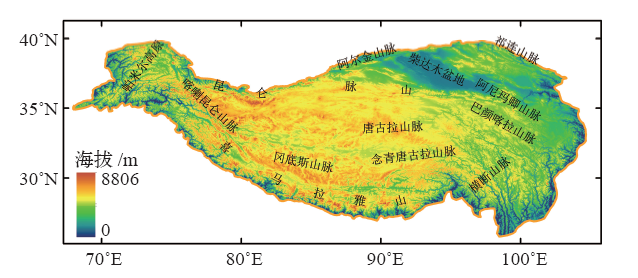
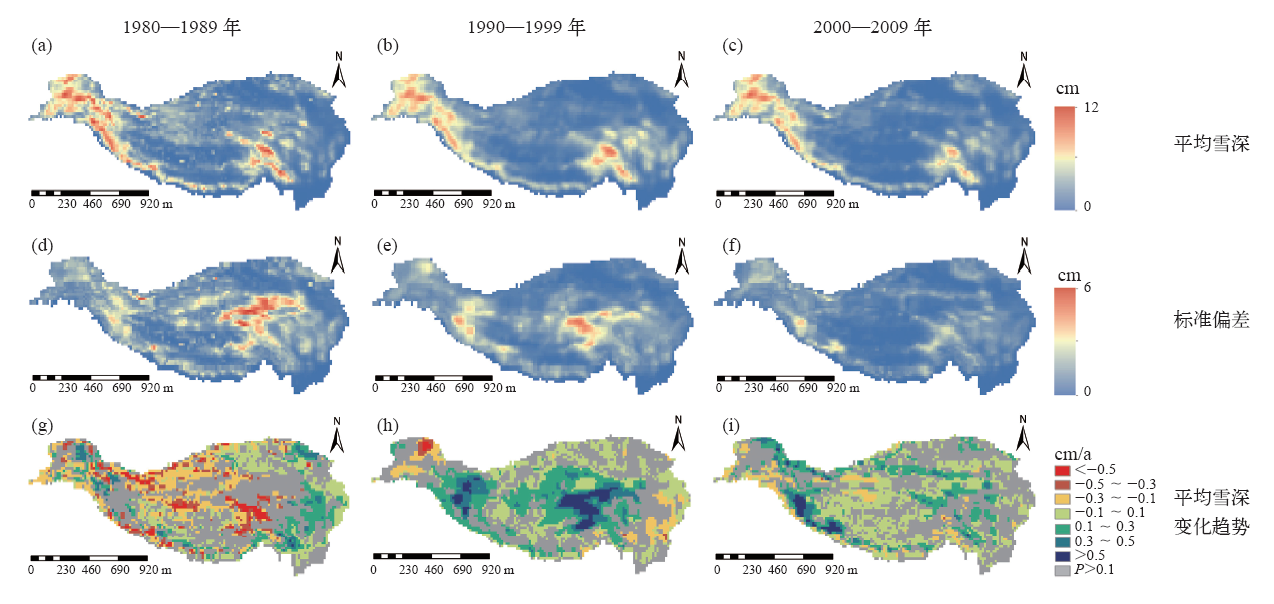
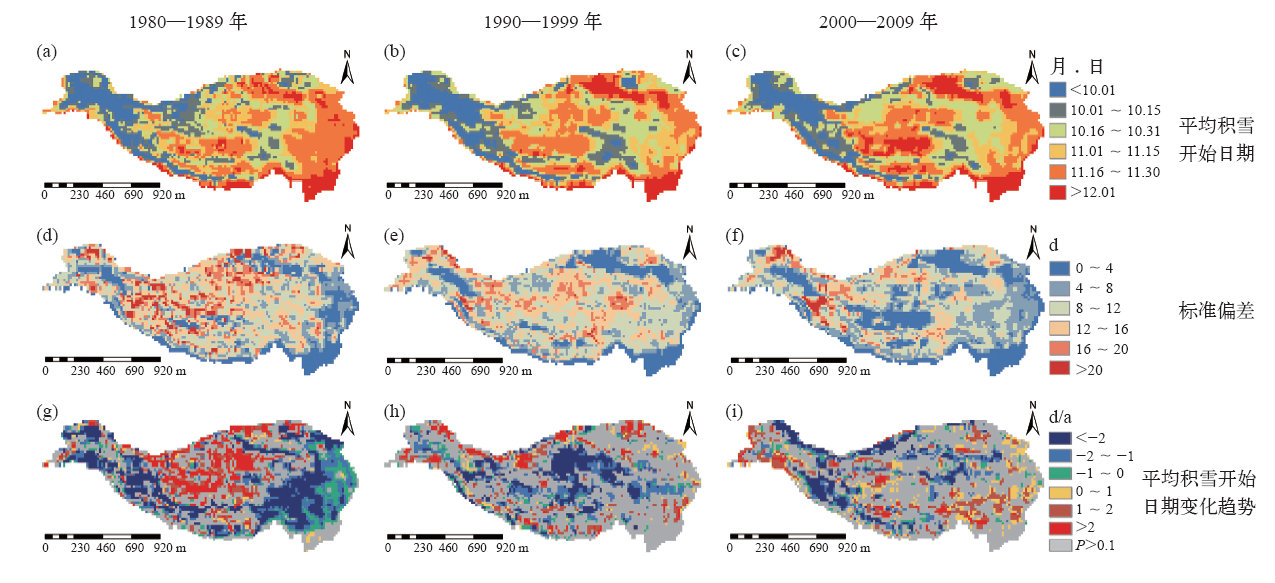
| [1] | Chen X N, Liang S L, Gao Y F, et al. Observed contrast changes in snow cover phenology in northern middle and high latitudes from 2001-2014[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015 (5). DOI: 10.1038/srep16820 | | [2] | Wang K, Zhang L, Qiu Y B, et al. Snow effects on alpine vegetation in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Internation Journal of Digital Earth, 2015, 8(1): 56-73 | | [3] | 姚檀栋, 秦大河, 沈永平, 等. 青藏高原冰冻圈变化及其对区域水循环和生态条件的影响[J].自然杂志, 2013 (3): 179-186 | | [4] | 除多, 杨勇, 罗布坚参, 等. 1981—2010年青藏高原积雪日数时空变化特征分析[J].冰川冻土, 2015 (6): 1461-1472 | | [5] | 徐丽娇, 李栋梁, 胡泽勇. 青藏高原积雪日数与高原季风的关系[J]. 高原气象, 2010 (5): 1093-1101 | | [6] | 王增艳, 车涛. 2002—2009年中国干旱区积雪时空分布特征[J]. 干旱区研究, 2012 (3): 464-471 | | [7] | 郭建平, 刘欢, 安林昌, 等. 2001—2012年青藏高原积雪覆盖率变化及地形影响[J]. 高原气象, 2016 (1): 24-33 | | [8] | 汪箫悦, 王思远, 尹航, 等. 2002—2012年青藏高原积雪物候变化及其对气候的响应[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2016 (11): 1573-1579 | | [9] | 车涛, 李新. 利用被动微波遥感数据反演我国积雪深度及其精度评价[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 2004 (5): 301-306 | | [10] | 白淑英, 史建桥, 高吉喜, 等. 1979—2010年青藏高原积雪深度时空变化遥感分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2014 (4): 628-637 | | [11] | 戴声佩, 张勃, 程峰, 等. 基于被动微波遥感反演雪深的时间序列分析我国积雪时空变化特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 2010 (6): 1066-1073 | | [12] | 高懋芳, 邱建军. 青藏高原主要自然灾害特点及分布规律研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011 (8): 101-106 | | [13] | Che T, Li X, Jin R, et al. Snow depth derived from passive microwave remote-sensing data in China[J]. Annals of Glaciology, 2008, 49: 145-154 | | [14] | Dai L Y, Che T, Wang J, et al. Snow depth and snow water equivalent estimation from AMSR-E data based on a priori snow characteristics in Xinjiang, China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2012, 127: 14-29 | | [15] | Dai L Y, Che T, Ding Y J.Inter-calibrating SMMR, SSM/I and SSMI/S data to improve the consistency of snow-depth products in China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7: 7212-7230 | | [16] | 李小兰, 张飞民, 王澄海. 中国地区地面观测积雪深度和遥感雪深资料的对比分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2012 (4): 755-764 | | [17] | 安迪, 李栋梁, 袁云, 等. 基于不同积雪日定义的积雪资料比较分析[J]. 冰川冻土, 2009 (6): 1019-1027 | | [18] | Wei Z G, Huang R H, Chen W, et al. Spatial distributions and interdecadal variations of snow at the Tibetan Plateau weather stations[J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 2002, 26(4): 496-508 | | [19] | Stow D A, Hope A, McGuire D, et al. Remote sensing of vegetation and land-cover change in Arctic tundra ecosystems[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2004, 89: 281-308 | | [20] | 李培基, 米德生. 中国积雪的分布[J]. 冰川冻土, 1983, 5(4): 9-18 | | [21] | 柯长青, 李培基. 青藏高原积雪分布与变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 1998, 53(3): 209-215 | | [22] | 伯玥, 李小兰, 王澄海. 青藏高原地区积雪年际变化异常中心的季节变化特征[J]. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(6): 1353-1362 | | [23] | 田柳茜, 李卫忠, 张尧, 等. 青藏高原1979—2007年间的积雪变化[J]. 生态学报, 2014 (20): 5974-5983 |
|
 ), Nian-Qin WANG1, Zhen LI2, Jian-Min ZHOU2, Xi-You FU2
), Nian-Qin WANG1, Zhen LI2, Jian-Min ZHOU2, Xi-You FU2