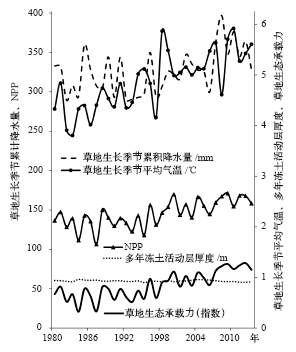
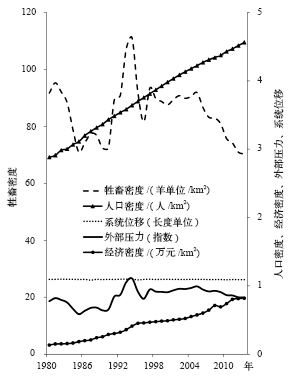
| [1] | David G S, Carvalho E D, Lemos D , et al. Ecological carrying capacity for intensive tilapia (Oreochromisniloticus) cage aquaculture in a large hydro electrical reservoir in southeastern Brazil[J]. Aquacultural Engineering, 2015,66:30-40 | | [2] | Costanza R . Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment[J]. Ecological Economics, 1995,15(2):89-90 | | [3] | Daily G C. Nature’s services: societal dependence on natural ecosystems [M]. Washington DC: Island Press, 1997 | | [4] | Graymore M L M, Sipe N G, Rickson R E . Sustaining human carrying capacity: a tool for regional sustainability assessment[J]. Ecological Economics, 2010 ( 69):459-468 | | [5] | Arrow K, Bolin B, Costanza R , et al. Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment[J]. Ecological Economics, 1995,15(2):91-95 | | [6] | Seidl I, Tisdell C A . Carrying capacity reconsidered: from Malthus’s population theory to cultural carrying capacity[J]. Ecological Economics, 1999,31:395-408 | | [7] | Prato T . Fuzzy adaptive management of social and ecological carrying capacities for protected areas[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2009,90:2551-2557 | | [8] | Rajaram T, Das A . Screening for EIA in India: enhancing effectiveness through ecological carrying capacity approach[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011 ( 92):140-148 | | [9] | Odum E P . Basic ecology[M]. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1983 | | [10] | Smaal A C, Prins T C, Dankers N , et al. Minimum requirements for modelling bivalve carrying[J]. Aquatic Ecology, 1998,31:423-428 | | [11] | Hudak A T . Rangeland mismanagement in South Africa: failure to apply ecological knowledge[J]. Human Ecology, 1999,27(1):55-78 | | [12] | Bailey J A . Principles of wildlife management[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1984 | | [13] | 杨志峰, 隋欣 . 基于生态系统健康的生态承载力评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2005,25(5):586-594 | | [14] | 杨贤智 . 环境管理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 1990: 150-155 | | [15] | 张传国, 方创琳, 全华 . 干旱区绿洲承载力研究的全新审视与展望[J]. 资源科学, 2002,24(2):42-47 | | [16] | 程国栋 . 承载力概念的演变及西北水资源承载力的应用框架[J]. 冰川冻土, 2002,24(4):361-367 | | [17] | 王中根, 夏军 . 区域生态环境承载力的量化方法研究[J]. 长江职工大学学报, 1999,16(4):9-12 | | [18] | 高吉喜 . 可持续发展理论探讨: 生态承载力理论、方法与应用[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2001: 12-28 | | [19] | 王家骥, 姚小红, 李京荣 . 黑河流域生态承载力估测[J]. 环境科学研究, 2000,13(2):44-48 | | [20] | Cheng J Y, Zhou K, Chen D , et al. Evaluation and analysis of provincial differences in resources and environment carrying capacity in China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2016,26(4):539-549 | | [21] | Fang C L, Liu X L . Comprehensive measurement for carrying capacity of resources and environment of city clusters in central China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2010,20(3):281-288 | | [22] | Peng J, Du Y Y, Liu Y X , et al. How to assess urban development potential in mountain areas? An approach of ecological carrying capacity in the view of coupled human and natural[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016,60:1017-1030 | | [23] | 钟茂初 . 如何表征区域生态承载力与生态环境质量?兼论以胡焕庸线生态承载力涵义重新划分东中西部[J]. 中国地质大学学报: 社会科学版, 2016,16(1):1-9 | | [24] | Ding L, Chen K L, Cheng S G , et al. Water ecological carrying capacity of urban lakes in the context of rapid urbanization: a case study of East Lake in Wuhan[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 2015 ( 89-90):104-113 | | [25] | 焦雯, 闵庆文, 李文华 , 等. 基于ESEF的水生态承载力:理论、模型与应用[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015,26(4) : 1041-1048 | | [26] | Zhang Z, Lu W X, Zhao Y , et al. Development tendency analysis and evaluation of the water ecological carrying capacity in the Siping area of Jilin province in China based on system dynamics and analytic hierarchy process[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2014 ( 275):9-21 | | [27] | Wang S, Xu L, Yang F L , et al. Assessment of water ecological carrying capacity under the two policies in Tieling city on the basis of the integrated system dynamics model[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014 ( 472):1070-1081 | | [28] | Scoones I . Economic and ecological carrying capacity applications to pastoral systems in Zimbabwe[M] //Barbier E B. Economics and ecology: new frontiers and sustainable development. London: Chapman & Hall, 1993: 96-117 | | [29] | Fang Y P, Qin D H, Ding Y J , et al. The impacts of permafrost change on NPP and implications: a case of the source regions of Yangtze and Yellow Rivers[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2011,8(3):437-447 | | [30] | 施开放, 刁承泰, 孙秀锋 , 等. 基于耕地生态足迹的重庆市耕地生态承载力供需平衡研究[J]. 生态学报, 2013,33(6):1872-1880 | | [31] | Wei C, Dai X Y, Ye S F , et al. Prediction analysis model of integrated carrying capacity using set pair analysis[J]. Ocean & Coastal Management, 2016,120:39-48 | | [32] | Cuadra M, Bjorklund J . Assessment of economic and ecological carrying capacity of agricultural crops in Nicaragua[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2007,7:133-149 | | [33] | Liu D, Feng Z M, Yang Y Z , et al. Spatial patterns of ecological carrying capacity supply-demand balance in China at county level[J]. Journal of Geography Science, 2011,21(5):833-844 | | [34] | Yue D X . RS & GIS-based spatial analysis on ecological carrying capacity pattern of Northwest China: does supply meet demand?[J]. Quaternary International, 2012: 279-280, 551. DOI: 10.1016/j.quaint.2012.08.1945 | | [35] | Jiang W M, Gibbs M T . Predicting the carrying capacity of bivalve shellfish culture using a steady, linear food web model[J]. Aquaculture, 2005,244:171-185 | | [36] | Byron C, Bengtso D, Costa-Pierce B , et al. Integrating science into management: ecological carrying capacity of bivalve shellfish aquaculture[J]. Marine Policy, 2011,35:363-370 | | [37] | Byron C, Link J, Costa-Pierce B , et al. Calculating ecological carrying capacity of shellfish aquaculture using mass-balance modeling: Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2011,222:1743-1755 | | [38] | Mckindsey C W, Thetmeyer H, Landry T , et al. Review of recent carrying capacity models for bivalve culture and recommendations for research and management[J]. Aquaculture, 2006,26(2):451-462 | | [39] | Thapa G B, Paudel G S . Evaluation of the livestock carrying capacity of land resources in the hills of Nepal based on total digestive nutrient analysis[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2000,78:223-235 | | [40] | Yu L, Zhou L, Liu W , et al. Using remote sensing and GIS technologies to estimate grass yield and livestock carrying capacity of alpine grasslands in Golog Prefecture, China[J]. Pedosphere, 2010,20(3):342-351 | | [41] | Zhang J P, Zhang L B, Liu W L , et al. Livestock-carrying capacity and overgrazing status of alpine grassland in the Three-River Headwaters region, China[J]. Journal of Geography Science, 2014,24(2):303-312 | | [42] | 刘东霞, 张兵兵, 卢欣石 . 草地生态承载力研究进展及展望[J]. 中国草地学报, 2007,29(1):91-96 | | [43] | 孙鸿烈, 郑度, 姚檀栋 , 等. 青藏高原国家生态安全屏障保护与建设[J]. 地理学报, 2012,67(1):3-12 | | [44] | 焦世晖, 王凌越, 刘耕年 . 全球变暖背景下青藏高原多年冻土分布变化预测[J]. 北京大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016,52(2):249-256 | | [45] | 张镱锂, 祁威, 周才平 , 等. 青藏高原高寒草地净初级生产力(NPP)时空分异[J]. 地理学报, 2013,68(9):1197-1211 | | [46] | 邹经湘, 于开平 . 结构动力学(第二版)[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2009 | | [47] | Fang Y P, Zhu F B, Qiu X P , et al. Effects of natural disasters on livelihood resilience of rural residents in Sichuan[J]. Habitat International, 2018,76:19-28 | | [48] | Scazzieri R . Structural dynamics and evolutionary change[J]. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.strueco.2018.03.007 | | [49] | Kraus M K, Park J W . The structural dynamics of social class[J]. Current Opinion in Psychology, 2017,18:55-60 | | [50] | Arena R, Porta P L. Introduction: structural dynamics and contemporary growth theory [M] //Arena R, Porta P L. Structural dynamics and economic growth. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 1-33 | | [51] | Yi S, Wang X, Qin Y , et al. Responses of alpine grassland on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau to climate warming and permafrost degradation: a modeling perspective[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2014,9(7):074014 | | [52] | 方水良 . 现代控制理论及其MATLAB实践[M]. 杭州: 浙江大学出版社, 2005 | | [53] | Jiang C, Zhang L B . Ecosystem change assessment in the Three-River headwater region, China: patterns, causes, and implications[J]. Ecological Engineering, 2016,93:24-36 | | [54] | Jiang C, Li D Q, Wang D W , et al. Quantification and assessment of changes in ecosystem service in the Three-River headwaters region, China as a result of climate variability and land cover change[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2016,66:199-211 | | [55] | 陈德亮, 徐柏青, 姚檀栋 , 等. 青藏高原环境变化科学评估:过去、现在与未来[J]. 科学通报, 2015,60(32):3025-3035 | | [56] | Che M L, Chen B Z, Innes J L , , et al. Spatial. Spatial and temporal variations in the end date of the vegetation growing season throughout the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2011[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 2014, 189- 190:81-90 | | [57] | 黄麟, 曹巍, 徐新良 , 等. 西藏生态安全屏障保护与建设工程的宏观生态效应[J]. 自然资源学报, 2018,33(3):398-411 | | [58] | Ye X, Liu G H, Li Z S , et al. Evaluation of ecological effectiveness of protected areas in Northwest China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science, 2017,27(2):259-272 |
|