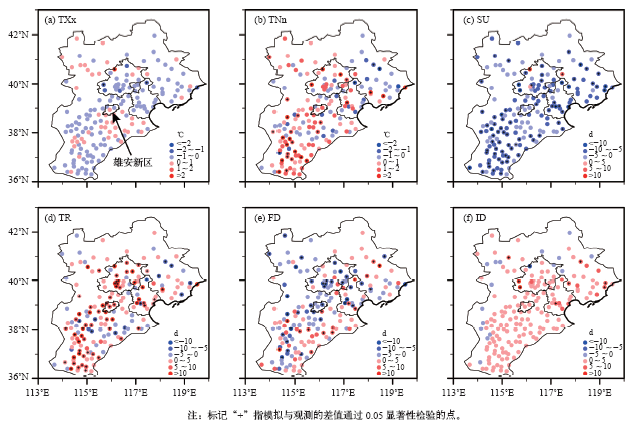
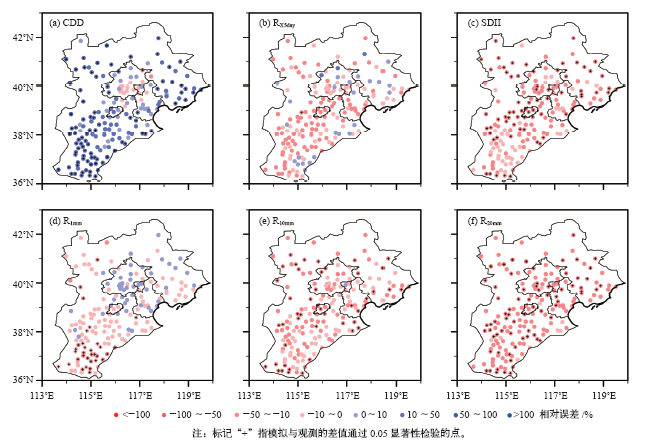
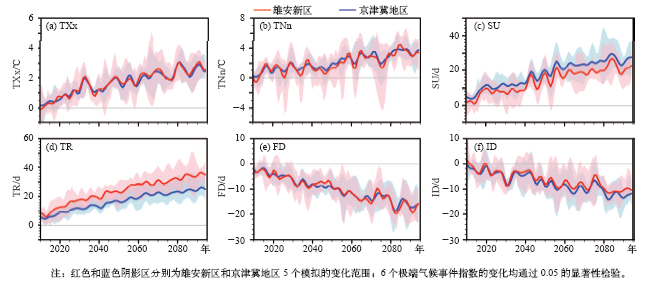
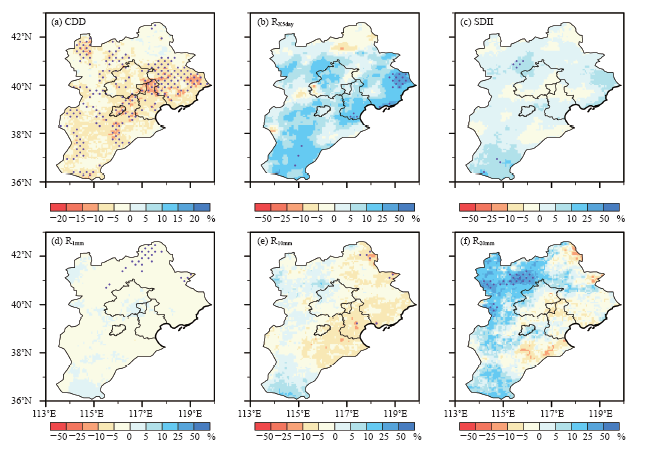
| [1] | Taylor K E, Stouffer B J, Meehl G A . An overview of CMIP5 and the experiment design[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2012,93:485-498 | | [2] | IPCC. Managing the risks of extreme events and disasters to advance climate change adaptation [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 582 | | [3] | 秦大河 . 中国极端天气气候事件和灾害风险管理与适应国家评估报告(精华版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2015: 109 | | [4] | 徐影 . 中国未来极端气候事件变化预估图集[M]. 北京: 气象出版社, 2015: 175 | | [5] | 徐影, 张冰, 周波涛 , 等. 基于CMIP5模式的中国地区未来洪涝灾害风险变化预估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014,10(4):268-275 | | [6] | Gao X J, Zhao Z C, Ding Y H , et al. Climate change due to greenhouse effects in China as simulated by a regional climate model[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2001,18(6):1224-1230 | | [7] | Zhou T J, Li Z X . Simulation of the East Asian summer monsoon by using a variable resolution atmospheric GCM[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2002,19:167-180 | | [8] | Xu Y, Gao X J, Giorgi F . Upgrades to the REA method for producing probabilistic climate change predictions[J]. Climate Research, 2010,41:61-81 | | [9] | Xu Y, Wu J, Shi Y , et al. Change in extreme climate events over China based on CMIP[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2015,8:185-192 | | [10] | Zhou T J, Yu R C . Twentieth century surface air temperature over China and the globe simulated by coupled climate models[J]. Journal of Climate, 2006,19:5843-5858 | | [11] | Gao X J, Shi Y, Song R Y , et al. Reduction of future monsoon precipitation over China: comparison between a high resolution RCM simulation and the driving GCM[J]. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 2008,100(1):73-86 | | [12] | Gao X J, Shi Y, Zhang D F , et al. Uncertainties in monsoon precipitation projections over China: results from two high-resolution RCM simulations[J]. Climate Research, 2012,52(1):213-226 | | [13] | Ji Z M, Kang S C . Evaluation of extreme climate events using a regional climate model for China[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015,35:888-902 | | [14] | 刘伟东, 尤焕苓, 孙丹 . 1961—2010年京津冀及其周边区域温度日较差变化特征[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2016,21(2):167-174 | | [15] | Mei C, Liu J H, Chen M T , et al. Multi-decadal spatial and temporal changes of extreme precipitation patterns in northern China (Jing-Jin-Ji district, 1960-2013)[J]. Quaternary International, 2018,476:1-13 | | [16] | Jiang R G, Yu X, Xie J C , et al. Recent changes in daily climate extremes in a serious water shortage metropolitan region, a case study in Jing-Jin-Ji of China[J]. Theoretical Applied Climatology, 2018,134:565-584 | | [17] | 闵晶晶, 曹晓钟, 段宇辉 , 等. 近30年京津冀地区冰雹的气候特征和突变分析[J]. 气象, 2012,38(2):189-196 | | [18] | Qian C, Cao L J . Linear trends in mean and extreme temperature in Xiongan New Area, China[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2018,11(3):246-254 | | [19] | 吴婕, 高学杰, 徐影 . RegCM4对雄安及周边区域气候变化的集合预估[J]. 大气科学, 2018,42(3):696-705 | | [20] | Han Z Y, Shi Y, Wu J , et al. High resolution combined statistical and dynamical downscaling for multi-variables in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region of China[J]. Submitted to International Journal of Climatology, 2018 | | [21] | Giorgi F, Coppola E, Solmon F , et al. RegCM4: model description and illustrative basic performance over selected CORDEX domains[J]. Climate Research, 2012,52:7-29 | | [22] | Giorgi F, Jones C, Asrar G . Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: the CORDEX framework[J]. WMO Bulletin, 2009,58:175-183 | | [23] | Han Z Y, Zhou B T, Xu Y , et al. Projected changes in haze pollution potential in China: an ensemble of regional climate model simulations[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2017,17(16):10109-10123 | | [24] | Gao X J, Wu J, Shi Y , et al. Future changes in thermal comfort conditions over China based on multi-RegCM4 simulations[J]. Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters, 2018. DOI: 10.1080/16742834.2018.147158 | | [25] | Shi Y, Wang G L, Gao X J . Role of resolution in regional climate change projections over China[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2018,51:2375-2396 | | [26] | 童尧, 高学杰, 韩振宇 , 等. 基于RegCM4的中国区域日尺度降水模拟误差订正[J]. 大气科学, 2017,41(6):1156-1166 | | [27] | 韩振宇, 童尧, 高学杰 , 等. 分位数映射法在RegCM4中国气温模拟订正中的应用[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018,14(4):331-340 | | [28] | Cannon A J, Sobie S R, Murdock T Q . Bias correction of GCM precipitation by quantile mapping: how well do methods preserve changes in quantiles and extremes?[J]. Journal of Climate, 2015,28(17):6938-6959 | | [29] | Shi C X, Xie Z H, Qian H , et al. China land soil moisture EnKF data assimilation based on satellite remote sensing data[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2011,54:1430-1440 | | [30] | Shi C X, Jiang L P, Zhang T , , et al. Status. Status and plans of CMA Land Data Assimilation System (CLDAS) project [C]. EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 2014, 16, EGU2014-5671 | | [31] | Zhang X B, Alexander L, Hegerl G C , et al. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data[J]. WIREs Climate Change, 2011,2:851-870 |
|
 ),Ying XU,Bo-Tao ZHOU,Jia WU
),Ying XU,Bo-Tao ZHOU,Jia WU