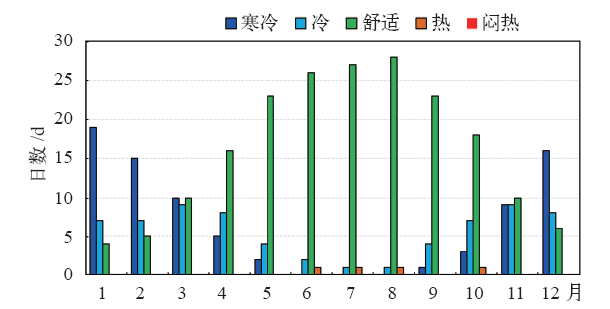
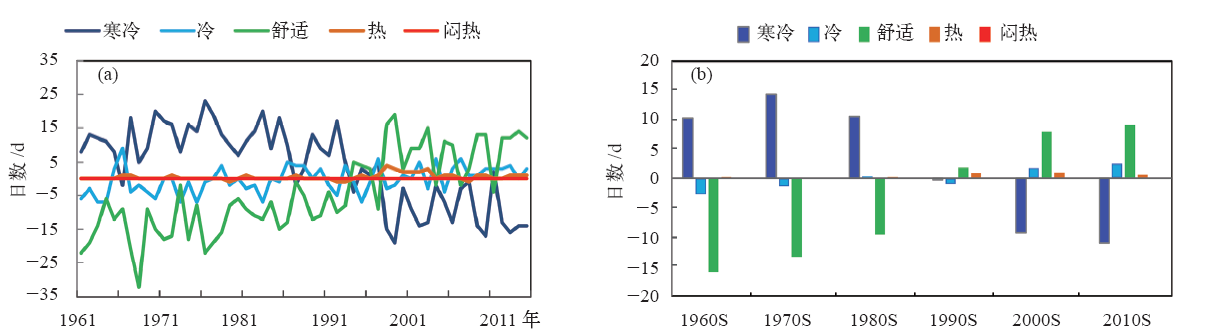
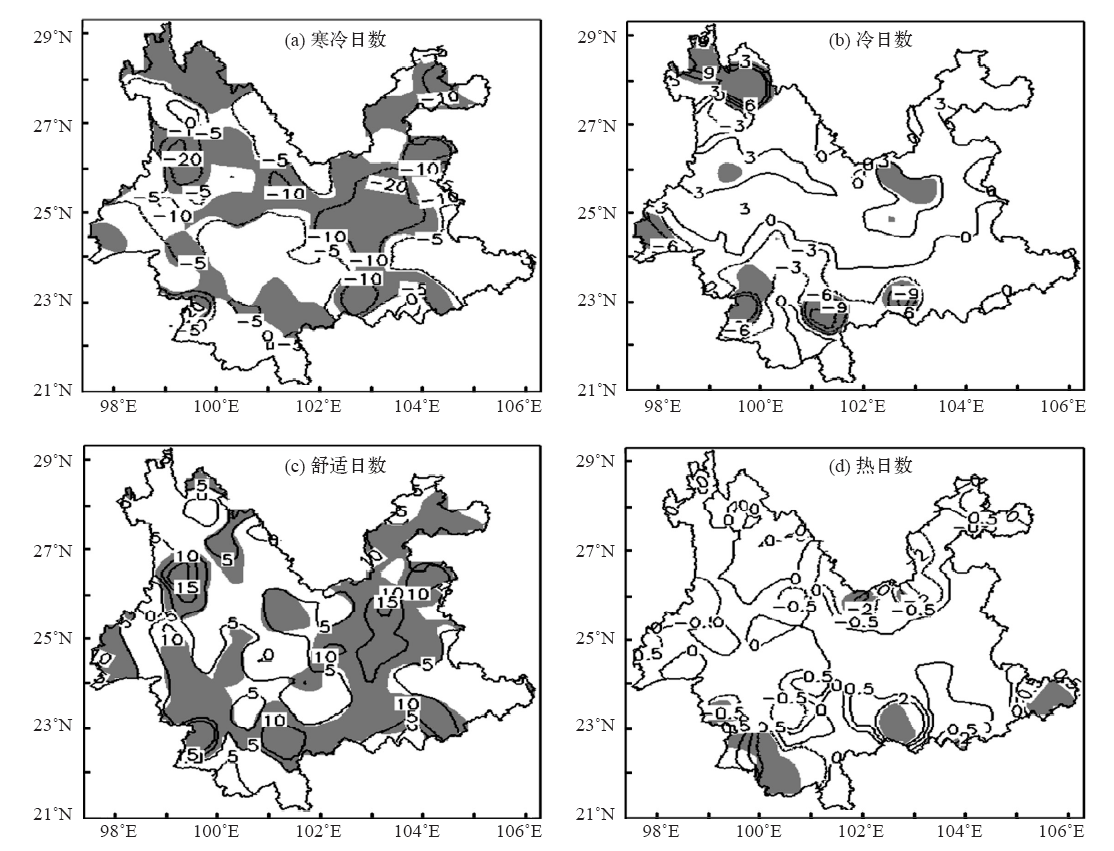
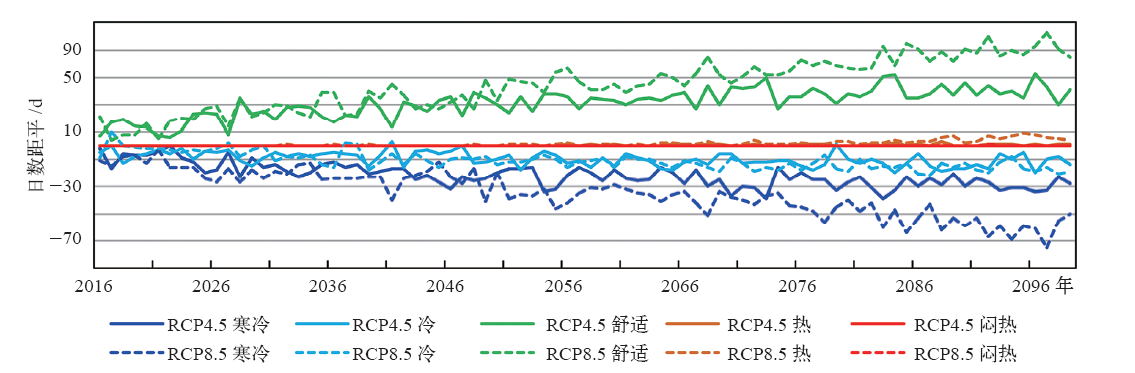
| [1] | 冯明, 毛飞, 王学良, 等. 人居环境气候舒适度评价: GB/T 27963—2011[S]. 中华人民共和国国标标准, 2011: 1-4 | | [2] | 黄海霞, 李建龙, 黄良美. 南京市小气候日变化规律及其对人体舒适度的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2008, 27(4): 601-606 | | [3] | 朱燕君, 陈峪, 李庆祥,等. 北京奥运会期间的气象条件分析[J]. 应用气象学报, 2006, 17(增刊): 35-41 | | [4] | 柏秦凤, 霍治囯, 贺楠, 等. 中国20座旅游城市人体舒适度指数分析[J]. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(8): 1607-1612 | | [5] | 于赓康, 徐敏, 于堃, 等. 近30年江苏人体舒适度指数变化特征分析[J]. 气象, 2011, 37(9): 1145-1150 | | [6] | 邹旭凯. 长江三峡库区旅游气候资源评估[J]. 气象, 2003, 29(11): 55-57 | | [7] | 张志薇. 基于舒适度研究的中国大陆健康气候评估[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2014: 1-174 | | [8] | 刘明. 从生活舒适度角度出发浅谈规划对城市生活状态的影响[J]. 基层建设, 2015, 1: 19 | | [9] | 秦剑, 琚建华, 解明恩. 低纬高原天气气候[M]. 北京:气象出版社, 1997: 1-210 | | [10] | 曹伟宏, 何元庆, 李宗省. 云南丽江旅游气候舒适度分析[J].冰川冻土, 2012, 34(1): 201-206 | | [11] | 王金亮, 王平. 香格里拉旅游气候的适宜度[J]. 热带地理, 1999, 19(3): 235-239 | | [12] | 王金亮, 王平, 蒋莲芳. 昆明人居环境气候适宜度分析[J]. 经济地理, 2002, 22(增刊): 196-200 | | [13] | 刘文杰, 李红梅. 西双版纳旅游气候资源[J]. 自然资源, 1997 (2): 62-66 | | [14] | 吴佳, 高学杰,韩振宇, 等. 基于有效气温指数的云南舒适度变化分析[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(2): 174-186 | | [15] | 中国气象局. 地面气候资料30年整编常规项目及其统计方法: GX/T 22—2004[S]. 北京:中华人民共和国气象行业标准, 2004: 1-9 | | [16] | 中国气象局. 地面气象观测规范[M]. 2004版.北京:气象出版社, 2003: 1-151 | | [17] | Giorgi F, Coppola E, Solmon F, et al. RegCM4: Model description and illustrative basic performance over Selected CORDEX domains[J]. Climate Research, 2012, 52: 7-29 | | [18] | Gao X J, Shi Y, Giorgi F.Comparison of convective parameterizations in RegCM4 experiments with CLM as the land surface model over China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2016, 9: 246-254, DOI: 10.1080/16742834.2016.1172938 | | [19] | Gao X J, Wang M L, Giorgi F.Climate change over China in the 21st century as simulated by BCC_CSM1.1-RegCM4.0[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2013, 6(5): 381-386 | | [20] | Moss R H, Edmonds J A, Hibbard K A, et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment[J]. Nature, 2010, 463: 747-756 | | [21] | 段旭,陶云,段长春. 云南省细网格气候区划及气候代表站选取[J]. 大气科学学报, 2011, 34(3): 336-342 | | [22] | 魏凤英. 现代气候统计诊断与预测技术[M]. 第2版.北京:气象出版社, 2007: 63-66 | | [23] | 朱卫浩, 张书余,罗斌. 近30 a全国人体舒适度指数变化特征[J]. 干旱气象, 2012, 30(2): 220-226 | | [24] | 郑有飞, 余永江,谈建国.气象参数对人体舒适度的影响研究[J]. 气象科技, 2007, 35(6): 827-831 | | [25] | Chen, X L, Zhou T J. Uncertainty in crossing time of 2℃ warming threshold over China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2016, 61(18): 1451-1459 |
|
 ), Wei HUANG1(
), Wei HUANG1( ), Yong ZHU1, Meng LI1, Bo-Tao ZHOU2
), Yong ZHU1, Meng LI1, Bo-Tao ZHOU2