气候变化研究进展 ›› 2020, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (3): 296-305.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2019.084
1984—2014年北京地区不透水地表的时空变化及其温度效应研究
张稼乐1,潘志华1( ),匡文慧2,潘宇鹰1,韩国琳1,王佳琳1,黄娜1,张子源1,尹文娟1
),匡文慧2,潘宇鹰1,韩国琳1,王佳琳1,黄娜1,张子源1,尹文娟1
- 1 中国农业大学资源与环境学院,北京 100193
2 中国科学院地理与资源研究所,北京 100101
-
收稿日期:2019-04-16修回日期:2019-06-13出版日期:2020-05-30发布日期:2020-06-15 -
通讯作者:潘志华 E-mail:panzhihua@cau.edu.cn -
作者简介:张稼乐,女,硕士研究生 -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划全球变化专项(2018YFA0606303)
Spatial-temporal change features of impervious surface and its effect on land surface temperature from 1984 to 2014 in Beijing
Jia-Le ZHANG1,Zhi-Hua PAN1( ),Wen-Hui KUANG2,Yu-Ying PAN1,Guo-Lin HAN1,Jia-Lin WANG1,Na HUANG1,Zi-Yuan ZHANG1,Wen-Juan YIN1
),Wen-Hui KUANG2,Yu-Ying PAN1,Guo-Lin HAN1,Jia-Lin WANG1,Na HUANG1,Zi-Yuan ZHANG1,Wen-Juan YIN1
- 1 College of Resources and Environmental Sciences, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100193, China
2 Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100101, China
-
Received:2019-04-16Revised:2019-06-13Online:2020-05-30Published:2020-06-15 -
Contact:Zhi-Hua PAN E-mail:panzhihua@cau.edu.cn
摘要:
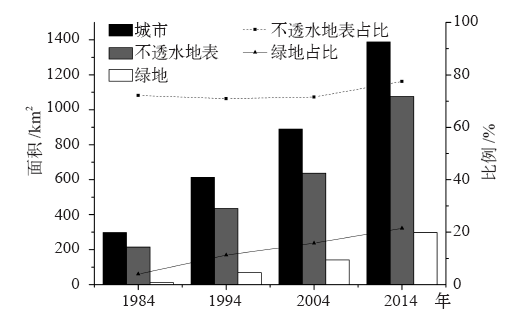
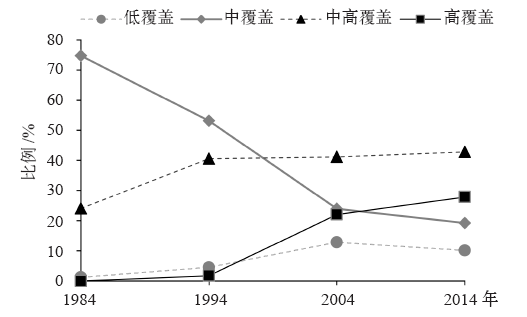
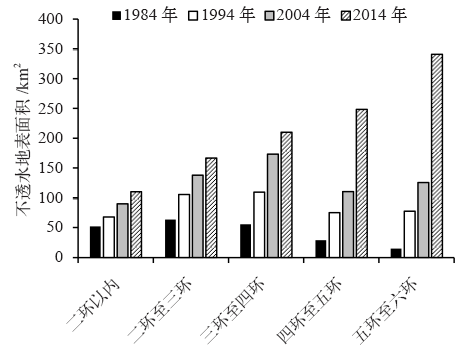
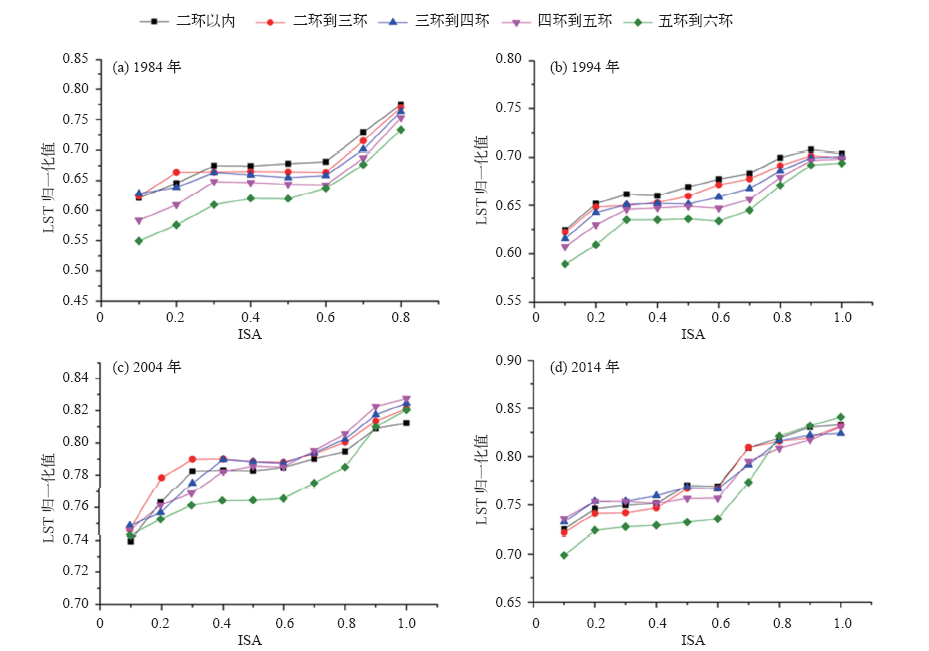
研究城市地表覆盖与地表温度(LST)的关系对改善城市生态环境具有重要科学意义。在Landsat TM数据支持下,利用线性光谱混合分析模型提取不透水地表信息,结合LST和地表热通量,分析不透水地表覆盖度(ISA)和LST的时空变化特征及其相互关系,探讨不透水地表对LST的影响机理。结果表明:1984—2014年北京不透水地表面积迅速增长,中覆盖度比例下降,高覆盖度比例增加;LST从市中心向郊区递减,高温区向外扩张;LST和ISA呈显著正相关,但不是简单的线性关系;ISA处于0.6~0.9时LST上升速率最快,减少ISA在此范围内的不透水地表集中分布可缓解高温区集中的现象。
引用本文
张稼乐,潘志华,匡文慧,潘宇鹰,韩国琳,王佳琳,黄娜,张子源,尹文娟. 1984—2014年北京地区不透水地表的时空变化及其温度效应研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(3): 296-305.
Jia-Le ZHANG,Zhi-Hua PAN,Wen-Hui KUANG,Yu-Ying PAN,Guo-Lin HAN,Jia-Lin WANG,Na HUANG,Zi-Yuan ZHANG,Wen-Juan YIN. Spatial-temporal change features of impervious surface and its effect on land surface temperature from 1984 to 2014 in Beijing[J]. Climate Change Research, 2020, 16(3): 296-305.

图1 北京市1984 (a)、1994 (b)、2004 (c)和2014 (d)年不透水地表覆盖度(ISA)分布
Fig. 1 Spatial distribution of impervious surface area (ISA) in Beijing in 1984, 1994 , 2004 and 2014
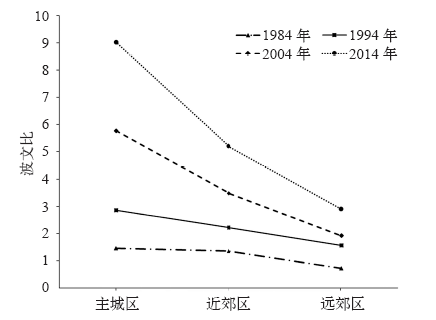
图5 1984、1994、2004和2014年北京市主城区、近郊区、远郊区LST对比
Fig. 5 Comparison of surface temperature in main city, near suburb and far suburb of Beijing in 1984, 1994, 2004 and 2014
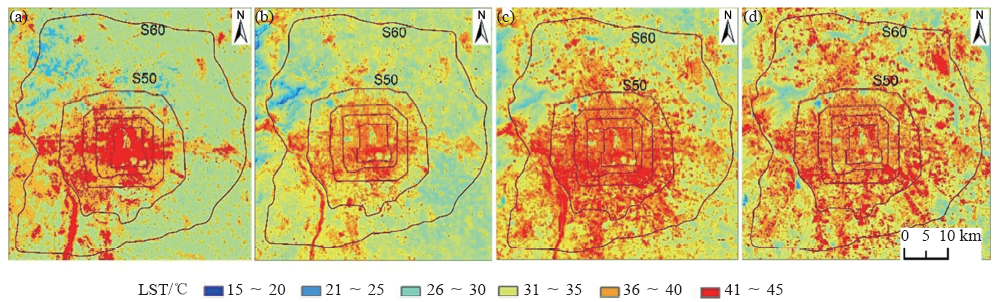
图6 北京市1984 (a)、1994 (b)、2004 (c)和2014 (d)年LST分布
Fig. 6 Spatial distribution of surface temperature in Beijing in 1984 (a), 1994 (b), 2004 (c) and 2014 (d)

图8 北京市1984 (a)、1994 (b)、2004 (c)和2014 (d)年下垫面显热通量分布
Fig. 8 Sensible heat flux of underlying surface in Beijing in 1984 (a), 1994 (b), 2004 (c) and 2014 (d)
|
| [1] | 张君枝,袁冯,王冀,孙赫敏,刘洪,马文林. 全球升温1.5℃和2.0℃背景下北京市暴雨洪涝淹没风险研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2020, 16(1): 78-87. |
| [2] | 毛明策,王琦,田亮. 2022年北京冬季奥运会人工造雪气象条件初步研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(6): 547-552. |
| [3] | 韩翠,尹义星,黄伊涵,刘梦洋,王小军. 江淮梅雨区1960—2014年夏季极端降水变化特征及影响因素[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 445-454. |
| [4] | 岳溪柳, 於琍, 黄玫, 吴绍洪, 周波涛, 徐影. 人类活动影响下的北京地区气候承载力初步评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(6): 517-525. |
| [5] | 杜吴鹏, 房小怡, 刘勇洪, 贺健, 程宸, 党冰, 邢佩. 面向特大城市的风环境容量指标和区划初探——以北京为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(6): 526-533. |
| [6] | 刘瑞霞, 刘杰, 刘月丽. AIRS反演中国区域上对流层水汽分布特征研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(1): 1-9. |
| [7] | 钱维宏 李进. 北京地区长期增暖中的一个减缓期[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2012, 8(3): 178-182. |
| [8] | 郑祚芳 丁海燕 范水勇. 北京1960—2008年气候变暖及极端气温指数变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2011, 7(3): 189-196. |
| [9] | 周荣卫;何晓凤;苗世光;李青春. 北京地区大气环流型及气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(05): 338-343. |
| [10] | 丁海燕;郑祚芳;刘伟东. 北京1951-2008年升温趋势和季节变化[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2010, 6(03): 187-191. |
| [11] | 何慧;陆虹;欧艺. 1959-2008年广西西江流域洪涝气候特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2009, 5(03): 134-138. |
| [12] | 郑祚芳 张秀丽 曹鸿兴 谢庄 徐影. 气候模拟数据的订正与应用 --以北京为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007, 03(05): 299-302. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||