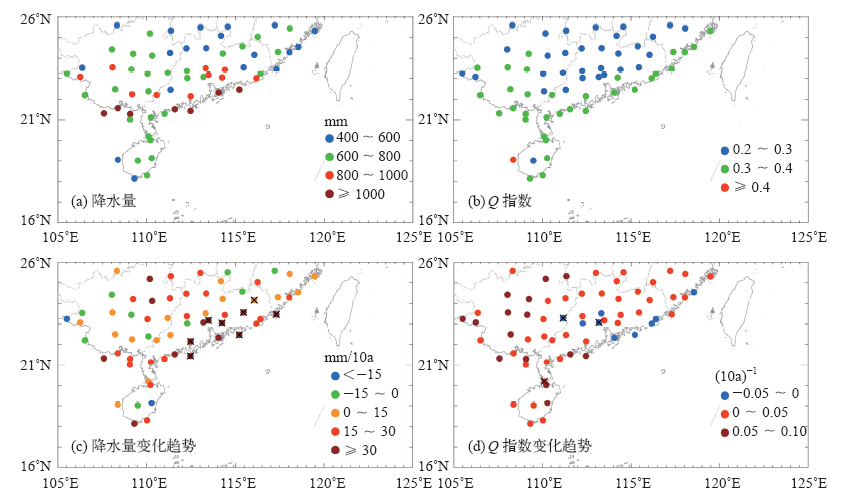
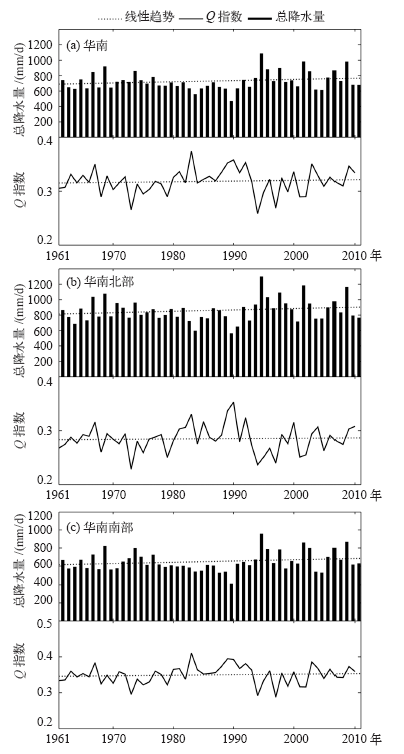
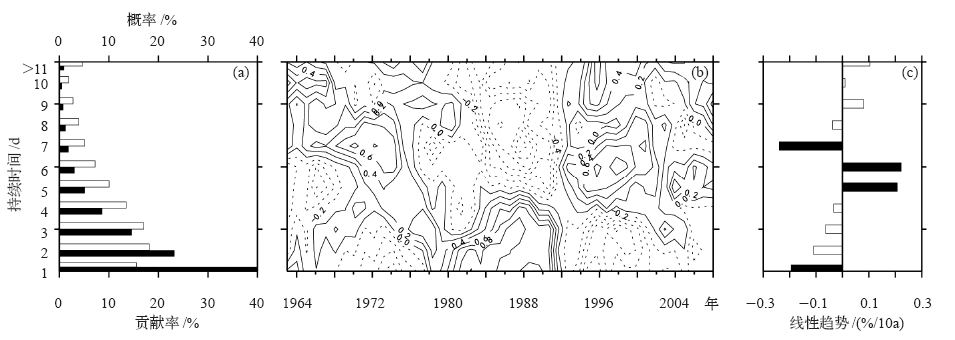
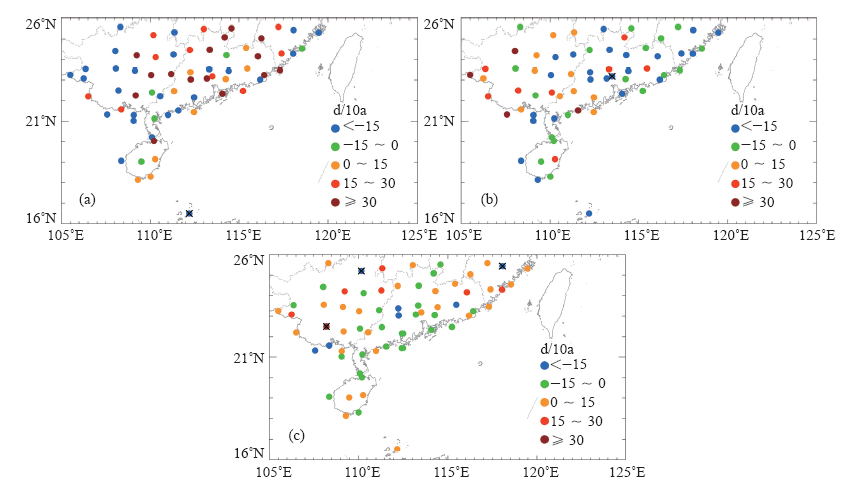
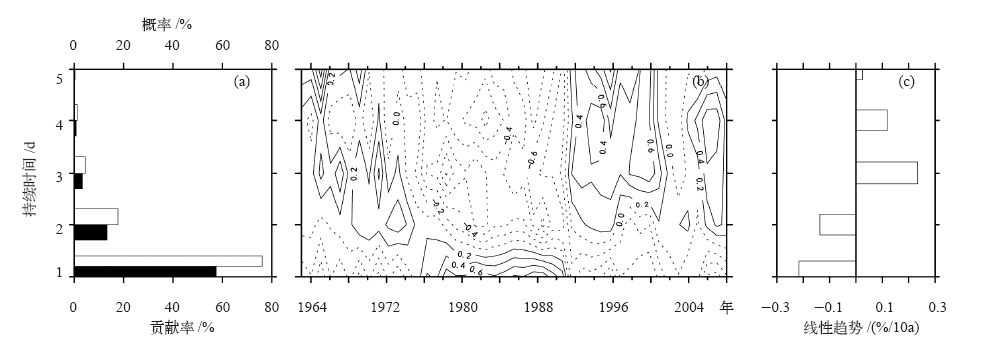
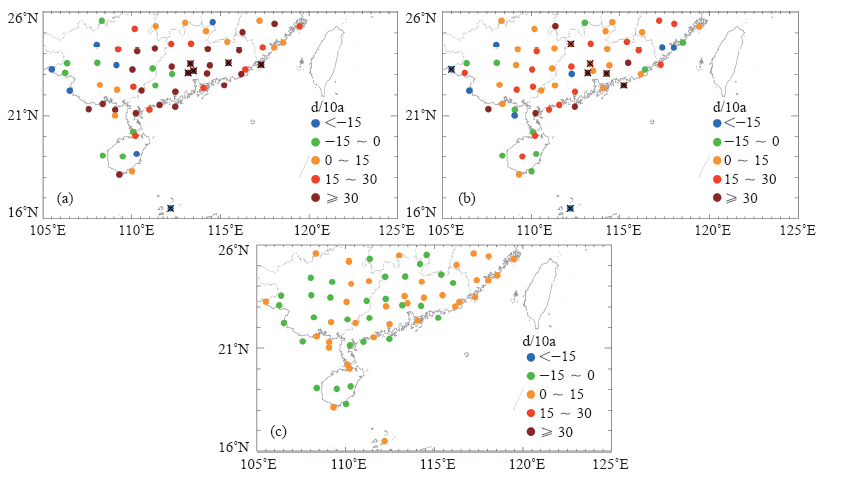
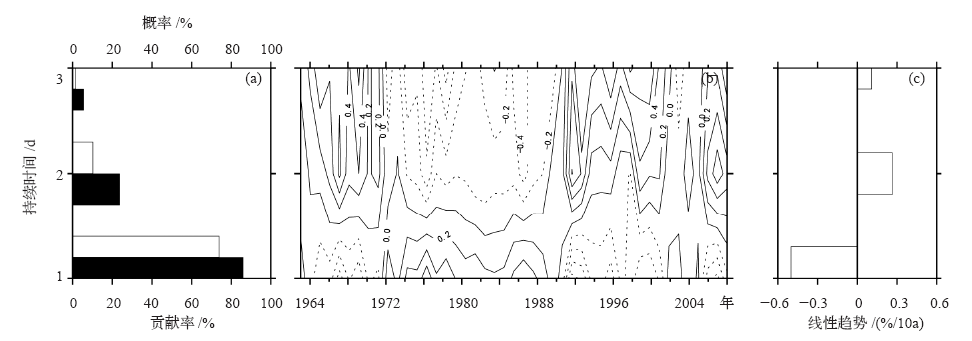
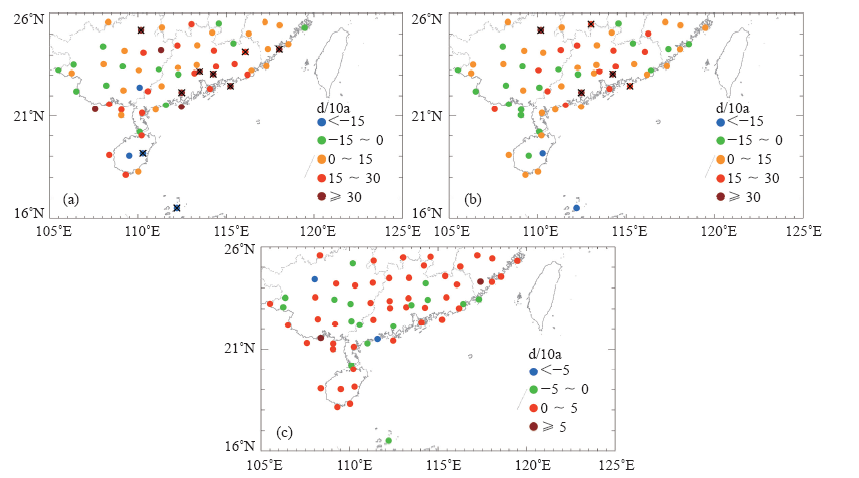
| [1] | 鲍名 . 近50年我国持续性暴雨的统计分析及其大尺度环流背景[J]. 大气科学, 2007,31(5):779-792 | | [2] | 陈文海, 柳艳香, 马柱国 . 中国1951—1997年气候变化趋势的季节特征[J]. 高原气象, 2002,21(3):251-257 | | [3] | 黄荣辉, 徐予红, 周连童 . 我国夏季降水的年代际变化及华北干旱化趋势[J]. 高原气象, 1999,18(4):465-475 | | [4] | 罗艳艳, 何金海, 邹燕 , 等. 华南前汛期雨涝强、弱年的确定及其环流特征对比[J]. 气象科学, 2015,35(2):160-166 | | [5] | 肖伟军, 陈炳洪, 刘云香 . 近45 a华南夏季降水时空演变特征[J]. 气象研究与应用, 2009,30(1):12-22 | | [6] | Roy S S, Balling R C . Trends in extreme daily precipitation indices in India[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2004,24(4):457-466 | | [7] | Zolina O, Simmer C, Gulev S K , et al. Changing structure of European precipitation: longer wet periods leading to more abundant rainfalls [J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37 (6): 460- 472. L06704. DOI: 10.1029/2010GL042468 | | [8] | 秦大河, 陈振林, 罗勇 , 等. 气候变化科学的最新认知[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007,3(2):63-73 | | [9] | 翟盘茂, 潘晓华 . 中国北方近50年温度和降水极端事件变化[J]. 地理学报, 2003,58(S1):1-10 | | [10] | 叶柏生, 李翀, 杨大庆 , 等. 我国过去50 a来降水变化趋势及其对水资源的影响(I): 年系列[J]. 冰川冻土, 2004,26(5):587-594 | | [11] | 吴志伟, 江志红, 何金海 . 近50年华南前汛期降水、江淮梅雨和华北雨季旱涝特征对比分析[J]. 大气科学, 2006,30(3):391-401 | | [12] | 张焱, 孙照渤, 白莹莹 , 等. 近47 a华南前汛期旱涝特征[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2008,31(2):176-182 | | [13] | 何编, 孙照渤 . “0806”华南持续性暴雨诊断分析与数值模拟[J]. 气象科学, 2010 ( 2):164-171 | | [14] | 张婷, 魏凤英 . 华南地区汛期极端降水的概率分布特征[J]. 气象学报, 2009,67(3):442-451 | | [15] | 闵屾, 钱永甫 . 我国近40年各类降水事件的变化趋势[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2008,47(3):105-110 | | [16] | 王颖, 施能, 顾俊强 , 等. 中国雨日的气候变化[J]. 大气科学, 2006,30(1):162-170 | | [17] | 王大钧, 陈列, 丁裕国 . 近40年来中国降水量、雨日变化趋势及与全球温度变化的关系[J]. 热带气象学报, 2006,22(3):283-289 | | [18] | 王小玲, 翟盘茂 . 1957—2004年中国不同强度级别降水的变化趋势特征[J]. 热带气象学报, 2008,24(5):459-466 | | [19] | Zhang L J, Qian Y F , Annual distribution features of precipitation in China and their annual variations[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2003,17(2):146-163 | | [20] | 杜银, 张耀存, 谢志清 , 等. 长江中下游梅汛期强降水过程非均匀特征[J]. 气象科学, 2007,27(2):133-139 | | [21] | 杨金虎, 王鹏祥, 白虎志 , 等. 中国西北降水年内非均匀性特征分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2007,3(5):276-281 | | [22] | 张天宇, 程炳岩, 王记芳 , 等. 华北雨季降水集中度和集中期的时空变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 2007,26(4):843-852 | | [23] | 张文, 张天宇, 刘剑 . 东北降水过程年集中度和集中期的时空变化特征[J]. 南京气象学院学报, 2008,31(3):403-410 | | [24] | 张运福, 胡春丽, 赵春雨 , 等. 东北地区降水年内分配的不均匀性[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2009,18(2):89-94 | | [25] | 杨玮, 何金海, 王盘兴 . 等. 近42年来青藏高原年内降水时空不均匀性特征分析[J]. 地理学报, 2011,66(30):376-384 | | [26] | 王睆, 陆尔, 赵玮 , 等. 一种新的反映我国降水季节内非均匀性特征的方法[J]. 热带气象学报, 2015,31(5):655-66 | | [27] | Li H, Zhai P M, Lu E , et al. Changes in temporal concentration property of summer precipitation in China during 1961-2010 based on a new index[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2017,31(2):336-349. DOI: 10.1007/s13351-017-6020-y | | [28] | 陆虹, 陈思蓉, 郭媛 , 等. 近50年华南地区极端强降水频次的时空变化特征. 热带气象学报, 2012,28(2):219-227 | | [29] | Wu H, Zhai P M, Chen Y . A comprehensive classification of anomalous circulation patterns responsible for persistent precipitation extremes in South China[J]. Journal of Meteorological Research, 2016,30(4):483-495 | | [30] | Shannon C E . A mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell System Technical Journal, 2014,27(3):379-423 | | [31] | Sen P K . Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1968,63(324):1379-1389 | | [32] | Zhai P M, Zhang X, Wan H , et al. Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005,18(7):1096-1108 | | [33] | 李丽平, 白婷 . 华南夏季多年平均降水低频特征及其与低频水汽输送关系[J]. 大气科学学报, 2014,37(3):323-332 |
|
 ),Er LU1,You-Shan JIANG3,Yun-Peng ZHANG4
),Er LU1,You-Shan JIANG3,Yun-Peng ZHANG4