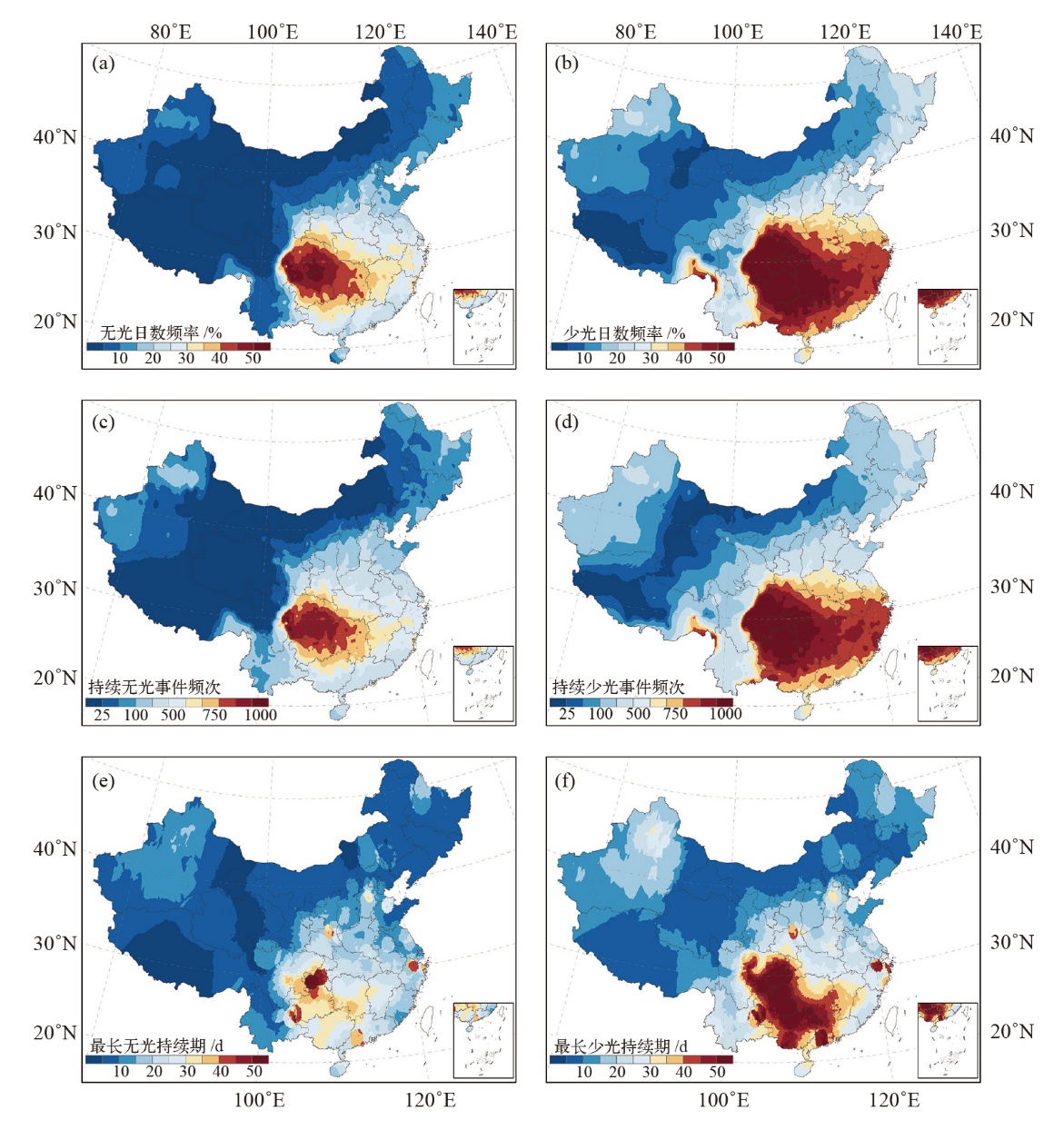
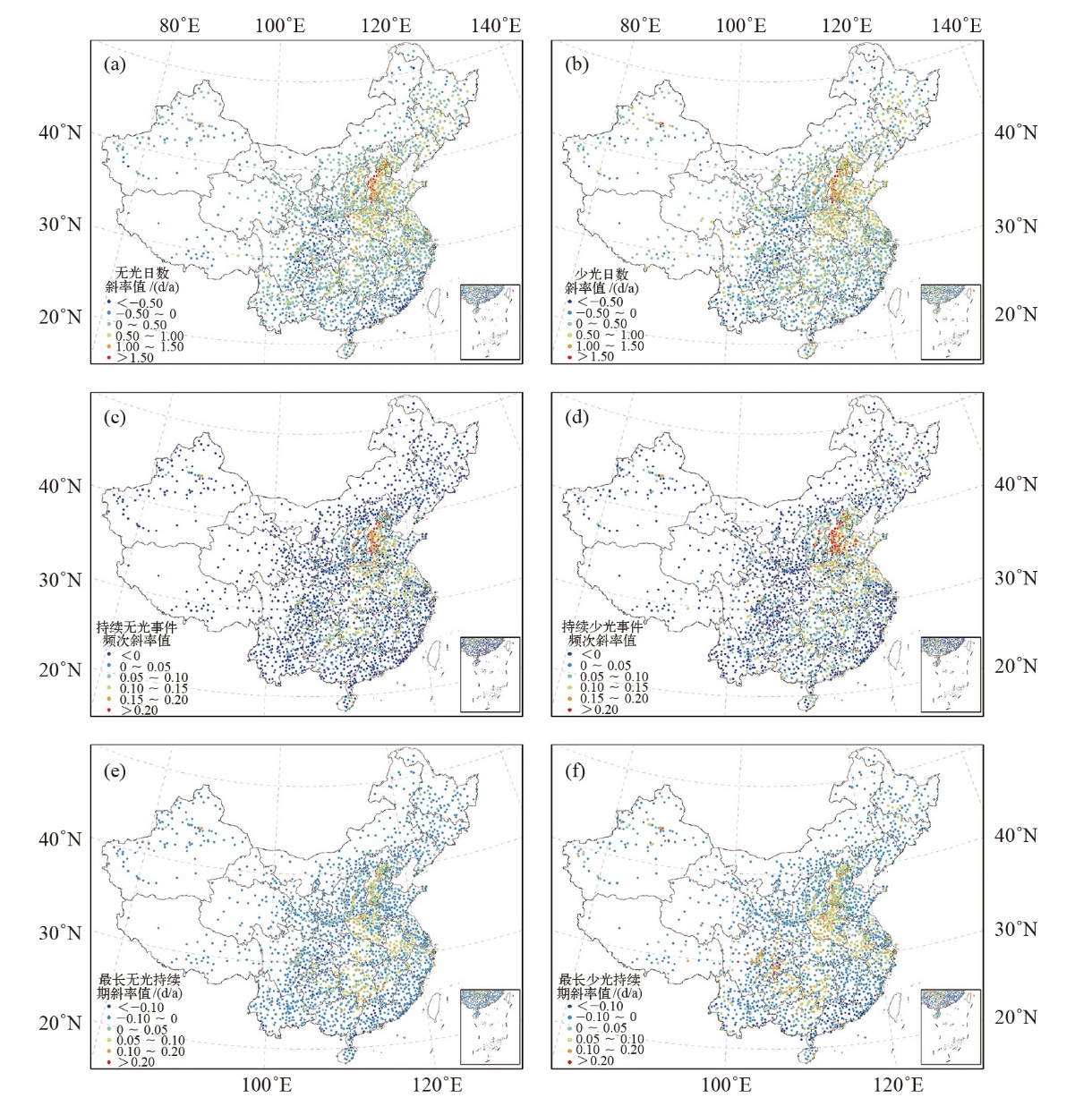
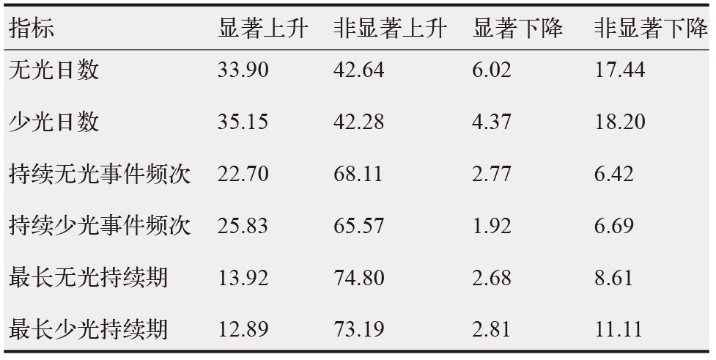
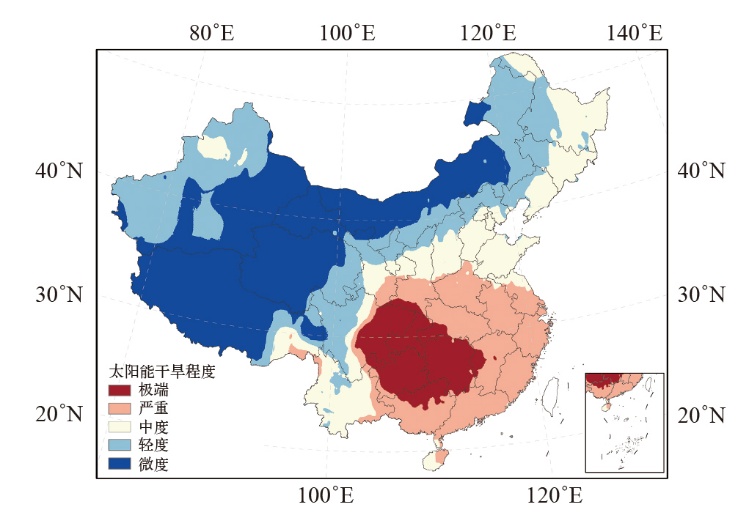
| [1] |
赵玉荣, 刘含眸, 李伟, 等. “双碳”目标下我国电力部门低碳转型政策研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19 (5): 634-644.
|
|
Zhao Y R, Liu H M, Li W, et al. Research on the low-carbon transition policies of power sector under the “Double Carbon” goal[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19 (5): 634-644 (in Chinese)
|
| [2] |
Trenberth K E. Climate variability and global warming[J]. Science, 2001, 293 (5527): 48-49
pmid: 11444289
|
| [3] |
Almasoud W A, Al-Sager S M, Almady S S, et al. A prediction of the monthly average daily solar radiation on a horizontal surface in Saudi Arabia using artificial neural network approach[J]. Processes, 2025, 13 (4): 1149
doi: 10.3390/pr13041149
URL
|
| [4] |
Hu L, Meng J, Xiong C, et al. City-level resilience to extreme weather shocks revealed by satellite nighttime lights in China[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2024, 101: 105167
doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2023.105167
URL
|
| [5] |
Wang L, Liu Y, Zhao L, et al. Unraveling climate change-induced compound low-solar-low-wind extremes in China[J]. National Science Review, 2025, 12 (1): nwae424
|
| [6] |
Lei Y, Wang Z, Xu Y, et al. Global solar droughts due to supply-demand imbalance exacerbated by anthropogenic climate change[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2024, 51 (22). DOI: 10.1029/2024GL112162
|
| [7] |
Wilczak J M, Akish E, Capotondi A, et al. A multi-decadal analysis of U.S. and Canadian wind and solar energy droughts[J]. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2024, 16 (5): 56502
doi: 10.1063/5.0219648
URL
|
| [8] |
Bracken C, Voisin N, Son Y, et al. Seasonal compound renewable energy droughts in the Unites States[J]. Environmental Research: Energy, 2025, 2 (2): 25005
doi: 10.1088/2753-3751/adc8ad
|
| [9] |
Zheng D S, Tong D, Davis S J, et al. Climate change impacts on the extreme power shortage events of wind-solar supply systems worldwide during 1980-2022[J]. Nature Communications, 2024, 15: 5225
doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48966-y
pmid: 38890272
|
| [10] |
Sun J B, Wang Y, He Y, et al. The energy security risk assessment of inefficient wind and solar resources under carbon neutrality in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 360: 122889
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.122889
URL
|
| [11] |
张少婷, 肖国杰, 范广洲, 等. 青海省日照时数的时空变化特征分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31 (1): 121-126.
|
|
Zhang S T, Xiao G J, Fan G Z, et al. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of sunshine duration in Qinghai province[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31 (1): 121-126 (in Chinese)
|
| [12] |
叶帮苹, 张小丽, 王雅琦, 等. 1961—2020年青藏高原日照时数时空演变特征[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28 (4): 851-858.
|
|
Ye B P, Zhang X L, Wang Y Q, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of sunshine duration over Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2020[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental, 2022, 28 (4): 851-858 (in Chinese)
|
| [13] |
Aryanpur V, O′Gallachoir B, Dai H, et al. A review of spatial resolution and regionalisation in national-scale energy systems optimisation models[J]. Energy Strategy Reviews, 2021, 37: 100702
doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2021.100702
URL
|
| [14] |
乌吉斯古冷, 郭恩亮, 王永芳, 等. 1980—2020年内蒙古暖季复合干旱热浪事件变化特征[J]. 地理科学, 2024, 44 (10): 1871-1880.
doi: 10.13249/j.cnki.sgs.20230511
|
|
Wu J S G L, Guo E L, Wang Y F, et al. Analysis of the variation characteristics of compound drought heatwave events during the warm season in Inner Mongolia from 1980 to 2020[J]. Geographical Science, 2024, 44 (10): 1871-1880 (in Chinese)
|
| [15] |
李佳文, 周育琳, 魏兴, 等. CMIP6 对三峡库区万州段降水和气温的模拟能力评估[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2023, 40 (7): 32.
|
|
Li J W, Zhou Y L, Wei X, et al. Evaluating the ability of CMIP6 models in simulating precipitation and temperature in Wanzhou city in the Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, 2023, 40 (7): 32 (in Chinese)
|
| [16] |
Grinsted A, Moore J C, Jevrejeva S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series[J]. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics, 2004, 11 (5-6): 561-566
doi: 10.5194/npg-11-561-2004
URL
|
| [17] |
Nathiya G, Punitha S C, Punithavalli M. An analytical study on behavior of clusters using EM and K-means algorithm[J]. International Journal of Computer Science, 2010, 7 (3): 185-190
|
| [18] |
任国玉, 郭军, 徐铭志, 等. 近50年中国地面气候变化基本特征[J]. 气象学报, 2005, 63 (6). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.06.011.
|
|
Ren G Y, Guo J, Xu M Z, et al. Climate changes of China’s Mainland over the past half century[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2005, 63 (6). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6619.2005.06.011 (in Chinese)
|
| [19] |
李小军, 辛晓洲, 彭志晴. 2003—2012年中国地表太阳辐射时空变化及其影响因子[J]. 太阳能学报, 2017, 38 (11): 3057-3066.
|
|
Li X J, Xin X Z, Peng Z Q. Change analysis of surface solar radiation in China from 2003 to 2012[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2017, 38 (11): 3057-3066 (in Chinese)
|
| [20] |
何彬方, 冯妍, 荀尚培, 等. 安徽省 50 年日照时数的变化特征及影响因素[J]. 自然资源学报, 2009, 24 (7): 1275-1285.
doi: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2009.07.015
|
|
He B F, Feng Y, Xun S P, et al. Climatic change of sunshine duration and its influencing factors over Anhui province during the last 50 years[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2009, 24 (7): 1275-1285 (in Chinese)
|
| [21] |
华维, 邓浩, 夏昌基. 青藏高原水循环中高原低涡及多季风交汇的研究进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2024, 18 (2): 1-11.
|
|
Hua W, Deng H, Xia C J, et al. Advance of research on plateau vortex and multi-monsoon interaction in water cycle of Tibetan Plateau[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2024, 18 (2): 1-11 (in Chinese)
|
| [22] |
陈福军, 沈彦俊, 李倩, 等. 中国陆地生态系统近30年NPP时空变化研究[J]. 地理科学, 2011, 31 (11): 1409-1414.
|
|
Chen F J, Shen Y J, Li Q, et al. Spatio-temporal variation analysis of ecological systems NPP in China in past 30 years[J]. Geographical Science, 2011, 31 (11): 1409-1414 (in Chinese)
|
| [23] |
姜雪梅, 曹永强, 么嘉棋, 等. 基于最大光能利用率动态校正的京津冀地区植被碳汇反演研究[J]. 生态学报, 2025 (13): 1-16.
|
|
Jiang X M, Cao Y Q, Yao J Q, et al. Research on vegetation carbon sink inversion in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region based on dynamic correction of maximum light use efficiency[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2025 (13): 1-16 (in Chinese)
|
 ), 王阳1(
), 王阳1( ), 巢清尘1, 郭恩亮2, 韩新阳3, 刘青3, 邹艺超4, 郑宇滢4
), 巢清尘1, 郭恩亮2, 韩新阳3, 刘青3, 邹艺超4, 郑宇滢4
 ), WANG Yang1(
), WANG Yang1( ), CHAO Qing-Chen1, GUO En-Liang2, HAN Xin-Yang3, LIU Qing3, ZOU Yi-Chao4, ZHENG Yu-Ying4
), CHAO Qing-Chen1, GUO En-Liang2, HAN Xin-Yang3, LIU Qing3, ZOU Yi-Chao4, ZHENG Yu-Ying4