气候变化研究进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (3): 329-339.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.090
1961—2018年长江中下游地区暴雨过程的客观识别及其变化特征
高筱懿1( ), 赵俊虎2, 周杰3, 钱忠华1(
), 赵俊虎2, 周杰3, 钱忠华1( ), 封国林1,2
), 封国林1,2
- 1 扬州大学物理科学与技术学院,扬州 225000
2 国家气候中心 中国气象局气候研究开放实验室,北京 100081
3 重庆市气候中心,重庆 400000
-
收稿日期:2020-04-24修回日期:2020-07-28出版日期:2021-05-30发布日期:2021-06-01 -
通讯作者:钱忠华 -
作者简介:高筱懿,女,硕士研究生,gaoxiaoyi1996@163.com -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(41675050);国家自然科学基金项目(42075017);国家自然科学基金项目(41875093);国家自然科学基金项目(41530531);国家重点研发计划项目(2017YFC1502303)
Objective identification and variation characteristics of regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018
GAO Xiao-Yi1( ), ZHAO Jun-Hu2, ZHOU Jie3, QIAN Zhong-Hua1(
), ZHAO Jun-Hu2, ZHOU Jie3, QIAN Zhong-Hua1( ), FENG Guo-Lin1,2
), FENG Guo-Lin1,2
- 1 School of Physical Science and Technology, Yangzhou University, Yangzhou 225000, China
2 Laboratory of Climate Studies, National Climate Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
3 Chongqing Climate Center, Chongqing 400000, China
-
Received:2020-04-24Revised:2020-07-28Online:2021-05-30Published:2021-06-01 -
Contact:QIAN Zhong-Hua
摘要:
利用区域性极端事件客观识别方法(OITREE)和长江中下游地区381站逐日降水资料对1961—2018年长江中下游地区的暴雨过程进行了客观识别。共识别挑选出245次区域性暴雨过程。长江中下游地区暴雨过程持续时间以2~3 d为主,最长为8 d,累积强度主要集中于(2~4)×103 mm之间,累积面积主要集中于(2~5)×105 km2之间。长江中下游地区暴雨过程主要发生在夏季,尤其是6—7月。湖北东南部、安徽南部和江西北部是长江中下游地区暴雨过程发生最频繁的地区。长江中下游地区暴雨过程既有长期变化趋势,又有年代际变化特征,近58年来发生频次显著增加(0.3次/(10 a)),暴雨过程频次及5项指标均呈现出明显的年代际变化特征,20世纪60—80年代末期为暴雨过程偏少阶段,90年代呈增加趋势并在90年代末期达到峰值,在21世纪初急速下降后又有缓慢增加趋势。
引用本文
高筱懿, 赵俊虎, 周杰, 钱忠华, 封国林. 1961—2018年长江中下游地区暴雨过程的客观识别及其变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(3): 329-339.
GAO Xiao-Yi, ZHAO Jun-Hu, ZHOU Jie, QIAN Zhong-Hua, FENG Guo-Lin. Objective identification and variation characteristics of regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 329-339.
 |
表1 OITREE方法识别长江中下游地区暴雨过程的参数赋值表
Table 1 Parameters for OITREE method to identify the regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
 |
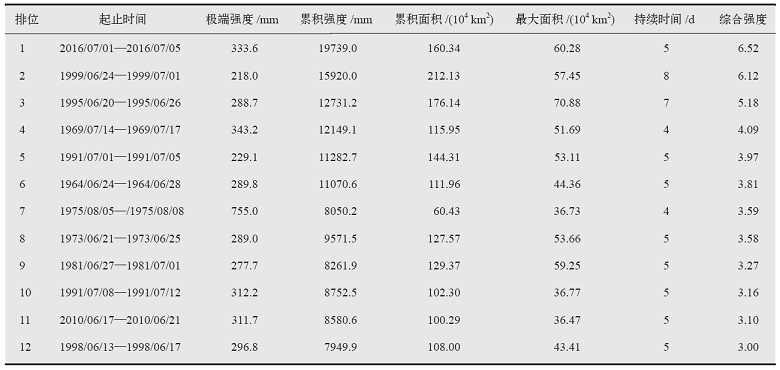 |
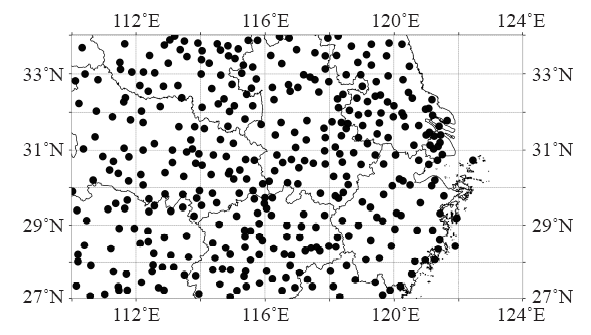
表2 1961—2018年长江中下游地区排名前12位的区域暴雨过程
Table 2 The top 12 regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018
 |
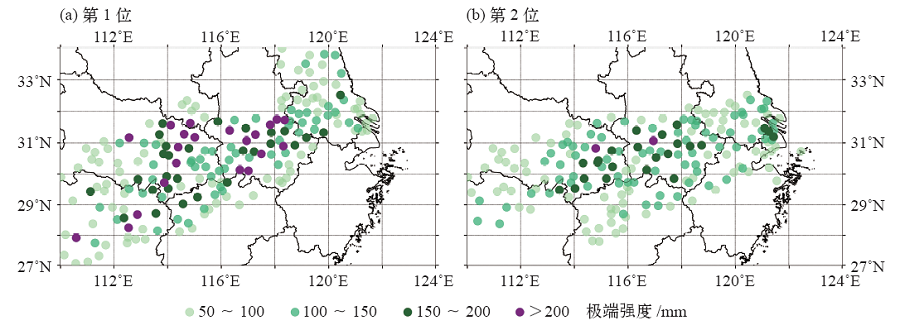
图2 综合强度前2位的暴雨过程极端强度空间分布
Fig. 2 Spatial distribution of extreme intensity of the regional heavy rainfall events with the comprehensive intensity of top 1-2
图3 1961—2018年长江中下游地区暴雨过程发生频次的年际变化
Fig. 3 Interannual changes in the frequency of the regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018

图4 1961—2018年长江中下游地区暴雨过程5项指标的年际变化
Fig. 4 Inter-annual changes of the five indicators of the regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018 (a) extreme intensity, (b) cumulative intensity, (c) maximum area, (d) cumulative area, (e) duration

图5 1961—2018年长江中下游地区暴雨过程发生频次的空间分布
Fig. 5 Spatial distribution of frequency of the regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018
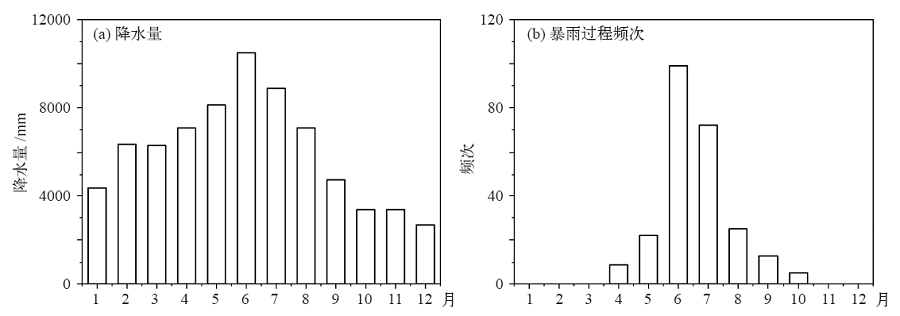
图6 1961—2018年长江中下游地区月平均降水量(a)和暴雨过程逐月发生频次(b)
Fig. 6 Monthly average precipitation (a) and the frequency of the regional heavy rainfall events (b) in the middle and lower reach of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018
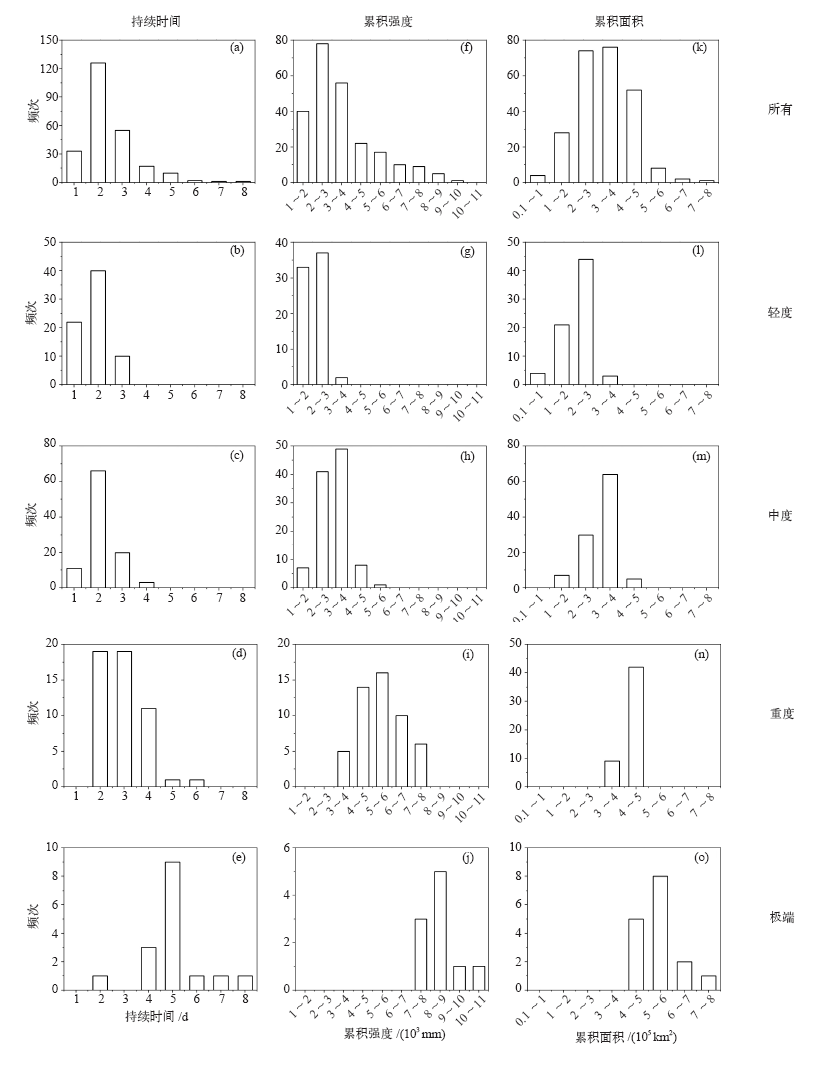
图7 1961—2018年长江中下游地区不同等级暴雨过程的持续时间、累积强度和累积面积分布
Fig. 7 Distribution of duration (a-e), cumulative intensity (f-j) and cumulative area (k-o) of the regional heavy rainfall events of different levels in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River from 1961 to 2018

图8 长江中下游地区轻度(a),中度(b),重度(c)和极端(d)暴雨过程的站点频次分布
Fig. 8 Site frequency distribution of mild (a), moderate (b), severe (c), extreme (d) regional heavy rainfall events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1535 |
| [2] |
Wolf T, Manfred D. The climate of China[J]. GeoJournal, 1987,14(2):265-266
doi: 10.1007/BF00435818 URL |
| [3] |
Zhai P M, Zhang X B, Wan H, et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005,18:1096-1108
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-3318.1 URL |
| [4] | 王莉萍, 王秀荣, 张立生, 等. 一种区域降水过程综合强度评估方法的探索和应用[J]. 气象, 2018,44(11):105-114. |
| Wang L P, Wang X R, Zhang L S, et al. Exploration and application of comprehensive intensity evaluation method for regional precipitation process[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2018,44(11):105-114 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 陶诗言. 1998年夏季中国暴雨的形成机理与预报研究 [M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2001. |
| Tao S Y. The mechanism and forecasting of torrential rain of China in summer 1998 [M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2001 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 鲍名. 近50年我国持续性暴雨的统计分析及其大尺度环流背景[J]. 大气科学, 2007 (5):25-38. |
| Bao M. The statistical analysis of the persistent heavy rain in the last 50 years over China and their backgrounds on the large scale circulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2007 (5):25-38 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 赵俊虎, 陈丽娟, 王东阡. 2016年我国梅雨异常特征及成因分析[J]. 大气科学, 2018,42(5):1055-1066. |
| Zhao J H, Chen L J, Wang D Q. Characteristics and causes analysis of abnormal Meiyu in China in 2016[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2018,42(5):1055-1066 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 鲍名, 黄荣辉. 近40年我国暴雨的年代际变化特征[J]. 大气科学, 2006,30(6):1057-1067. |
| Bao M, Huang R H. Characteristics of the interdecadal variations of heavy rain over China in the last 40 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2006,30(6):1057-1067 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 陶诗言. 中国之暴雨 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1980: 45-46. |
| Tao S Y. Heavy rainfall in China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1980: 45-46(in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 钱维宏. 气候变化与中国极端气候事件图集 [M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2011: 146-156. |
| Qian W H. Atlas of climate change and China extreme climate events [M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2011: 146-156(in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 张世轩, 封国林, 赵俊虎. 长江中下游地区暴雨“积成效应”[J]. 物理学报, 2013,62(6):69201. |
| Zhang S X, Feng G L, Zhao J H. “Cumulative effect” of torrential rain in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Acta Physical Sinica, 2013,62(6):69201 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 汪汇洁, 孙建华, 卫捷, 等. 近30年我国南方区域持续性暴雨过程的分类研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2014,19(6):713-725. |
| Wang H J, Sun J H, Wei J, et al. Classification of persistent heavy rainfall events over southern China during recent 30 years[J]. Climatic Environmental Research, 2014,19(6):713-725 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] |
Chen Y, Zhai P M. Persistent extreme precipitation events in China during 1951-2010[J]. Climate Research, 2013,57(2):143-155
doi: 10.3354/cr01171 URL |
| [14] |
Ren F M, Cui D L, Gong Z Q, et al. An objective identification technique for regional extreme events[J]. Journal of Climate, 2012,25(20):7015-7027
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00489.1 URL |
| [15] |
Zou X, Ren F M. Changes in regional heavy rainfall events in China during 1961-2012[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2015,32(5):704-714
doi: 10.1007/s00376-014-4127-y URL |
| [16] | 龚志强, 王晓娟, 崔冬林. 区域性极端低温事件的识别及其变化特征[J]. 应用气象学报, 2012,23(2):195-204. |
| Gong Z Q, Wang X J, Cui D L. The identification and changing characteristics of regional low temperature extreme events[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2012,23(2):195-204 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 任福民, 龚志强, 王艳姣, 等. 中国干旱、强降水、高温和低温区域性极端事件 [M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2015: 90-95. |
| Ren F M, Gong Z Q, Wang Y J, et al. Regional extreme events of drought, rainstorm, high temperature and low temperature in China [M]. Beijing: China Meteorological Press, 2015: 90-95(in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 叶殿秀, 王遵娅, 高荣, 等. 1961—2016年我国区域性暴雨过程的客观识别及其气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019,15(6):575-583. |
| Ye D X, Wang Z Y, Gao R, et al. Objective identification and climatic characters of the regional rainstorm event in China from 1961 to 2016[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019,15(6):575-583 (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 胡娅敏, 翟盘茂, 陈阳. “75?8”持续性强降水事件及其大尺度水汽输送特征[J]. 气象与环境科学, 2015,38(3):13-18. |
| Hu Y M, Zhai P M, Chen Y. “75?8” persistent heavy precipitation event and the characteristics of large-scale water vapor transport[J]. Meteorological and Environmental Sciences, 2015,38(3):13-18 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 赵娴婷, 廖移山, 闵爱荣, 等. 2016年4—10月我国主要暴雨天气过程简述[J]. 暴雨灾害, 2017,36(2):182-191. |
| Zhao X T, Liao Y S, Min A R, et al. Major heavy rain events in China from April to October in 2016[J]. Torrential Rain and Disasters, 2017,36(2):182-191 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 隆霄, 程麟生, 王文. 1999年6月长江中下游梅雨暴雨的环流特征分析[J]. 高原气象, 2007 (3):563-571. |
| Long X, Cheng L S, Wang W. Analysis on circulation characteristics of Meiyu rainstorm in the lower and middle-reaches of Changjiang River during June 1999[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2007 (3):563-571 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 李勇, 金荣花, 周宁芳, 等. 江淮梅雨季节强降雨过程特征分析[J]. 气象学报, 2017 (5):35-46. |
| Li Y, Jin R H, Zhou N F, et al. An analysis on characteristics of heavy rainfall processes during the Meiyu season in Jianghuai region[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2017 (5):35-46 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | Tu K, Yan Z W, Wang Y. A spatial cluster analysis of heavy rains in China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2011 (1):36-40 |
| [24] | 翟盘茂, 李蕾, 周佰铨, 等. 江淮流域持续性极端降水及预报方法研究进展[J]. 应用气象学报, 2016,27(5):631-640. |
| Zhai P M, Li L, Zhou B Q, et al. Progress on mechanism and prediction methods for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtz-Huai River valley[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2016,27(5):631-640 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] |
Chen Y, Zhai P M. Synoptic-scale precursors of the East Asia/Pacific teleconnection pattern responsible for persistent extreme precipitation in the Yangtze River valley[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2015,141(689):1389-1403
doi: 10.1002/qj.2015.141.issue-689 URL |
| [26] | 刘蕾, 周晶, 刘俊杰, 等. 长江中下游地区持续性暴雨年代际变化特征及环流形势[J]. 气象与环境学报, 2018,34(3):30-38. |
| Liu L, Zhou J, Liu J J, et al. Decadal characteristics of persistent heavy precipitation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its circulation pattern[J]. Journal of Meteorology and Environment, 2018,34(3):30-38 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 刘冲,赵平. 1979—2016年四川盆地低涡的气候特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(2): 203-214. |
| [2] | 叶殿秀,王遵娅,高荣,王荣,肖潺. 1961—2016年我国区域性暴雨过程的客观识别及其气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6): 575-583. |
| [3] | 贾孜拉·拜山, 李维京, 孙丞虎, 左金清, 张若楠, 刘景鹏. 1961—2014年我国西南地区干湿季变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(2): 103-116. |
| [4] | 周荣卫;何晓凤;苗世光;李青春. 北京地区大气环流型及气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(05): 338-343. |
| [5] | 张春花;吴胜安;林建兴;许向春;郭冬艳. 1969-2008年海南省雾的气候特征与变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(05): 349-355. |
| [6] | 伍红雨;杜尧东. 1961-2008年华南区域寒潮变化的气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(03): 192-197. |
| [7] | 胡娅敏;宋丽莉. 登陆中国热带气旋台风季参数的气候特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2009, 5(02): 90-094. |
| [8] | 王小玲 宋文玲. 近30a我国5级以上风日数的时空变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(006): 347-351. |
| [9] | 张艳梅 江志红 王冀 刘毅. 贵州夏季暴雨的气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(003): 182-186. |
| [10] | 王绍武. 中国冷冬的气候研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(002): 68-072. |
| [11] | 王遵娅 张强 陈峪 赵珊珊 曾红玲 张勇 刘秋锋. 2008年初我国低温雨雪冰冻灾害的气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(002): 63-067. |
| [12] | 陈潇潇 郭品文 罗勇. 中国不同等级雾日的气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(002): 106-110. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||