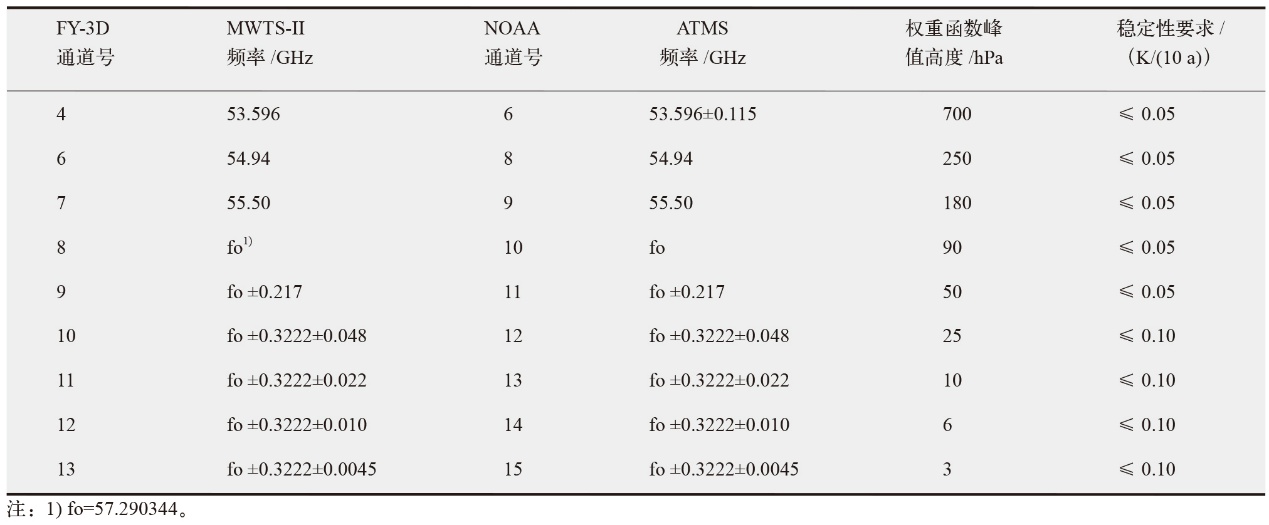
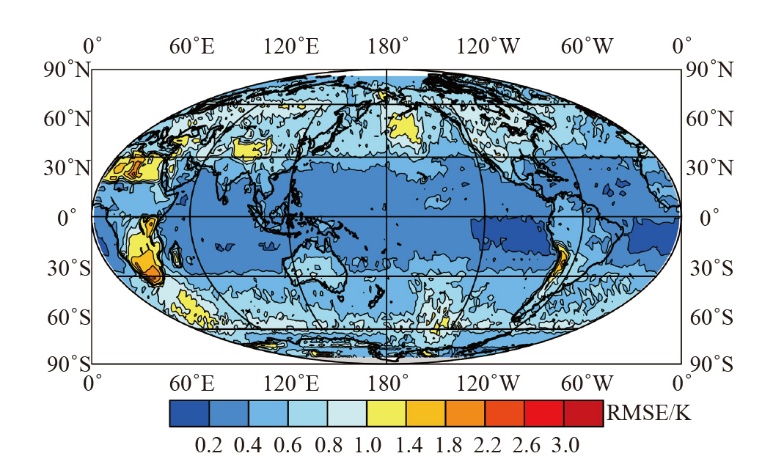
Climate Change Research ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (6): 733-741.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.083
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation of temporal stability in atmospheric temperature observations from FengYun-3D satellite for climate change research
GUO Yan-Jun1( ), ZOU Cheng-Zhi2
), ZOU Cheng-Zhi2
- 1 National Climate Centre, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
2 Independent Researcher, Laurel, Maryland 20723, USA
-
Received:2025-04-15Revised:2025-06-10Online:2025-11-30Published:2025-10-22
Cite this article
GUO Yan-Jun, ZOU Cheng-Zhi. Evaluation of temporal stability in atmospheric temperature observations from FengYun-3D satellite for climate change research[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 733-741.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.083
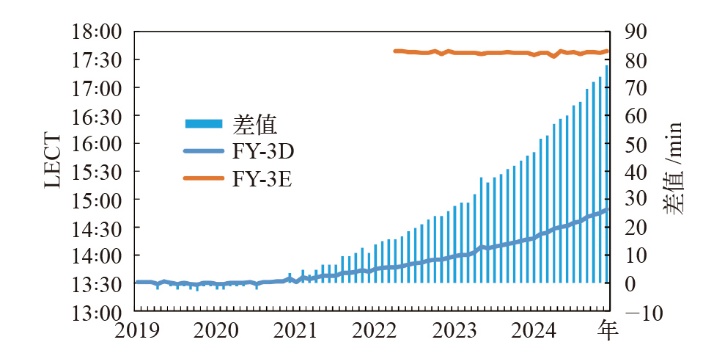
Fig. 1 Monthly mean Ascending Local Equator Crossing Time (LECT) for the FY-3D and FY-3E satellites from 2019 to 2024, along with the FY-3D LECT differences relative to its January 2019
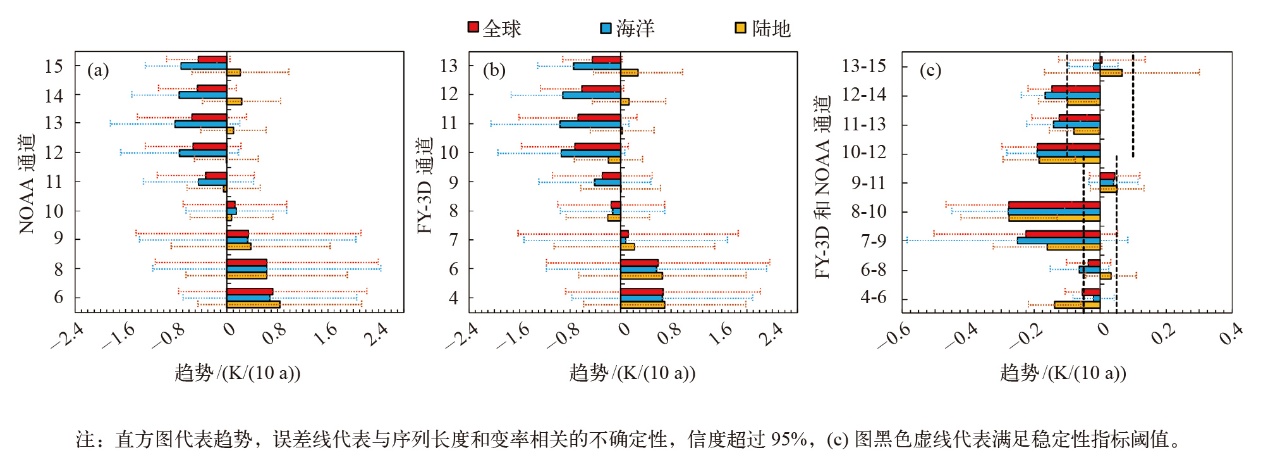
Fig. 2 Trends of mean-layer temperature anomalies during 2019-2024 for the 9 channels analyzed in this study, averaged over the globe, ocean, and land for NOAA (a), FY-3D (b), and their differences (c). (The bars represent trends with error bars superimposed on them. The trend uncertainty represents 95% confidence intervals with autocorrelation adjustments, which account for time length limitations and temporal variability. The black dashed lines in (c) represent the stability thresholds for the 9 channels)

Fig. 3 Monthly temperature anomaly time series from 2019 to 2024 for FY-3D and NOAA, and their differences, averaged over the ocean (a) and land (b). (Anomalies are calculated as departures from the 2019-2024 base period. The labels in each panel from left to right represent linear trend and uncertainty, standard deviation, and correlation coefficient, respectively. Blue represents NOAA, red represents FY-3D, and black represents their difference or correlation)
| [1] |
Hurrell J, Trenberth K. Spurious trends in satellite MSU temperatures from merging different satellite records[J]. Nature, 1997, 386: 164-167
doi: 10.1038/386164a0 |
| [2] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007: 265-271 |
| [3] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 194-201 |
| [4] | IPCC. Climate change: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021: 327-329 |
| [5] | Zou C Z, Goldberg M, Cheng Z, et al. Recalibration of microwave sounding unit for climate studies using simultaneous nadir overpasses[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 2006, 111: 1-24 |
| [6] | Zou C Z, Xu H, Hao X, et al. Mid-tropospheric layer temperature record derived from satellite microwave sounder observations with backward merging approach[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2023, 128: e2022JD037472 |
| [7] |
Mears C A, Schabel M C, Wentz F J. A reanalysis of the MSU channel 2 tropospheric temperature record[J]. Journal of Climate, 2003, 16: 3650-3664
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<3650:AROTMC>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [8] |
Mears C A, Wentz F J. Sensitivity of satellite-derived tropospheric temperature trends to the diurnal cycle adjustment[J]. Journal of Climate, 2016, 29: 3629-3646
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0744.1 URL |
| [9] |
Spencer R W, Christy J R. Precision and radiosonde validation of satellite grid point temperature anomalies. Part I: MSU channel 2[J]. Journal of Climate, 1992, 5: 847-857
doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1992)005<0847:PARVOS>2.0.CO;2 URL |
| [10] |
Spencer R W, Christy J R, Braswell W D. UAH version 6 global satellite temperature products: methodology and results[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 53: 121-130
doi: 10.1007/s13143-017-0010-y URL |
| [11] |
Steiner A K, Ladst?dter F, Randel W, et al. Observed temperature changes in the troposphere and stratosphere from 1979 to 2018[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33: 8165-8194
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0998.1 |
| [12] |
Guo Y, Weng F, Wang G, et al. The long-term trend of upper-air temperature in China derived from microwave sounding data and its comparison with radiosonde observations[J]. Journal of Climate, 2020, 33: 7875-7895
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-19-0742.1 URL |
| [13] |
Santer B D, Solomon S, Pallotta G, et al. Comparing tropospheric warming in climate models and satellite data[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30: 373-392
doi: 10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0333.1 URL |
| [14] |
Zou X. Studies of FY-3 observations over the past 10 years: a review[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13: 673
doi: 10.3390/rs13040673 URL |
| [15] |
Xian D, Zhang P, Gao L, et al. Fengyun meteorological satellite products for Earth system science applications[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Science, 2021, 38: 1267-1284
doi: 10.1007/s00376-021-0425-3 |
| [16] | 谷松岩, 郭杨, 谢鑫新, 等. 风云三号卫星微波载荷历史数据再定标[J]. 遥感学报, 2023, 27 (10): 2252-2269. |
|
Gu S Y, Gou Y, Xie X X, et al. Recalibration of the FY-3 microwave payload historical data records[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2023, 27 (10): 2252-2269 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11834/jrs.20221436 URL |
|
| [17] | 曹皓东, 张鹏, 廖蜜, 等. 风云三号微波温度计长序列再定标历史数据集质量评估[J]. 大气科学学报, 2024, 47 (4): 669-680. |
| Cao H D, Zhang P, Liao M, et al. Quality assessment of the long-term recalibration history dataset of the FY-3 microwave temperature sounder[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2024, 47 (4): 669-680 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | GCOS (Global Climate Observing Systems)-245. The 2022 GCOS ECVs requirements[R]. Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2022: 1-244 |
| [19] |
Carminati F, Atkinson N, Candy B, et al. Insights into the microwave instruments onboard the Fengyun 3D satellite: data quality and assimilation in the Met Office NWP system[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Science, 2021, 38 (8): 1379-1396
doi: 10.1007/s00376-020-0010-1 |
| [20] | 陆其峰. 风云三号A星大气探测资料数据在欧洲中期天气预报中心的初步评价与同化研究[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41 (7): 890-894. |
| Lu Q F. Initial evaluation and assimilation of FY-3A atmospheric sounding data in the ECMWF System[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2011, 41 (7): 890-894 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王祥, 任义方, 吴彬. 用GPS资料对风云三号微波温度计资料进行绝对校准[J]. 大气科学学报, 2017, 40 (1): 81-89. |
| Wang X, Ren Y F, Wu B. Absolute calibration of MWTS sounding channels using GPS RO data[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2017, 40 (1): 81-89 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | GCOS-107. Systematic observation requirements for satellite-based products for climate[R]. Switzerland: World Meteorological Organization, 2006: 1-103 |
| [23] | Zou C Z, Goldberg M, Hao X. New generation of U.S. satellite microwave sounder achieves high radiometric stability performance for reliable climate change detection[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4 (10): eaau0049 |
| [24] | Zou C Z, Xu H, Hao X, et al. Post-millennium atmospheric temperature trends observed by satellites on stable orbits[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48 (13): e2021GL093291 |
| [25] | Zou C Z, Wang W. Inter-satellite calibration of AMSU-A observations for weather and climate applications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmosphere, 2011, 116: D23113 |
| [26] |
Christy J R, Spencer R W, Braswell W D, et al. Examination of space-based bulk atmospheric temperatures used in climate research[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2018, 39 (11): 3580-3607
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1444293 URL |
| [27] |
Dee D P, Uppala S. Variational bias correction of satellite radiance data in the ERA-Interim reanalysis[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 2009, 135: 1830-1841
doi: 10.1002/qj.v135:644 URL |
| [28] | Fu Y, Zou C Z, Zhang P, et al. A climate data record of atmospheric moisture and sea surface temperature from satellite observations[J]. Earth System Science Data Discuss, 2025, 17: 4651-4670. DOI: 10.5194/essd-17-4651-2025 |
| [1] | ZENG Ying-Ting, TANG Zhen-Fei, WU Bin, ZHOU Ming-Zhu. Estimation of China’s offshore photovoltaic power generation potential and analysis of driving factors [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 830-838. |
| [2] | XIAO Xue, HUANG Meng-Tian, ZHOU Bai-Quan, WANG Chen-Peng, ZHAI Pan-Mao. Impact of the 2022 compound hot-dry extreme events on vegetation growth over the Tibetan Plateau [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 777-788. |
| [3] | WANG Sheng, CHEN Jian, ZHOU Yu, SUN Jia-Li, ZHAI Zhen-Fang, XIE Wu-San, DAI Juan, DING Xiao-Jun, WU Rong. Projection of the suitable cultivation area for single-cropping rice in the Jianghuai region based on CMIP6 and MaxEnt model [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 766-776. |
| [4] | HAN Chi, WEN Hong-Qi, ZHANG Shu-Lin, ZHANG Jun-Long, LI Wei, CHEN Ming-Shuai, YOU Li. Effectiveness of cross-industry water rights trading on water management in water-deficient basins under multiple climate change scenarios [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(6): 753-765. |
| [5] | HE Hao, LI Man, LIU Miao, CHEN Ming-Jie, LI Qi, HU Zheng-Hua. Impact of climate change on rice diseases: research progress and future prospects [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(5): 641-658. |
| [6] | HU Jin-Peng, HE Yan, SHI Pei-Jun. Research progress and prospects on the impacts of compound hot and dry events on wheat yield [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(5): 625-640. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xin-Yue, LI Kuo, ZHAO Ming-Yue, XU Yin-Long. Review and prospect of agricultural adaptive capacity building to climate change in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(5): 613-624. |
| [8] | FANG Jia-Yi, ZHANG Tong, XIAO Cun-De. Risk of sea level rise in China under extreme scenarios of rapid ice sheet retreat [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(5): 602-612. |
| [9] | FAN Xing, LIANG Qi-Di, WU Cheng-Lin, GAO Xiang. Stocktaking on the Baku Climate Change Conference and perspectives on global climate governance [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 583-592. |
| [10] | SUN Ruo-Shui, LIANG Mei-Cong. From Paris to Belém: progress and forecast at the decennial of Paris Agreement [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 574-582. |
| [11] | TAN Xian-Chun, CHENG Yong-Long, YAN Hong-Shuo, XING Xiu-Cheng, ZHU Kai-Wei, WANG Chen-Xu. Interpretation and implications of the summary on climate change mitigation in the IPCC Seventh Assessment Report Working Group III [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 494-501. |
| [12] | CHEN Xian-Yao, BI Han-Wen, HAO Xiao-Jie, MA Tian-Jiao, GUO Ling-Rui. Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and its impact on global climate change [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 469-476. |
| [13] | ZHU Song-Li. The evolution of country classification under UNFCCC system [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 565-573. |
| [14] | DING Jie, CAO Zuo-Nan, HU Guo-Zheng, HASBAGAN Ganjurjav, ZHAO Fen, WANG Hai-Feng, GAO Qing-Zhu. Climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability and implications in Working Group II of the IPCC Seventh Assessment Report [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 484-493. |
| [15] | WANG Bo-Wen, HE Yi, TENG Fei. Attribution and assessment of direct and indirect economic losses from extreme weather events in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 502-518. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||