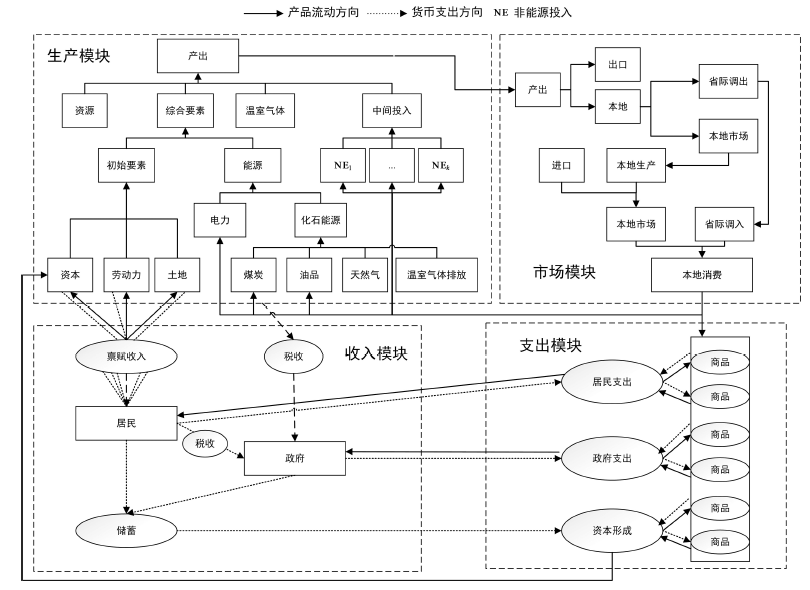
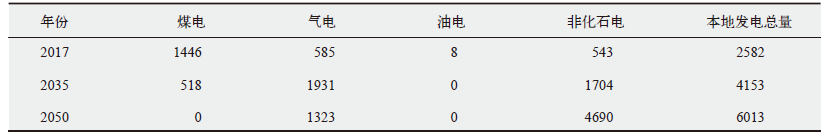
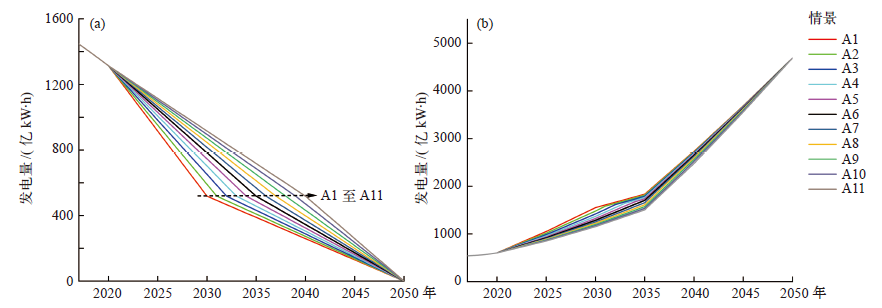
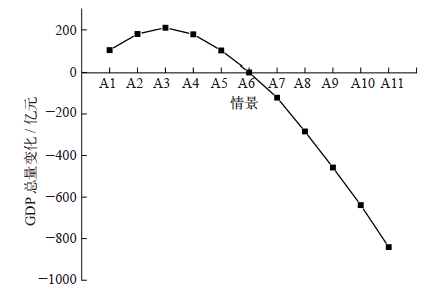
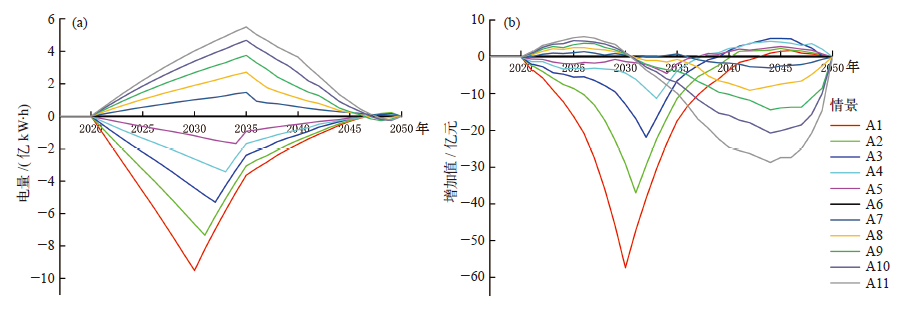
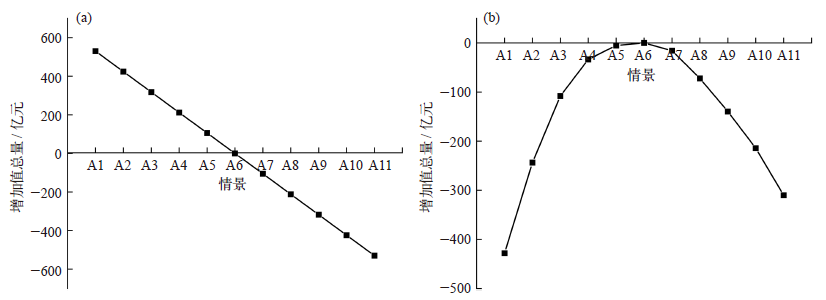
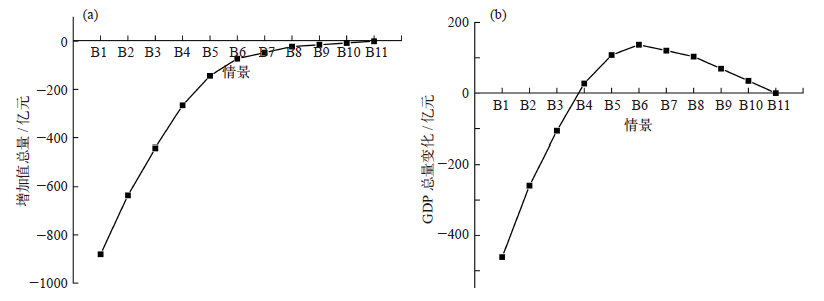
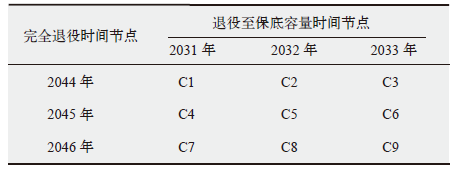
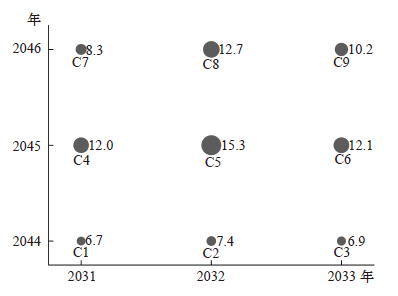
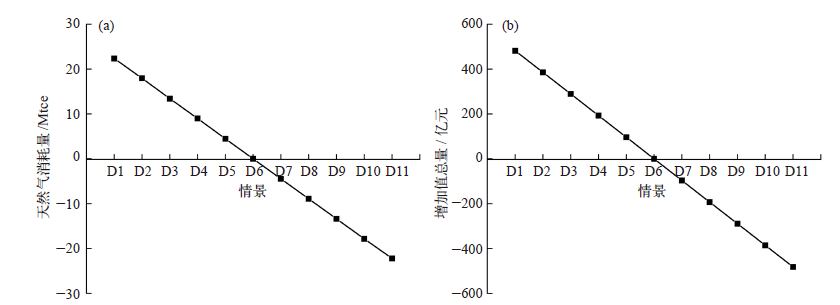
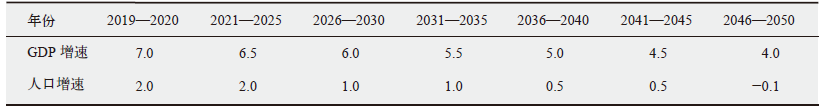Climate Change Research ›› 2022, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (1): 81-96.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.049
• Greenhouse Gas Emissions • Previous Articles Next Articles
Research on the speed control strategy of low carbon power transition based on CGE model—take the GBA as an example
XU Hong-Wei1,2,3,4, WANG Peng1,2,3( ), REN Song-Yan1,2,3, LIN Ze-Wei1,2,3, ZHAO Dai-Qing1,2,3
), REN Song-Yan1,2,3, LIN Ze-Wei1,2,3, ZHAO Dai-Qing1,2,3
- 1 Guangzhou Institute of Energy Conversion, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 Key Laboratory of Renewable Energy, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510640, China
3 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of New and Renewable Energy Research and Development, Guangzhou 510640, China
4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
-
Received:2021-03-15Revised:2021-04-27Online:2022-01-30Published:2021-12-27 -
Contact:WANG Peng E-mail:wangpeng@ms.giec.ac.cn
Cite this article
XU Hong-Wei, WANG Peng, REN Song-Yan, LIN Ze-Wei, ZHAO Dai-Qing. Research on the speed control strategy of low carbon power transition based on CGE model—take the GBA as an example[J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(1): 81-96.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.049
| [1] | 新华网. 习近平在第七十五届联合国大会一般性辩论上的讲话(全文) [EB/OL]. 2020 [2020-10-05]. http://www.xinhuanet.com/2020-09/22/c_1126527652.htm. |
| Xinhuanet. Full text of Xi’s statement at the general debate of the 75th session of the United Nations general assembly [EB/OL]. 2020 [2020-10-05]. http://www.xinhuanet.com/2020-09/22/c_1126527652.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2020 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2020. |
| National Bureau of Statistics. China statistical yearbook 2020 [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 《粤港澳大湾区能源转型中长期情景研究》项目组. 粤港澳大湾区能源转型中长期情景研究 [M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020. |
| Project Group of “Mid- and long-term Scenario Study on Energy Transformation of Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area”. Medium- and long-term scenario study of energy transformation in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 国家可再生能源中心. 美丽中国2050年的能源生态系统 [R/OL]. 2018 [2020-01-01]. https://max.book118.com/html/2018/0420/162194247.shtm. |
| National Renewable Energy Center. Beautiful China’s energy ecosystem in 2050 [R/OL]. 2018 [2020-01-01]. https://max.book118.com/html/2018/0420/162194247.shtm. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | IRENA. Global energy transformation: a roadmap to 2050 [R/OL]. Abu Dhabi: International Renewable Energy Agency, 2018 [2020-01-01]. https://www.irena.org/publications/2019/Apr/Global-energy-transformation-A-roadmap-to-2050-2019Edition |
| [6] | Jiang K J, He C M, Xu X Y, et al. Transition scenarios of power generation in China under global 2℃ and 1.5℃ targets[J]. Global Energy Interconnection, 2018 (1): 477-486 |
| [7] | 张文华, 闫庆友, 何钢, 等. 气候变化约束下中国电力系统低碳转型路径及策略[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 18-26. |
| Zhang W H, Yan Q Y, He G, et al. The pathway and strategy of China’s power system low-carbon transition under the constraints of climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(1): 18-26 (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 张小丽, 刘俊伶, 王克, 等. 中国电力部门中长期低碳发展路径研究[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2018, 28(4): 68-77. |
| Zhang X L, Liu J L, Wang K, et al. Study on medium and long-term low-carbon development pathway of China’s power sector[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2018, 28(4): 68-77 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 李政, 陈思源, 董文娟, 等. 现实可行且成本可负担的中国电力低碳转型路径[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(2): 1-7. |
|
Li Z, Chen S Y, Dong W J, et al. Feasible and affordable decarbonization pathways of China’s power sector[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2021, 27(2): 1-7. DOI: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.CCUS20091801 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.CCUS20091801 |
|
| [10] |
Cui Q, Liu Y, Ali T, et al. Economic and climate impacts of reducing China’s renewable electricity curtailment: a comparison between CGE models with alternative nesting structures of electricity[J]. Energy Economics, 2020, 91:104892
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2020.104892 URL |
| [11] |
Dai H C, Xie X X, Xie Y, et al. Green growth: the economic impacts of large-scale renewable energy development in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 162:435-449
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.10.049 URL |
| [12] | Yao X L, Lei H T, Yang L L, et al. Low-carbon transformation of the regional electric power supply structure in China: a scenario analysis based on a bottom-up model with resource endowment constraints[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2020: 105315 |
| [13] |
Wing I S. The synjournal of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technologies and the cost of limiting US CO2 emissions[J]. Energy Policy, 2006, 34(18): 3847-3869
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2005.08.027 URL |
| [14] |
Wing I S. The synjournal of bottom-up and top-down approaches to climate policy modeling: electric power technology detail in a social accounting framework[J]. Energy Economics, 2008, 30(2): 547-573
doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2006.06.004 URL |
| [15] | 广东省统计局. 广东省统计年鉴2018—2019 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2018— 2019. |
| Statistics Bureau of Guangdong Province. Statistical Yearbook of Guangdong Province 2018-2019 [M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2018- 2019 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 澳门统计局. 澳门统计年鉴 [R/OL]. 2016—2019 [2021-01-03]. http://www.tjcn.org/tjnj/33am/37957.html. |
| Macao Statistical Bureau. Macao statistical yearbook [R/OL]. 2016-2019 [2021-01-03]. http://www.tjcn.org/tjnj/33am/37957.html (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 经济合作与发展组织. 香港投入产出表2015 [EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-08]. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=IOTSI4_2018. |
| Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Hong Kong input-output table 2015[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-08]. https://stats.oecd.org/Index.aspx?DataSetCode=IOTSI4_2018. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 澳门统计年鉴委员会. 澳门能源统计 [R/OL]. 2016—2019 [2021-01-08]. https://www.dsec.gov.mo/ts/#!/step1/zh-MO. |
| Macao Statistical Yearbook Committee. Energy statistics of Macao [R/OL]. 2016—2019 [2021-01-08]. https://www.dsec.gov.mo/ts/#!/step1/zh-MO. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 香港特别行政区政府统计处. 香港能源统计2016年年刊 [EB/OL]. 2016 [2021-01-10]. https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/hkstat/sub/sp90_tc.jsp?productCode=B1100002. |
| Census and Statistics Department, the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region. Hong Kong energy statistics 2016 annual journal[EB/OL]. 2016 [2021-01-10]. https://www.censtatd.gov.hk/hkstat/sub/sp90_tc.jsp?productCode=B1100002. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | Ministry of Science and Technology, Economy and Energy. Supply of an instrument for estimating the emissions of greenhouse effect gases coupled with the energy matrix [R/OL]. 2010 [2014-06-11]. http://ecen.com/matriz/eee24/coefycin.htm |
| [21] | 广东省人民政府. 广东省人民政府关于印发《广东省国民经济和社会发展第十三个五年规划纲要》的通知 [R/OL]. 2016 [2021-01-01]. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/0/146/post_146576.html#7. |
| People’s Government of Guangdong Provincial. Notice of the people’s government of Guangdong province on printing and distributing the 13th Five-year Plan of Guangdong province for national economic and social development [R/OL]. 2016 [2021-01-01]. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/0/146/post_146576.html#7 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 广东省人民政府. 广东省人民政府关于印发广东省人口发展规划(2017—2030年)的通知 [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/0/146/post_146685.html#7. |
| People’s Government of Guangdong Provincial. The people’s government of Guangdong province on the issuance of Guangdong province population development plan (2017-2030) [R/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. http://www.gd.gov.cn/gkmlpt/content/0/146/post_146685.html#7 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 广东省发展和改革委员会. 广东省能源发展“十二五”规划 [EB/OL]. 2013 [2014-07-01]. http://www.gddpc.gov.cn/fgzl/fzgh/zxgh/sewzx/201309/t20130926_220199.htm. |
| Guangdong Provincial Development and Reform Commission. Energy development 12th Five-year Plan of Guangdong province [EB/OL]. 2013 [2014-07-01]. http://www.gddpc.gov.cn/fgzl/fzgh/zxgh/sewzx/201309/t20130926_220199.htm (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 香港特别行政区政府新闻公报. 香港气候行动蓝图2030+ [EB/OL]. 2017 [2021-01-10]. https://sc.isd.gov.hk/TuniS/www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/201701/20/P2017012000724.htm?fontSize=1. |
| Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government Press Release. Hong Kong climate action blueprint 2030+ [EB/OL]. 2017 [2021-01-10]. https://sc.isd.gov.hk/TuniS/www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/201701/20/P2017012000724.htm?fontSize=1. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 南方电网能源发展研究院. 粤港澳大湾区能源规划研究 [R]. 广州: 南方电网能源发展研究院有限责任公司, 2020. |
| China Southern Power Grid Energy Development Research Institute. Development plan for the energy of the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area [R]. Guangzhou: China Southern Power Grid Energy Development Research Institute Co., LTD., 2020 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | LIN Ze-Wei, WANG Peng, REN Song-Yan, XU Hong-Wei, ZHANG Cong, ZHAO Dai-Qing. Assessment of economic, environmental and health benefits of the energy transition path—take the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area as an example [J]. Climate Change Research, 2022, 18(6): 777-790. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||