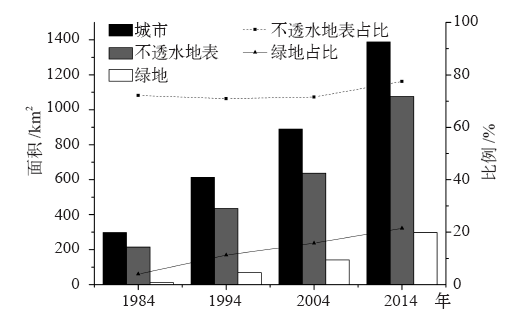
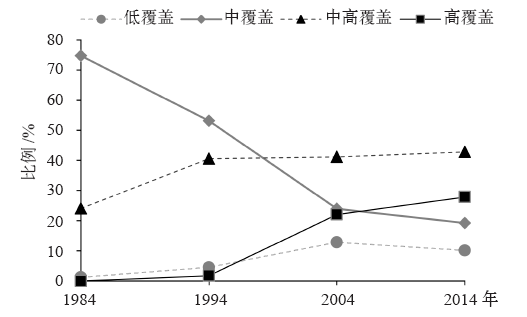
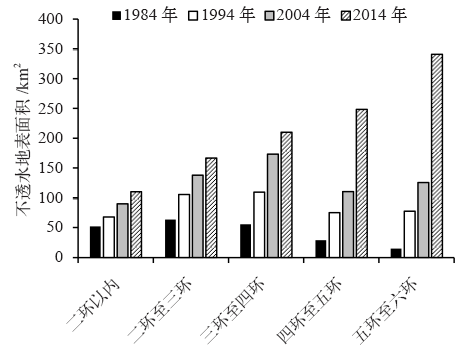
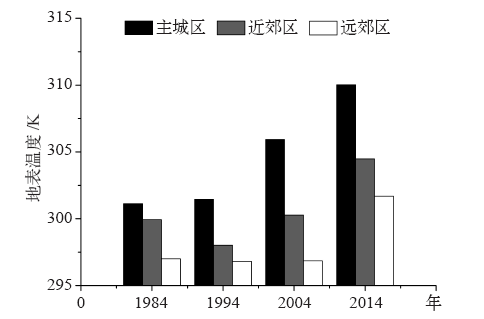
| [1] | 周玄德, 郭华东, 孜比布拉, 等. 城市扩张过程中不透水面空间格局演变以及对地表温度的影响: 以乌鲁木齐市为例[J]. 生态学报, 2018,38(20):7336-7347. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201711122022. | | [1] | Zhou X D, Guo H D, Zibibula S, et al. Spatial pattern evolution of impervious surfaces and its influence on surface temperature in the process of urban expansion: a case study of Urumqi[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018,38(20):7336-7347. DOI: 10.5846/stxb201711122022 (in Chinese) | | [2] | Roth M. Review of urban climate research in (sub) tropical regions[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2007,27:1859-1873. DOI: 10.1002/joc.1591 | | [3] | Akio O, Cao X, Ito T, et al. Evaluating the potential for urban heat-island mitigation by greening parking lots[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2010,9:323-332. DOI: 10.1016/j.ufug.2010.06.002 | | [4] | 谢启娇. 武汉市城市热岛特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016,25(3):462-469. DOI: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201603013. | | [4] | Xie Q J. Analysis on characteristics and influence factors of urban heat island effect in Wuhan[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2016,25(3):462-469. DOI: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201603013 (in Chinese) | | [5] | 尹昌应, 石忆邵, 王贺封, 等. 城市地表形态对热环境的影响: 以上海市为例[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2015,24(1):97-105. DOI: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201501013. | | [5] | Yin C Y, Shi Y S, Wang H F, et al. Impacts of urban landscape form on thermal environment at multi-spatial levels[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2015,24(1):97-105. DOI: 10.11870/cjlyzyyhj201501013 (in Chinese) | | [6] | 杨可明, 周玉洁, 齐建伟, 等. 城市不透水面及地表温度的遥感估算[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2014,26(2):134-139. DOI: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2014.02.22. | | [6] | Yang K M, Zhou Y J, Qi J W, et al. Remote sensing estimating of urban impervious surface area and land surface temperature[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2014,26(2):134-139. DOI: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2014.02.22 (in Chinese) | | [7] | 北京市统计局. 北京统计年鉴2015 [M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2015. | | [7] | Beijing Statistics Bureau. Beijing statistical year book 2015 [M]. Beijing: China Statistical Press, 2015 ( in Chinese) | | [8] | 牟雪洁, 赵昕奕. 珠三角地区地表温度与土地利用类型关系[J]. 地理研究, 2012,31(9):1589-1597. DOI: 10.11821/yj2012090005. | | [8] | Mou X J, Zhao X Y. Study on the relationship between surface temperature and land use in Pearl River Delta[J]. Geographical Research, 2012,31(9):1589-1597. DOI: 10.11821/yj2012090005 (in Chinese) | | [9] | 郑祚芳, 郑艳, 李青春. 近30年来城市化进程对北京区域气温的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2007,15(4):26-29. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011. | | [9] | Zheng Z F, Zheng Y, Li Q C. Effect of urbanization on the temperature of Beijing metropolis in recent 30 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2007,15(4):26-29. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011 (in Chinese) | | [10] | 张光智, 徐祥德, 王继志, 等. 北京及周边地区城市尺度热岛特征及其演变[J]. 应用气象学报, 2002 ( S1):43-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2002.z1.005. | | [10] | Zhang G Z, Xu X D, Wang J Z, et al. A study of characteristics and evolution of urban heat island over Beijing and its surrounding area[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science, 2002 ( S1):43-50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7313.2002.z1.005 (in Chinese) | | [11] | 宋艳玲, 张尚印. 北京市近40年城市热岛效应研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2003,11(4):126-129. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011. | | [11] | Song Y L, Zhang S Y. The study on heat island effect in Beijing during last 40 years[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2003,11(4):126-129. DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1011 (in Chinese) | | [12] | 屈益挺, 孟丹, 李小娟. 北京市城市扩张及其对城市增温效应的影响[J]. 首都师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2017,38(2):77-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9398.2017.02.016. | | [12] | Qu Y T, Meng D, Li X J. Study on urban expansion and its influence on urban warming effect in Beijing[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2017,38(2):77-83. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9398.2017.02.016 (in Chinese) | | [13] | Qiao K, Zhu W Q, Hu D Y, et al. Examining the distribution and dynamics of impervious surface in different function zones in Beijing[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2018,28(5):669-684. DOI: 10.1007/s11442-018-1498-5 | | [14] | 匡文慧, 杨天荣, 刘爱琳, 等. 城市地表覆盖结构组分与热环境调控模型(EcoCity)研究: 以北京城市为例[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017,47(7):847-859. DOI: 10.1360/N072016-00273. | | [14] | Kuang W H, Yang T R, Liu A L, et al. An Ecocity model for regulating urban land cover structure and thermal environment: taking Beijing as an example[J]. Scientia Sinica: Terrae, 2017,47(7):847-859. DOI: 10.1360/N072016-00273 (in Chinese) | | [15] | Elvidge C D, Tuttle B T, Sutton P C, et al. Global distribution and density of constructed impervious surfaces[J]. Sensors, 2007,7:1962-1979. DOI: 10.3390/s7091962 | | [16] | 徐涵秋, 王美雅. 地表不透水面信息遥感的主要方法分析[J]. 遥感学报, 2016,20(5):1270-1289. DOI: 10.11834/jrs.20166210. | | [16] | Xu H Q, Wang M Y. Remote sensing-based retrieval of ground impervious surfaces[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016,20(5):1270-1289. DOI: 10.11834/jrs.20166210 (in Chinese) | | [17] | Wu C S, Murray A T. Estimating impervious surface distribution by spectral mixture analysis[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2003,84(4):493-505. DOI: 10.1016/S0034-4257(02)00136-0 | | [18] | Kuang W H, Chi W F, Lu D S, et al. A comparative analysis of megacity expansions in China and the U.S.: patterns, rates and driving forces[J]. Landscape Urban Plan, 2014,13(2):121-135. DOI: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.08.015 | | [19] | Carlson T N, Arthur S T. The impact of land use-land cover changes due to urbanization on surface microclimate and hydrology: a satellite perspective[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2000,25(1/2):49-65. DOI: 10.1016/S0921-8181(00)00021-7 | | [20] | 覃志豪, Zhang M H, Arnon K, et al. 用陆地卫星TM6数据演算地表温度的单窗算法[J]. 地理学报, 2001,56(4):456-466. DOI: 10.1142/S0252959901000401. | | [20] | Qin Z H, Zhang M H, Arnon K, et al. Mono-window algorithm for retrieving land surface temperature from Landsat TM6 data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2001,56(4):456-466. DOI: 10.1142/S0252959901000401 (in Chinese) | | [21] | 覃志豪, 李文娟, 徐斌, 等. 陆地卫星TM6波段范围内地表比辐射率的估计[J]. 国土资源遥感, 2004,61(3):28-30. DOI: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2004.03.07. | | [21] | Qin Z H, Li W J, Xu B, et al. The estimation of land surface emissivity for Landsat TM6[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2004,61(3):28-30. DOI: 10.6046/gtzyyg.2004.03.07 (in Chinese) | | [22] | Kuang W H, Dou Y Y, Zhang C, et al. Quantifying the heat flux regulation of metropolitan land use/land cover components by coupling remote sensing modeling with in situ measurement[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2015,120(1):113-130. DOI: 10.1002/2014JD022249 | | [23] | 张仁华. 定量热红外遥感模型及地面实验基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009. | | [23] | Zhang R H. Quantitative thermal infrared remote sensing model and ground experiment basis [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009 ( in Chinese) | | [24] | 陈松林, 王天星. 等间距法和均值标准差法界定城市热岛的对比研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2009,11(2):145-150. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1560-8999. | | [24] | Chen S L, Wang T X. Comparison analyses of equal interval method and mean standard deviation method used to delimitate urban heat island[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2009,11(2):145-150. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1560-8999 (in Chinese) | | [25] | 宋小宁, 赵英时, 冯晓明. 基于卫星遥感数据改进区域尺度的显热通量模型[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2007,23(1):36-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2007.01.009. | | [25] | Song X N, Zhao Y S, Feng X M. An improved regional scale sensible heat flux model using remote sensing[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2007,23(1):36-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0504.2007.01.009 (in Chinese) |
|
 ),Wen-Hui KUANG2,Yu-Ying PAN1,Guo-Lin HAN1,Jia-Lin WANG1,Na HUANG1,Zi-Yuan ZHANG1,Wen-Juan YIN1
),Wen-Hui KUANG2,Yu-Ying PAN1,Guo-Lin HAN1,Jia-Lin WANG1,Na HUANG1,Zi-Yuan ZHANG1,Wen-Juan YIN1