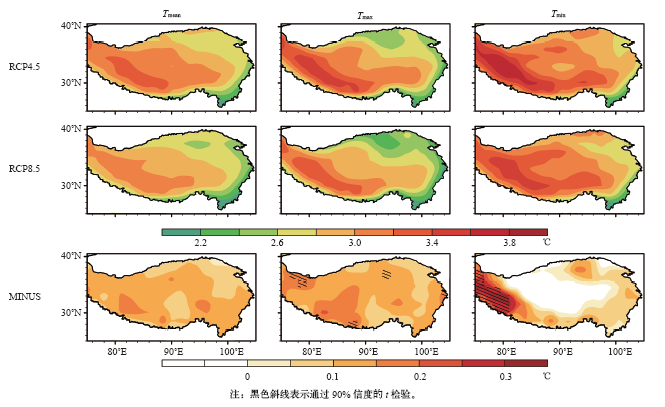
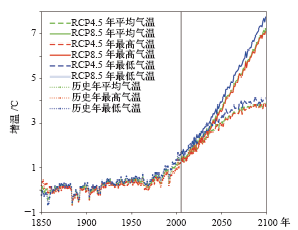
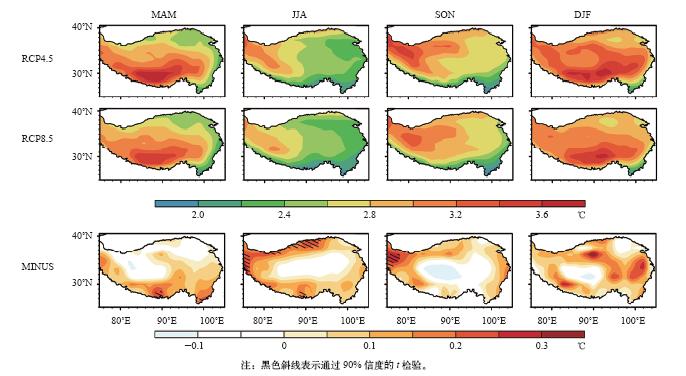
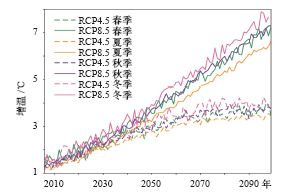
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 95-123 | | [2] | Ding Z L, Duan X N, Ge Q S , et al. Control of atmospheric CO2 concentrations by 2050: a calculation on the emission rights of different countries[J]. Science in China, 2009,52(10):1447 | | [3] | 叶笃正 . 青藏高原气象学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1979 | | [4] | 戴加洗 . 青藏高原气候[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 1990 | | [5] | 冯松, 汤懋苍 . 青藏高原是我国气候变化启动区的新证据[J]. 科学通报, 1998,43(6):633-636 | | [6] | 潘保田, 李吉均 . 青藏高原: 全球气候变化的驱动机与放大器: III青藏高原隆起对气候变化的影响[J]. 兰州大学学报: 自然科学版, 1996 ( 1):108-115 | | [7] | 吴祥定, 林振耀 . 历史时期青藏高原气候变化特征的初步分析[J]. 气象学报, 1981 ( 1):92-99 | | [8] | 汤懋苍, 白重瑗, 冯松 , 等. 本世纪青藏高原气候的三次突变及与天文因素的相关[J]. 高原气象, 1998,17(3):250-257 | | [9] | Fang X, Luo S, Lyu S H . Observed soil temperature trends associated with climate change in the Tibetan Plateau, 1960-2014[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2337-9 | | [10] | Liu X, Chen B . Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2000,20(14):1729-1742 | | [11] | 郑然, 李栋梁, 蒋元春 . 全球变暖背景下青藏高原气温变化的新特征[J]. 高原气象, 2015,34(6):1531-1539 | | [12] | Kang S C, You Q L, Flugel W A , et al. Review of climate and cryospheric change in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2010,5(1):015101 | | [13] | 段安民, 肖志祥, 吴国雄 . 1979—2014年全球变暖背景下青藏高原气候变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016,12(5):374-381 | | [14] | Cai D L, You Q L, Fraedrich K , et al. Spatiotemporal temperature variability over the Tibetan Plateau: altitudinal dependence associated with the global warming hiatus[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017,30(3):684-696 | | [15] | 吴成启, 唐登勇 . 近50年来全球变暖背景下青藏高原气温变化特征[J]. 水土保持研究, 2017,24(6):262-266 | | [16] | 张人禾, 苏凤阁, 江志红 , 等. 青藏高原21世纪气候和环境变化预估研究进展[J]. 科学通报, 2015,60(32):3036-3047 | | [17] | 程志刚, 刘晓东, 范广洲 , 等. 21世纪青藏高原气候时空变化评估[J]. 干旱区研究, 2011,28(4):669-676 | | [18] | 李红梅, 李林 . 2℃全球变暖背景下青藏高原平均气候和极端气候事件变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015,11(3):157-164 | | [19] | 孔莹, 王澄海 . 全球升温1.5℃时北半球多年冻土及雪水当量的响应及其变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(4):316-326 | | [20] | 翟盘茂, 余荣, 周佰铨 , 等. 1.5℃增暖对全球和区域影响的研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017,13(5):465-472 | | [21] | 姜大膀, 富元海 . 2℃全球变暖背景下中国未来气候变化预估[J]. 大气科学, 2012,36(2):234-246 | | [22] | 郎咸梅, 隋月 . 全球变暖2℃情景下中国平均气候和极端气候事件变化预估[J]. 科学通报, 2013,58(8):734-742 | | [23] | 张莉, 丁一汇, 吴统文 , 等. CMIP5模式对21世纪全球和中国年平均地表气温变化和2℃升温阈值的预估[J]. 气象学报, 2013 ( 6):1047-1060 | | [24] | 胡婷, 孙颖, 张学斌 . 全球1.5和2℃温升时的气温和降水变化预估[J]. 科学通报, 2017 ( 26):3098-3111 | | [25] | Shi C, Jiang Z H, Chen W L , et al. Changes in temperature extremes over China under 1.5℃ and 2℃ global warming targets[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2018,9(2):120-129 | | [26] | 周天军, 邹立维, 吴波 , 等. 中国地球气候系统模式研究进展: CMIP计划实施近20年回顾[J]. 气象学报, 2014,72(5):892-907 | | [27] | 叶笃正, 季劲钧 . 迎接大气科学发展即将到来的新飞跃[J]. 地球科学进展, 2005,20(10):1047-1052 | | [28] | 胡芩, 姜大膀, 范广洲 . CMIP5全球气候模式对青藏高原地区气候模拟能力评估[J]. 大气科学, 2014,38(5):924-938 | | [29] | 许崇海, 沈新勇, 徐影 . IPCC AR4模式对东亚地区气候模拟能力的分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007,3(5):287-292 | | [30] | Zhang Y Q, You Q L, Mao G X , et al. Short-term concurrent drought and heatwave frequency with 1.5 and 2.0℃ global warming in humid subtropical basins: a case study in the Gan River Basin, China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018: 1-21. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-018-4398-6 | | [31] | Zhou T J, Yu R C . Twentieth-century surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by Coupled Climate Models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006,19(22):5843 | | [32] | 除多, 达娃, 拉巴卓玛 , 等. 基于MODIS数据的青藏高原积雪时空分布特征分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2017,29(2):117-124 | | [33] | 赵宗慈, 罗勇, 黄建斌 . 从CMIP5看全球1.5℃升温[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018,14(2):218-220 | | [34] | Schleussner C F, Lissner T K, Fischer E M , et al. Differential climate impacts for policy-relevant limits to global warming: the case of 1.5℃ and 2℃[J]. Earth System Dynamics, 2016,6(2):2447-2505 | | [35] | 王绍武, 罗勇, 赵宗慈 , 等. 全球气候变暖原因的争议[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011,7(2):79-84 | | [36] | 王宁练, 姚檀栋 . 20世纪全球变暖的冰冻圈证据[J]. 地球科学进展, 2001,16(1):98-105 | | [37] | 秦大河 . 气候变化的事实与影响及对策[J]. 中国科学基金, 2003,17(1):1-3 | | [38] | 张人禾, 周顺武 . 青藏高原气温变化趋势与同纬度带其他地区的差异以及臭氧的可能作用[J]. 气象学报, 2008,66(6):916-925 | | [39] | 程译萱, 范广洲, 张永莉 , 等. 青藏高原及周边地区垂直温度梯度特征及其成因分析[J]. 高原气象, 2018,37(2):333-348 |
|
 ),Wen-Xin XIE1,Ling ZHANG1
),Wen-Xin XIE1,Ling ZHANG1