气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (2): 221-235.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2024.246
多情景下我国氢能产业中长期供需结构及碳排放模拟研究
许传博1( ), 王乐凯1, 史超凡1, 秦光宇2, 刘建国3, 刘琦4, 刘畅4(
), 王乐凯1, 史超凡1, 秦光宇2, 刘建国3, 刘琦4, 刘畅4( )
)
- 1 华北电力大学经济与管理学院,北京 102206
2 北京建筑大学城市经济与管理学院,北京 102616
3 华北电力大学能源电力创新研究院,北京 102206
4 北京国氢中联氢能科技研究院有限公司,北京 100007
-
收稿日期:2024-09-18修回日期:2024-11-04出版日期:2025-03-30发布日期:2025-02-28 -
通讯作者:刘畅,女,高级工程师,liuchang@h2cn.org -
作者简介:许传博,男,讲师,chuanbo_xu@ncepu.edu.cn -
基金资助:中国氢能联盟2022政研项目(CHA2022RP001);国家自然科学基金项目“面向新型能源体系的氢储能资源协同优化配置及激励机制研究”(72303063);国家自然科学基金重点项目“电-碳-氢融合的综合能源系统长周期平衡机理与规划方法”(U23B20124)
Multi-scenario simulation study on medium- and long-term supply and demand structure and carbon emissions of China’s hydrogen energy industry
XU Chuan-Bo1( ), WANG Le-Kai1, SHI Chao-Fan1, QIN Guang-Yu2, LIU Jian-Guo3, LIU Qi4, LIU Chang4(
), WANG Le-Kai1, SHI Chao-Fan1, QIN Guang-Yu2, LIU Jian-Guo3, LIU Qi4, LIU Chang4( )
)
- 1 School of Economics and Management, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China
2 School of Urban Economics and Management, Beijing University of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Beijing 102616, China
3 Institute of Energy Power Innovation, North China Electric Power University, Beijing 102206, China
4 China Hydrogen Alliance Research Institute, Beijing 100007, China
-
Received:2024-09-18Revised:2024-11-04Online:2025-03-30Published:2025-02-28
摘要:
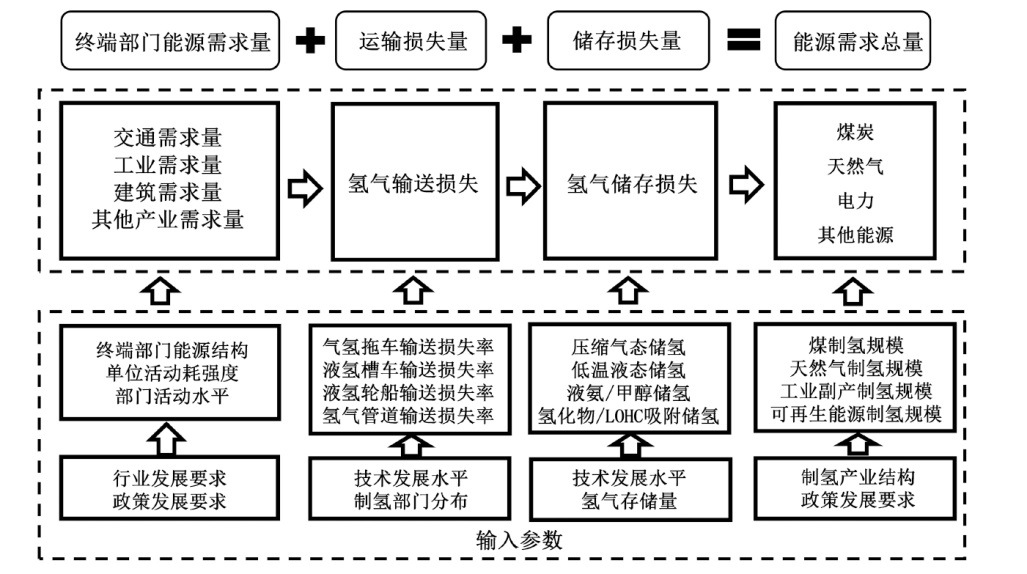
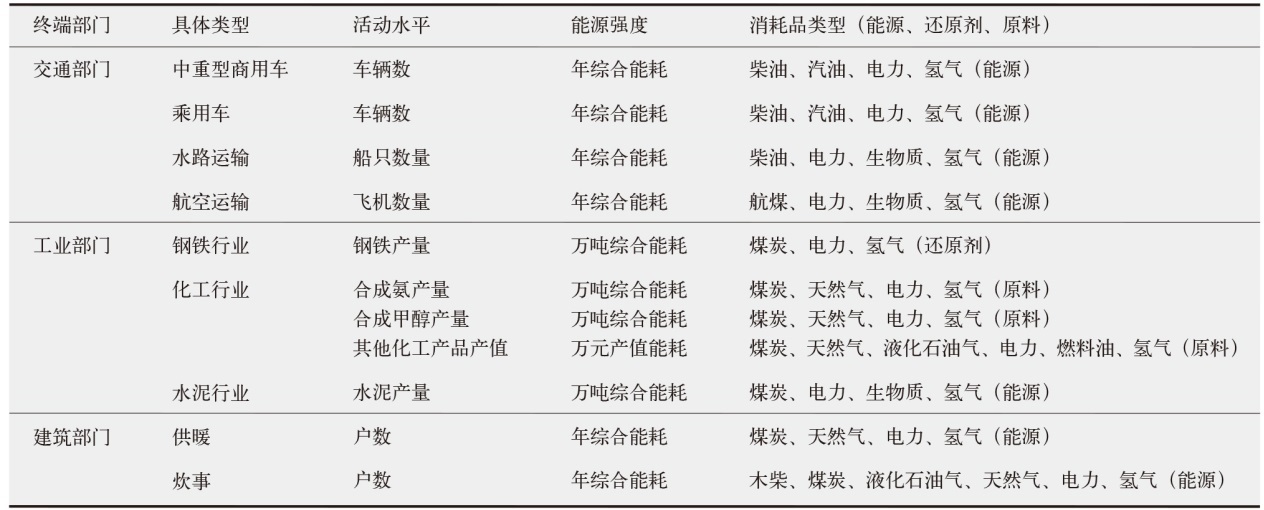
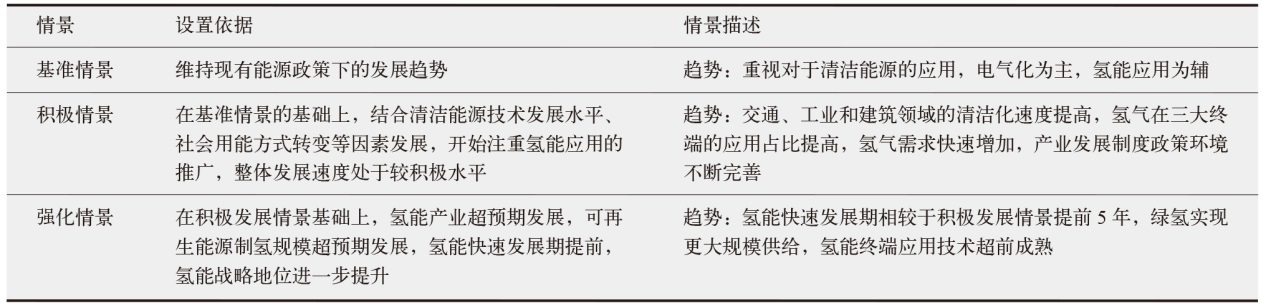
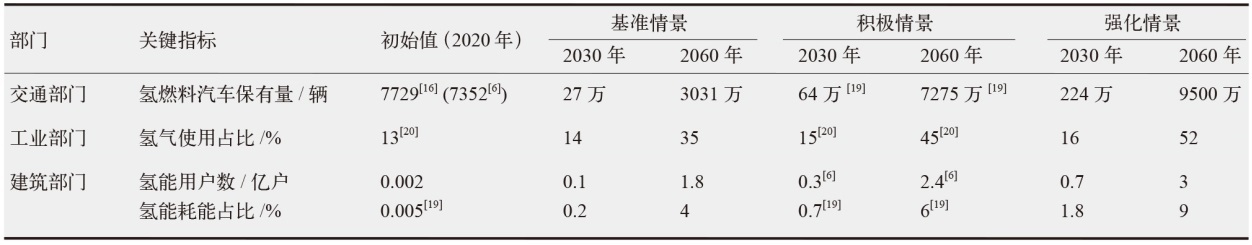
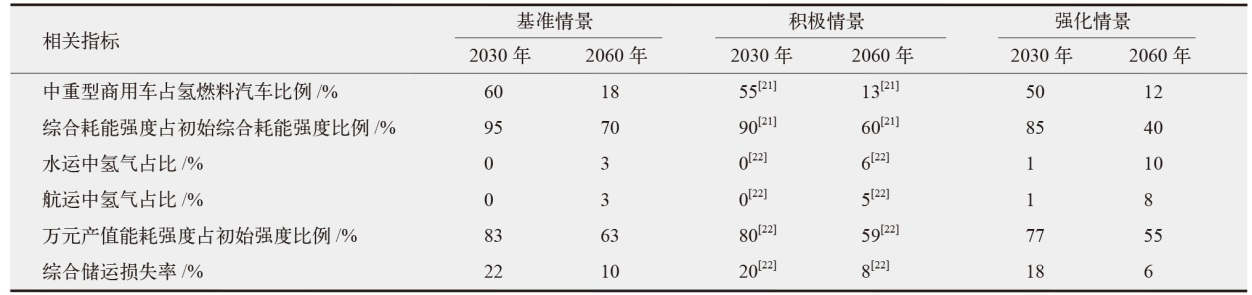
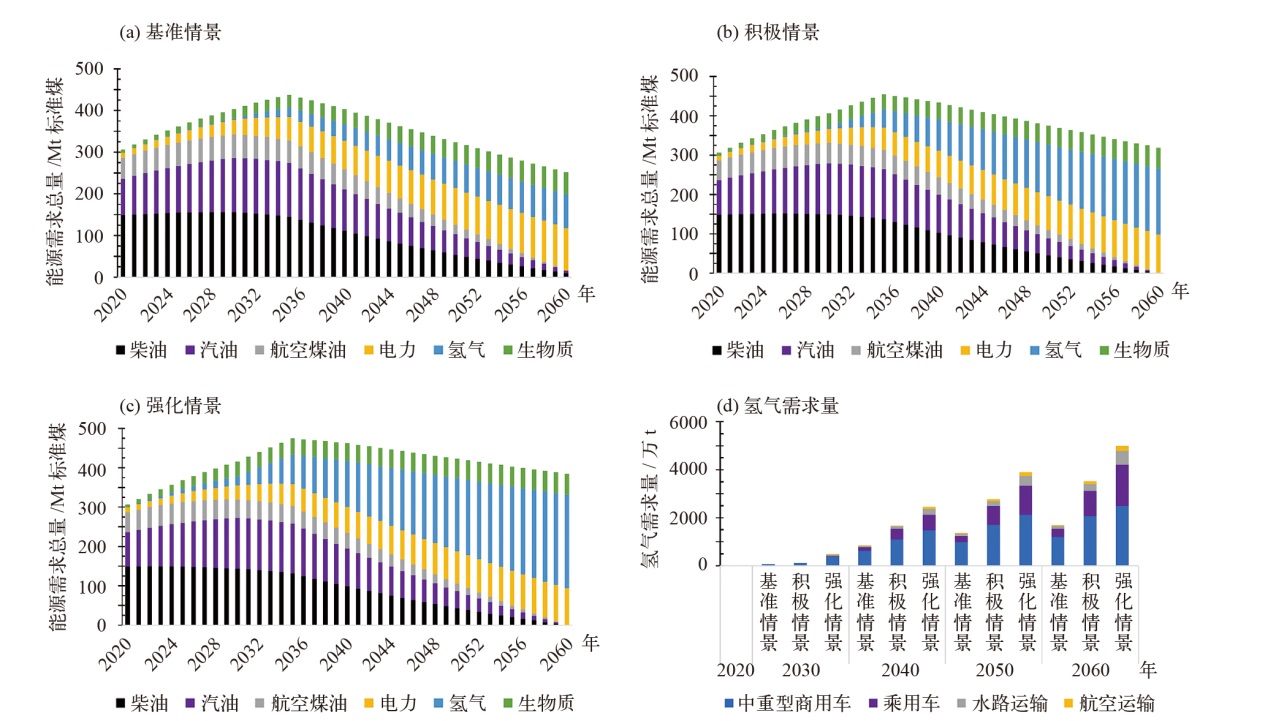
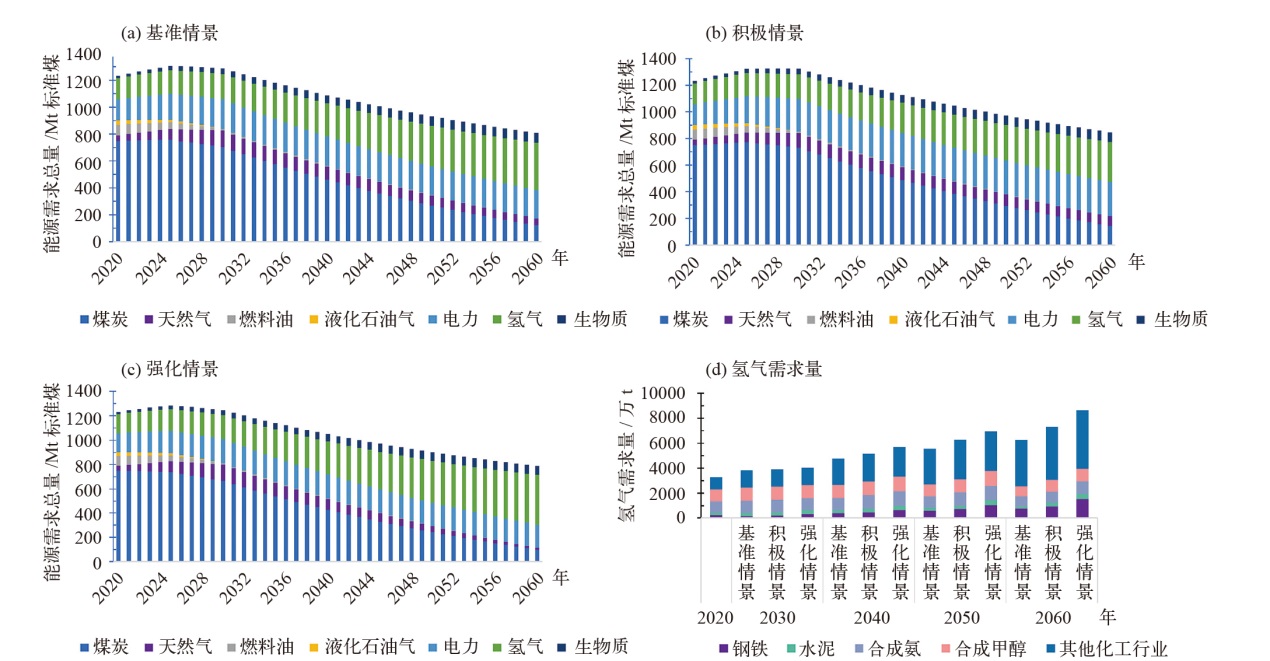
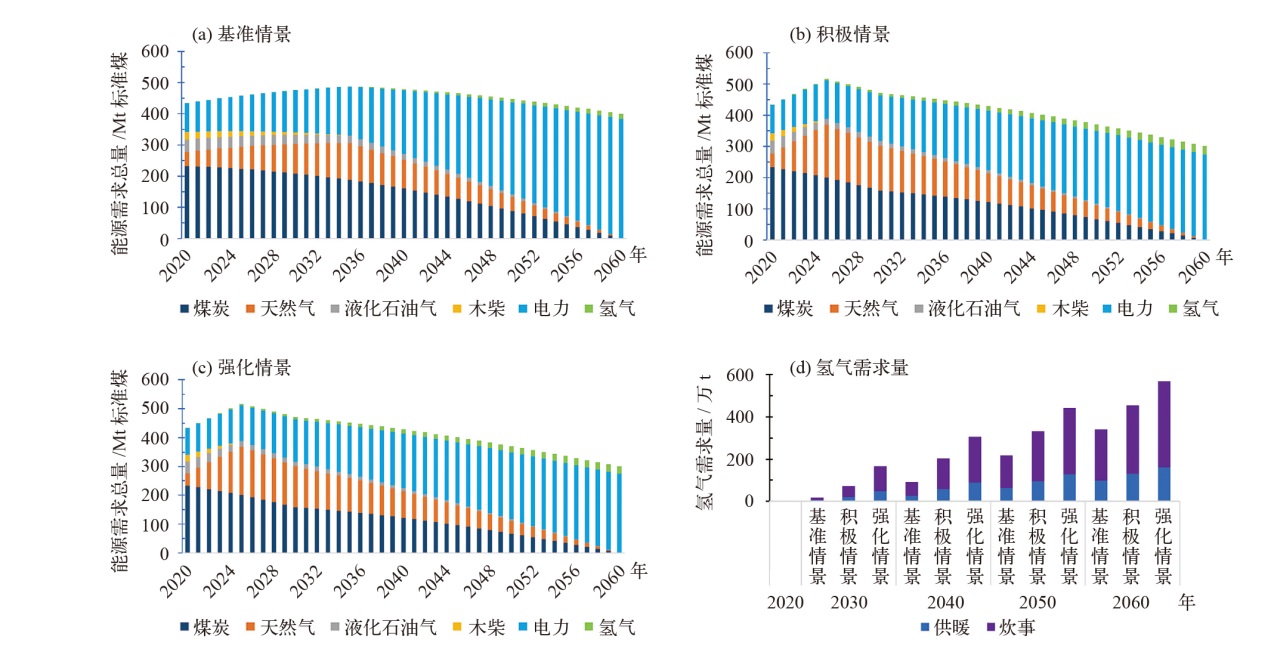
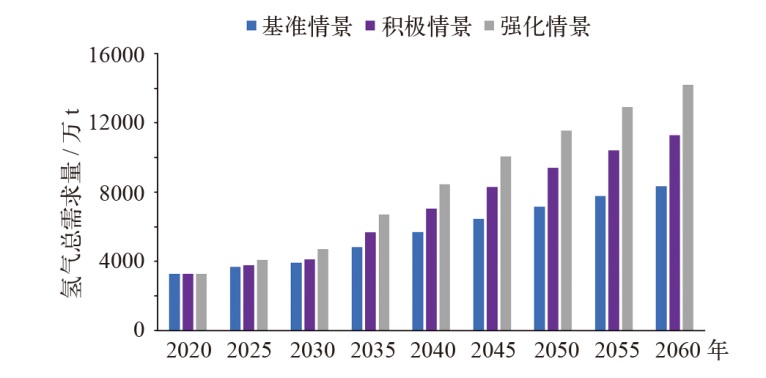
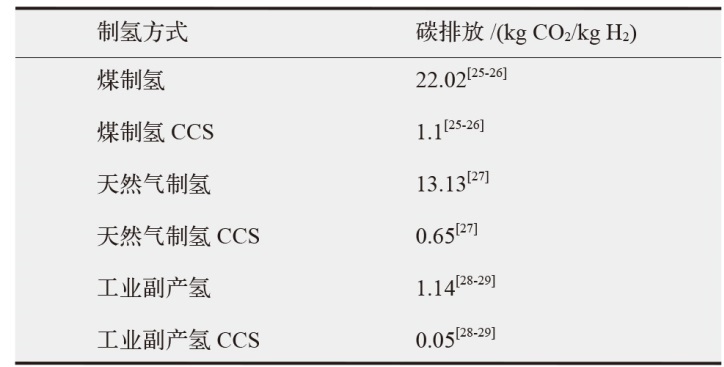
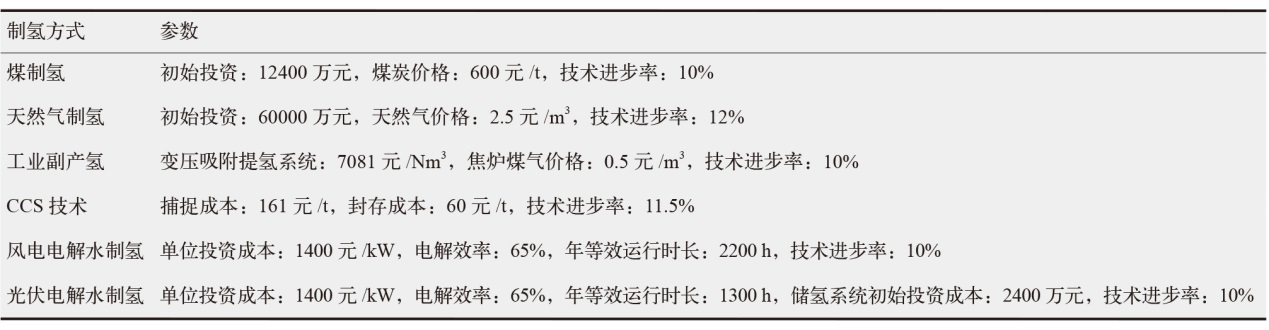
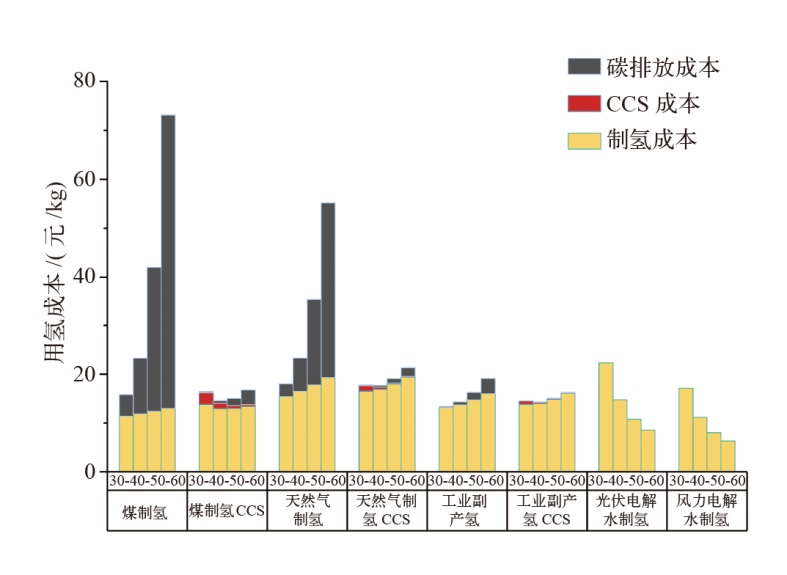
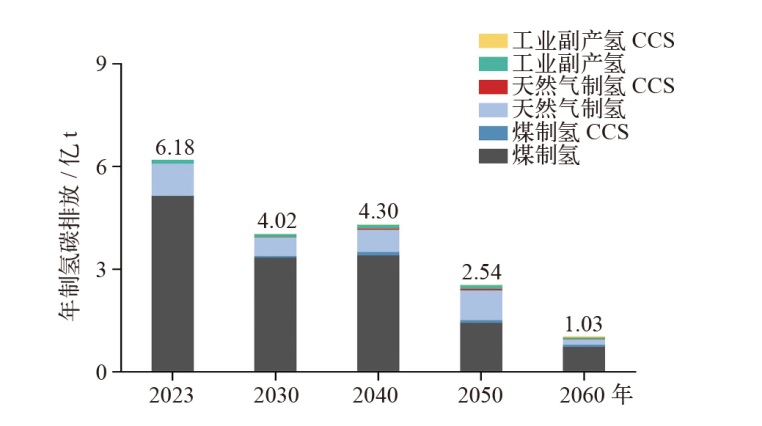
对不同情景下我国氢能中长期供给和需求结构进行模拟预测。首先,设置基准、积极和强化情景,构建自下而上的低排放分析平台(LEAP)模型,对多情景下交通、工业和建筑等终端部门的氢能中长期需求进行预测;其次,测算计及碳排放的8类制氢方式的平准化单位制氢成本(LCOH),并基于成本学习曲线预测未来成本趋势;最后,以最小化制氢成本为目标函数,构建氢能供给结构优化模型,得出2025—2060年各类制氢方式的占比,模拟碳排放演化过程。结果显示:从消费结构来看,工业部门占据了氢能消费的主导地位,2060年积极情景占比65%,交通是重要的氢能消费增长点;从供给结构来看,短期内仍以化石能源制氢供给为主,碳捕集与封存技术起到重要的过渡作用,远期逐渐形成以绿氢供应为主体的制氢结构,2060年可再生能源制氢比例将达到75%;从碳排放来看,得益于制氢产业结构的清洁化转型,碳排放将从2023年的6.18亿t下降至2060年的1.03亿t,2030和2060年关键时点的碳排放下降相较其他时点更显著。基于上述研究结果,提出了促进我国氢能产业高质量发展的政策建议。
引用本文
许传博, 王乐凯, 史超凡, 秦光宇, 刘建国, 刘琦, 刘畅. 多情景下我国氢能产业中长期供需结构及碳排放模拟研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(2): 221-235.
XU Chuan-Bo, WANG Le-Kai, SHI Chao-Fan, QIN Guang-Yu, LIU Jian-Guo, LIU Qi, LIU Chang. Multi-scenario simulation study on medium- and long-term supply and demand structure and carbon emissions of China’s hydrogen energy industry[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(2): 221-235.
| [1] | 邵志刚, 衣宝廉. 氢能与燃料电池发展现状及展望[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2019, 34 (4): 469-477. |
| Shao Z G, Yi B L. Developing trend and present status of hydrogen energy and fuel cell development[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019, 34 (4): 469-477 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] |
许传博, 刘建国. 氢储能在我国新型电力系统中的应用价值、挑战及展望[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24 (3): 89-99.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.010 |
|
Xu C B, Liu J G. Hydrogen energy storage in China’s new-type power system: application value, challenges, and prospects[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24 (3): 89-99 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.010 |
|
| [3] | 金瑞庭. 全球主要国家发展氢能的实践经验与政策建议[J]. 中国能源, 2022, 44 (7): 5-9. |
| Jing R T. Practical experience and policy suggestion of developing hydrogen energy in major countries in the world[J]. Energy of China, 2022, 44 (7): 5-9 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] |
凌文, 李全生, 张凯. 我国氢能产业发展战略研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24 (3): 80-88.
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.009 |
|
Ling W, Li Q S, Zhang K. Development strategy of hydrogen energy industry in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24 (3): 80-88 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.009 |
|
| [5] | 孟翔宇, 陈铭韵, 顾阿伦, 等. “双碳”目标下中国氢能发展战略[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42 (4): 156-179. |
| Meng X Y, Chen M Y, Gu A L, et al. China’s hydrogen development strategy in the context of double carbon targets[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42 (4): 156-179 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 北京金正纵横信息咨询有限公司. 中国氢能产业发展蓝皮书(2023)[R]. 北京: 金正纵横信息咨询有限公司能源战略研究中心, 2024. |
| Beijing Jin Zheng Zong Heng Information Consulting Co., Ltd. Blue book on the development of China’s hydrogen energy industry (2023)[R]. Beijing: Energy Strategy Research Center of Jin Zheng Zong Heng Information Consulting Co, Ltd.., 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 彭生江, 孙传帅, 妥建军, 等. 面向统一能源系统的中长期氢负荷预测[J]. 中国电力, 2022, 55 (1): 84-90. |
| Peng S J, Sun C S, Tuo J J, et al. Medium and long-term hydrogen load forecast for unified energy system[J]. Electric Power, 2022, 55 (1): 84-90 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 马涛, 孙佰清, 郭海凤, 等. 我国中长期经济发展中氢能消费量及CO2减排效果估算[J]. 太阳能学报, 2010, 31 (11): 1521-1526. |
| Ma T, Sun B Q, Guo H F, et al. Evaluation on hydrogen consumption and ITS reduction of CO2 emission of Chinese medium and long-term economic development[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2010, 31 (11): 1521-1526 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | Yusaf T, Laimon M, Alrefae W, et al. Hydrogen energy demand growth prediction and assessment (2021-2050) using a system thinking and system dynamics approach[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12 (2): 781 |
| [10] | Yang X, Nielsen C P, Song S J, et al. Breaking the hard-to-abate bottleneck in China’s path to carbon neutrality with clean hydrogen[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7 (10): 955-965 |
| [11] | 袁家海, 牟琪林, 许传博, 等. 基于系统动力学的中国绿氢产业发展政策仿真[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2023, 33 (6): 49-58. |
| Yuan J H, Mou Q L, Xu C B, et al. Simulation study on the development policy of China’s green hydrogen industry based on system dynamics[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2023, 33 (6): 49-58 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | Heap C. Long range energy alternative planning system-user guide for version 2008[Z]. Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme, 2010 |
| [13] | Loulou R, Goldstein G, Noble K. Documentation for the MARKAL family of models[Z]. Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme, 2004: 65-73 |
| [14] | Loulou R, Remme U, Kanudia A, et al. Documentation for the TIMES model part II[Z]. Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme, 2005: 384 |
| [15] |
熊亚林, 刘玮, 高鹏博, 等. “双碳”目标下氢能在我国合成氨行业的需求与减碳路径[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11 (12): 4048-4058.
doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2022.0364 |
| Xiong Y L, Liu W, Gao P B, et al. Research on the hydrogen energy demand and carbon-reduction path in China’s synthetic ammonia industry to achieve the “carbon peak” and “carbon neutrality” goals[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11 (12): 4048-4058 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
刘玮, 万燕鸣, 熊亚林, 等. “双碳”目标下我国低碳清洁氢能进展与展望[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11 (2): 635-642.
doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0385 |
| Liu W, Wan Y M, Xiong Y L. Outlook of low carbon and clean hydrogen in China under the goal of “carbon peak and neutrality”[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11 (2): 635-642 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 李忻颖, 唐旭, 许传博, 等. “双碳”目标下中国工业部门氢能需求量测算及供给结构路径优化[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44 (5): 146-156. |
| Li X Y, Tang X, Xu C B, et al. Towards China’s “dual carbon” goals: industrial hydrogen demand estimation and supply structure optimization[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44 (5): 146-156 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 吴沛泽, 陈莎, 刘影影, 等. 低排放分析平台 LEAP: 应对气候变化下的应用与挑战[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20 (5): 611-623. |
| Wu P Z, Chen S, Liu Y Y, et al. Low Emissions Analysis Platform (LEAP): applications and challenges in addressing climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20 (5): 611-623 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 李婷, 刘玮, 万燕鸣, 等. 开启绿色氢能新时代之匙: 中国2030年“可再生氢100”发展路线图[R]. 落基山研究所, 中国氢能联盟研究院, 2022. |
| Li T, Liu W, Wan Y M, et al. The key to a new era of green hydrogen: China’s 2030 “renewable hydrogen 100” development roadmap[R]. Rocky Mountain Institute, China Hydrogen Alliance Research Institute, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 曹勇, 罗大清, 刘潇潇, 等. 基于情景分析的中国氢能产业中长期预测研究[J]. 当代石油石化, 2024, 32 (2): 8-14. DOI: 10.20132/j.cnki.ddsysh.2024.02.008. |
| Cao Y, Luo D Q, Liu X X, et al. Medium and long term forecast of China hydrogen energy industry based on scenario analysis[J]. Petroleum & Petrochemical Today, 2024, 32 (2): 8-14 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | Shi C, Qin G, Tan Q, et al. Simulation of hydrogen transportation development path and carbon emission reduction path based on LEAP model: a case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region[J]. Energy Policy, 2024, 194: 114337 |
| [22] | 中国氢能联盟. 中国氢能源及燃料电池产业白皮书 (2020)[R]. 北京: 中国氢能联盟研究院, 2020. |
| China Hydrogen Alliance Research Institute. White paper on China’s hydrogen energy and fuel cell industry[R]. Beijing: China Hydrogen Alliance Research Institute, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 李婷, 谭光瑀, 王喆, 等. 中国氢储运中长期布局图景和技术展望[R]. 落基山研究所, 2024. |
| Li T, Tan G Y, Wang Z, et al. Long term outlook on hydrogen storage and transportation landscape and technology evolution in China[R]. Rocky Mountain Institute, 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 中国石化集团经济技术研究院有限公司. 中国氢能产业展望报告[R]. 北京: 中国石化集团经济技术研究院有限公司, 2023. |
| Sinopec Economics & Development Research Institute Company Limited. China hydrogen energy industry outlook[R]. Beijing: Sinopec Economics & Development Research Institute Company Limited, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 张贤, 许毛, 徐冬, 等. 中国煤制氢CCUS技术改造的碳足迹评估[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2021, 31 (12): 1-11. |
| Zhang X, Xu M, Xu D, et al. Carbon footprint assessment of coal-to-hydrogen technology combined with CCUS in China[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2021, 31 (12): 1-11 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 魏一鸣, 李家全, 刘兰翠, 等. 碳中和背景下煤炭制氢的低碳发展[R]. 北京: 北京理工大学能源与环境政策研究中心, 2024. |
| Wei Y M, Li J Q, Liu L C, et al. Low-carbon development of coal-to-hydrogen production in the context of carbon neutrality[R]. Beijing: Energy and Environmental Policy Research Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 陈馨. 典型制氢工艺生命周期碳排放对比研究[J]. 当代石油石化, 2023, 31 (1): 19-25. |
| Chen X. Comparative study on life-cycle carbon emissions of typical hydrogen production processes[J]. Petroleum & Petrochemical Today, 2023, 31 (1): 19-25 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
姬存民, 惠武卫, 赵合楠, 等. 焦炉煤气制氢的二氧化碳排放分析[J]. 现代化工, 2024, 44 (5): 224-227.
doi: 10.16606/j.cnki.issn0253-4320.2024.05.039 |
| Ji C M, Hui W W, Zhao H N, et al. Analysis on carbon dioxide emission in hydrogen production from coke oven gas[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2024, 44 (5): 224-227 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
陈健, 姬存民, 卜令兵. 碳中和背景下工业副产气制氢技术研究与应用[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41 (3): 1479-1486.
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-2240 |
|
Chen J, Ji C M, Pu L B. Research and application of hydrogen production technology from industrial by-product gas under the background of carbon neutrality[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41 (3): 1479-1486 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.16085/j.issn.1000-6613.2021-2240 |
|
| [30] | 王科, 吕晨. 中国碳市场建设成效与展望 (2024)[R]. 北京: 北京理工大学能源与环境政策研究中心, 2024. |
| Wang K, Lv C. Effectiveness and prospect of China’s carbon market construction (2024)[R]. Beijing: Energy and Environment Policy Research Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 清华大学气候变化与可持续发展研究院. 中国长期低碳发展战略与转型路径研究[R]. 北京: 清华大学气候变化与可持续发展研究院, 2024. |
| Institute of Climate Change and Sustainable Development, Tsinghua University. Research on China’s long-term low-carbon development strategy and transition pathway[R]. Beijing: Institute of Climate Change and Sustainable Development, Tsinghua University, 2024 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 陶学宗, 林泽宇, 许登豪. 集装箱港口集疏运重卡电动化的经济性分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(3): 351-360. |
| [2] | 陶学宗, 王谦益, 李汉卿. 船舶使用岸电的经济性分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 492-502. |
| [3] | 王彦哲, 欧训民, 周胜. 基于学习曲线的中国未来制氢成本趋势研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(3): 283-293. |
| [4] | 田惠玲, 朱建华, 李宸宇, 肖文发. 基于自然的解决方案:林业增汇减排路径、潜力与经济性评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(2): 195-203. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||