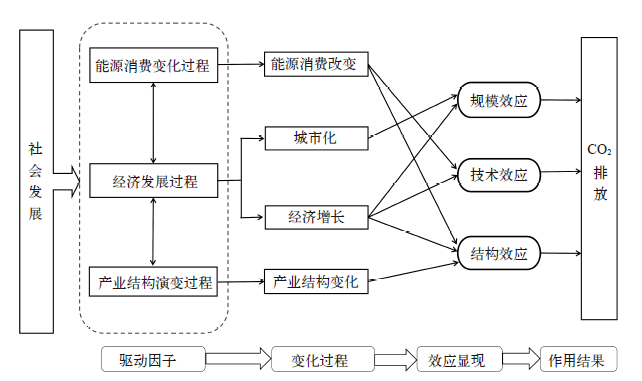
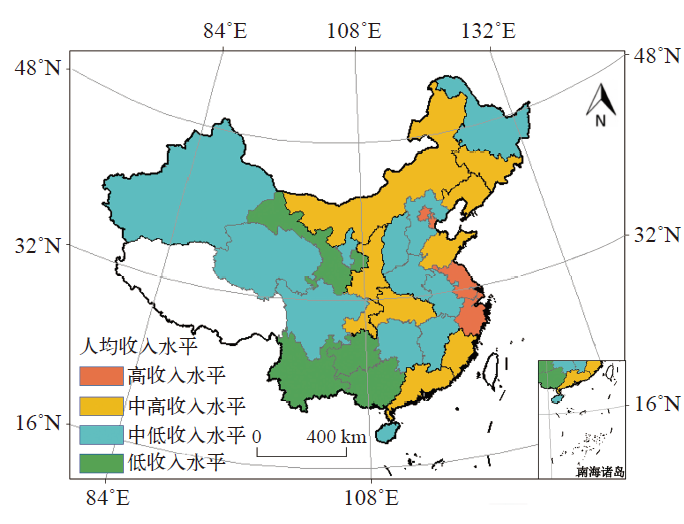
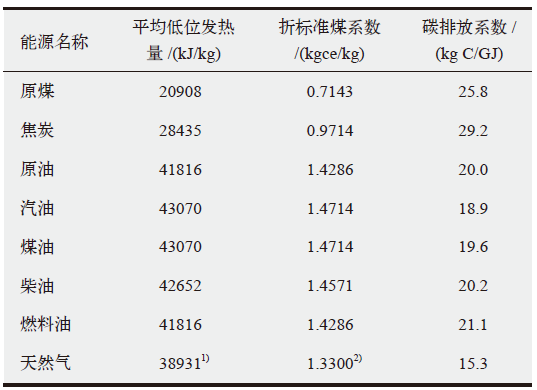
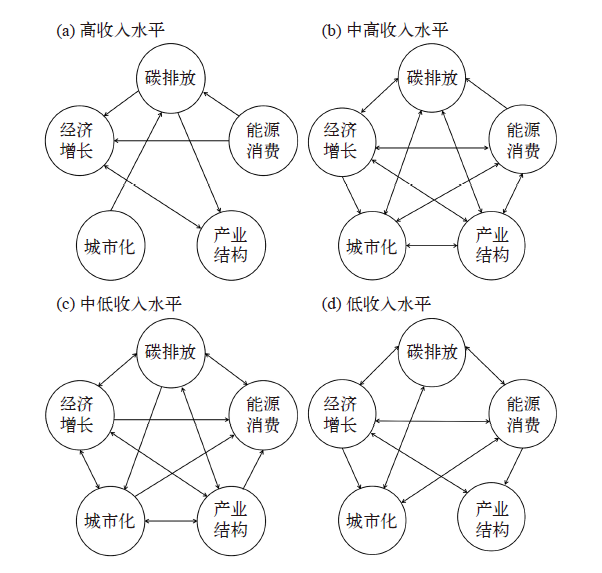
Climate Change Research ›› 2020, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (6): 738-747.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.192
• Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Previous Articles Next Articles
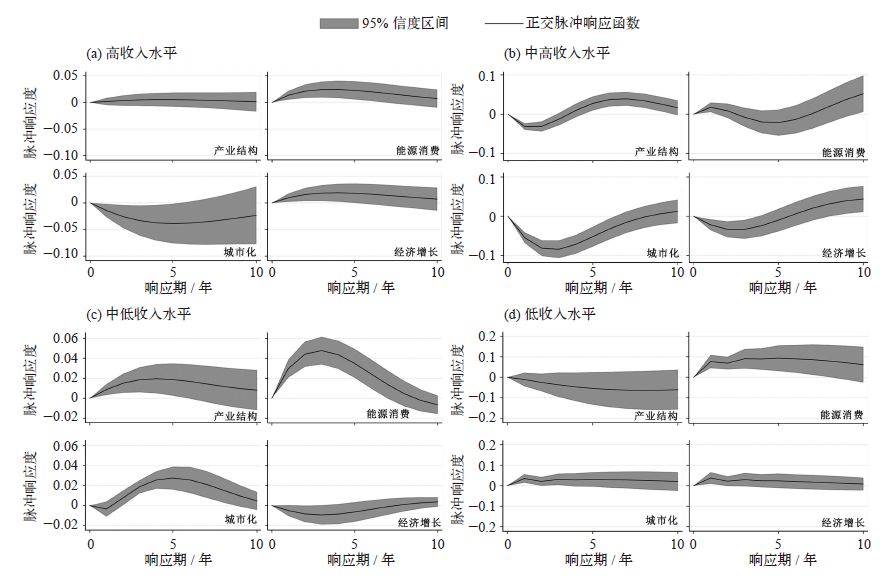
Exploring the relationship between urbanization, industrial structure, energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions: an empirical study based on the heterogeneity of inter-provincial income levels in China
- School of Humanities, Economics and Laws, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072, China
-
Received:2019-08-15Revised:2019-10-16Online:2020-11-30Published:2020-12-03
Cite this article
YUAN Yuan, SUN Xin-Tong. Exploring the relationship between urbanization, industrial structure, energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions: an empirical study based on the heterogeneity of inter-provincial income levels in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(6): 738-747.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.192
| [1] | Azomahoua T, Laisney F, van Nguyen P. Economic development and CO2 emissions: a nonparametric panel approach[J]. Journal of Public Economics, 2005,90(6):1347-1363 |
| [2] | Wang S, Li G, Fang C. Urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from countries with different income levels[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2018,81:2144-2159 |
| [3] | Liu Z, Guan D, Crawford-Brown D, et al. Energy policy: a low-carbon road map for China[J]. Nature, 2013,500(7461):143-145 |
| [4] | Dong K Y, Sun R J, Li H, et al. A review of China's energy consumption structure and outlook based on a long-range energy alternatives modeling tool[J]. Petroleum Science, 2017,14(1):214-227 |
| [5] | British P. Statistical review of world energy [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2017 |
| [6] | Dong K, Sun R, Wu J, et al. The growth and development of natural gas supply chains: the case of China and the US[J]. Energy Policy, 2018,123:64-71 |
| [7] | 马慧强, 刘嘉乐, 弓志刚. 山西省旅游交通碳排放测度及其演变机理[J]. 经济地理, 2019,39(4):223-231. |
| Ma H Q, Liu J L, Gong Z G. Carbon emission and evolution mechanism of tourism transportation in Shanxi province[J]. Economic Geography, 2019,39(4):223-231 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 韩坚, 盛培宏. 产业结构、技术创新与碳排放实证研究: 基于我国东部15个省(市)面板数据[J]. 上海经济研究, 2014 (8):67-74. |
| Han J, Sheng P H. An empirical study about industrial structure, technological innovation and carbon emissions: panel data based on the 15 provinces (city) of eastern China[J]. Shanghai Journal of Economics, 2014 (8):67-74 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 程叶青, 王哲野, 张守志, 等. 中国能源消费碳排放强度及其影响因素的空间计量[J]. 地理学报, 2013,68(10):1418-1431. |
| Cheng Y Q, Wang Z Y, Zhang S Z. Spatial econometric analysis of carbon emission intensity and its driving factors from energy consumption in China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013,68(10):1418-1431 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 雷于蓝, 张枫, 彭希哲, 等. 广东省“十二五”人口发展战略研究[M]. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2012. |
| Lei Y L, Zhang F, Peng X Z, et al. Research on population development strategy of Guangdong province during the 12th Five-Year Plan [M]. Shanghai: Fudan University Press, 2012 (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 徐丽杰. 中国城市化对碳排放的影响关系研究[J]. 宏观经济研究, 2014 (6):63-70, 79. |
| Xu L J. Research on the influence relationship of urbanization on carbon emission[J]. Macroeconomics, 2014 (6):63-70, 79 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 刘梦琴, 刘轶俊. 中国城市化发展与碳排放关系: 基于30个省区数据的实证研究[J]. 城市发展研究, 2011,18(11):27-32. |
| Liu M Q, Liu Y J. The relationship between the development of China's urbanization and carbon emissions: an empisical study based on 30 provinces' data[J]. Urban Development Studies, 2011,18(11):27-32 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 王少剑, 黄永源. 中国城市碳排放强度的空间溢出效应及驱动因素[J]. 地理学报, 2019,74(6):1131-1148. |
| Wang S J, Huang Y Y. Spatial spillover effect and driving forces of carbon emission intensity at city level in China[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019,74(6):1131-1148 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Sheng P F, Guo X H. The long-run and short-run impacts of urbanization on carbon dioxide emissions[J]. Economic Modelling, 2016,53:208-215 |
| [15] | Sharma S S. Determinants of carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from 69 countries[J]. Applied Energy, 2011,88(1):376-382 |
| [16] | Li C, Kuang Y Q, Huang N S. The long-term relationship between population growth and vegetation cover: an empirical analysis based on the panel data of 21 cities in Guangdong province, China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2013,10(2):660-677 |
| [17] | Martínez-Zarzoso I, Maruotti A. The impact of urbanization on CO2 emissions: evidence from developing countries[J]. Ecological Economics, 2011,70(7):1344-1353 |
| [18] | 姬世东, 吴昊, 王铮. 贸易开放、城市化发展和二氧化碳排放: 基于中国城市面板数据的边限协整检验分析[J]. 经济问题, 2013 (12):31-35. |
| Ji S D, Wu H, Wang Z. Openness to trade, urbanization and carbon dioxide emissions: based on panel data of China's urban bound co-integration analysis[J]. On Economic Problems, 2013 (12):31-35 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | Tucker M. Carbon dioxide emissions and global GDP[J]. Ecological Economics, 1995,15(3):215-223 |
| [20] | 杨子晖. “经济增长”与“二氧化碳排放”关系的非线性研究: 基于发展中国家的非线性Granger因果检验[J]. 世界经济, 2010,33(10):139-160. |
| Yang Z H. Nonlinear study of the relationship between“economic growth” and “carbon dioxide emissions”: based on the nonlinear Granger causality test in developing countries[J]. The Journal of World Economy, 2010,33(10):139-160 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 原嫄, 席强敏, 孙铁山, 等. 产业结构对区域碳排放的影响: 基于多国数据的实证分析[J]. 地理研究, 2016,35(1):82-94. |
| Yuan Y, Xi Q M, Sun T S, et al. The impact of the industrial structure on regional carbon emission: empirical evidence across countries[J]. Geographical Research, 2016,35(1):82-94 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | Grossman G M, Krueger A B. Economic growth and the environment[J]. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 1995,110(2):353-377 |
| [23] | 陶长琪, 彭永樟, 琚泽霞. 经济增长、产业结构与碳排放关系的实证分析: 基于PVAR模型[J]. 经济经纬, 2015,32(4):126-131. |
| Tao C Q, Peng Y Z, Ju Z X. An empirical study on economic growth, industrial structure and the carbon emissions: based on PVAR model[J]. Economic Survey, 2015,32(4):126-131 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | Holtz-Eakin D, Newey W, Rosen H S. Estimating vector autoregressions with panel data[J]. Econometrica, 1988,56(6):1371-1395 |
| [25] | Antonakakis N, Chatziantoniou I, Filis G. Energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth: an ethical dilemma[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017,68:808-824 |
| [26] | 邹平. 金融计量学[M]. 上海: 上海财经大学出版社, 2014. |
| Zou P. Financial econometrics [M]. Shanghai: Shanghai University of Finance & Economics Press, 2014 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | Dinda S. Does environment link to economic growth[J]. Human Security and Climate Change, 2005: 1-26 |
| [28] | 臧良震, 张彩虹. 中国城市化、经济发展方式与CO2排放量的关系研究[J]. 统计与决策, 2015 (20):124-126. |
| Zang L Z, Zhang C H. Study on the relationship between urbanization, economic development pattern and CO2 emission in China[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2015 (20):124-126 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | WANG Jiao-Yue, XI Feng-Ming, HOU Wei, BING Long-Fei, YIN Yan, XU Ting-Ting, WANG Jia-Feng, MA Ming-Jing. Variations of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in wetland water along the urban-rural gradients in Shenyang [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(4): 453-465. |
| [2] | Jun-Ling LIU, Ke WANG, Qin-Rui XIAHOU, Fang-Ming LIU, Ji ZOU, Ying KONG. Study on China’s long-term low carbon transition pathway under the urbanization process [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(3): 355-366. |
| [3] | CAO Ying,ZHENG Xiao-Qi,LIU Qiang. The correlation analysis between urbanization mode and low carbon development—taking Shijiazhuang as an example [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(2): 223-231. |
| [4] | Jing-Fu CAO,Ming-Cai LI,Mei-Ling SUN,Yue-Hao CHEN,Yan-Juan YANG,Rui-Xue ZHANG. Applicability of cooling degree-days based on wet bulb temperature as an index of cooling energy consumption [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6): 617-623. |
| [5] | Ji-Feng LI,A-Lun GU,Cheng-Long ZHANG,Zhen-Qing SUN. Economic development, energy demand and carbon emission prospects of China’s provinces during the 14th Five-Year Plan—an application of CMRCGE model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6): 649-659. |
| [6] | Xiao-Ting CHEN, Ying CHEN. The scientific and political views of carbon budget for global climate governance [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(6): 632-639. |
| [7] | Zhi-Xin FAN,Xiu-Qi FANG,Yun SU. Changes in global grid pattern of carbon emissions [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(5): 505-512. |
| [8] | Xiao-Jiang DING,Fang-Lei ZHONG,Jin-Huang MAO,Xiao-Yu SONG,Chun-Lin HUANG. Provincial urbanization projected to 2050 under the shared socioeconomic pathways in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(4): 392-401. |
| [9] | Qing-Qing LI,Ying SU,Li SHANG,Wei WEI,Mao-Hua WANG. Comparison analysis of China’s emissions accounting by typical international carbon databases [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(3): 275-280. |
| [10] | Tao BIAN, Guo-Yu REN, Li-Xia ZHANG. Significant urbanization effect on decline of near-surface wind speed at Shijiazhuang station [J]. Climate Change Research, 2018, 14(1): 21-30. |
| [11] | Jin Kai, Wang Fei, Gou Jiaojiao. Urbanization Effects on the Observed Temperature of Two Meteorological Stations in Changsha City [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(5): 456-464. |
| [12] | Song Jingni, Wu Qunqi, Yuan Changwei, Zhang Shuai, Bao Xu, Du Kai. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of China Transport Carbon Emissions Based on Geostatistical Analysis [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(5): 502-511. |
| [13] | Tao Yin, Huang Yong, Yang Yuanjian, Wang Kai, Cheng Xiangyang, Wang Mingguang, Wu Rong. Impact of Urbanization on Wind Speed in Anhui Province [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(6): 519-526. |
| [14] | Wu Rong, Sun Yi, Yang Yuanjian, Xie Wusan, Tao Yin, Zhang Hao, Shi Tao. Effects of Urbanization on Extreme Temperature Events in Anhui Province [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(6): 527-537. |
| [15] | Hu Lei. Research on the Mechanism of How Urbanization Effect on Carbon Emissions in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4): 341-347. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||