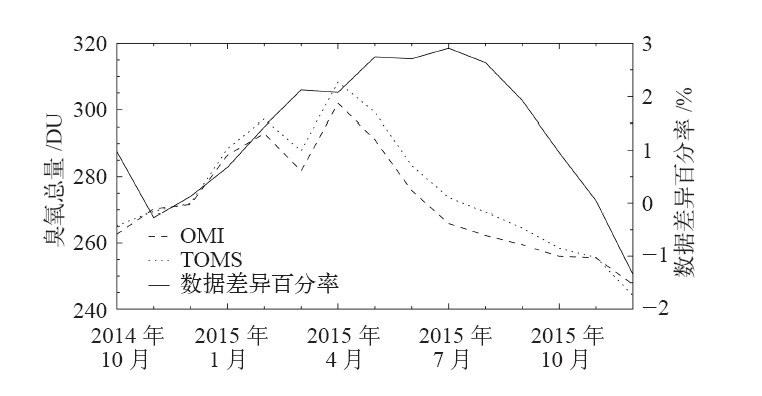
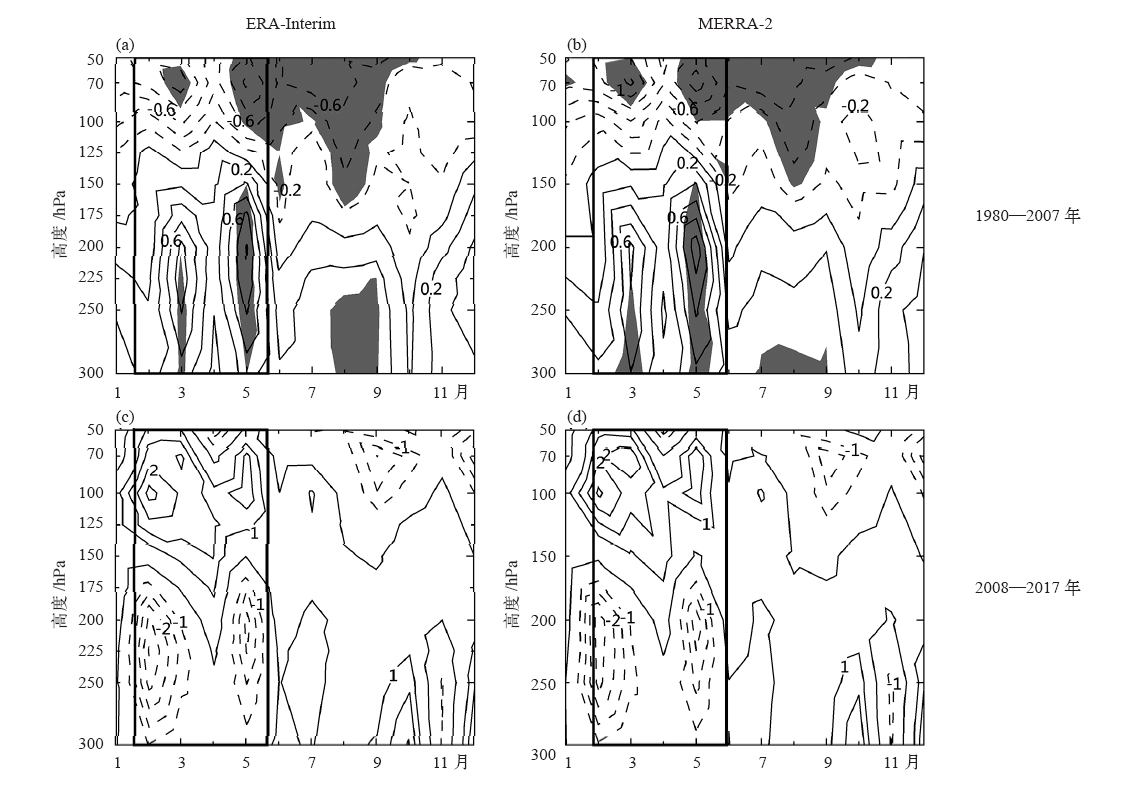
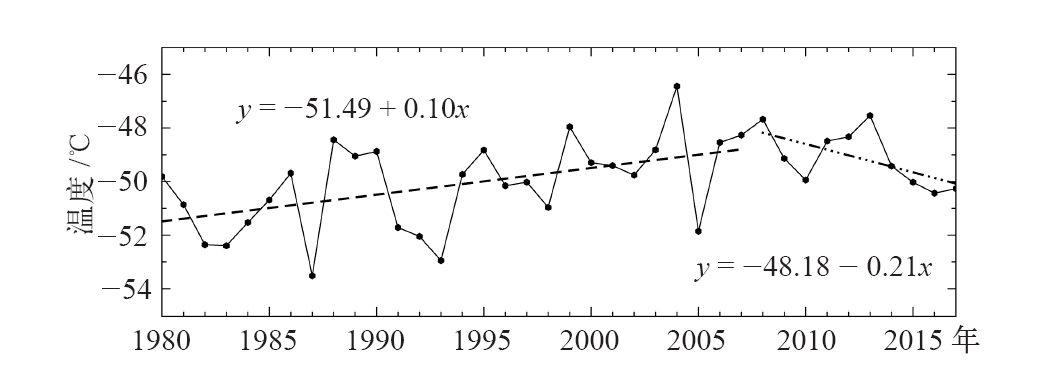
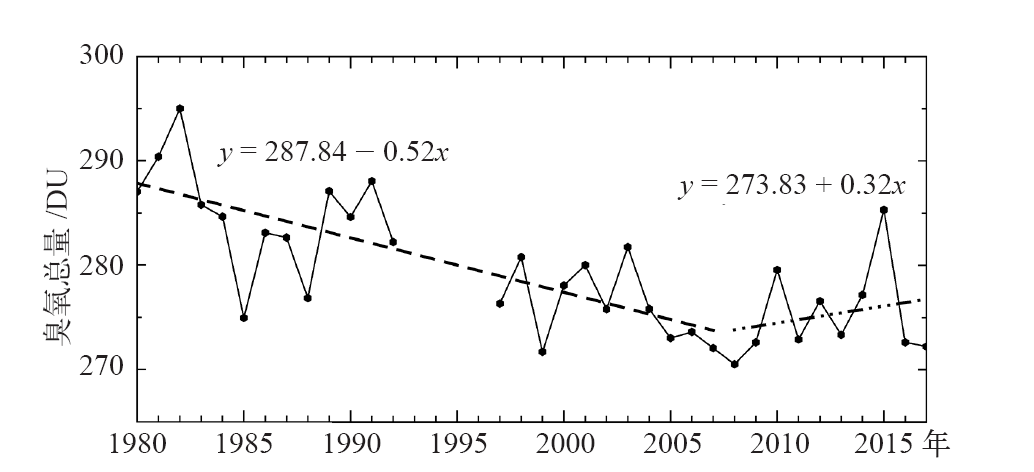
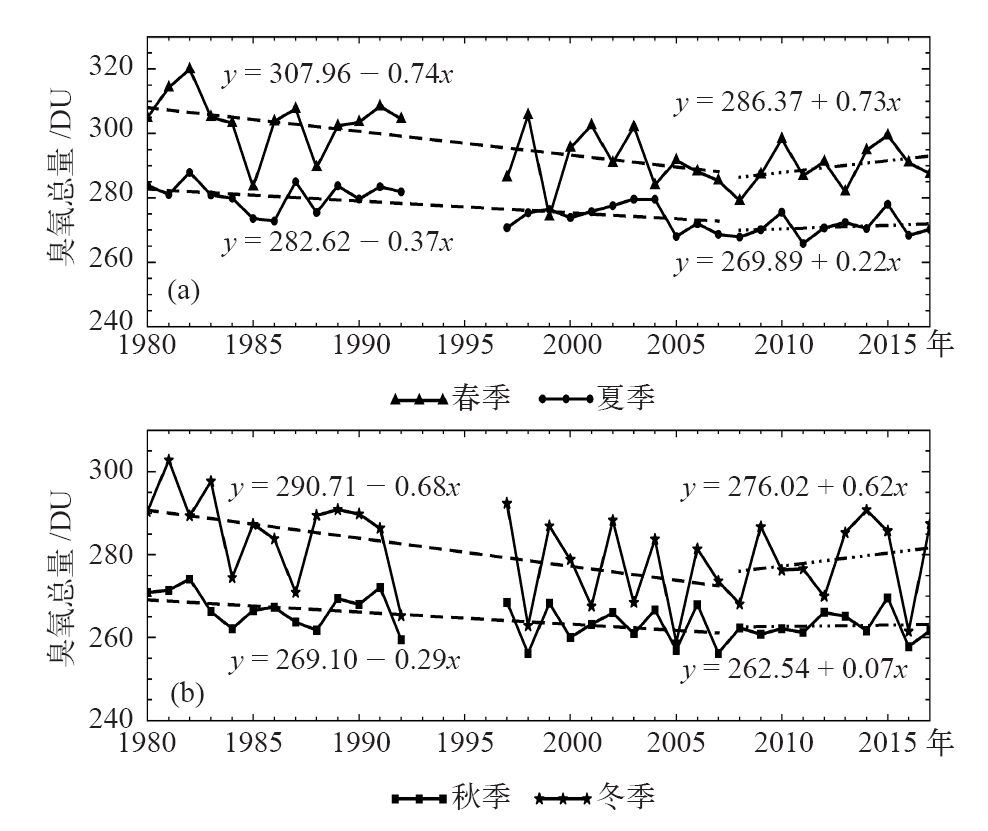
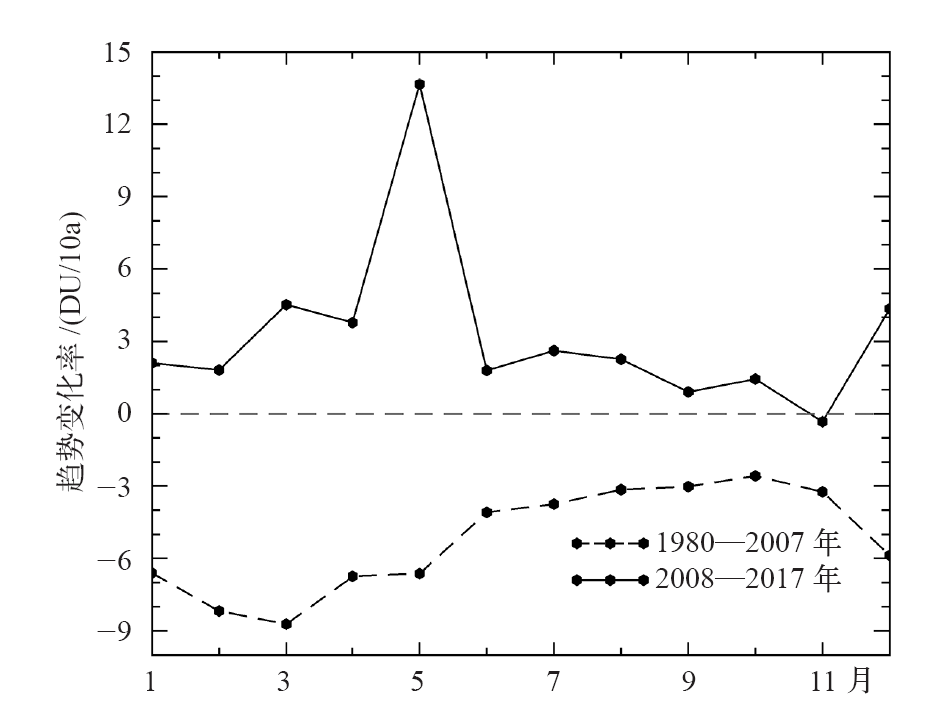
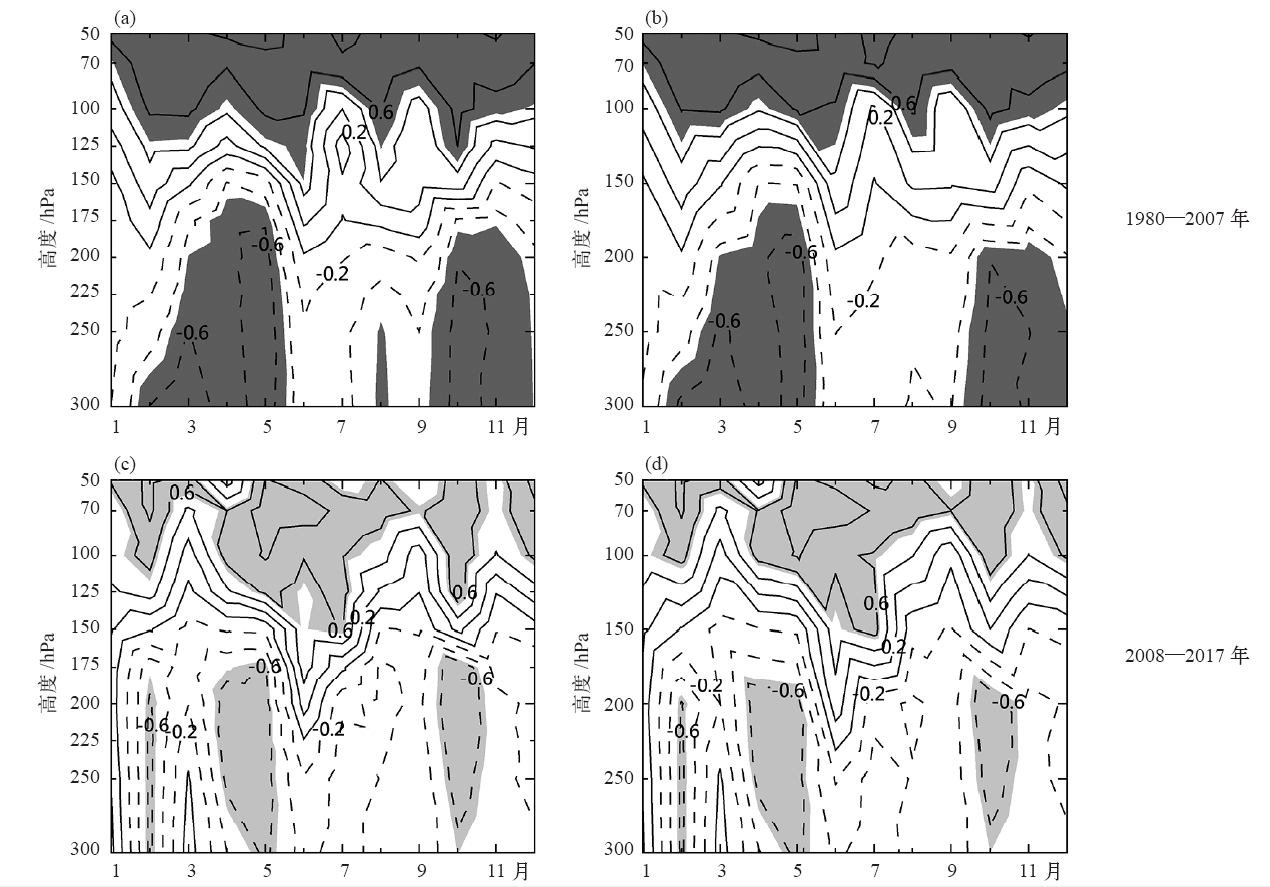
| [1] | You Q L, Kang S C, Aguilar E , et al. Changes in daily climate extremes in the eastern and central Tibetan Plateau during 1961-2005[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2008,113, D07101 | | [2] | You Q L, Fraedrich K, Ren G Y , et al. Variability of temperature in the Tibetan Plateau based on homogenized surface stations and reanalysis data[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2013,33:1337-1347 | | [3] | Kang S C, Xu Y W, You Q L , et al. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2010,5(1):015101 | | [4] | Liu Z C, Yang M X, Wan G N , et al. The spatial and temporal variation of temperature in the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau during 1971-2015[J]. Atmosphere, 2017,8(11):214 | | [5] | Zhang R H, Zhou S W . Air temperature changes over the Tibetan Plateau and other regions in the same latitudes and the role of ozone depletion[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2009,23(3):290-299 | | [6] | 郭艳君 . 高空大气温度变化趋势不确定性的研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2008,23(1):24-30. | | [6] | Guo Y J . Advances in uncertainties in upper air temperature trends[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2008,23(1):24-30 (in Chinese) | | [7] | Liu X D, Chen B D . Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2000,20:1729-1742 | | [8] | Zou H, Zhu J H, Zhou L B , et al. Validation and application of reanalysis temperature data over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2014,28(1):139-149 | | [9] | 廖蜜, 张鹏, 吴雪宝 , 等. 利用MSU序列研究高空大气温度变化的进展[J]. 气象, 2011,37(9):1151-1157. | | [9] | Liao M, Zhang P, Wu X B , et al. Research advance of the temperature changes in the upper air using MSU time series[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2011,37(9):1151-1157 (in Chinese) | | [10] | 周秀骥, 罗超, 李维亮 . 中国地区臭氧总量变化与青藏高原低值中心[J]. 科学通报, 1995,40(15):1396-1398. | | [10] | Zhou X J, Luo C, Li W L . Changes of the total ozone in China and the low-value centers in the Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995,40(15):1396-1398 (in Chinese) | | [11] | Zhou X J, Li W L, Chen L X , et al. study on ozone change over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2006,20(2):129-143 | | [12] | Zou H . Seasonal variation and trends of TOMS ozone over Tibet[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1996,23(9):1029-1032 | | [13] | Chen S B, Zhao L, Tao Y L . Stratospheric ozone change over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 2017,8:528-534 | | [14] | Tzanis C . On the relationship between total ozone and temperature in the troposphere and the lower stratosphere[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2009,30(23):6075-6084 | | [15] | Zhang J K, Tian W S, Xie F , et al. Climate warming and decreasing total column ozone over the Tibetan Plateau during winter and spring[J]. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 2014,66:23415. DOI: 10.3402/tellusb.v66.23415 | | [16] | Zhou S W, Zhang R H . Decadal variations of temperature and geopotential height over the Tibetan Plateau and their relations with Tibet ozone depletion[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2005,32, L18705 | | [17] | 黄富祥, 刘年庆, 赵明现 , 等. 风云三号卫星紫外臭氧垂直廓线产品反演试验[J]. 科学通报, 2009,54:2556-2561. | | [17] | Huang F X, Liu N Q, Zhao M X , et al. Vertical ozone profiles deduced from measurements of SBUS on FY-3 satellite[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009,54:2556-2561 (in Chinese) | | [18] | 周顺武, 张人禾 . 青藏高原地区上空NCEP/NCAR再分析温度和位势高度资料与观测资料的比较分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2009,14(2):284-292. | | [18] | Zhou S W, Zhang R H . Comparison of NCEP/NCAR reanalysis data and radiosonde data about temperature and geopotential height of upper air over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2009,14(2):284-292 (in Chinese) | | [19] | 何冬燕, 田红, 邓伟涛 . 三种再分析地表温度资料在青藏高原区域的适用性分析[J]. 大气科学学报, 2013,36(4):458-465. | | [19] | He D Y, Tian H, Deng W T . Applicability analysis of three reanalysis surface temperature data over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Science, 2013,36(4):458-465 (in Chinese) | | [20] | Gao L, Hao L, Chen X W . Evaluation of ERA-Interim monthly temperature data over the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2014,11(5):1154-1168 | | [21] | Hurrell J W, Trenberth K E . An evaluation of monthly mean MSU and ECMWF global atmospheric temperatures for monitoring climate[J]. Journal of Climate, 1991,5:1424-1440 | | [22] | Huang F X, Ren S L, Han S S, et al. Spatiotemporal variations of correlation between the Arctic atmospheric ozone and temperature[C]. Valencia, Spain: 2018 IEEE IGARS, 2018: 6548-6551 | | [23] | Humlum O, Stordahl K, Solheim J . The phase relation between atmospheric carbon dioxide and global temperature[J]. Global and Planetary Chang, 2013,100:51-59 | | [24] | Cubasch U, Voss R, Hegerl G C , et al. Simulation of the influence of solar radiation variations on the global climate with an ocean-atmosphere general circulation model[J]. Climate Dynamics, 1997,13:757-767 | | [25] | Dai A, Trenberth K E . Effects of clouds, soil moisture, precipitation, and water vapor on diurnal temperature range[J]. Journal of Climate, 1999,12:2451-2473 |
|
 ),Xue-Qi XIA1
),Xue-Qi XIA1