Climate Change Research ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (3): 278-292.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.191
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis on the evolution of atmospheric boundary layer in Yunnan province and its effect on the change of PM2.5 concentration
ZHAO Ping-Wei1( ), DUAN Shao-Ling1, SHI Jian-Wu2(
), DUAN Shao-Ling1, SHI Jian-Wu2( ), LUO Cheng-Xian3, ZHANG Jing4, ZHONG Min-Han5, LI Si-Lan1, CHEN Jing1
), LUO Cheng-Xian3, ZHANG Jing4, ZHONG Min-Han5, LI Si-Lan1, CHEN Jing1
- 1 Lincang Meteorological Bureau of Yunnan Province, Lincang 677099, China
2 Faculty of Environment Science and Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650500, China
3 Ecological Environment Monitoring Station of Yunnan Provincial, Department of Ecology and Environment in Lincang, Lincang 677099, China
4 Sun Yat-Sen University School of Atmospheric Sciences, Zhuhai 519082, China
5 Sichuan Academy of Botanical Engineering, Neijiang 641201, China
-
Received:2022-08-16Revised:2022-10-05Online:2023-05-30Published:2023-04-28
Cite this article
ZHAO Ping-Wei, DUAN Shao-Ling, SHI Jian-Wu, LUO Cheng-Xian, ZHANG Jing, ZHONG Min-Han, LI Si-Lan, CHEN Jing. Analysis on the evolution of atmospheric boundary layer in Yunnan province and its effect on the change of PM2.5 concentration[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(3): 278-292.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2022.191

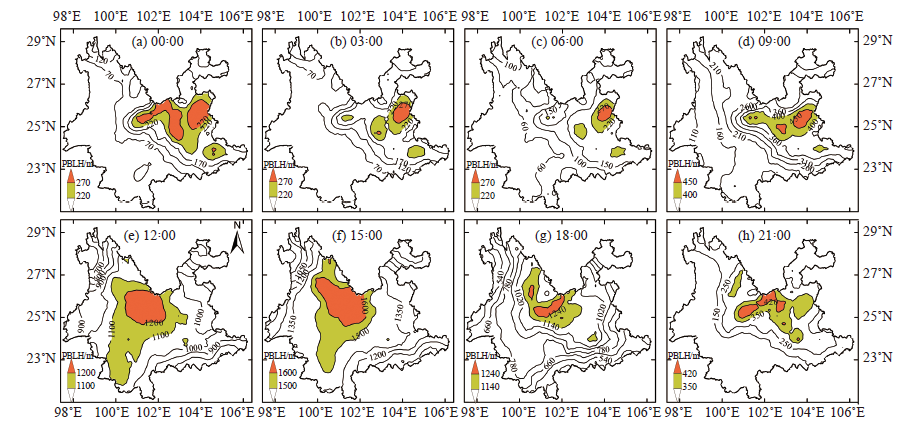
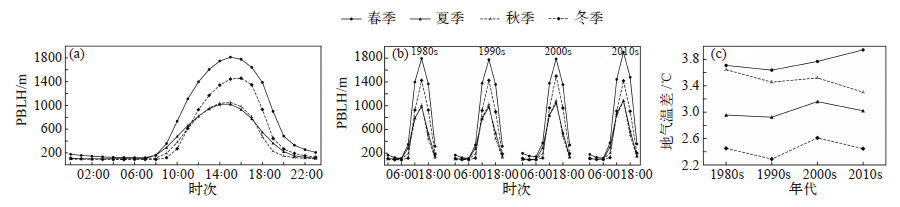
Fig. 8 Combined dependence diagram of PM2.5 concentration of air temperature (a0-d0), relative humidity (a1-d1), 10 m maximum wind speed (a2-d2) and PBLH in Yunnan’s four seasons from 2015 to 2020

Fig. 9 Spatial distribution of Pearson correlation coefficient between PM2.5 and PBLH for different times in the four seasons of Yunnan from 2015 to 2020
| [1] |
Garratt J R. The atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37 (1/2): 89-134
doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90026-4 URL |
| [2] |
Compton J C, Delgado R, Berkoff T A, et al. Determination of planetary boundary layer height on short spatial and temporal scales: a demonstration of the covariance wavelet transform in ground-based wind profiler and Lidar measurements[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2013, 30 (7): 1566-1575
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-12-00116.1 URL |
| [3] |
Molod A, Salmun H, Dempsey M. Estimating planetary boundary layer heights from NOAA profiler network wind profiler data[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2015, 32 (9): 1545-1561
doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-14-00155.1 URL |
| [4] |
Seibert P, Beyrich F, Gryning S E, et al. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2000, 34 (7): 1001-1027
doi: 10.1016/S1352-2310(99)00349-0 URL |
| [5] | 刘树华, 刘振鑫, 郑辉, 等. 多尺度大气边界层与陆面物理过程模式的研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 物理学, 力学, 天文学, 2013, 43 (10): 1332-1355. |
| Liu S H, Liu Z X, Zheng H, et al. Multi-scale atmospheric boundary-layer and land surface physics process models[J]. Scientia Sinica Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2013, 43 (10): 1332-1355 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
Miao Y C, Hu X M, Liu S H, et al. Seasonal variation of local atmospheric circulations and boundary layer structure in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and implications for air quality[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2015, 7 (4): 1602-1626
doi: 10.1002/2015MS000522 URL |
| [7] |
Deardorff J W. Numerical investigation of neutral and unstable planetary boundary layers[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1972, 29 (1): 91-115
doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1972)029<0091:NIONAU>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [8] | 朱春玲, 马耀明, 陈学龙. 青藏高原西部及东南周边地区季风前大气边界层结构分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2011, 33 (2): 325-333. |
| Zhu C L, Ma Y M, Chen X L. Atmospheric boundary layer structure in the west and the southeastern periphery of the Tibetan Plateau during the pre-monsoon period[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2011, 33 (2): 325-333 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 王学忠, 胡邦辉, 李昀英. 基于ERA-40资料的边界层厚度气候特征分析[J]. 气象科学, 2011, 31 (3): 339-346. |
| Wang X Z, Hu B H, Li Y Y. Analysis of planetary boundary layer depth climatic features based on ERA 40 dataset[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences, 2011, 31 (3): 339-346 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] |
Engeln A V, Teixeira J. A planetary boundary layer height climatology derived from ECMWF reanalysis data[J]. Journal of Climate, 2013, 26 (17): 6575-6590
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00385.1 URL |
| [11] |
Darand M, Zandkarimi F. Identification of atmospheric boundary layer height and trends over Iran using high resolution ECMWF reanalysis dataset[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2019, 137 (1/2): 1457-1465
doi: 10.1007/s00704-018-2691-2 URL |
| [12] |
徐潇然, 赵艳茹, 黄山, 等. 东亚、北非干旱半干旱区边界层高度的特征研究[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38 (5): 1038-1047.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00144 |
| Xu X R, Zhao Y R, Huang S, et al. Study on the characteristics of boundary layer height in arid and semiarid regions of Asia and North Africa[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2019, 38 (5): 1038-1047 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | Seidel D J, Zhang Y, Beljaars A, et al. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2012, 117 (D17): 1-15 |
| [14] | Guo J P, Miao Y C, Zhang Y, et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 16 (20): 13309-13319 |
| [15] |
赵采玲, 李耀辉, 柳媛普, 等. 中国西北地区大气边界层高度变化特征: 基于探空资料与ERA-Interim再分析资料[J]. 高原气象, 2019, 38 (6): 1181-1193.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00152 |
|
Zhao C L, Li Y H, Liu Y P, et al. The variation characteristics of planetary boundary layer height in Northwest China: based on radiosonde and ERA-Interim reanalysis data[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2019, 38 (6): 1181-1193 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00152 |
|
| [16] | Ding A J, Fu C B, Yang X Q, et al. Intense atmospheric pollution modifies weather: a case of mixed biomass burning with fossil fuel combustion pollution in eastern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2013, 13 (20): 10545-10554 |
| [17] | 娄梦筠. 我国不同地区大气边界层与PM2.5相互作用的观测研究[D]. 北京: 中国气象科学研究院, 2019. |
| Lou M Y. On the atmospheric boundary layer and PM2.5 interaction in China: a perspective from radiosonde observations[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 段旭, 陶云, 段长春. 云南省细网格气候区划及气候代表站选取[J]. 大气科学学报, 2011, 34 (3): 336-342. |
| Duan X, Tao Y, Duan C C. A fine mesh climate division and the selection of representative climate stations in Yunnan province[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2011, 34 (3): 336-342 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 周茹, 朱君. 东南亚生物质燃烧输送影响我国西南气溶胶辐射特性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40 (4): 1429-1436. |
| Zhou R, Zhu J. Study on the influence of transport of biomass burning materials from Southeast Asia on aerosol radiation effects in Southwest China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40 (4): 1429-1436 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 王继康, 江琪, 尤媛, 等. 东南亚生物质燃烧对我国霾和降水的影响[J]. 气象, 2021, 47 (3): 348-358. |
| Wang J K, Jiang Q, You Y, et al. Effects of biomass burning aerosol in Southeast Asia on haze and precipitation over China[J]. Meteorology Monthly, 2021, 47 (3): 348-358 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | Yin X, Kang S, Rupakheti M, et al. Influence of transboundary air pollution on air quality in southwestern China[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 112 (2021): 101239 |
| [22] |
Holtslag A A M, de Bruijn E I F, Pan H L. A high resolution air mass transformation model for short-range weather forecasting[J]. Monthly Weather Review, 1990, 118: 1561-1575
doi: 10.1175/1520-0493(1990)118<1561:AHRAMT>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [23] | 徐桂荣, 崔春光, 周志敏, 等. 利用探空资料估算青藏高原及下游地区大气边界层高度[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2014, 33 (3): 217-227. |
| Xu G R, Cui C G, Zhou Z M, et al. Atmospheric boundary layer heights estimated from radiosonde observations over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its downstream area[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2014, 33 (3): 217-227 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | Nozaki K Y. Mixing Depth Model using hourly surface observations[J]. USAF Environmental Technical Applications Center Report, 1973: 7053 |
| [25] | 马金, 郑向东. 混合层厚度的经验计算及与探空观测对比分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2011, 22 (5): 567-576. |
| Ma J, Zheng X D. Comparisons of boundary mixing layer depths determined by the empirical calculation and radiosonde profiles[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2011, 22 (5): 567-576 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 赵平伟, 李斌, 王佳妮, 等. GPM IMERG和ERA5降水数据精度在云南复杂地形区域的评估检验[J]. 气象科技, 2021, 49 (1): 114-123. |
| Zhao P W, Li B, Wang J N, et al. Accuracy evaluation and comparison of GPM IMERG and ERA5 precipitation product over complex terrain of Yunnan[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2021, 49 (1): 114-123 | |
| [27] | 梁智豪, 王东海, 梁钊明. 探空观测的边界层高度时空变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2020, 31 (4): 447-459. |
| Liang Z H, Wang D H, Liang Z M. Spatio-temporal characteristics of boundary layer height derived from soundings[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2020, 31 (4): 447-459 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
王倩茹, 范广洲, 葛非, 等. 基于CERA-20C资料青藏高原边界层高度日变化气候特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37 (6): 1486-1498.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00042 |
| Wang Q R, Fan G Z, Ge F, et al. Climatic characteristics of the diurnal variation of the boundary layer height in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau based on CERA-20C[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37 (6): 1486-1498 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
苏彦入, 吕世华, 范广洲. 青藏高原夏季大气边界层高度与地表能量输送变化特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018, 37 (6): 1470-1485.
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00040 |
|
Su Y R, Lyu S H, Fan G Z. The characteristics analysis on the summer atmospheric boundary layer height and surface heat fluxes over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2018, 37 (6): 1470-1485 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-0534.2018.00040 |
|
| [30] |
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Qiao J, et al. Relationship of atmospheric boundary layer depth with thermodynamic processes at the land surface in arid regions of China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 54 (10): 1586-1594
doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4207-0 URL |
| [31] | 张强, 乔梁, 岳平, 等. 干旱区夏季晴空期超厚对流边界层发展的能量机制[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64 (15): 1637-1650. |
| Zhang Q, Qiao L, Yue P, et al. The energy mechanism controlling the continuous development of a super-thick atmospheric convective boundary layer during continuous summer sunny periods in an arid area[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64 (15): 1637-1650 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] |
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 1996, 77 (3): 437-471
doi: 10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [33] |
Zhou L T, Huang R H. An assessment of the quality of surface sensible heat flux derived from reanalysis data through comparison with station observations in Northwest China[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2010, 27 (3): 500-512
doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-9081-8 URL |
| [34] | 范丽军, 韦志刚, 董文杰. 西北干旱地区地气温差的时空特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2004, 23 (3): 360-367. |
| Fan L J, Wen Z G, Dong W J. The characteristic of temporal and spatial distribution of the differences between ground and air temperature in the arid region of Northwest China[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2004, 23 (3): 360-367 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] |
Zhou L T, Wu R G, Huang R H. Variability of surface sensible heat flux over Northwest China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2010, 3 (2): 75-80
doi: 10.1080/16742834.2010.11446847 URL |
| [36] |
Zhang N, Wang X Y, Peng Z. Large-eddy simulation of mesoscale circulations forced by inhomogeneous urban heat island[J]. Bound-Layer Meteorology, 2014, 151 (1): 179-194
doi: 10.1007/s10546-013-9879-x URL |
| [37] | 张一平, 范淼淼, 李萌, 等. 昆明城市太阳辐射资源及利用现状初探[J]. 自然资源学报, 2002, 17 (5): 640-643. |
|
Zhang Y P, Fan M M, Li M, et al. A preliminary study on the solar radiation resources and actuality in use of the Kunming city[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2002, 17 (5): 640-643 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2002.05.017 |
|
| [38] | 栾天, 郭学良, 张天航, 等. 不同降水强度对PM2.5的清除作用及影响因素[J]. 应用气象学报, 2019, 30 (3): 279-291. |
| Luan T, Guo X L, Zhang T H, et al. The scavenging process and physical removing mechanism of pollutant aerosols by different by different precipitation intensities[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2019, 30 (3): 279-291 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] |
Tie X, Huang R J, Cao J, et al. Severe pollution in China amplified by atmospheric moisture[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7 (1): 15760
doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15909-1 URL pmid: 29150676 |
| [40] | 周志凌, 程先富. 基于MGWR模型的中国城市PM2.5影响因素空间异质性[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41 (6): 2552-2561. |
| Zhou Z L, Cheng X F. Spatial heterogeneity of influencing factors of PM2.5 in Chinese cities based on MGWR model[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41 (6): 2552-2561 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 刘彩霞, 边玮瓅. 天津市空气质量与气象因子相关分析[J]. 中国环境监测, 2007, 23 (5): 63-65, 70. |
| Liu C X, Bian W L. The correlation of air quality and meteorologic factors in Tianjin[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2007, 23 (5): 63-65, 70 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] |
Liu L, Guo J, Miao Y, et al. Elucidating the relationship between aerosol concentration and summertime boundary layer structure in Central China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2018, 241: 646-653
doi: S0269-7491(18)31002-9 URL pmid: 29902747 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||