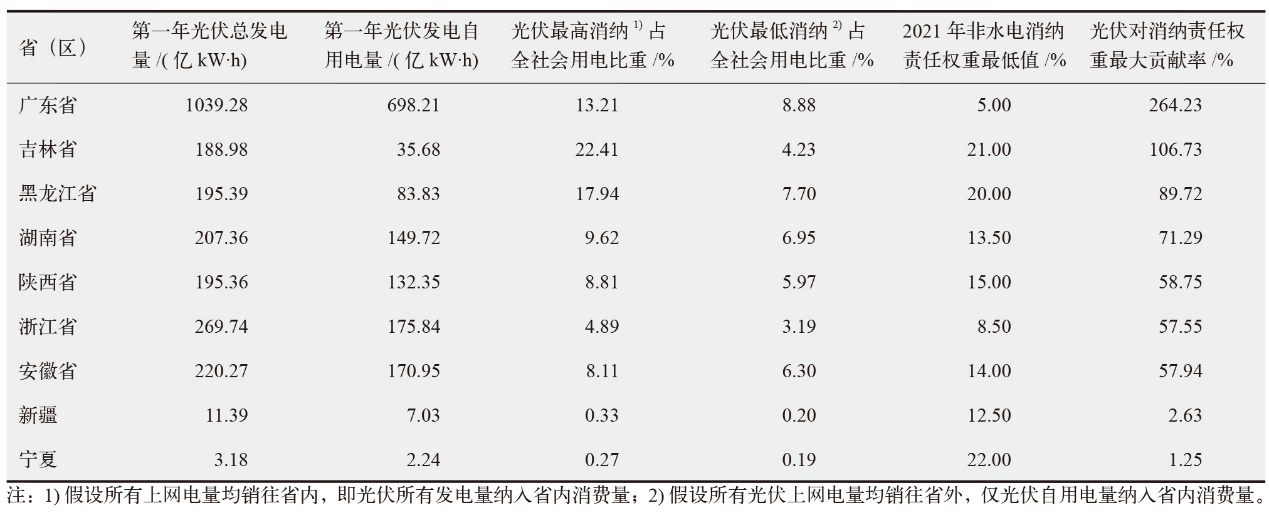 |
表4 各省(区)屋顶光伏对可再生能源电力消纳责任权重目标的潜在贡献
Table 4 Potential contribution of residential and commercial rooftop photovoltaics to the renewable energy power consumption obligation targets
 |
| [1] |
Wang T T, Wang Y H, Wang K, et al. Five-dimensional assessment of China’s centralized and distributed photovoltaic potential: from solar irradiation to CO2 mitigation[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 356: 122326
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122326 URL |
| [2] |
Qiu T Z, Wang L C, Lu Y B, et al. Potential assessment of photovoltaic power generation in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 154: 111900
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111900 URL |
| [3] | 国家能源局. 国家能源2024年第四季度新闻发布会文字实录[EB/OL]. 2024 [2024-11-02]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-10/31/c_1310787069.htm. |
| National Energy Administration. Transcript of the press conference on energy situation in the fourth quarter of 2024[EB/OL]. 2024 [2024-11-02]. https://www.nea.gov.cn/2024-10/31/c_1310787069.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 关于加强绿色电力证书与节能降碳政策衔接大力促进非化石能源消费的通知[EB/OL]. 2024 [2024-08-28]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202402/t20240202_1363857_ext.html. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. Notice on strengthening the connection between green electricity certificates and energy conservation & carbon reduction policies to vigorously promote non-fossil energy consumption[EB/OL]. 2024 [2024-08-28]. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202402/t20240202_1363857_ext.html (in Chinese) | |
| [5] |
柳君波, 张静静, 徐向阳, 等. 中国城市分布式光伏发电经济性与区域利用研究[J]. 经济地理, 2019, 39 (10): 54-61.
doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.10.008 |
|
Liu J B, Zhang J J, Xu X Y, et al. Economy and regional utilization of urban distributed photovoltaic power generation in China[J]. Economic Geography, 2019, 39 (10): 54-61 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2019.10.008 |
|
| [6] |
Ramírez-Sagner G, Mata-Torres C, Pino A, et al. Economic feasibility of residential and commercial PV technology: the Chilean case[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 111: 332-343
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2017.04.011 URL |
| [7] |
王怀斌. 基于资源与电价的分布式光伏项目经济性研究[J]. 经济地理, 2023, 43 (12): 135-142.
doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.12.013 |
| Wang H B. Economic evaluation of distributed photovoltaic power plants: based on regional solar resources and electricity prices[J]. Economic Geography, 2023, 43 (12): 135-142 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
Xue L Y, Liu J L, Lin X J, et al. Assessing urban rooftop PV economics for regional deployment by integrating local socioeconomic, technological, and policy conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 353: 122058
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.122058 URL |
| [9] |
Pillot B, De Siqueira S, Dias J B. Grid parity analysis of distributed PV generation using Monte Carlo approach: the Brazilian case[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 127: 974-988
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.032 URL |
| [10] |
Joshi S, Mittal S, Holloway P, et al. High resolution global spatiotemporal assessment of rooftop solar photovoltaics potential for renewable electricity generation[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12 (1): 1-15
doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20314-w |
| [11] |
Breyer C, Gerlach A. Global overview on grid-parity[J]. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2013, 21 (1): 121-136
doi: 10.1002/pip.v21.1 URL |
| [12] |
Yan J Y, Yang Y, Elia Campana P, et al. City-level analysis of subsidy-free solar photovoltaic electricity price, profits and grid parity in China[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4 (8): 709-717
doi: 10.1038/s41560-019-0441-z |
| [13] |
Hagerman S, Jaramillo P, Morgan M G. Is rooftop solar PV at socket parity without subsidies?[J]. Energy Policy, 2016, 89: 84-94
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2015.11.017 URL |
| [14] |
Orioli A, Di Gangi A. Six-years-long effects of the Italian policies for photovoltaics on the grid parity of grid-connected photovoltaic systems installed in urban contexts[J]. Energy, 2017, 130: 55-75
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.04.069 URL |
| [15] |
Zou H Y, Du H B, Brown M A, et al. Large-scale PV power generation in China: a grid parity and techno-economic analysis[J]. Energy, 2017, 134: 256-268
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2017.05.192 URL |
| [16] |
Zhao X G, Wang Z. Technology, cost, economic performance of distributed photovoltaic industry in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019, 110: 53-64
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2019.04.061 URL |
| [17] |
邵汉桥, 张籍, 张维. 分布式光伏发电经济性及政策分析[J]. 电力建设, 2014, 35 (7): 51-57.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7229.2014.07.009 |
| Shao H Q, Zhang J, Zhang W. Economy and policy analysis of distributed photovoltaic generation[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2014, 35 (7): 51-57 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Yuan J H, Sun S H, Zhang W, et al. The economy of distributed PV in China[J]. Energy, 2014, 78: 939-949
doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.10.091 URL |
| [19] |
Han M Y, Xiong J, Wang S Y, et al. Chinese photovoltaic poverty alleviation: geographic distribution, economic benefits and emission mitigation[J]. Energy Policy, 2020, 144: 111685
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2020.111685 URL |
| [20] | 罗西, 刘加平. 居住建筑分布式光伏发电系统经济性分析[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报 (自然科学版), 2015, 47 (3): 437-441. |
| Luo X, Liu J P. Economic analysis of residential distributed PV project[J]. Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 47 (3): 437-441 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] |
Song P Y, Zhou Y, Yuan J H. Peer-to-peer trade and the economy of distributed PV in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 280: 124500
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124500 URL |
| [22] | 李雅超, 撖晨宇, 肖艳炜, 等. 基于可再生能源经济调度时序模拟的绿色证书市场交易研究[J]. 智慧电力, 2021, 49 (4): 58-65. |
| Li Y C, Han C Y, Xiao Y W, et al. Tradable green certificate market transaction based on economic scheduling timing simulation of renewable energy[J]. Electric Economy & Management, 2021, 49 (4): 58-65 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 王辉, 陈波波, 赵文会, 等. 可再生能源配额制下跨省区电力交易主体最优决策[J]. 电网技术, 2019, 43 (6): 1987-1995. |
| Wang H, Chen B B, Zhao W H, et al. Optimal decision-making of trans-provincial power transaction subjects under renewable portfolio standard[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43 (6): 1987-1995 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 赵新刚, 王晓永. 基于双边拍卖的可再生能源配额制的绿色证书交易机制设计[J]. 可再生能源, 2015, 33 (2): 275-282. |
| Zhao X G, Wang X Y. The design of green certificate trading mechanism based on double auction under the renewable energy quota system[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2015, 33 (2): 275-282 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 董福贵, 时磊. 可再生能源配额制及绿色证书交易机制设计及仿真[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43 (12): 113-121. |
| Dong F G, Shi L. Design and simulation of renewable portfolio standard and tradable green certificate mechanism[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43 (12): 113-121 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Gelaro R, Mccarty W, Suarez M J, et al. The modern-era retrospective analysis for research and applications, Version 2 (MERRA-2)[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30 (14): 5419-5454
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0758.1 URL |
| [27] | King A. SIREN: SEN’s interactive renewable energy network tool[M/OL]. 2018 [2025-02-10]. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-69844-1_19 |
| [28] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2021年中国城市建设统计年鉴[M/OL]. 2022 [2023-09-06]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. China urban construction statistical yearbook 2021[M/OL]. 2022 [2023-09-06]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 人民网. 助力碳达峰、碳中和国家能源局力推整县屋顶分布式光伏开发试点[EB/OL]. 2021 [2024-08-28]. http://finance.people.com.cn/n1/2021/0705/c1004-32149142.html. |
| People’s Daily Online. Assisting carbon peaking and carbon neutrality: national energy administration promotes pilot projects for distributed photovoltaic development on rooftops in counties[EB/OL]. 2021 [2024-08-28]. http://finance.people.com.cn/n1/2021/0705/c1004-32149142.html (in Chinese) | |
| [30] |
Kobashi T, Yoshida T, Yamagata Y, et al. On the potential of “Photovoltaics+ Electric Vehicles” for deep decarbonization of Kyoto’s power systems: techno-economic-social considerations[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 275: 115419
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115419 URL |
| [31] | NREL (National Renewable Energy Laboratory). System Advisor Model (SAM) 2022[EB/OL]. 2022 [2025-02-10]. https://sam.nrel.gov/ |
| [32] |
Kobashi T, Jittrapirom P, Yoshiday T, et al. Solar EV city concept: building the next urban power and mobility systems[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16 (2): 024042
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/abd430 |
| [33] | 中国电力企业联合会. 中国电力统计年鉴2022[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2022. |
| China Electricity Council. China electric power statistical yearbook 2022[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2022年城市建设统计年鉴[M/OL]. 2023 [2024-02-23]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. China urban construction statistical yearbook 2022[M/OL]. 2023 [2024-02-23]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 2020年城市建设统计年鉴[M/OL]. 2021 [2023-09-06]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. China urban construction statistical yearbook 2020[M/OL]. 2021 [2023-09-06]. https://www.mohurd.gov.cn/gongkai/fdzdgknr/sjfb/tjxx/index.html (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | 广东电力交易中心. 《广东电力市场低压工商业用户参与市场化交易试点实施方案》印发[EB/OL]. 中国能源新闻网, 2023 [2025-05-14]. https://www.cpnn.com.cn/news/hy/202310/t20231009_1639821.html. |
| Guangdong Electric Power Trading Center. Implementation plan for low-voltage industrial and commercial users participating in market-oriented transactions in Guangdong electric power market issued[EB/OL]. China Energy News Network, 2023 [2025-05-14]. https://www.cpnn.com.cn/news/hy/202310/t20231009_1639821.html (in Chinese) | |
| [37] |
Shi Z Y, Wu L B, Zhou Y. Predicting household energy consumption in an aging society[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 352: 121899
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121899 URL |
| [38] | 中国光伏行业协会. 《中国光伏产业发展路线图》2021年版[R/OL]. 2022 [2024-02-22]. http://39.105.34.117/road_map/1016.html. |
| China Photovoltaic Industry Association. China PV industry development roadmap (2021 Edition)[R/OL]. 2022 [2024-02-22]. http://39.105.34.117/road_map/1016.html (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 中国人民银行. 贷款市场报价利率 (LPR)[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-09-16]. http://www.pbc.gov.cn/rmyh/108976/index.html#LPR. |
| People’s Bank of China. Loan Prime Rate (LPR)[EB/OL]. 2019 [2021-09-16]. http://www.pbc.gov.cn/rmyh/108976/index.html#LPR (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 德邦证券. 公用事业行业点评: 绿证制度不断完善, 新能源运营商有望受益[R/OL]. 2023 [2025-03-16]. https://pdf.dfcfw.com/pdf/H3_AP202308041593319732_1.pdf?1691177332000.pdf=. |
| Debon Securities. Utility industry review: green certificate system continues to improve, new energy operators expected to benefit[R/OL]. 2023 [2025-03-16]. https://pdf.dfcfw.com/pdf/H3_AP202308041593319732_1.pdf?1691177332000.pdf= (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 周琪, 包晨, 朱一木. IIGF 两会观点:我国绿证交易现状分析及未来展望[EB/OL]. 中央财经大学绿色金融国际研究院, 2022 [2024-08-28]. https://iigf.cufe.edu.cn/info/1012/4871.htm. |
| Zhou Q, Bao C, Zhu Y M. IIGF view on two sessions:analysis of current situation and future outlook of China’s green certificate trading[EB/OL]. International Institute of Green Finance, Central University of Finance and Economics, 2022 [2024-08-28]. https://iigf.cufe.edu.cn/info/1012/4871.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 伍梦尧. 我国可再生能源电力市场交易发展与思考[EB/OL]. 中国能源新闻网, 2024 [2024-03-16]. https://www.escn.com.cn/20240124/a57aec05751c4c21bbf5b98ff4b57216/c.html. |
| Wu M Y. Development and reflection on China’s renewable energy power market transactions[EB/OL]. China Energy News Network, 2024 [2024-03-16]. https://www.escn.com.cn/20240124/a57aec05751c4c21bbf5b98ff4b57216/c.html (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 国家能源局. 国家能源局发布2025年3月全国可再生能源绿色电力证书核发及交易数据[EB/OL]. 2025 [2025-05-20]. https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202504/content_7019898.htm. |
| National Energy Administration. National energy administration releases data on issuance and transaction of national renewable energy green electricity certificates in March 2025[EB/OL]. 2025 [2025-05-20]. https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202504/content_7019898.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 国家发展改革委, 国家能源局. 关于深化新能源上网电价市场化改革促进新能源高质量发展的通知:发改价格 [2025]136号[EB/OL]. 2025 [2025-05-10]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202502/content_7002959.htm. |
| National Development and Reform Commission, National Energy Administration. Notice on deepening the market-oriented reform of new energy grid-connected tariffs to promote high-quality development of new energy (Fagai price [2025] No. 136)[EB/OL]. 2025 [2025-05-10]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/202502/content_7002959.htm (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 徐燕, 裴佳梅, 张欣钰. 中国海上风电制氢技术经济性研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(5): 698-708. |
| [2] | 许传博, 王乐凯, 史超凡, 秦光宇, 刘建国, 刘琦, 刘畅. 多情景下我国氢能产业中长期供需结构及碳排放模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(2): 221-235. |
| [3] | 陶学宗, 林泽宇, 许登豪. 集装箱港口集疏运重卡电动化的经济性分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(3): 351-360. |
| [4] | 陶学宗, 王谦益, 李汉卿. 船舶使用岸电的经济性分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 492-502. |
| [5] | 田惠玲, 朱建华, 李宸宇, 肖文发. 基于自然的解决方案:林业增汇减排路径、潜力与经济性评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(2): 195-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||