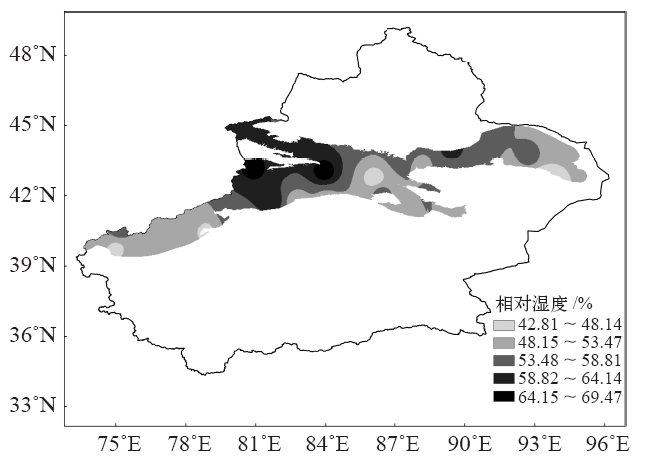
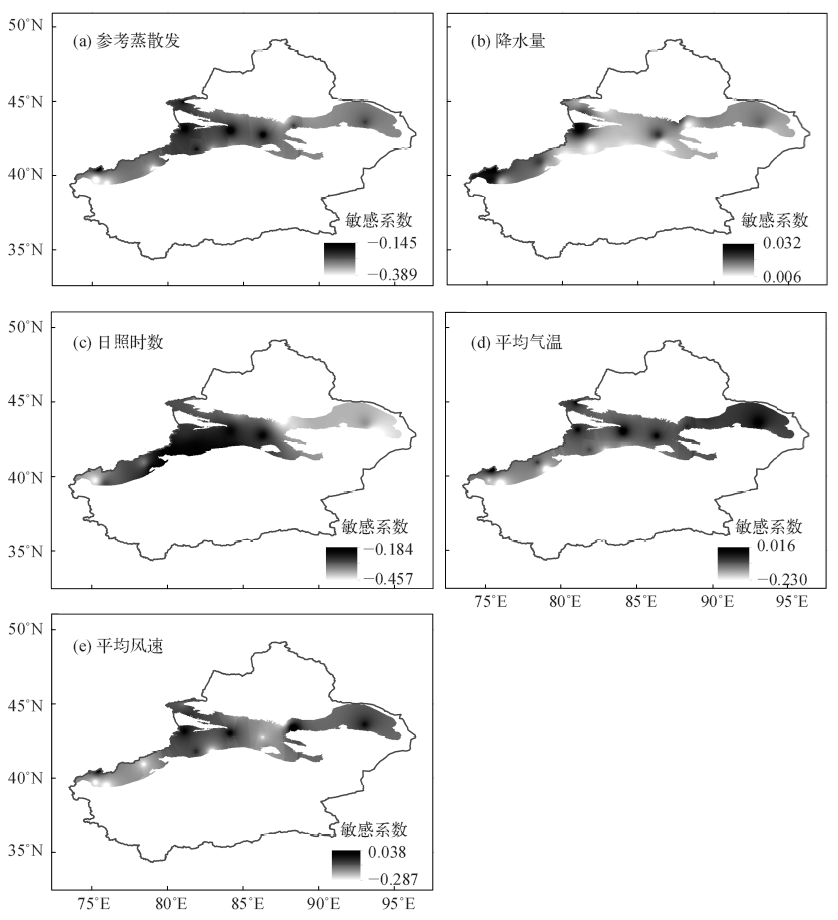
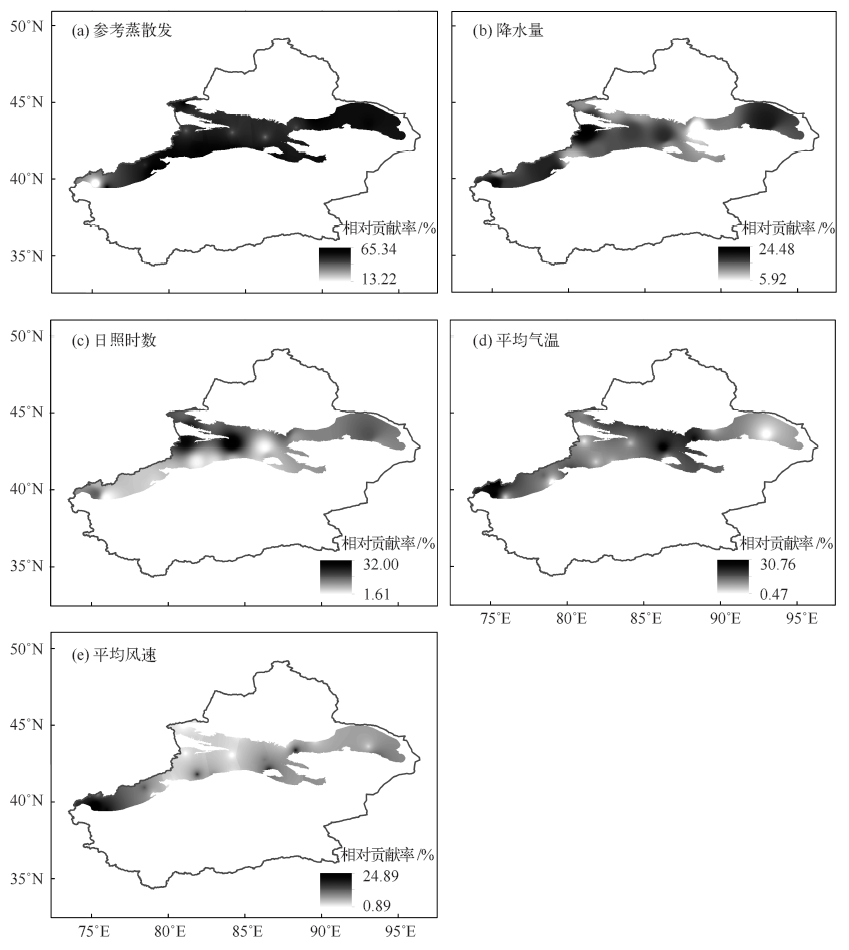
| [1] | Held I M, Soden B J . Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006,19(21):5686-5699 | | [2] | Dessler A E, Zhang Z, Yang P . Water-vapor climate feedback inferred from climate fluctuations, 2003-2008[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008,35(20):293-310 | | [3] | 盛裴轩, 毛节泰, 李建国 , 等. 大气物理学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2003 | | [4] | Lu E, Takle E S . Spatial variabilities and their relationships of the trends of temperature, water vapor, and precipitation in the North American regional reanalysis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2010,115(D6):620-631 | | [5] | Gaffen D J, Ross R J . Climatology and trends of US surface humidity and temperature[J]. Journal of Climate, 1999,12(3):811-828 | | [6] | Bauer H, Ache P, Lautner S , et al. The stomatal response to reduced relative humidity requires guard cell-autonomous ABA synjournal[J]. Current Biology, 2013,23(1):53-57 | | [7] | Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang Y , et al. Influences of relative humidity and particle chemical composition on aerosol scattering properties during the 2006 PRD campaign[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008,42(7):1525-1536 | | [8] | 秦大河, 陈宜瑜, 李学勇 . 中国气候与环境演变: 上卷[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005 | | [9] | Wang J X L, Gaffen D J . Late-twentieth-century climatology and trends of surface humidity and temperature in China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2001,14(13):2833-2845 | | [10] | 王遵娅, 丁一汇, 何金海 , 等. 近50年来中国气候变化特征的再分析[J]. 气象学报, 2004 (2):228-236 | | [11] | Song Y, Liu Y, Ding Y . A study of surface humidity changes in China during the recent 50 years[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2012,26(5):541-553 | | [12] | Surratt G, Aronowicz J, Shine W , et al. Change in aqueous tear evaporation with change in relative humidity[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 2004,45(13):92 | | [13] | Vincent L A, van Wijngaarden W A, Hopkinson R . Surface temperature and humidity trends in Canada for 1953-2005[J]. Journal of Climate, 2007,20(20):5100-5113 | | [14] | Eludoyin O M . Air temperature and relative humidity areal distribution over Nigeria[J]. Ife Research Publications in Geography, 2016,10(1):134-145 | | [15] | Han S, Tang Q, Xu D , et al. Observed near-surface atmospheric moisture content changes affected by irrigation development in Xinjiang, Northwest China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2017,130(1-2):511-521 | | [16] | 何毅, 杨太保, 陈杰 , 等. 1955—2012年南北疆气温、降水及相对湿度趋势分析[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015,22(2):269-277 | | [17] | 牛建龙, 王家强, 彭杰 , 等. 南疆阿拉尔地区近31年沙尘天气变化特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2016,30(6):102-107 | | [18] | 付爱红, 陈亚宁, 李卫红 . 新疆塔里木河下游柽柳茎水势变化与影响因子研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2007 (1):108-114 | | [19] | 普宗朝, 张山清, 李景林 , 等. 近36年新疆天山山区气候暖湿变化及其特征分析[J]. 干旱区地理, 2008 (3):409-415 | | [20] | 普宗朝, 张山清 . 气候变化对新疆天山山区自然植被净第一性生产力的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2009,26(2):11-18 | | [21] | 张明军, 李瑞雪, 贾文雄 , 等. 中国天山山区潜在蒸发量的时空变化[J]. 地理学报, 2009,64(7):798-806 | | [22] | 李艳忠, 罗格平, 周德成 , 等. 天山北坡高山林线分布的生态地理特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012,32(1):122-131 | | [23] | Mann H B . Nonparametric tests against trend[J]. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 1945 (13):245-259 | | [24] | Kendall M G . Rank correlation methods[M]. London: Griffin, 1975 | | [25] | 刘昌明, 郑红星 . 黄河流域水循环要素变化趋势分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2003 (2):129-135 | | [26] | Hamed K H . Trend detection in hydrologic data: the Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypojournal[J]. Journal of hydrology, 2008,349(3):350-363 | | [27] | Li Z, Chen Y, Yang J , et al. Potential evapotranspiration and its attribution over the past 50 years in the arid region of Northwest China[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2014,28(3):1025-1031 | | [28] | 张嘉琪, 任志远 . 1977—2010年柴达木盆地地表潜在蒸散时空演变趋势[J]. 资源科学, 2014,36(10):2103-2112 | | [29] | Zheng H, Zhang L, Zhu R , et al. Responses of streamflow to climate and land surface change in the headwaters of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Water Resources Research, 2009,45(7):641-648 | | [30] | 姜大膀, 苏明峰, 魏荣庆 , 等. 新疆气候的干湿变化及其趋势预估[J]. 大气科学, 2009,33(1):90-98 | | [31] | 普宗朝, 张山清, 王胜兰 , 等. 近48 a新疆干湿气候时空变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011,31(6):1563-1572 | | [32] | Wang H, Pan Y, Chen Y N . Comparison of three drought indices and their evolutionary characteristics in the arid region of northwestern China[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2017,18(3):132-139 | | [33] | 张彦龙, 刘普幸 . 基于AI指数的新疆干湿时空变化及其影响因素分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2016,31(4):658-671 | | [34] | 邢楠, 周海, 尚可政 , 等. 青藏高原上空经向环流与新疆干旱的关系[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010,24(12):121-127 | | [35] | 赵兵科, 蔡承侠, 杨莲梅 , 等. 新疆夏季变湿的大气环流异常特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 2006 (3):434-442 | | [36] | 袁中友 . 厄尔尼诺和拉尼娜事件与广东省干旱关系探讨[D]. 广东: 华南师范大学, 2004 | | [37] | 袁薇, 邹立尧, 孙建奇 . 1961—2005年新疆地区夏季气温的时空变化特征及其与大气环流的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 2009,31(5):801-807 | | [38] | 元慧慧, 滕军, 李杰 , 等. 南疆夏季高温干旱时空变化特征及环流异常形势分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010,24(12):73-79 | | [39] | Zhao Y, Wang M Z, Huang A N , et al. Relationships between the West Asian subtropical westerly jet and summer precipitation in northern Xinjiang[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2014,116(3-4):403-411 | | [40] | Li B, Chen Y, Chen Z , et al. Why does precipitation in Northwest China show a significant increasing trend from 1960 to 2010?[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2016,167:275-284 | | [41] | Wei W, Zhang R, Wen M , et al. Relationship between the Asian westerly jet stream and summer rainfall over Central Asia and North China: roles of the Indian Monsoon and the South Asian High[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017,30(2):537-552 | | [42] | 李万莉, 王可丽, 傅慎明 , 等. 区域西风指数对西北地区水汽输送及收支的指示性[J]. 冰川冻土, 2008 (1):28-34 | | [43] | Peng D, Zhou T . Why was the arid and semiarid Northwest China getting wetter in the recent decades?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017,122(17):9060-9075 |
|