Climate Change Research ›› 2023, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (5): 605-615.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.048
• Changes in Climate System • Previous Articles Next Articles
A comparative study of atmospheric and surface urban heat island effects in China’s major cities
LI Yu( ), LI Ya-Qin, ZHAO Ju-Shuang
), LI Ya-Qin, ZHAO Ju-Shuang
- Fuyang Meteorological Bureau, Fuyang 236000, China
-
Received:2023-03-20Revised:2023-05-19Online:2023-09-30Published:2023-08-08
Cite this article
LI Yu, LI Ya-Qin, ZHAO Ju-Shuang. A comparative study of atmospheric and surface urban heat island effects in China’s major cities[J]. Climate Change Research, 2023, 19(5): 605-615.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2023.048
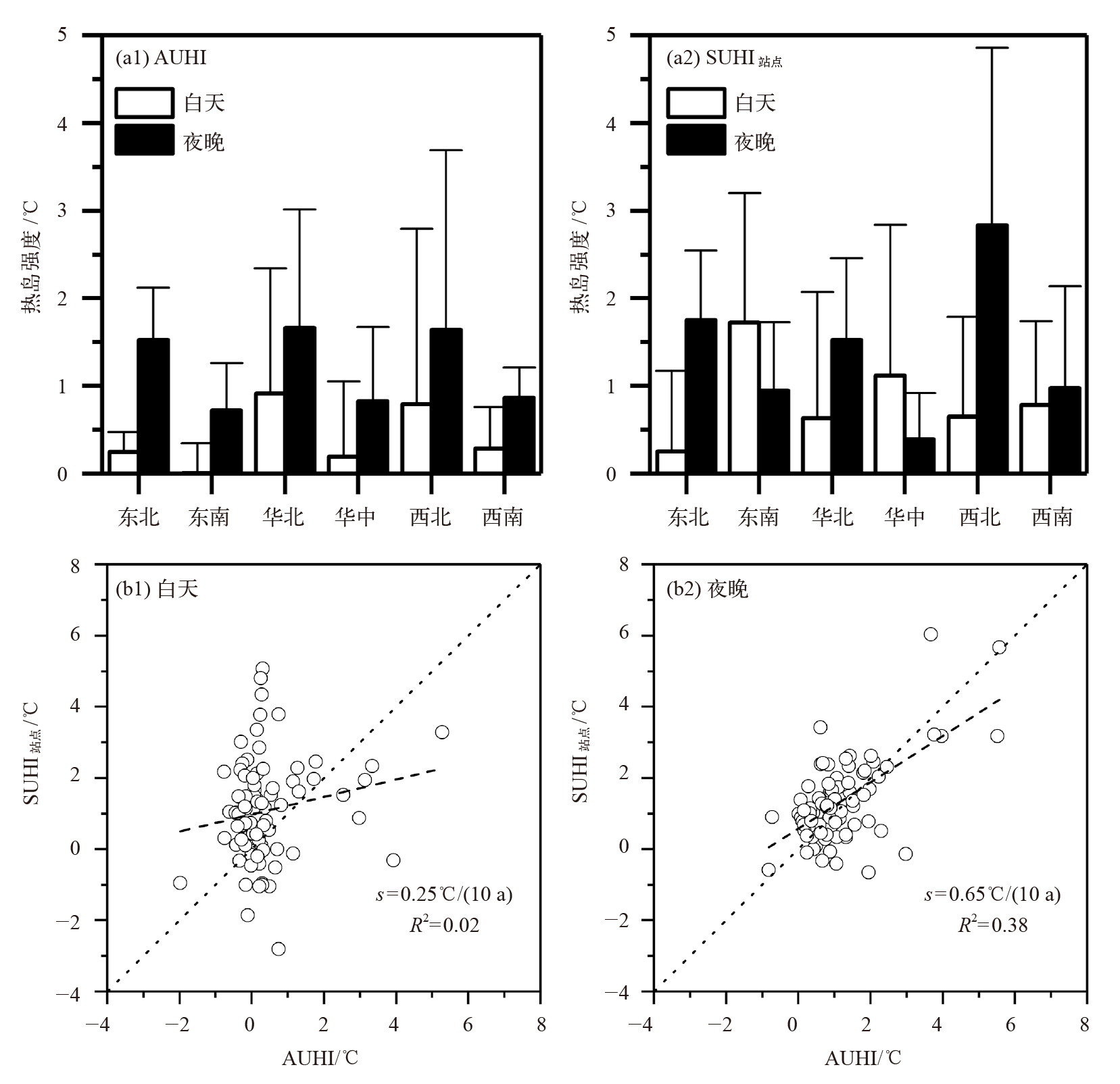
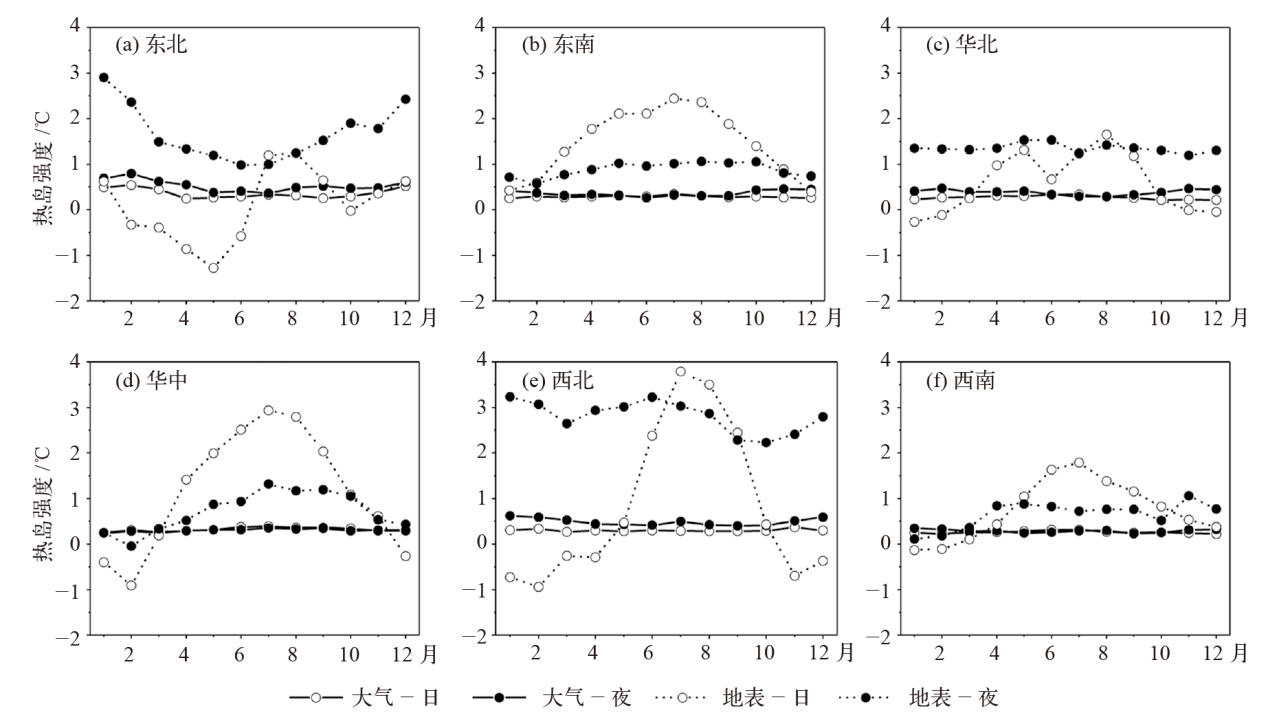
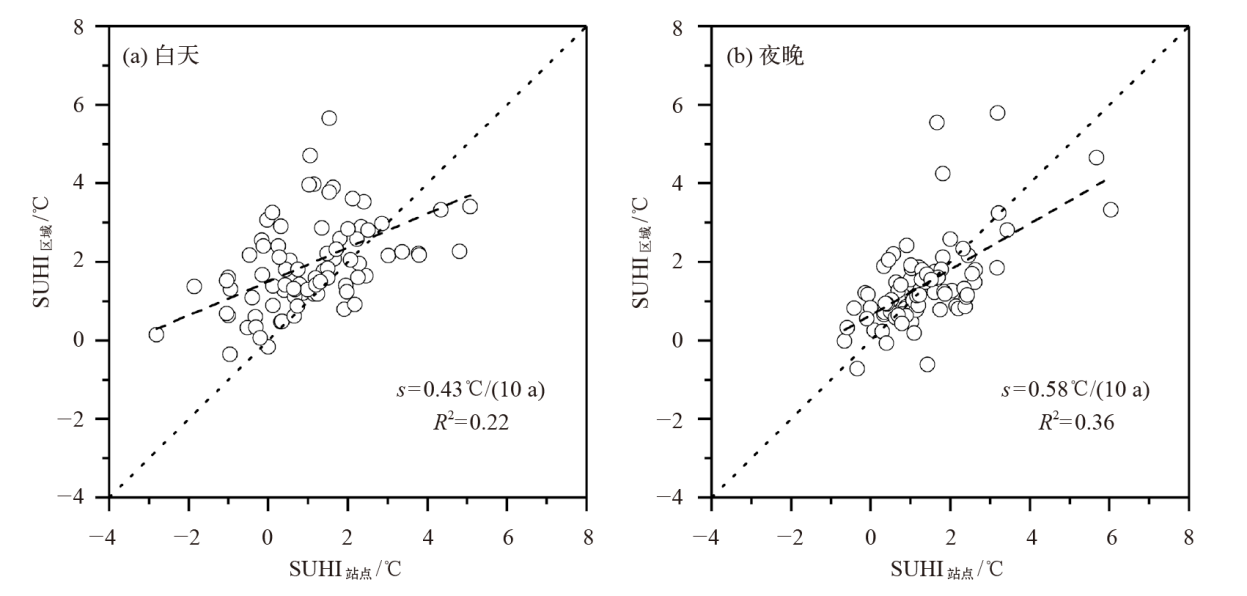
Fig. 2 Atmospheric (a1) and surface (a2) heat island intensity in different regions of China, and scatter diagram of atmospheric and surface heat island intensity of major cities in China during the day (b1) and night (b2) from 2007 to 2017
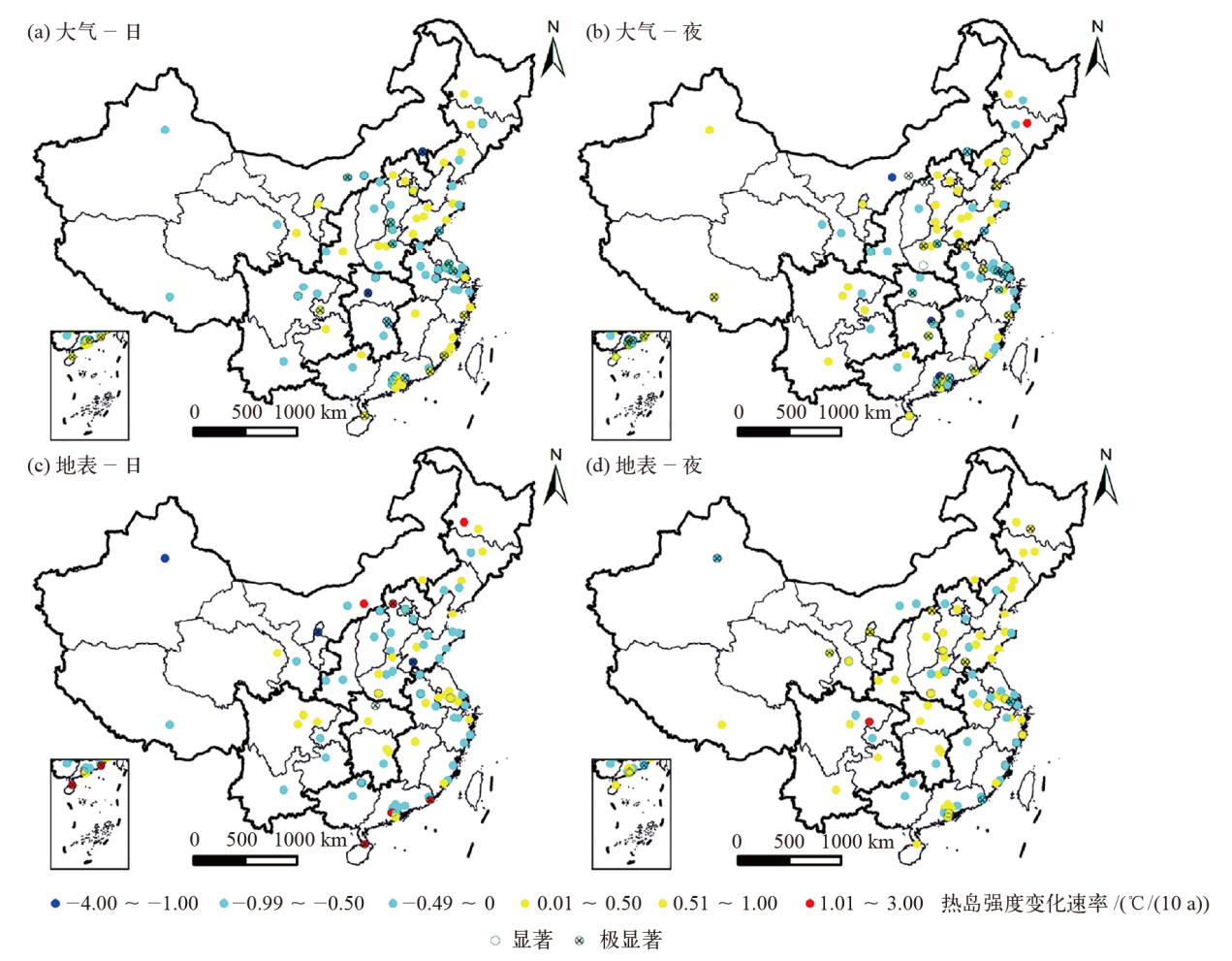
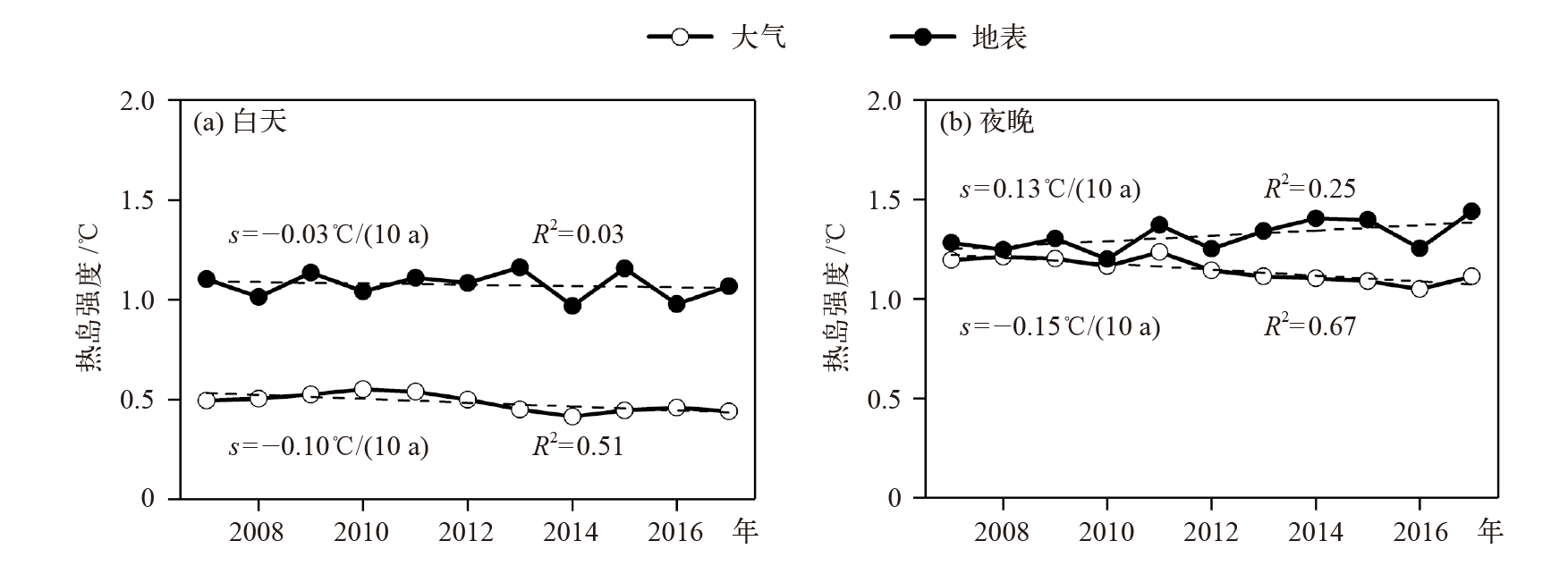
Fig. 4 Distribution of interannual variation rate of atmospheric and surface heat island intensity based on stations in major cities of China from 2007 to 2017
| [1] | Chen L, Frauenfeld O W. Impacts of urbanization on future climate in China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2016, 47 (1): 345-357. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-015-2840-6 |
| [2] | Sun Y, Zhang X B, Ren G Y, et al. Contribution of urbanization to warming in China[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2016, 6 (7): 706-709. DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2956 |
| [3] |
邱国玉, 张晓楠. 21世纪中国的城市化特点及其生态环境挑战[J]. 地球科学进展, 2019, 34 (6): 640-649.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2019.06.0640 |
| Qiu G Y, Zhang X N. China’s urbanization and its ecological environment challenges in the 21st century[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2019, 34 (6): 640-649 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | Goddard I L M, Tett S F B. How much has urbanisation affected United Kingdom temperatures?[J]. Atmospheric Science Letters, 2019, 20 (5): 1-6. DOI: 10.1002/asl.896 |
| [5] | Lin L, Gao T, Luo M, et al. Contribution of urbanization to the changes in extreme climate events in urban agglomerations across China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 744: 1-12. DOI: 10.1038/nclimate2956 |
| [6] | Howard L. The climate of London:deduced from meteorological observations. Vol I[M]. London: Harvey and Dorton Press, 1820 |
| [7] | Oke T R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island[J]. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 1982, 108: 1-24. DOI: 10.1002/qj.497108455 |
| [8] | Shepherd J M. A review of current investigations of urban-induced rainfall and recommendations for the future[J]. Earth Interactions 2005, 9: 1-27. DOI: 10.1175/EI156.1 |
| [9] | Wu X, Wang L, Yao R, et al. Quantitatively evaluating the effect of urbanization on heat waves in China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2020, 731: 1-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138857 |
| [10] | Liao W L, Li D, Liu X P, et al. Examination and projection of urbanization effect on summertime hot extremes in China[R]. Online: EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 2020. DOI: 10.5194/egusphere-egu2020-8611 |
| [11] | Zhao S Q, Liu S G, Zhou D C. Prevalent vegetation growth enhancement in urban environment[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113 (22): 1-6. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1602312113 |
| [12] | Zhou D C, Zhao S Q, Zhang L X, et al. Remotely sensed assessment of urbanization effects on vegetation phenology in China’s 32 major cities[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2016, 176: 272-281. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2016.02.010 |
| [13] | Nancy B, Grimm S H. Global change and the ecology of cities[J]. Science, 2008, 319: 755-760. DOI: 10.1126/science.1150195 |
| [14] | Patz J A, Campbell-Lendrum D, Holloway T, et al. Impact of regional climate change on human health[J]. Nature, 2005, 438 (7066): 310-317. DOI: 10.1038/nature04188 |
| [15] | Zhou D C, Xiao J F, Bonafoni S, et al. Satellite remote sensing of surface urban heat islands: progress, challenges, and perspectives[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11 (1): 1-36. DOI: 10.3390/rs11010048 |
| [16] | 姚远, 陈曦, 钱静. 城市地表热环境研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38: 1134-1147. |
| Yao Y, Chen X, Qian J. Research progress on the thermal environment of the urban surfaces[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38: 1134-1147. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201611022233 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | O’Malley C, Piroozfar P, Farr E R, et al. Urban Heat Island (UHI) mitigating strategies: a case-based comparative analysis[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2015, 19: 222-235. DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2015.05.009 |
| [18] | Hertel W F, Mykleby P M, Twine T E, et al. Dense network observations of the twin cities canopy-layer urban heat island[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2015, 54 (9): 1899-1917. DOI: 10.1175/jamc-d-14-0239.1 |
| [19] | Clay R, Guan H, Wild N, et al. Urban heat island traverses in the city of Adelaide, South Australia[J]. Urban Climate, 2016, 17: 89-101. DOI: 10.1016/j.uclim.2016.06.001 |
| [20] | Sheng L, Tang X L, You H Y, et al. Comparison of the urban heat island intensity quantified by using air temperature and Landsat land surface temperature in Hangzhou, China[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2017, 72: 738-746. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.09.009 |
| [21] |
江斯达, 占文凤, 杨俊, 等. 局地气候分区框架下城市热岛时空分异特征研究进展[J]. 地理学报, 2020, 75 (9): 1860-1878.
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202009004 |
|
Jiang S D, Zhan W F, Yang J, et al. Urban heat island studies based on local climate zones: a systematic overview[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020, 75 (9): 1860-1878 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.11821/dlxb202009004 |
|
| [22] | Li Z L, Tang B H, Wu H, et al. Satellite-derived land surface temperature: current status and perspectives[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2013, 131: 14-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2012.12.008 |
| [23] | Voogt J A, Oke T R. Thermal remote sensing of urban climates[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003, 86 (3): 370-384. DOI: 10.1016/s0034-4257(03)00079-8 |
| [24] | Schwarz N, Schlink U, Franck U, et al. Relationship of land surface and air temperatures and its implications for quantifying urban heat island indicators: an application for the city of Leipzig (Germany)[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2012, 18: 693-704. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.01.001 |
| [25] | Yao R, Wang L C, Huang X, et al. Temporal trends of surface urban heat islands and associated determinants in major Chinese cities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609: 742-754. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.217 |
| [26] | 周明煜, 曲绍厚, 李玉英, 等. 北京地区热岛和热岛环流特征[J]. 环境科学, 1980 (5): 12-18. |
| Zhou M Y, Qu S H, Li Y Y, et al. Characteristics of heat island and heat island circulation in Beijing area[J]. Environment Science, 1980 (5): 12-18 (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 杨敏, 杨贵军, 王艳杰, 等. 北京城市热岛效应时空变化遥感分析[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2018, 30 (3): 213-223. |
| Yang M, Yang G J, Wang Y J, et al. Remote sensing analysis of temporal-spatial variations of urban heat island effect over Beijing[J]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources, 2018, 30 (3): 213-223 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 张茜, 李国栋. 威海城市热岛效应特征及其与城市化进程的关系[J]. 气象与减灾研究, 2016, 39 (3): 224-231. |
| Zhang Q, Li G D. Urban heat island effect and its relationship with urbanization process in Weihai city[J]. Meteorology and Disaster Reduction Research, 2016, 39 (3): 224-231 (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 邱新法, 顾丽华, 曾燕, 等. 南京城市热岛效应研究[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2008, 13 (6): 807-814. |
| Qiu X F, Gu L H, Zeng Y, et al. Study on urban heat island effect of Nanjing[J]. Climatic and Environmental Research, 2008, 13 (6): 807-814 (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 黄利萍, 苗峻峰, 刘月琨. 天津城市热岛效应的时空变化特征[J]. 大气科学学报, 2012, 35 (5): 620-632. |
| Huang L P, Miao J F, Liu Y K. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of urban heat island in Tianjin[J]. Transactions of Atmospheric Sciences, 2012, 35 (5): 620-632 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | Yao R, Wang L, Huang X, et al. Long-term trends of surface and canopy layer urban heat island intensity in 272 cities in the mainland of China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 772: 1-14. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145607 |
| [32] | Du H L, Zhan W F, Liu Z H, et al. Simultaneous investigation of surface and canopy urban heat islands over global cities[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2021, 181: 67-83. DOI: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2021.09.003 |
| [33] |
Gong P, Li X C, Zhang W. 40-Year (1978-2017) human settlement changes in China reflected by impervious surfaces from satellite remote sensing[J]. Science Bulletin, 2019, 64 (11): 756-763. DOI: 110.1016/j.scib.2019.04.024
URL pmid: 36659545 |
| [34] | Zhou D C, Zhao S Q, Liu S G, et al. Surface urban heat island in China’s 32 major cities: spatial patterns and drivers[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2014, 152: 51-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2014.05.017 |
| [35] | 李宇, 周德成, 闫章美. 中国84个主要城市大气热岛效应的时空变化特征及影响因子[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42 (10): 475-483. |
| Li Y, Zhou D C, Yan Z M. Spatiotemporal variations in atmospheric urban heat island effects and their driving factors in 84 major Chinese cities[J]. Environment Science, 2021, 42 (10): 475-483 DOI: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202102003 (in Chinese). | |
| [36] | Zhou D C, Zhang L X, Li D, et al. Climate-vegetation control on the diurnal and seasonal variations of surface urban heat islands in China[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11 (7): 1-11. DOI: 10.1088/1748-9326/11/7/074009 |
| [37] | 孙艳伟, 王润, 郭青海, 等. 基于人居尺度的中国城市热岛强度时空变化及其驱动因子解析[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42 (1): 501-512. |
| Sun Y W, Wang R, Guo Q H, et al. Estimation of the urban heat island intensity change and its relationships with driving factors across China based on the human settlement scale[J]. Environment Science, 2021, 42 (1): 501-512 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | Dirksen M, Ronda R, Theeuwes N, et al. Sky view factor calculations and its application in urban heat island studies[J]. Urban Climate, 2019, 30: 1-16. DOI: 10.1016/j.uclim.2019.100498 |
| [39] | Wang K C, Jiang S J, Wang J K, et al. Comparing the diurnal and seasonal variabilities of atmospheric and surface urban heat islands based on the Beijing urban meteorological network[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2017, 122 (4): 2131-2154. DOI: 10.1002/2016jd025304 |
| [40] | Wang W, Yao X F, Shu J. Air advection induced differences between canopy and surface heat islands[J]. Science of Total Environment, 2020, 725: 1-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138120 |
| [41] | 潘蔚娟, 吴晓绚, 何健, 等. 基于均一化资料的广州近百年气温变化特征研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17 (4): 444-454. |
| Pan W J, Wu X X, He J, et al. Study on the change characteristics of Guangzhou centennial air temperature based on the homogenization data[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17 (4): 444-454 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | Acosta M P, Vahdatikhaki F, Santos J, et al. How to bring UHI to the urban planning table? A data-driven modeling approach[J]. Sustainable Cities and Society, 2021, 71: 1-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.scs.2021.102948 |
| [43] | Talukdar S, Rihan M, Hang H T, et al. Modelling urban heat island (UHI) and thermal field variation and their relationship with land use indices over Delhi and Mumbai metro cities[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2022, 24 (3): 3762-3790. DOI: 10.1007/s10668-021-01587-7 |
| [44] | 寿亦萱, 张大林. 城市热岛效应的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70 (3): 338-353. |
| Shou Y X, Zhang D L. Recent advances in understanding urban heat island effects with some future prospects[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2012, 70 (3): 338-353 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | Elliot T, Almenar J B, Rugani B. Modelling the relationships between urban land cover change and local climate regulation to estimate urban heat island effect[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2020, 50: 126650. DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126650 |
| [46] | Runnalls K, Oke T. Dynamics and controls of the near-surface heat island of Vancouver, British Columbia[J]. Physical Geography, 2000, 21 (4): 283-304. DOI: 10.1080/02723646.2000.10642711 |
| [1] | ZHAO Min, ZHANG Hua, WANG Hai-Bo, ZHU Li. The change of cloud top height over East Asia during 2000-2018 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(5): 591-599. |
| [2] | Xin MA,Wen-Tao WANG,Xue-Yan ZHANG,Shao-Hong WU,Yan-Hua LIU. Analysis on China’s climate securitization based on Copenhagen School [J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6): 693-699. |
| [3] | Cheng Zhigang, Yang Xinyue, Sun Chen, Xu Yajin. The Trend of Summer Urban Heat Island Effect and Its Relationship with Urban Development in Chengdu [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4): 322-331. |
| [4] | Gao Lei, Chen Haishan, Sun Shanlei. Impacts of Three Gorges Project on Land Surface Temperature Based on MODIS Dataset [J]. Climate Change Research, 2014, 10(3): 226-234. |
| [5] | Cheng Xiaoyu Wang Yanhua Li Guochun Li Qingxiang. Evaluation of Three Reanalysis Precipitation Datasets in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2013, 9(4): 258-265. |
| [6] | . Lake Ice and Its Effect Factors in the Nam Co Basin, Tibetan Plateau [J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8(5): 327-333. |
| [7] | . Distribution and Variation of Snow Cover in China [J]. Climate Change Research, 2012, 8(5): 364-371. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||