Climate Change Research ›› 2025, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (4): 469-476.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.001
• 20th Anniversary of Climate Change Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and its impact on global climate change
CHEN Xian-Yao1( ), BI Han-Wen1,2,3, HAO Xiao-Jie1,2, MA Tian-Jiao1,2,3, GUO Ling-Rui1,2
), BI Han-Wen1,2,3, HAO Xiao-Jie1,2, MA Tian-Jiao1,2,3, GUO Ling-Rui1,2
- 1 Frontier Science Center for Deep Ocean Multispheres and Earth System/Key Laboratory of Physical Oceanography, Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
2 College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
3 Academy of the Future Ocean, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
-
Received:2025-01-02Revised:2025-05-29Online:2025-07-30Published:2025-06-27
Cite this article
CHEN Xian-Yao, BI Han-Wen, HAO Xiao-Jie, MA Tian-Jiao, GUO Ling-Rui. Variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and its impact on global climate change[J]. Climate Change Research, 2025, 21(4): 469-476.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2025.001

Fig. 1 Meridional cross section of salinity in the western Atlantic Ocean constructed from the measurements during the German Atlantic expeditions from 1925 to 1927
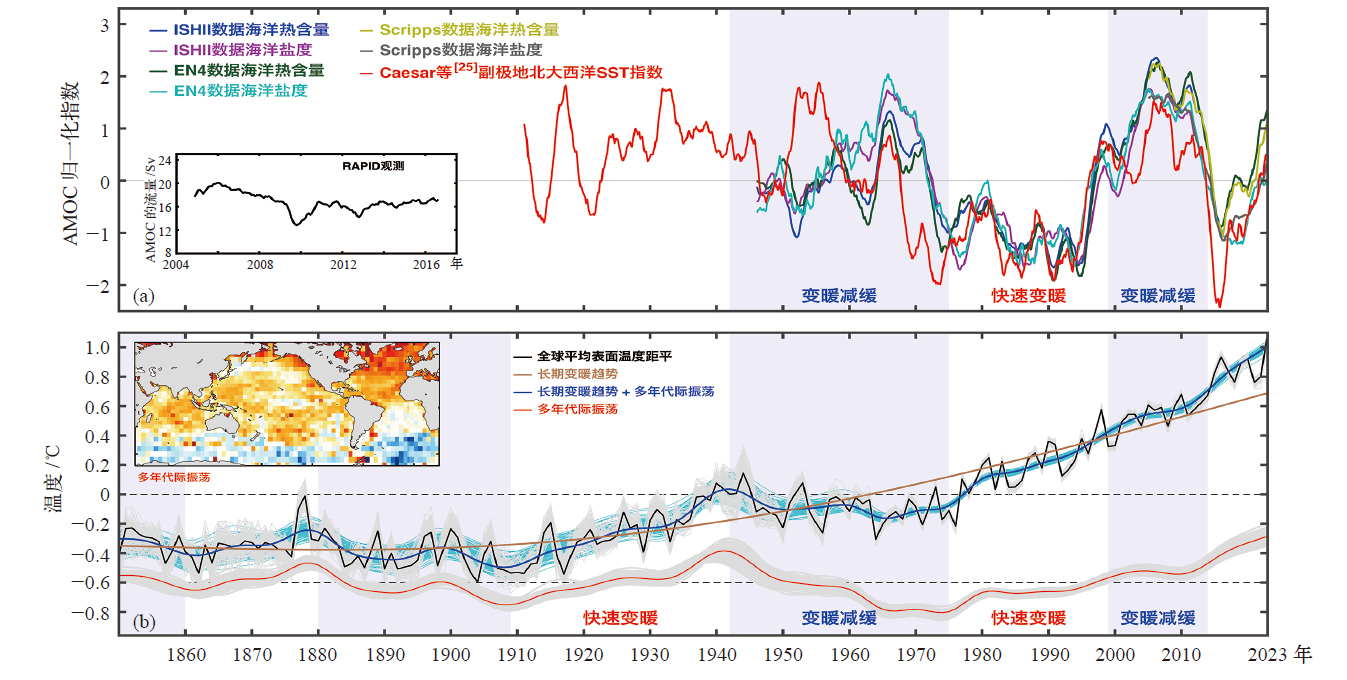
Fig. 3 AMOC and GSTA variations. (a) The AMOC fingerprint[24-26], (b) GSTA variations[24] (The inset shows the SST spatial pattern associated with MDV obtained by regressing SST onto its time series. The blue curve is the smoothed version of GSTA obtained as the sum of the secular trend and MDV. The faint lines around the solid lines are from 100 ensemble members of the HadCRUT4.6, which assess the range of uncertainty of the data used in the solid lines)
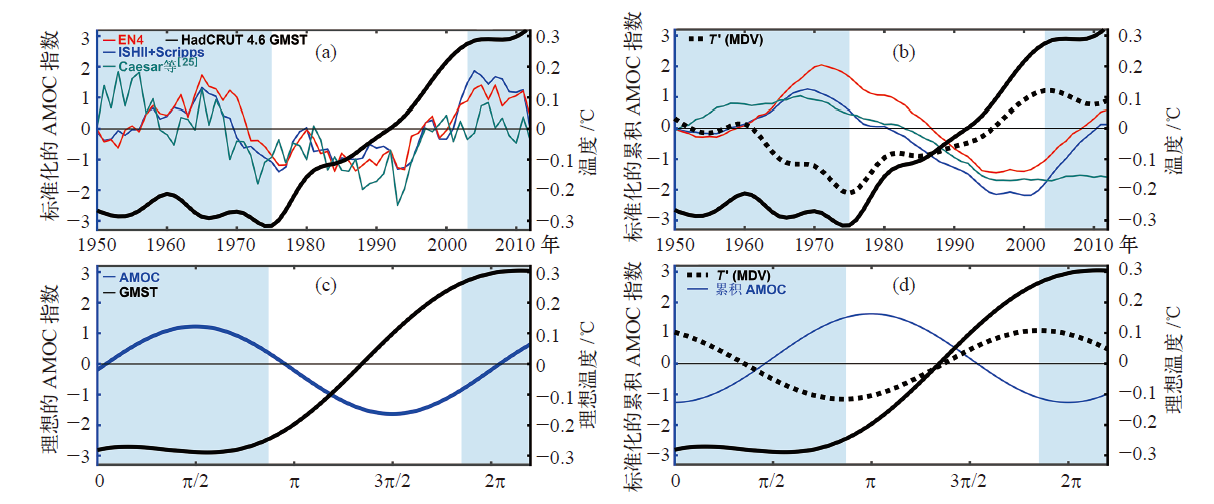
Fig. 4 Observed and theoretical solution of anomalous global mean surface temperature (GMST). (a) Observed GMST plotted with various normalized AMOC indices [38], (b) observed GMST plotted with the integral of various AMOC indices, normalized, (c), (d) Same as (a), (b) but for the theoretical solution of Equation (1). (The black solid line is the GMST, and the red and blue lines represent the subpolar upper-ocean salinity indices [24]. The green line denotes the SST-based AMOC fingerprint [25]. Black dash line T′ (MDV) is the multidecadal variability of GMST. The shade areas denote periods of warming slowdown and the unshaded area the period of accelerated warming [38])
| [1] | Wu Z, Huang N E, Wallace J M, et al. On the time-varying trend in global-mean surface temperature[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2011, 37: 759-773 |
| [2] | Jeong D, Yoo C, Yeh S W, et al. Contributions of external forcing and internal variability to the multidecadal warming rate of East Asia in the present and future climate[J]. NPJ Climate Atmospheric Science, 2024, 7: 22 |
| [3] | Qian C, Yu J Y, Chen G. Decadal summer drought frequency in China: the increasing influence of the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2014, 9: 124004 |
| [4] | Miles M W, Divine D V, Furevik T, et al. A signal of persistent Atlantic multidecadal variability in Arctic sea ice[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41 (2): 463-469 |
| [5] | Li X, Holland D, Gerber E, et al. Impacts of the north and tropical Atlantic Ocean on the Antarctic Peninsula and sea ice[J]. Nature, 2014, 505: 538-542 |
| [6] | Gao M, Yang J, Gong D, et al. Footprints of Atlantic multidecadal oscillation in the low-frequency variation of extreme high temperature in the Northern Hemisphere[J]. Journal of Climate, 2019, 32: 791-802 |
| [7] |
Goldenberg S B, Landsea C W, Mestas-Nuñez A M, et al. The recent increase in Atlantic hurricane activity: causes and implications[J]. Science, 2001, 293 (5529): 474-479
pmid: 11463911 |
| [8] | Kosaka Y, Xie S P. Recent global-warming hiatus tied to equatorial Pacific surface cooling[J]. Nature, 2013, 501: 403-407 |
| [9] | Stommel Henry M. Evolution of physical oceanography: scientific surveys in honor of Henry Stommel[M]. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press, 1981: 61-64 |
| [10] | Rumford B. The propagation of heat in fluids[J]. Essays, Political, Economical, and Philosophical, 1800: 197-386 |
| [11] |
Lozier M S. Overturning in the North Atlantic[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2012, 4: 291-315
pmid: 22457977 |
| [12] | Broecker W S. The great ocean conveyor[J]. Oceanography, 1991, 4 (2): 79-89 |
| [13] | Kuhlbrodt T, Griesel A, Montoya M, et al. On the driving processes of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2007, 45: RG2001 |
| [14] | Bryan K. Measurements of meridional heat transport by ocean currents[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1962, 67 (9): 3403-3414 |
| [15] | Ganachaud A, Wunsch C. Improved estimates of global ocean circulation, heat transport and mixing from hydrographic data[J]. Nature, 2000, 408 (6811): 453-457 |
| [16] | Hastenrath S. On meridional heat transports in the world ocean[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1982, 12 (8): 922-927 |
| [17] | Hastenrath S. Heat budget of tropical ocean and atmosphere[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1980, 10 (2): 159-170 |
| [18] | Sverdrup H U. Oceanography[M]. Handbuch der Physik, 1957, 48: 608-670 |
| [19] | Talley L D. Shallow, intermediate, and deep overturning components of the global heat budget[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2003, 33 (3): 530-560 |
| [20] | Toggweiler J R, Samuels B. On the ocean’s large-scale circulation near the limit of no vertical mixing[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 1998, 28 (9): 1832-1852 |
| [21] | Munk W, Wunsch C. Abyssal recipes II: energetics of tidal and wind mixing[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 1998, 45 (12): 1977-2010 |
| [22] | McCarthy G, Frajka-Williams E, Johns W E, et al. Observed interannual variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at 26.5°N[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L19609 |
| [23] |
Lozier M S, Li F, Bacon S, et al. A sea change in our view of overturning in the subpolar North Atlantic[J]. Science, 2019, 363: 516-521
doi: 10.1126/science.aau6592 pmid: 30705189 |
| [24] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Global surface warming enhanced by weak Atlantic overturning circulation[J]. Nature, 2018, 559: 387-391 |
| [25] | Caesar L, Rahmstorf S, Robinson A, et al. Observed fingerprint of a weakening Atlantic Ocean overturning circulation[J]. Nature, 2018, 556: 191-196 |
| [26] | Zhang R. Coherent surface-subsurface fingerprint of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2008, 35: L20705 |
| [27] |
Moat B I, Smeed D A, Frajka-Williams E, et al. Pending recovery in the strength of the meridional overturning circulation at 26 degrees N[J]. Ocean Science, 2020, 16: 863-874
doi: 10.5194/os-16-863-2020 |
| [28] | Wunsch C, Heimbach P. Estimated decadal changes in the North Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and heat flux 1993-2004[J]. Journal of Physical Oceanography, 2006, 36: 2012-2024 |
| [29] | Balmaseda M A, Smith G C, Haines K, et al. Historical reconstruction of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation from the ECMWF operational ocean reanalysis[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34: L23615 |
| [30] | Bakker P, Schmittner A, Lenaerts J T M, et al. Fate of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: strong decline under continued warming and Greenland melting[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2016, 43: 12252-12260 |
| [31] | Weijer W, Cheng W, Garuba O A, et al. CMIP6 models predict significant 21st century decline of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47: e2019GL086075 |
| [32] | Jungclaus J H, Fischer N, Haak H, et al. Characteristics of the ocean simulations in the Max Planck Institute Ocean Model (MPIOM) the ocean component of the MPI-Earth system model[J]. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 2013, 5: 422-446 |
| [33] |
Renssen H, Mairesse A, Goosse H, et al. Multiple causes of the Younger Dryas cold period[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2015, 8: 946-949
doi: 10.1038/NGEO2557 |
| [34] | Stolpe M, Medhaug I, Sedláček J, et al. Multidecadal variability in global surface temperatures related to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Journal of Climate, 2018, 31: 2889-2906 |
| [35] | Trenberth K E, Fasullo J T. Atlantic meridional heat transports computed from balancing Earth’s energy locally[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44: 1919-1927 |
| [36] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Varying planetary heat sink led to global-warming slowdown and acceleration[J]. Science, 2014, 345: 897-903 |
| [37] | Caesar L, Rahmstorf S, Feulner G. On the relationship between Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation slowdown and global surface warming[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2020, 15: 024003 |
| [38] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Comment on ‘On the relationship between Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation slowdown and global surface warming’[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2021, 16: 038001 |
| [39] | Zhang L P, Wang C Z. Multidecadal North Atlantic sea surface temperature and Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation variability in CMIP5 historical simulations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2013, 118: 5772-5791 |
| [40] | Buckley M W, Marshall J. Observations, inferences, and mechanisms of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a review[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2015, 54: 5-63 |
| [41] | McCarthy G D, Brown P J, Flagg C N, et al. Sustainable observations of the AMOC: methodology and technology[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2020, 58: e2019RG000654 |
| [42] | Johnson H L, Cessi P, Marshall D P, et al. Recent contributions of theory to our understanding of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124: 5376-5399 |
| [43] |
Lynch-Stieglitz J. The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and abrupt climate change[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2017, 9: 83-104
doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060415 pmid: 27814029 |
| [44] | Zhang R, Sutton R, Danabasoglu G, et al. A review of the role of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in Atlantic Multidecadal Variability and associated climate impacts[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 2019, 57: 316-375 |
| [45] | Weijer W, Cheng W, Drijfhout S S, et al. Stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a review and synthesis[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 2019, 124: 5336-5375 |
| [46] | Manabe S, Stouffer R J. Two stable equilibria of a coupled ocean-atmosphere model[J]. Journal of Climate, 1988, 1: 841-866 |
| [47] | Weaver A, Sedláček J, Edy M, et al. Stability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: a model intercomparison[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L20709 |
| [48] | Weijer W, Maltrud M E, Hecht M W, et al. Response of the Atlantic Ocean circulation to Greenland Ice Sheet melting in a strongly-eddying ocean model[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39: L09606 |
| [49] | Menary M B, Robson J, Allan R P, et al. Aerosol-forced AMOC changes in CMIP6 historical simulations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47: e88166 |
| [50] | Bellomo K, Angeloni M, Corti S, et al. Future climate change shaped by inter-model differences in Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation response[J]. Nature Communication, 2021, 12: 3659 |
| [51] | Rahmstorf S. On the freshwater forcing and transport of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation[J]. Climate Dynamics, 1996, 12 (12): 799-811 |
| [52] | Vellinga M, Wood R A. Global climatic impacts of a collapse of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation[J]. Climatic Change, 2002, 54: 251-267 |
| [53] | van Westen R M, Michael K, Henk A D, et al. Physics-based early warning signal shows that AMOC is on tipping course[J]. Science Advance, 2024, 10: eadk1189 |
| [54] | Boers N. Observation-based early-warning signals for a collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2021, 11: 680-688 |
| [55] | Ditlevsen P, Ditlevsen S. Warning of a forthcoming collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Communication, 2023, 14: 4254 |
| [56] | Fu Y, Li F, Karstensen J, et al. A stable Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation in a changing North Atlantic Ocean since the 1990s[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6: eabc8736 |
| [57] | Chen X Y, Tung K K. Evidence lacking for a pending collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation[J]. Nature Climate Change, 2023, 14: 1 |
| [1] | Zhai Panmao, Yu Rong, Zhou Baiquan, Chen Yang, Guo Jianping, Lu Yanyu. Research Progress in Impact of 1.5℃Global Warming on Global and Regional Scales [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(5): 465-472. |
| [2] | Zhang Yongxiang, Chao Qingchen, Zheng Qiuhong, Huang Lei. The Impacts on Global Climate Governance Due to the United States Dropping off the Paris Agreement [J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(5): 407-414. |
| [3] | Tan Hongjian, Cai Rongshuo, Huang Ronghui. Enhanced Responses of Sea Surface Temperature over Offshore China to Global Warming and Hiatus [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(6): 500-507. |
| [4] | . Review of Global Climate Change in 2007 [J]. Climate Change Research, 2008, 04(001): 53-56. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
