气候变化研究进展 ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (2): 177-187.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.104
SSP“双碳”路径下赣江流域径流变化趋势
- 南京信息工程大学地理科学学院/灾害风险管理研究院,南京 210044
-
收稿日期:2021-06-16修回日期:2021-07-31出版日期:2022-03-30发布日期:2021-12-23 -
通讯作者:姜彤 -
作者简介:杨晨辉,男,硕士研究生 -
基金资助:教育事业发展2021年双一流人才启动(1521582101003);中国气象局气候变化专项“鄱阳湖典型流域大气降水对地表水质影响研究”(CCSF)
Runoff variation trend of Ganjiang River basin under SSP “Double Carbon” path
YANG Chen-Hui, WANG Yan-Jun, SU Bu-Da, PU Yang, WANG Yuan, JIANG Tong( )
)
- Institute for Disaster Risk Management (IDRM)/School of Geographical Science, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
-
Received:2021-06-16Revised:2021-07-31Online:2022-03-30Published:2021-12-23 -
Contact:JIANG Tong
摘要:
根据共享社会经济情景(SSPs)分为“双碳”路径(SSP1-1.9、SSP1-2.6、SSP2-4.5、SSP4-3.4、SSP4-6.0)和“高碳”路径(SSP3-7.0、SSP5-8.5)。在碳达峰(2028—2032年)和碳中和(2058—2062年)两个时期,采用5个气候模式,7个情景驱动SWAT水文模型,分析赣江流域径流演变特征,主要结论如下:1961—2017年赣江流域观测到的年均气温以0.17℃/(10 a)的速率呈显著上升趋势(p<0.01),降水以17 mm/(10 a)的速率呈不显著上升。“双碳”和“高碳”路径下,2021—2100年赣江流域均呈现暖湿态,气温持续变暖,降水有所增加;碳达峰、碳中和时期,“双碳”路径下年径流呈现增加趋势;“双碳”路径下,月径流在汛期呈现增加趋势,枯水期在SSP1-1.9、SSP1-2.6、SSP2-4.5、SSP4-3.4下呈现增加趋势,在SSP4-6.0下呈现减少趋势。“双碳”路径下极端水文事件强度将可能小于“高碳”路径。
引用本文
杨晨辉, 王艳君, 苏布达, 蒲阳, 王媛, 姜彤. SSP“双碳”路径下赣江流域径流变化趋势[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(2): 177-187.
YANG Chen-Hui, WANG Yan-Jun, SU Bu-Da, PU Yang, WANG Yuan, JIANG Tong. Runoff variation trend of Ganjiang River basin under SSP “Double Carbon” path[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(2): 177-187.
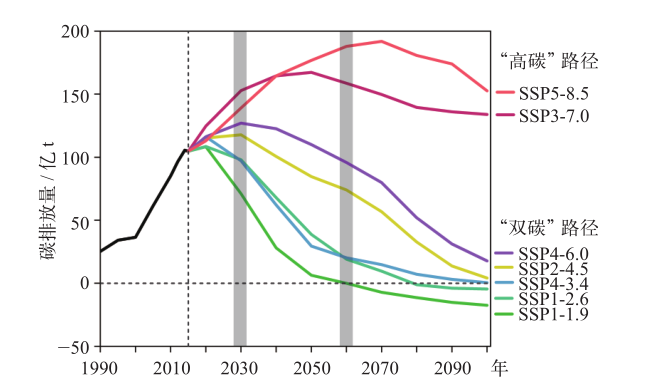
图2 中国“双碳”路径方案 注:两条灰色阴影分别代表2028—2032年碳达峰时期和2058—2062年碳中和时期。
Fig. 2 The plan of “double carbon” pathway in China. (The gray shaded areas represent the period of peak carbon dioxide emissions (2028-2032) and the period of carbon neutral (2058-2062), respectively)
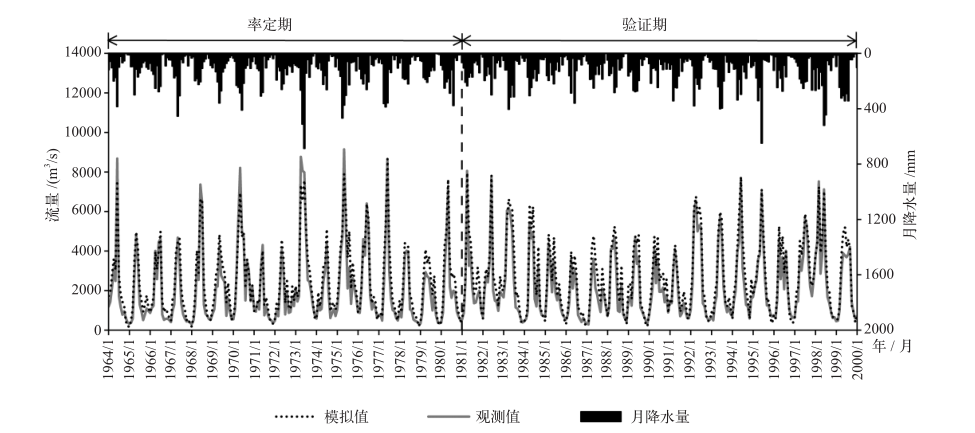
图3 率定期(1964—1980年)和验证期(1981—2000年)月径流模拟值与观测值比较
Fig. 3 Comparison of simulated and observed monthly runoff during calibration period (1964-1980) and validation period (1981-2000)
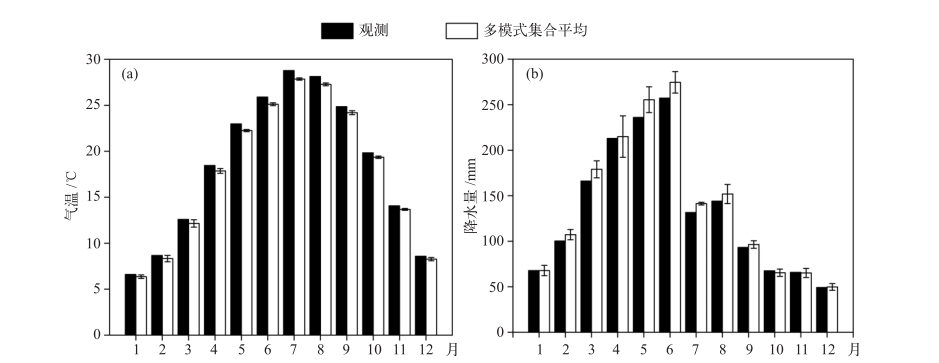
图4 1961—2014年气象观测数据和多模式集合平均数据的月均气温(a)与月降水(b)的年内分布 注:上、下限代表模式最大值和最小值。
Fig. 4 Comparison of monthly mean temperature (a) and monthly precipitation (b) by multi-model ensemble mean and observation in 1961-2014. (The upper and lower limits represent the maximum and minimum values of multiple models)
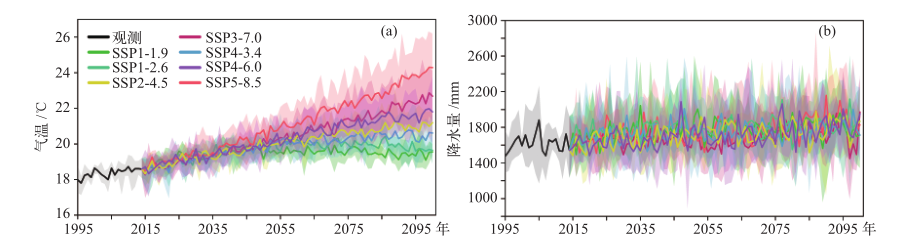
图5 SSPs下1995—2100年赣江流域年均气温(a)及年降水量(b)变化 注:实线为多模式集合平均,阴影表示多个模式的上下限。
Fig. 5 The mean of multi-model annual temperature (a) and precipitation (b) change under different SSPs scenarios from 1995 to 2100 in Ganjiang River basin. (Solid lines represent the multi-model mean, shadows represent the range of multiple models)
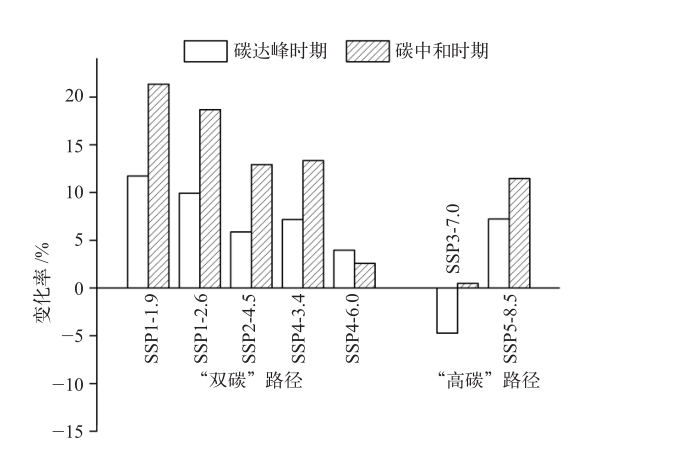
图6 碳达峰、碳中和时期年径流较基准期(1995—2014年)变化率
Fig. 6 The change rate of annual runoff in the period of peak carbon dioxide emissions and carbon neutral relative to the base period (1995-2014)

图7 碳达峰、碳中和时期月径流较基准期变化
Fig. 7 The change rate of monthly runoff in the period of peak carbon dioxide emissions (a, c) and carbon neutral (b, d)relative to the base period
 |
表4 碳达峰、碳中和时期Q10和Q90较基准期变化率(括号内为变化率最大、最小值,括号外为平均值)
Table 4 The change rate of Q10 and Q90 in the period of peak carbon dioxide emissions and carbon neutral relative to the base period. (The maximum and minimum value of change rate is in brackets, and the average value is outside brackets) %
 |
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis[J]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 |
| [2] | Santikarn M, Theuer S L, Eden A, et al. Emissions trading worldwide: status report 2019 [R]. Berlin: ICAP, 2019 |
| [3] |
Beaulieu E, Goddéris Y, Donnadieu Y, et al. High sensitivity of the continental-weathering carbon dioxide sink to future climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2012, 2(5):346-349
doi: 10.1038/nclimate1419 URL |
| [4] |
Griffin M T, Montz B E, Arrigo J S. Evaluating climate change induced water stress: a case study of the lower cape fear basin, NC[J]. Applied Geography, 2013, 40:115-128
doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.02.009 URL |
| [5] | 刘璇, 郭家力, 张静文, 等. 气候变化影响下的赣江流域水资源变化趋势与幅度分析[J]. 水利水电技术, 2018, 49(6):39-46. |
| Liu X, Guo J L, Zhang J W, et al. Analysis on variation trend and amplitude of water resources in Ganjiang River basin under impact of climate change[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2018, 49(6):39-46 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 刘子豪, 陆建忠, 黄建武, 等. 基于CMIP5模式鄱阳湖流域未来参考作物蒸散量预估[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(6):1685-1697. |
| Liu Z H, Lu J Z, Huang J W, et al. Prediction and trend of future reference crop evapotranspiration in the Poyang Lake basin based on CMIP5 models[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(6):1685-1697 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 赵梦霞, 苏布达, 王艳君, 等. 气候变化对东部季风区赣江和官厅流域径流的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6):679-689. |
| Zhao M X, Su B D, Wang Y J, et al. Impacts of climate change on river runoff at the Ganjiang and Guanting River basins in the eastern monsoon region[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(6):679-689 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 周梦瑶, 袁飞, 张利敏, 等. 未来气候变化对赣江上游区极端径流影响预估[J]. 水电能源科学, 2020, 38(1):5-8. |
| Zhou M Y, Yuan F, Zhang L M, et al. Projection of future climate change impacts on extreme runoff in the upper reaches of Ganjiang River basin[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2020, 38(1):5-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
O'neill B C, Tebaldi C, van Vuuren D P, et al. The Scenario Model Intercomparison Project (ScenarioMIP) for CMIP6[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2016, 9(9):3461-3482
doi: 10.5194/gmd-9-3461-2016 URL |
| [10] |
Riahi K, van Vuuren D P, Kriegler E, et al. The shared socioeconomic pathways and their energy, land use, and greenhouse gas emissions implications: an overview[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2017, 42:153-168
doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2016.05.009 URL |
| [11] | 姜彤, 王艳君, 苏布达, 等. 全球气候变化中的人类活动视角: 社会经济情景的演变[J]. 南京信息工程大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 12(1):68-80. |
| Jiang T, Wang Y J, Su B D, et al. Perspectives of human activities in global climate change: evolution of socio-economic scenarios[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2020, 12(1):68-80 (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 姜彤, 吕嫣冉, 黄金龙, 等. CMIP6模式新情景(SSP-RCP)概述及其在淮河流域的应用[J]. 气象科技进展, 2020, 10(5):102-109. |
| Jiang T, Lǚ Y R, Huang J L, et al. New scenarios of CMIP6 model (SSP-RCP) and its application in the Huaihe River basin[J]. Advances in Meteorological Science and Technology, 2020, 10(5):102-109 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] |
Li H, Sheffield J, Wood E F. Bias correction of monthly precipitation and temperature fields from Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change AR4 models using equidistant quantile matching[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2010, 115:D10101
doi: 10.1029/2009JD012882 URL |
| [14] |
Wood A W, Leung L R, Sridhar V, et al. Hydrologic implications of dynamical and statistical approaches to downscaling climate model outputs[J]. Climate Change, 2004, 62(1-3):189-216
doi: 10.1023/B:CLIM.0000013685.99609.9e URL |
| [15] |
Rogelj J, Popp A, Calvin K V, et al. Scenarios towards limiting global mean temperature increase below 1.5℃[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2018, 8(4):325-332
doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0091-3 |
| [16] |
Gidden M J, Riahi K, Smith S J, et al. Global emissions pathways under different socioeconomic scenarios for use in CMIP6: a dataset of harmonized emissions trajectories through the end of the century[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2019, 12(4):1443-1475
doi: 10.5194/gmd-12-1443-2019 URL |
| [17] |
van Marle M J E, Kloster S, Magi B I, et al. Historic global biomass burning emissions for CMIP6 (BB4CMIP) based on merging satellite observations with proxies and fire models (1750-2015)[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2017, 10(9):3329-3357
doi: 10.5194/gmd-10-3329-2017 URL |
| [18] |
Hoesly R M, Smith S J, Feng L, et al. Historical (1750-2014) anthropogenic emissions of reactive gases and aerosols from the Community Emissions Data System (CEDS)[J]. Geoscientific Model Development, 2018, 11(1):369-408
doi: 10.5194/gmd-11-369-2018 URL |
| [19] | 王书霞, 张利平, 喻笑勇, 等. 遥感降水产品在澜沧江流域径流模拟中的适用性研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2019, 28(6):1365-1374. |
| Wang S X, Zhang L P, Yu X Y, et al. Application of remote sensing precipitation products in runoff simulation over the Lancang River basin[J]. Resources and Environment in The Yangtze Basin, 2019, 28(6):1365-1374 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] |
Kundzewicz Z W, Huang S, Szcześniak M, et al. Projections of runoff in the Vistula and the Odra river basins with the help of the SWAT model[J]. Hydrology Research, 2018, 49(2):303-317
doi: 10.2166/nh.2017.280 URL |
| [21] |
Worku T, Khare D, Tripathi S K. Modeling runoff-sediment response to land use/land cover changes using integrated GIS and SWAT model in the Beressa watershed[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(16):1-14
doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6304-z URL |
| [22] | Bieger K, Hörmann G, Fohrer N. Detailed spatial analysis of SWAT-simulated surface runoff and sediment yield in a mountainous watershed in China[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2015, 60(5):784-800 |
| [23] | Alavian V, Qaddumi H M, Dickson E, et al. Water and climate change: understanding the risks and making climate-smart investment decisions[M]. Washington, DC: World Bank, 2009 |
| [24] |
Guo H, Hu Q, Jiang T. Annual and seasonal streamflow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 355(1-4):106-122
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.03.020 URL |
| [25] | 熊翰林. 赣江流域径流对气候变化的响应[D]. 南昌: 南昌工程学院, 2018: 29-33. |
| Xiong H L. Runoff simulation in Ganjiang River basin and its response to climate change[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Institute of Technology, 2018: 29-33 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Su B, Huang J, Zeng X, et al. Impacts of climate change on streamflow in the upper Yangtze River basin[J]. Climatic Change, 2016, 141(3):533-546
doi: 10.1007/s10584-016-1852-5 URL |
| [27] |
Wen S, Su B, Wang Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of hydrological models for climate change impact assessment in the upper Yangtze River basin, China[J]. Climatic Change, 2020, 163(3):1207-1226
doi: 10.1007/s10584-020-02929-6 URL |
| [1] | 赵梦霞, 苏布达, 王艳君, 王安乾, 姜彤. 气候变化对东部季风区赣江和官厅流域径流的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(6): 679-689. |
| [2] | 王珂,蒲焘,史晓宜,孔彦龙. 澜沧江源区气温与降水对径流变化的影响[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3): 306-315. |
| [3] | 李凌程, 张利平, 夏军, 闪丽洁, 刘恋. 气候波动和人类活动对南水北调中线工程典型流域径流影响的定量评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(2): 118-126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||