气候变化研究进展 ›› 2018, Vol. 14 ›› Issue (4): 402-410.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2018.027
未来气候变化背景下我国橡胶树寒害事件的变化特征
李宁1,2,白蕤3( ),李玮1,2,张蕾4,易克贤1,陈淼1,2,陈歆1,2
),李玮1,2,张蕾4,易克贤1,陈淼1,2,陈歆1,2
- 1 中国热带农业科学院环境与植物保护研究所,海口 571101
2 农业部儋州农业环境科学观测实验站,儋州 571737
3 海南省气象科学研究所,海口 570203
4 中国气象局国家气象中心,北京 100081
Changes of chilling injury events on China’s rubber tree under future climate change
Ning LI1,2,Rui BAI3( ),Wei LI1,2,Lei ZHANG4,Ke-Xian YI1,Miao CHEN1,2,Xin CHEN1,2
),Wei LI1,2,Lei ZHANG4,Ke-Xian YI1,Miao CHEN1,2,Xin CHEN1,2
- 1 Environment and Plant Protection Institute, Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, Haikou 571101, China
2 Danzhou Scientific Observing and Experimental Station of Agro-Environment, Ministry of Agriculture, Danzhou 571737, China
3 Hainan Institute of Meteorological Science, Haikou 570203, China
4 National Meteorological Center, China Meteorological Administration, Beijing 100081, China
摘要:
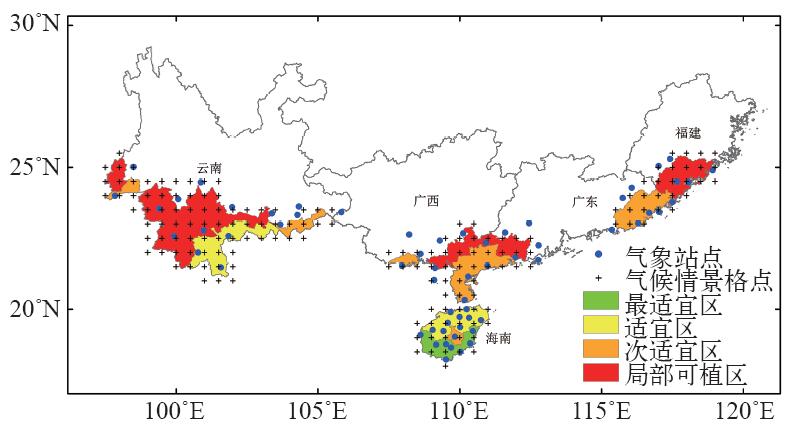
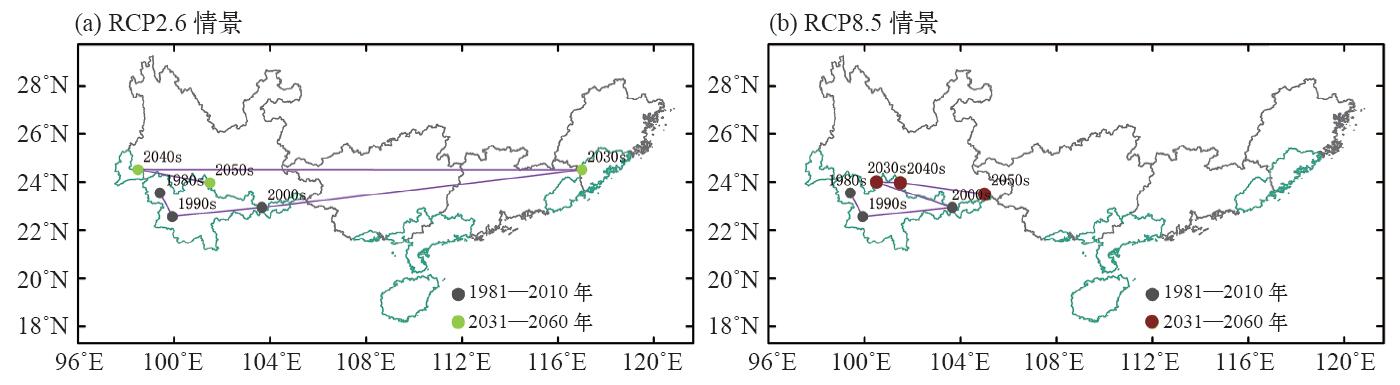
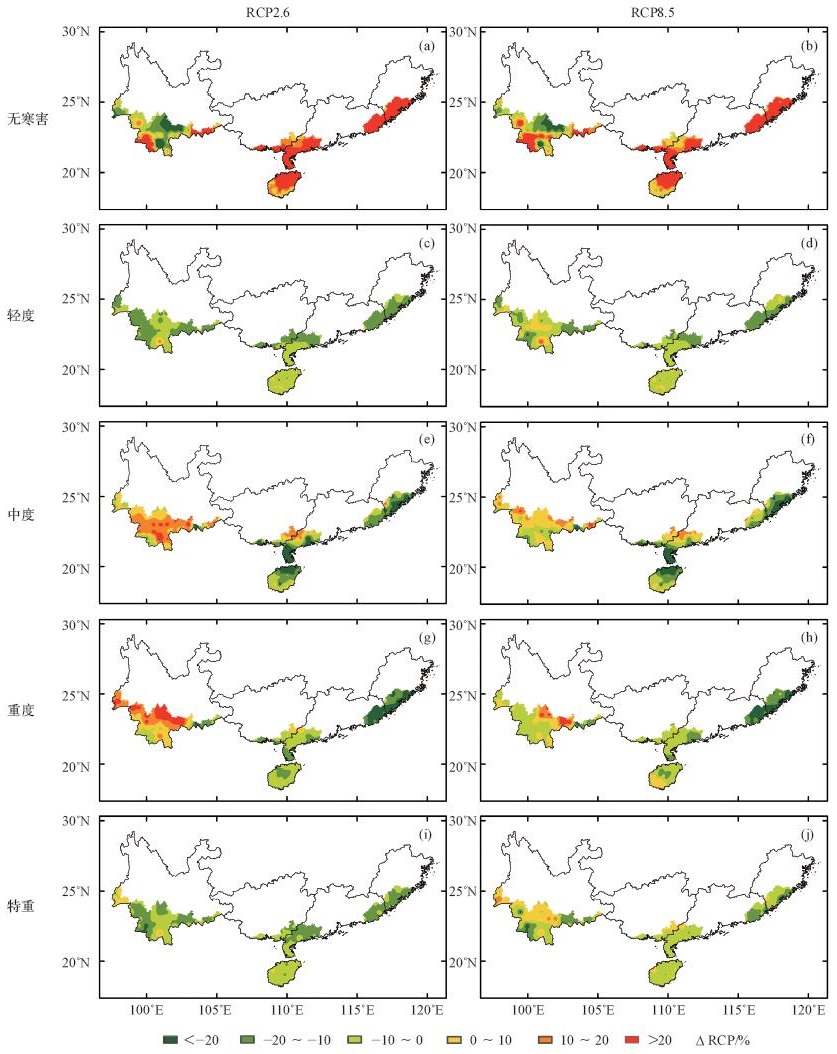
利用1981—2010年历史气象数据和2031—2060年(RCP2.6和RCP8.5)气候情景数据,根据橡胶寒害等级指标,结合插值分析、提取分析和地图代数等空间分析方法,研究在未来气候情景下我国橡胶树寒害事件的变化特征。结果表明:(1) RCP2.6和RCP8.5气候情景下2031—2060年我国橡胶种植适宜区基本呈现寒害发生降低的趋势,其中次适宜区(III)和局部可植区(IV)的降低幅度较为明显,有向高一等级适宜区转化的趋势。(2)我国橡胶树寒害中心的纬度,由1981—2010年的22.5°~23.5°N向北移动至2031—2060年RCP2.6情景下的24.0°~24.5°N和RCP8.5情景下的23.5°~24.0°N。(3) 2种气候情景下,2031—2060年我国海南、广西、广东、福建等植胶区橡胶树寒害发生概率(较基准时段1981—2010年)主要呈现降低趋势,云南植胶区在2种气候情景下有明显的差异,表现为RCP2.6情景下,轻度和特重寒害呈现降低趋势,中度和重度寒害呈现增加趋势;RCP8.5情景下,轻度和重度寒害呈现降低趋势,中度和特重寒害呈现增加趋势。(4)对比2种气候情景较基准时段的变化情况,RCP2.6情景对橡胶树轻度和特重寒害影响较大,RCP8.5情景对橡胶树中度和重度寒害影响较大。