气候变化研究进展 ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 502-518.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2024.305
我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因
- 清华大学能源环境经济研究所,北京 100084
-
收稿日期:2024-12-16修回日期:2025-04-07出版日期:2025-07-30发布日期:2025-07-03 -
通讯作者:滕飞,男,教授,tengfei@tsinghua.edu.cn -
作者简介:王博文,女,博士研究生 -
基金资助:科技部重点研发项目“重点行业气候变化适应关键技术体系、决策支持系统和恢复力评估”(2023YFF0805902)
Attribution and assessment of direct and indirect economic losses from extreme weather events in China
WANG Bo-Wen, HE Yi, TENG Fei( )
)
- Institute of Energy, Environment and Economy, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2024-12-16Revised:2025-04-07Online:2025-07-30Published:2025-07-03
摘要:
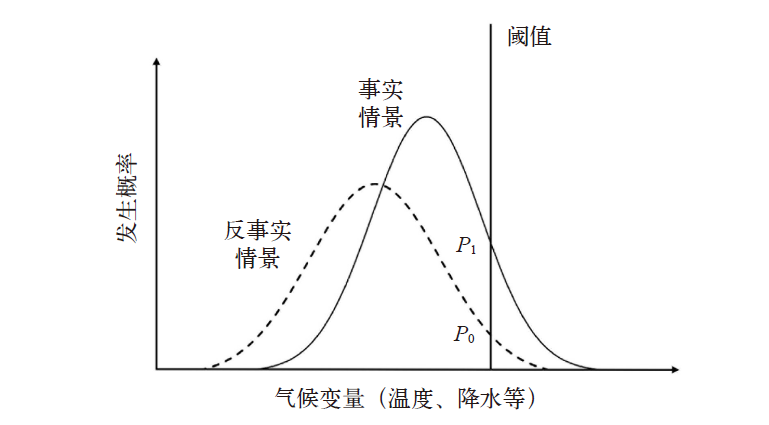
气候变化增加了极端天气气候事件发生的范围、频率和强度,带来巨大的经济损失。尽管现有归因研究量化了人类活动导致的气候变化对极端事件发生概率的贡献,但气候变化对极端事件经济损失的贡献尚不明确,难以有效支撑适应政策的制定。文中基于极端事件归因研究的最新进展及多区域投入产出模型,全面核算了我国各省极端事件的直接和间接经济损失,对损失进行归因分析,并识别了重点适应部门和地区。研究发现,在中国极端事件造成的直接经济损失中,约有27%(约798亿元)可归因于人类活动导致的气候变化。这部分归因损失经由经济系统传导和放大,进一步造成了约911亿元的间接经济损失。其中,制造业和农业是最主要的承灾部门,未受直接影响的金融房地产、批发零售以及商务服务业也受到较大损失。
引用本文
王博文, 贺一, 滕飞. 我国极端天气气候事件直接和间接经济损失的评估及归因[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2025, 21(4): 502-518.
WANG Bo-Wen, HE Yi, TENG Fei. Attribution and assessment of direct and indirect economic losses from extreme weather events in China[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 502-518.
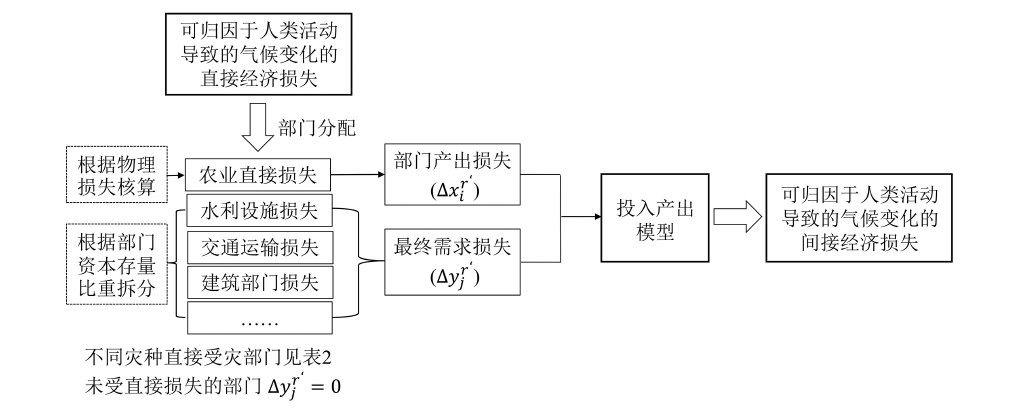
图2 直接经济损失部门分解及利用投入产出模型测算间接经济损失的方法
Fig. 2 Sectoral decomposition of direct economic losses and the use of input-output modelling to estimate indirect economic losses
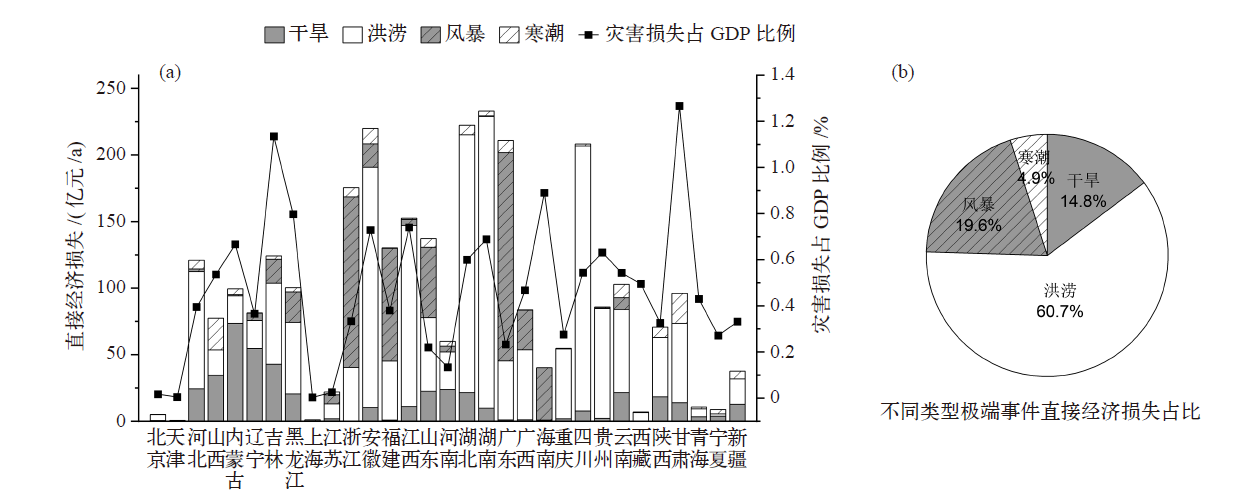
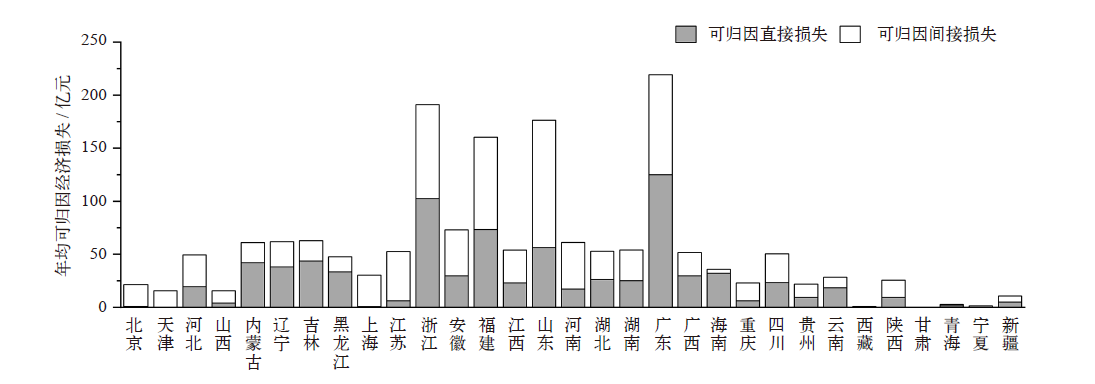
图3 各省极端事件的年均直接经济损失(a)和全国不同类型极端事件直接经济损失占比(b)
Fig. 3 Annual average direct economic losses of extreme events by province (a) and proportion of direct economic losses from different types of extreme events across the country (b)

图4 各类极端事件年均损失的可归因情况(a)和乘数效应(b) 注:“乘数效应”为极端事件的可归因总损失与可归因直接损失之比,用来反映投入产出关系导致的损失放大效应。
Fig. 4 Attributable losses (a) and multiplier effect of attributable losses (b) of extreme events
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2021: the physical science basis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2023 |
| [2] | Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED). EM-DAT: the international disaster database [DS/OL]. 2024 [2024-07-05]. https://www.emdat.be/ |
| [3] | 中国气象局气候变化中心. 中国气候变化蓝皮书(2024)[R]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2024. |
| National Climate Centre of China Meteorological Administration. China climate change blue book (2024)[R]. Beijing: Science Press, 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 巢清尘. 把脉极端天气事件提升科研综合能力[Z]. 中国气象局, 2023. |
| Chao Q C. Understanding extreme weather events and enhancing integrated scientific research capacity [Z]. China Meteorological Administration, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | Ilan Noy, Stone D, Uher T. Extreme events impact attribution: a state of the art[J]. Cell Reports Sustainability, 2024, 1 (5) |
| [6] | Stott P A, Stone D A, Allen M R. Human contribution to the European heatwave of 2003[J]. Nature, 2004, 432 (7017): 610-614 |
| [7] | Shepherd T G. A common framework for approaches to extreme event attribution[J]. Current Climate Change Reports, 2016, 2 (1): 28-38 |
| [8] | Wang J, Chen Y, Tett S F B, et al. Storyline attribution of human influence on a record-breaking spatially compounding flood-heat event[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9 (48): eadi2714 |
| [9] |
Wang J, Chen Y, Nie J, et al. On the role of anthropogenic warming and wetting in the July 2021 Henan record-shattering rainfall[J]. Science Bulletin, 2022, 67 (20): 2055-2059
doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2022.09.011 pmid: 36546103 |
| [10] | King A D, Grose M R, Kimutai J, et al. Event attribution is not ready for a major role in loss and damage[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2023, 13 (5): 415-417 |
| [11] |
Smiley K T, Noy I, Wehner M F, et al. Social inequalities in climate change-attributed impacts of Hurricane Harvey[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13 (1): 3418
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31056-2 pmid: 36008390 |
| [12] | Lott F C, Ciavarella A, Kennedy J J, et al. Quantifying the contribution of an individual to making extreme weather events more likely[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16 (10): 104040 |
| [13] | Li S, Otto F E L. The role of human-induced climate change in heavy rainfall events such as the one associated with Typhoon Hagibis[J]. Climatic Change, 2022, 172 (1): 7 |
| [14] | Frame D J, Wehner M F, Noy I, et al. The economic costs of Hurricane Harvey attributable to climate change[J]. Climatic Change, 2020, 160 (2): 271-281 |
| [15] | Frame D J, Rosier S M, Noy I, et al. Climate change attribution and the economic costs of extreme weather events: a study on damages from extreme rainfall and drought[J]. Climatic Change, 2020, 162 (2): 781-797 |
| [16] |
Newman R, Noy I. The global costs of extreme weather that are attributable to climate change[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14 (1): 6103
doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41888-1 pmid: 37775690 |
| [17] | 贺一. 人为气候变化导致的中国极端气候事件经济损失研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2024. |
| He Y. Study on the economic losses of extreme weather events in China caused by anthropogenic climate change[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2024 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Malik A, Li M, Lenzen M, et al. Impacts of climate change and extreme weather on food supply chains cascade across sectors and regions in Australia[J]. Nature Food, 2022, 3 (8): 631-643
doi: 10.1038/s43016-022-00570-3 pmid: 37118599 |
| [19] | Wei S, Zhou Q, Luo Z, et al. Economic impacts of multiple natural disasters and agricultural adaptation measures on supply chains in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 418: 138095 |
| [20] | Wirtz A, Kron W, Löw P, et al. The need for data: natural disasters and the challenges of database management[J]. Natural Hazards, 2014, 70 (1): 135-157 |
| [21] | Clarke B, Otto F, Jones R. When don’t we need a new extreme event attribution study?[J]. Climatic Change, 2023, 176 (5): 60 |
| [22] | 郑慧, 高梦莎. 基于投入产出模型的海洋灾害间接经济损失评估[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2015, 30 (12): 68-73. |
| Zheng H, Gao M S. Assessment of indirect economic losses of marine disasters based input-output model[J]. Journal of Statistics and Information, 2015, 30 (12): 68-73 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 谭玲. 城市暴雨洪涝灾害的经济损失评估研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2023. |
| Tan L. Research on economic loss assessment of urban rainstorm flood disasters[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
宁思雨, 黄晶, 汪志强, 等. 基于投入产出法的洪涝灾害间接经济损失评估: 以湖北省为例[J]. 地理科学进展, 2020, 39 (3): 420-432.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.007 |
|
Ning S Y, Huang J, Wang Z Q, et al. Indirect economic losses of flood disaster based on an input-output model: a case study of Hubei province[J]. Progress in Geography, 2020, 39 (3): 420-432 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.03.007 |
|
| [25] | 周蕾, 吴先华, 高歌. 基于MRIO模型的“一带一路”典型国家气象灾害间接经济损失分析: 以2014年中国“威马逊”台风灾害为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2018, 27 (5): 1-11. |
| Zhou L, Wu X H, Gao G. Analysis of indirect economic loss of meteorological disasters among the Belt and Road typical countries based on the MRIO model: taking the China’s typhoon Rammasun in 2014 as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2018, 27 (5): 1-11 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | Lyu Y, Xiang Y, Wang D. Evaluating indirect economic losses from flooding using input-output analysis: an application to China’s Jiangxi province[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20 (5): 4509 |
| [27] |
Hallegatte S. An adaptive regional input-output model and its application to the assessment of the economic cost of Katrina[J]. Risk Analysis, 2008, 28 (3): 779-799
doi: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2008.01046.x pmid: 18643833 |
| [28] | 刘远, 李莹, 王国复, 等. 河南省“21∙7”极端暴雨灾害多区域间接经济损失评估[J]. 灾害学, 2022, 37 (4): 45-51. |
| Liu Y, Li Y, Wang G F, et al. Multi-regional indirect economic loss assessment of “21∙7” extreme rainstorm in Henan province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2022, 37 (4): 45-51 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | Wang S, Huang J, Yuan X. Attribution of 2019 extreme spring-early summer hot drought over Yunnan in Southwestern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102 (1): S91-S96 |
| [30] | Luo F, Wang S, He Y, et al. Anthropogenic warming has increased the 2020 extreme hot and dry conditions over Southwest China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S124-S129 |
| [31] | Li W, Jiang Z, Li L. Anthropogenic influence on the record-breaking compound hot and dry event in summer 2022 in the Yangtze River Basin in China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2023, 104 (11): E1928-E1934 |
| [32] | Li Y, Chen L, Zhang Y, et al. Anthropogenic influence on the occurrence of extreme drought like that in eastern China in 2019[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2023, 16 (3): 100296 |
| [33] | Zhang L, Zhou T, Zhang X, et al. Attribution of the extreme 2022 summer drought along the Yangtze River valley in China based on detection and attribution system of Chinese Academy of Sciences[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2024, 105 (7): E1062-E1067 |
| [34] | Zhang Y, Chen L, Li Y, et al. Anthropogenic influence on the extreme drought in eastern China in 2022 and its future risk[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2024, 17 (1): 100390 |
| [35] | Wang Y, Yuan X. Anthropogenic speeding up of South China flash droughts as exemplified by the 2019 summer-autumn transition season[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48 (9): e2020GL091901 |
| [36] | Wang S, Yuan X, Wu R. Attribution of the persistent spring-summer hot and dry extremes over Northeast China in 2017[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2019, 100 (1): S85-S89 |
| [37] | Du J, Wang K, Cui B, et al. Attribution of the record-breaking consecutive dry days in winter 2017/18 in Beijing[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2020, 101 (1): S95-S102 |
| [38] | Zhang L, Zhou T, Chen X, et al. The late spring drought of 2018 in South China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2020, 101 (1): S59-S64 |
| [39] | Tan X, Wu X, Huang Z, et al. Detection and attribution of the decreasing precipitation and extreme drought 2020 in southeastern China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 610: 127996 |
| [40] | Lu C, Jiang J, Chen R, et al. Anthropogenic influence on 2019 May-June extremely low precipitation in Southwestern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102 (1): S97-S102 |
| [41] | Ma S, Zhou T, Angélil O, et al. Increased chances of drought in Southeastern Periphery of the Tibetan Plateau induced by anthropogenic warming[J]. Journal of Climate, 2017, 30 (16): 6543-6560 |
| [42] | Yuan X, Wang Y, Zhou S, et al. Multiscale causes of the 2022 Yangtze mega-flash drought under climate change[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2024, 67 (8): 2649-2660 |
| [43] | Liu X, Jie H, Zou Y, et al. Anthropogenic influence on 2022 June extreme rainfall over the Pearl River basin[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2024, 105 (2): E418-E424 |
| [44] | Sheng B, Dong B, Wang H, et al. Anthropogenic influences on extremely persistent seasonal precipitation in Southern China during May-June 2022[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2024, 105 (2): E425-E431 |
| [45] | Qiao S, Chen D, He M, et al. Was the February 2022 persistent heavy precipitation event over South China enhanced by anthropogenic climate change?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2023, 104 (11): E2088-E2094 |
| [46] | Li R, Li D, Nanding N, et al. Anthropogenic influences on heavy precipitation during the 2019 extremely wet rainy season in Southern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102 (1): S103-S109 |
| [47] | Zhao D, Xu H, Wang H, et al. Quantitative attribution of historical anthropogenic warming on the extreme rainfall event over Henan in July 2021[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2023, 18 (10): 104037 |
| [48] | Ye Y, Qian C. Conditional attribution of climate change and atmospheric circulation contributing to the record-breaking precipitation and temperature event of summer 2020 in southern China[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16 (4): 044058 |
| [49] | Pei L, Yan Z, Chen D, et al. The contribution of human-induced atmospheric circulation changes to the record-breaking winter precipitation event over Beijing in February 2020[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S55-S60 |
| [50] | Zhao R, Tam C Y, Lee S M. Attribution of the December 2013 extreme rainfall over the Pearl River delta to anthropogenic influences[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2023, 61 (11): 5533-5549 |
| [51] | Hirabayashi Y, Alifu H, Yamazaki D, et al. Anthropogenic climate change has changed frequency of past flood during 2010-2013[J]. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science, 2021, 8 (1): 36 |
| [52] | Burke C, Stott P, Ciavarella A, et al. Attribution of extreme rainfall in Southeast China during May 2015[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2016, 97 (12): S92-S96 |
| [53] | Sun Y, Dong S, Hu T, et al. Anthropogenic influence on the heaviest June precipitation in Southeastern China since 1961[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2019, 100 (1): S79-S83 |
| [54] | Lu C, Sun Y, Zhang X. The 2020 record-breaking Mei-yu in the Yangtze River valley of China: the role of anthropogenic forcing and atmospheric circulation[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S98-S104 |
| [55] | Ma Y, Hu Z, Li C, et al. Anthropogenic climate change enhances the July 2021 super-heavy rainfall event in Central China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2023, 104 (4): E736-E741 |
| [56] | Ji P, Yuan X, Jiao Y, et al. Anthropogenic contributions to the 2018 extreme flooding over the Upper Yellow River basin in China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2020, 101 (1): S89-S94 |
| [57] | Luo F, Wang S, Wang H, et al. Differing contributions of anthropogenic aerosols and greenhouse gases on precipitation intensity percentiles over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2024, 129 (12): e2023JD040202 |
| [58] | Wang Q, Zhai P, Zhou B. Attribution of tropical sea surface temperature change on extreme precipitation over the Yangtze River valley in 2020[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2023, 61 (7): 3417-3429 |
| [59] | Wang W, Yuan X. Climate change and La Niña increase the likelihood of the ‘7∙20’ extraordinary typhoon-rainstorm in Zhengzhou, China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2024, 44 (5): 1355-1370 |
| [60] | Yuan X, Wang S, Hu Z. Do climate change and El Niño increase likelihood of Yangtze River extreme rainfall?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99 (1): S113-S117 |
| [61] | Zhou C, Wang K, Qi D. Attribution of the July 2016 extreme precipitation event over China’s Wuhang[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99 (1): S107-S112 |
| [62] | Qin H, Yuan W, Wang J, et al. Climate change attribution of the 2021 Henan extreme precipitation: impacts of convective organization[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2022, 65 (10): 1837-1846 |
| [63] | Qian C, Ye Y, Zhang W, et al. Heavy rainfall event in Mid-August 2020 in Southwestern China: contribution of anthropogenic forcings and atmospheric circulation[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S111-S117 |
| [64] | Sun Q, Miao C. Extreme rainfall (R20mm, RX5day) in Yangtze-Huai, China, in June-July 2016: the role of ENSO and anthropogenic climate change[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99 (1): S102-S106 |
| [65] | Du J, Fu K, Wang K, et al. Anthropogenic influences on 2020 extreme dry-wet contrast over South China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S68-S75 |
| [66] | Tang H, Wang Z, Tang B, et al. Reduced probability of 2020 June-July persistent heavy Mei-yu rainfall event in the middle to lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin under anthropogenic forcing[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S83-S89 |
| [67] | Li X, Zhang L, Wang G, et al. Anthropogenic forcing decreases the probability of the 2020 Yangtze River extreme flood and future risk[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2024, 311: 107662 |
| [68] | Hu T, Sun Y, Zhang X, et al. Anthropogenic influence on the 2021 wettest September in Northern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2023, 104 (11): E243-E248 |
| [69] | Hu Y, Dong B, Xie J, et al. Anthropogenic influence on 2022 extreme January-February precipitation in Southern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2023, 104 (11): E1935-E1940 |
| [70] | Zhang W, Li W, Zhu L, et al. Anthropogenic influence on 2018 summer persistent heavy rainfall in Central Western China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2020, 101 (1): S65-S70 |
| [71] | Hu Z, Li H, Liu J, et al. Was the extended rainy winter 2018/19 over the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River driven by anthropogenic forcing?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102 (1): S67-S73 |
| [72] | Zhou T, Ren L, Zhang W. Anthropogenic influence on extreme Meiyu rainfall in 2020 and its future risk[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 64 (10): 1633-1644 |
| [73] | Wang L, Gu X, Slater L J, et al. Attribution of the record-breaking extreme precipitation events in July 2021 over Central and Eastern China to anthropogenic climate change[J]. Earth’s Future, 2023, 11 (9): e2023EF003613 |
| [74] | Zou S, Duan W L, Christidis N, et al. An extreme rainfall event in summer 2018 of Hami city in eastern Xinjiang, China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2021, 12 (6): 795-803 |
| [75] | Nanding N, Chen Y, Wu H, et al. Anthropogenic influences on 2019 July precipitation extremes over the mid-lower reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2020, 8 |
| [76] | Zhang W, Vecchi G A, Murakami H, et al. Influences of natural variability and anthropogenic forcing on the extreme 2015 accumulated cyclone energy in the Western North Pacific[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2016, 97 (12): S131-S135 |
| [77] | Duan J, Chen L, Li L, et al. Anthropogenic influences on the extreme cold surge of early spring 2019 over the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2021, 102 (1): S111-S116 |
| [78] | Liu Y, Li C, Sun Y, et al. The January 2021 cold air outbreak over Eastern China: is there a human fingerprint?[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S50-S54 |
| [79] | Yu H, Yu X, Zhou Z, et al. Attribution of April 2020 exceptional cold spell over Northeast China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2022, 103 (3): S61-S67 |
| [80] | Qian C, Wang J, Dong S, et al. Human influence on the record-breaking cold event in January of 2016 in eastern China[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99 (1): S118-S122 |
| [81] | Sun Y, Hu T, Zhang X, et al. Anthropogenic influence on the eastern China 2016 super cold surge[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2018, 99 (1): S123-S127 |
| [82] | 田友春. 中国分行业资本存量估算:1990—2014年[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2016, 33 (6): 3-21, 76. |
| Tian Y C. Estimation on capital stock of sectors in China: 1990-2014 [J]. Journal of Quantitative & Technological Economics, 2016, 33 (6): 3-21, 76 (in Chinese) | |
| [83] | 李善同, 何建武, 祝坤福, 等. 中国多区域投入产出模型:1987—2017年[M]. 北京: 经济科学出版社, 2023. |
| Li S T, He J W, Zhu K F, et al.China’s multi-regional input-output model:1987- 2017[M]. Beijing: Economic Science Press, 2023 (in Chinese) | |
| [84] | Allen M. Liability for climate change[J]. Nature, 2003, 421 (6926): 891-892 |
| [85] | Brown P T. When the fraction of attributable risk does not inform the impact associated with anthropogenic climate change[J]. Climatic Change, 2023, 176 (8): 115 |
| [86] |
Vicedo-Cabrera A M, Scovronick N, Sera F, et al. The burden of heat-related mortality attributable to recent human-induced climate change[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11 (6): 492-500
doi: 10.1038/s41558-021-01058-x pmid: 34221128 |
| [87] | Mitchell D, Heaviside C, Vardoulakis S, et al. Attributing human mortality during extreme heat waves to anthropogenic climate change[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11 (7): 074006 |
| [88] | O’Neill B et al. Key risks across sectors and regions[M]//Climate change 2022: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022 |
| [89] | National Drought Resilience Partnership (NDRP). Drought and infrastructure: a planning guide[R]. Washington, D. C.: CISA, 2025 |
| [90] | Vereinte Nationen. Special report on drought 2021[M]. Geneva: United Nations, 2021 |
| [91] | 李建利, 王灿. 基于投入产出模型的气象灾害间接经济损失评估: 以广东省台风灾害为例[C]//2018中国环境科学学会科学技术年会论文集(第一卷). 中国环境科学学会, 2018: 11. |
| Li J L, Wang C. Assessment of indirect economic losses from meteorological disasters based on the input-output model: a case study of typhoon disasters in Guangdong province[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 Annual Conference of the Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences (Volume I). Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, 2018: 11 (in Chinese) | |
| [92] | 范玲. “一带一路”沿线国家台风灾害关联经济损失研究[D]. 太原: 山西财经大学, 2022. |
| Fan L. The study on the relational economic losses assessment of typhoon disaster among the Belt and Road countrie[D]. Taiyuan: Shanxi University of Finance & Economics, 2022 (in Chinese) | |
| [93] | 刘远, 李宁, 张正涛, 等. 台风“艾云尼”动态间接经济损失评估[J]. 灾害学, 2019, 34 (3): 178-183. |
| Liu Y, Li N, Zhang Z T, et al. Indirect economic loss and its dynamic change assessment of Typhoon Ewiniar in Guangdong[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2019, 34 (3): 178-183 (in Chinese) | |
| [94] | 胡爱军, 李宁, 史培军, 等. 极端天气事件导致基础设施破坏间接经济损失评估[J]. 经济地理, 2009, 29 (4): 529-534. |
| Hu A J, Li N, Shi P J, et al. Indirect effects of infrastructure disruptions caused by extreme weather events with application of the inoperabilit input-output model[J]. Economic Geography, 2009, 29 (4): 529-534 (in Chinese) | |
| [95] |
刘丽, 李宁, 张正涛, 等. 中国省域尺度17部门资本存量的时空特征分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 2019, 38 (4): 546-555.
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.04.007 |
|
Liu L, Li N, Zhang Z T, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of capital stock exposure of 17 sectors for individual provinces in China[J]. Progress in Geography, 2019, 38 (4): 546-555 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2019.04.007 |
|
| [96] | 孙辉, 支大林, 李宏瑾. 对中国各省资本存量的估计及典型性事实: 1978—2008[J]. 广东金融学院学报, 2010, 25 (3): 103-116, 129. |
| Sun H, Zhi D L, Li H J. Estimate of the capital stock of provinces in China and the typical fact from 1978 to 2008[J]. Financial Economics Research, 2010, 25 (3): 103-116, 129 (in Chinese) | |
| [97] | Steinback S R. Using ready-made regional input-output models to estimate backward-linkage effects of exogenous output shocks[J]. Review of Regional Studies, 2004, 34 (1) |
| [98] | Arto I, Andreoni V, Cantuche J M R. Global impacts of the automotive supply chain disruption following the Japanese Earthquake of 2011[J]. Economic Systems Research, 2015 |
| [99] | Koks E E, Jongman B, Husby T G, et al. Combining hazard, exposure and social vulnerability to provide lessons for flood risk management[J]. Environmental Science & Policy, 2015, 47: 42-52 |
| [100] | 谭显春, 张倩倩, 曾桉, 等. 典型发达国家适应气候变化资金机制及对中国的启示[J]. 中国环境管理, 2023, 15 (1): 64-73. |
| Tan X C, Zhang Q Q, Zeng A, et al. The climate adaptation financial mechanisms in typical developed countries and implications for China[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 15 (1): 64-73 (in Chinese) | |
| [101] | European Environment Agency. Assessing the costs and benefits of climate change adaptation[R]. European Environment Agency, 2023 |
| [102] | 唐彦东, 张佳丽, 于汐. 灾害间接经济损失评估研究综述[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2023, 32 (6): 1-11. |
| Tang Y D, Zhang J L, Yu X. Review on disaster indirect economic loss assessment[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2023, 32 (6): 1-11 (in Chinese) | |
| [103] | Carrera L, Standardi G, Bosello F, et al. Assessing direct and indirect economic impacts of a flood event through the integration of spatial and computable general equilibrium modelling[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2015, 63: 109-122 |
| [104] |
Koks E E, Bočkarjova M, de Moel H, et al. Integrated direct and indirect flood risk modeling: development and sensitivity analysis[J]. Risk Analysis, 2015, 35 (5): 882-900
doi: 10.1111/risa.12300 pmid: 25515065 |
| [105] |
Willner S N, Otto C, Levermann A. Global economic response to river floods[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2018, 8 (7): 594-598
doi: 10.1038/s41558-018-0173-2 |
| [106] | Koks E. Moving flood risk modelling forwards[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2018, 8 (7): 561-562 |
| [107] | Caracalla V T. The impact of natural hazards and disasters on agriculture, food security, and nutrition[J]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2015 |
| [1] | 罗慧, 刘杰, 王丽, 唐智亿. 西北气候暖湿化的农业经济影响评估:以宁夏为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(3): 293-304. |
| [2] | 袁媛, 李国庆. 日本多主体适应气候变化框架机制及对中国的启示——基于法律政策的视角[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(4): 505-515. |
| [3] | 韩中,王刚. 基于多区域投入产出模型中美贸易隐含能源、碳排放的测算[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(4): 416-426. |
| [4] | 胡恒智, 顾婷婷, 田展. 气候变化背景下的洪涝风险稳健决策方法评述[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(1): 77-85. |
| [5] | 苗秋菊 张婉佩 沈永平. 2006年全球气候异常,多项纪录被打破[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 03(01): 50-053. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||