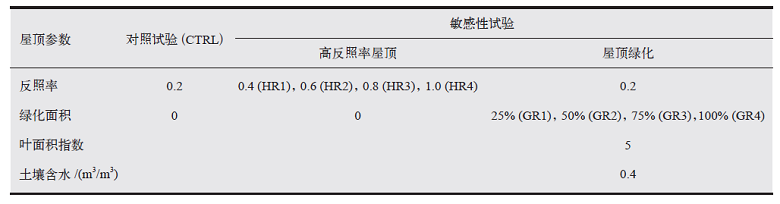
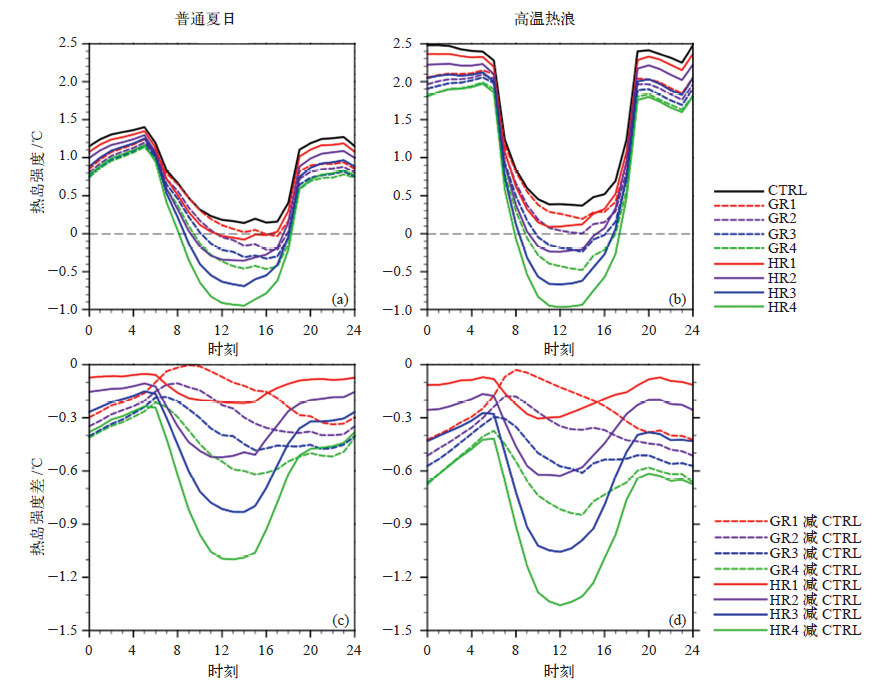
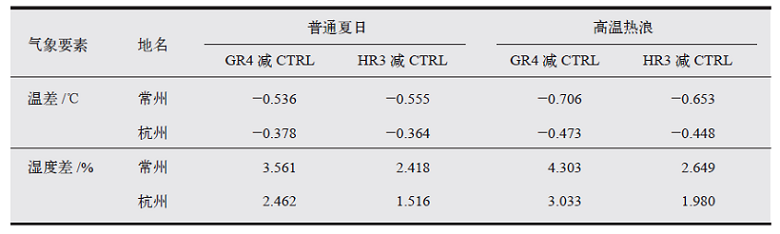
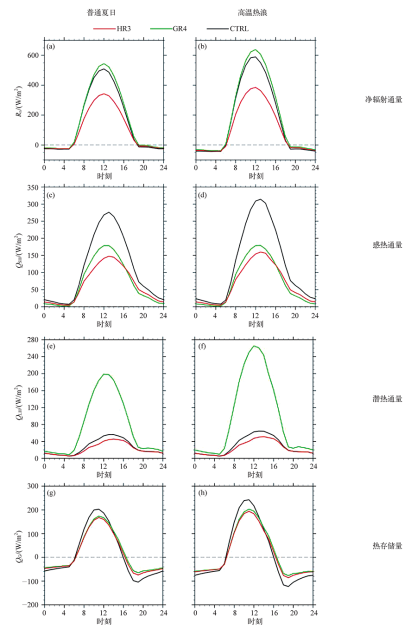
气候变化研究进展 ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (1): 45-57.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2020.163
• 巴黎协定目标下我国的减排路径和政策专栏 • 上一篇 下一篇
不同类型冷却屋顶方案对城市群热环境的缓解效果
张弥1( ), 马红云1(
), 马红云1( ), 林卉娇1, 李海俊2, 王莹1
), 林卉娇1, 李海俊2, 王莹1
- 1 南京信息工程大学气象灾害预报预警与评估协同创新中心/气象灾害教育部重点实验室/大气科学学院气候与应用前沿研究院(ICAR),南京 210044
2 江西省气象局,南昌 330000
-
收稿日期:2020-07-30修回日期:2020-09-30出版日期:2021-01-30发布日期:2021-02-04 -
通讯作者:马红云 -
作者简介:张弥,女,硕士研究生,2374078862@qq.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目“工业革命以来年代际气候变化的全球格局及归因”(2016YFA0600402)
Mitigation effect of different cool roof schemes on thermal environment of urban agglomeration
ZHANG Mi1( ), MA Hong-Yun1(
), MA Hong-Yun1( ), LIN Hui-Jiao1, LI Hai-Jun2, WANG Ying1
), LIN Hui-Jiao1, LI Hai-Jun2, WANG Ying1
- 1 Collaborative Innovation Center on Forecast and Evaluation of Meteorological Disasters (CIC-FEMD) / Key Laboratory of Meteorological Disaster, Ministry of Education (KLME) / Institute for Climate and Application Research (ICAR), Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangxi Meteorological Bureau, Nanchang 330000, China
-
Received:2020-07-30Revised:2020-09-30Online:2021-01-30Published:2021-02-04 -
Contact:MA Hong-Yun
摘要:
利用耦合单层城市冠层模型的中尺度数值模式WRF/UCM,选取8组不同反照率和绿化比例的屋顶冷却方案进行敏感性试验,模拟研究不同冷却屋顶方案对长三角城市群2013年夏季城市热环境的影响,并分析其影响机制。结果表明:不同冷却屋顶方案对城市群热环境的缓解效果与屋顶参数之间呈很强的线性关系。高温热浪天气下,HR4(反照率为1.0)和GR4(屋顶绿化率为100%)方案的制冷度日数分别降低了14.7%和10.9%,节约的能源比普通夏日更多。同时,高温热浪天气会增强热岛强度,高反照率屋顶方案在白天对热岛起到更有效的缓解,热浪天气下日平均热岛强度最大可降低1.36℃。相同方案下,在高温热浪天气下的缓解效果均胜于普通夏日,平均而言,高反照率屋顶和屋顶绿化的降温效果分别增大38.5%和34.9%,增湿效果分别增大29.5%和21.9%,这主要是由于在高温热浪天气下,高反照率屋顶方案能够减少更多的净辐射通量,屋顶绿化方案能够释放更多的潜热通量。此外,城市格点密集区域的降温效果优于分散的城市区域,处于城市群中的常州区域较单独的杭州区域的降温幅度平均高32%。
引用本文
张弥, 马红云, 林卉娇, 李海俊, 王莹. 不同类型冷却屋顶方案对城市群热环境的缓解效果[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2021, 17(1): 45-57.
ZHANG Mi, MA Hong-Yun, LIN Hui-Jiao, LI Hai-Jun, WANG Ying. Mitigation effect of different cool roof schemes on thermal environment of urban agglomeration[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(1): 45-57.
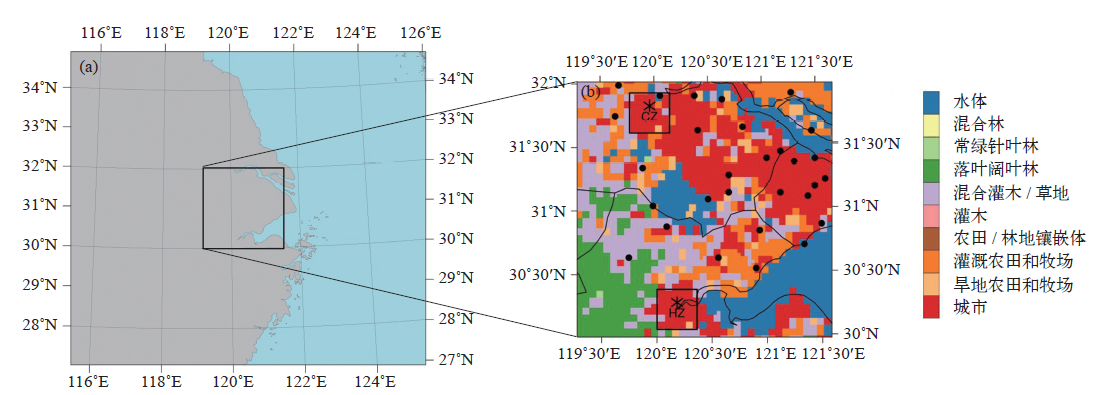
图1 WRF模拟的双重嵌套设置(a)和研究区域下垫面的土地覆盖类型(b) 注:黑色圆点代表30个观测站点的位置,CZ代表常州城区的位置,HZ代表杭州城区的位置。
Fig. 1 WRF simulation of double nested settings (a) and land cover type (b) of underlying surface in the study area (Black dots represent the locations of 30 observation stations, CZ represents the location of Changzhou city area, HZ represents the location of Hangzhou city area)
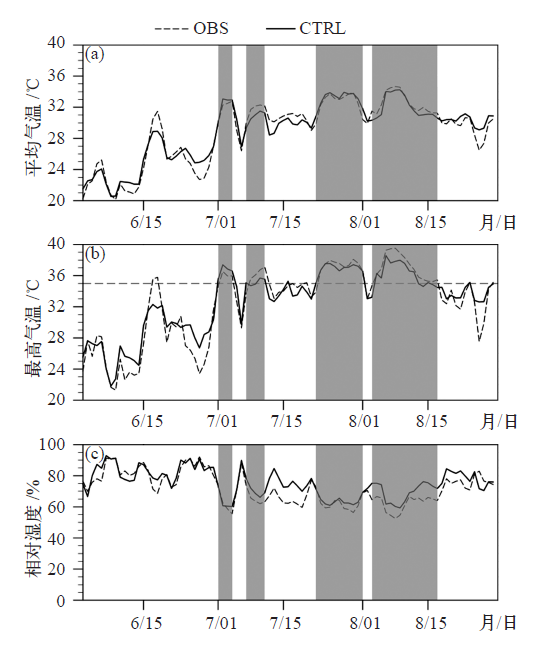
图2 对照试验2 m平均气温、最高气温和相对湿度的逐日模拟值(CTRL)与观测值(OBS)对比 注:阴影部分为选取的高温热浪时段。
Fig. 2 Comparison of simulated values (CTRL) with observed values (OBS), including daily mean temperature (a), maximum temperature (b), and relative humidity (c) (The shadow parts are the selected heat-wave periods)

图3 不同比例冷却屋顶的最低气温、平均气温、最高气温和相对湿度与对照试验的差值
Fig. 3 Difference between the minimum (a, b), mean (c, d), maximum (e, f) temperature and relative humidity (g, h) of different proportion cooling roof and the control test
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1535 |
| [2] |
秦大河, Thomas Stocker, 259名作者,等. IPCC第五次评估报告第一工作组报告的亮点结论[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2014.01.001 URL |
| Qin D H, Stocker T, 259 Authors, et al. Highlights of the IPCC Working Group I Fifth assessment report[J]. Climate Change Research, 2014, 10(1): 1-6 (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 翟盘茂, 余荣, 周佰铨, 等. 1.5℃增暖对全球和区域影响的研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(5): 465-472. |
| Zhai P M, Yu R, Zhou B Q, et al. Research progress in impact of 1.5℃ global warming on global and regional scales[J]. Climate Change Research, 2017, 13(5): 465-472 (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | UNFCCC. The Paris Agreement [EB/OL]. 2015 [2019-01-20]. http://unfccc.int/files/essential_background/convention/application/pdf/english_paris_agreement.pdf |
| [5] | 王田, 董亮, 高翔. 《巴黎协定》强化透明度体系的建立与实施展望[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2019, 15(6): 684-692. |
| Wang T, Dong L, Gao X. Establishment and implementation prospects of the enhanced transparency system under the Paris Agreement[J]. Climate Change Research, 2019, 15(6): 684-692 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | Zhong W Y, Jun W, Jiang J X, et al. Review of recent studies of the climatic effects of urbanization in China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2016 (3): 154-168 |
| [7] |
Tao S, Yong H, Hong W, et al. Influence of urbanization on the thermal environment of meteorological station: satellite-observed evidence[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2015, 6(1): 7-15
doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2015.07.001 URL |
| [8] |
寿亦萱, 张大林. 城市热岛效应的研究进展与展望[J]. 气象学报, 2012, 70(3): 338-353.
doi: 10.11676/qxxb2012.031 URL |
| Shou Y X, Zhang D L. Research progress and prospect of urban heat island effect[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2012, 70(3): 338-353 (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
Zhang N, Gao Z, Wang X, et al. Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China[J]. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 2010, 102(3-4): 331-342
doi: 10.1007/s00704-010-0263-1 URL |
| [10] |
Kovats R S, Hajat S. Heat stress and public health: a critical review[J]. Annual Review of Public Health, 2008, 29(1): 41-55
doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090843 URL |
| [11] |
Hou A, Ni G, Yang H, et al. Numerical analysis on the contribution of urbanization to wind stilling: an example over the greater Beijing metropolitan area[J]. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, 2013, 52(5): 1105-1115
doi: 10.1175/JAMC-D-12-013.1 URL |
| [12] | 徐洪, 杨世莉. 城市热岛效应与生态系统的关系及减缓措施[J]. 北京师范大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 54(6): 790-798. |
| Xu H, Yang S L. Relationship between urban heat island effect and ecosystem and mitigation measures[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 54(6): 790-798 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 朱正伟, 王猛. 城市热岛效应的危害及对策[J]. 污染防治技术, 2009 (2): 94-96. |
| Zhu Z W, Wang M. Harm and countermeasures of urban heat island effect[J]. Pollution Control Technology, 2009 (2): 94-96 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] |
Amir B, Sailor D J, Crank P J, et al. Direct and indirect effects of high-albedo roofs on energy consumption and thermal comfort of residential buildings[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2018. DOI: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.08.048
doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2004.06.019 URL pmid: 32288121 |
| [15] | Memon R A, Leung D Y C, Chunho L. A review on the generation, determination and mitigation of urban heat island[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2008 (1): 122-130 |
| [16] |
Courts A M, Daly E, Beringer J, et al. Assessing practical measures to reduce urban heat: green and cool roofs[J]. Building and Environment, 2013, 70: 266-276
doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2013.08.021 URL |
| [17] | 王恪非. 城市对重庆高温热浪的贡献及冷却屋顶的缓解效应模拟研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2018. |
| Wang K F. Simulation study on contribution of city to high temperature heat wave and mitigation effect of cooling roof in Chongqing[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Akbari H, Rose L S. Urban surfaces and heat island mitigation potentials[J]. Journal of the Human-Environment System, 2010, 11(2): 85-101
doi: 10.1618/jhes.11.85 URL |
| [19] |
Campra P, Garcia M, Canton Y, et al. Surface temperature cooling trends and negative radiative forcing due to land use change toward greenhouse farming in southeastern Spain[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2008, 113(18): D18109
doi: 10.1029/2008JD009912 URL |
| [20] | Francis L F M, Jensen M B. Benefits of green roofs: a systematic review of the evidence for three ecosystem services[J]. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2017, S1618866717302479 |
| [21] |
Santamouris M. Cooling the cities: a review of reflective and green roof mitigation technologies to fight heat island and improve comfort in urban environments[J]. Solar Energy, 2014, 103: 682-703
doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2012.07.003 URL |
| [22] | 周晓宇, 王咏薇, 孙绩华, 等. 冷却屋顶对北京城市热环境影响的模拟研究[J]. 气象学报, 2019, 77(1): 131-143. |
| Zhou X Y, Wang Y W, Sun J H, et al. Simulation study on the influence of cooling roof on urban thermal environment in Beijing[J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica, 2019, 77(1): 131-143 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 郭良辰, 王咏薇, 张艳晴. 冷却屋顶对南京夏季高温天气的缓解作用[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2018, 18(21): 16-23. |
| Guo L C, Wang Y W, Zhang Y Q. Mitigation effect of cooling roof on summer high temperature weather in Nanjing[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2018, 18(21): 16-23 (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | Millstein D, Menon S. Regional climate response to surface albedo changes from cool (reflective) roofs and desert based solar electricity generation[C]// AGU Fall Meeting. AGU: Fall Meeting Abstracts, 2010 |
| [25] |
Li D, Zeideb Oppenheimer M. The effectiveness of cool and green roofs as urban heat island mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2014, 9: 055002
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/9/5/055002 URL |
| [26] | Liu X J, Tian G J, Feng J M, , et al. Assessing summertime urban warming. Assessing summertime urban warming and the cooling efficacy of adaptation strategy in the Chengdu-Chongqing metropolitan region of China [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 610-611(S): 1092-1102 |
| [27] |
Sun T, Grimmond C S B, Guang-Heng N. How do green roofs mitigate urban thermal stress under heat waves?[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2016, 121(10): 5320-5335
doi: 10.1002/2016JD024873 URL |
| [28] | Sharma A, Conry P, Fernando H J S, et al. Green and cool roofs to mitigate urban heat island effects in the Chicago metropolitan area: evaluation with a regional climate model[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2016, 11(6): 064004 |
| [29] |
Li J X, Song C H, Cao L, et al. Impacts of landscape structure on surface urban heat islands: a case study of Shanghai, China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(12): 3249-3263
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2011.07.008 URL |
| [30] | Takebayashi H, Moriyama M. Surface heat budget on green roof and high reflection roof for mitigation of urban heat island[J]. Building & Environment, 2007, 42(8): 2971-2979 |
| [31] |
Santamouris M, Gaitani N, Spanou A, et al. Using cool paving materials to improve microclimate of urban areas-design realization and results of the Flisvos project[J]. Building and Environment, 2012, 53: 128-136
doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.01.022 URL |
| [32] |
Cao M, Rosado P, Lin Z, et al. Cool roofs in Guangzhou, China: outdoor air temperature reductions during heat waves and typical summer conditions[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(24): 14672-14679
doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b04886 URL pmid: 26523605 |
| [33] |
程志刚, 杨欣悦, 孙晨, 等. 成都地区夏季城市热岛变化及其与城市发展的关系[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(4): 322-331.
doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2015.176 URL |
| Cheng Z G, Yang X Y, Sun C, et al. The trend of summer urban heat island effect and its relationship with urban development in Chengdu[J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(4): 322-331 (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | Yang Y, Xiao P, Feng X, et al. Accuracy assessment of seven global land cover datasets over China[J]. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 2017, 125: 156-173 |
| [35] | 李海俊, 马红云, 林益同, 等. 长三角城市群非均匀性对区域热岛效应影响的数值模拟[J]. 气象科学, 2019, 39(2): 194-205. |
| Li H J, Ma H Y, Lin Y T, et al. Numerical simulation of the influence of urban agglomeration heterogeneity on regional heat island effect in Yangtze River Delta[J]. Meteorological Science, 2019, 39(2): 194-205 (in Chinese) | |
| [36] | Lazzarin R M, Castellotti F, Busato F. Experimental measurements and numerical modelling of a green roof[J]. Energy & Buildings, 2005, 37(12): 1260-1267 |
| [37] |
Yang J C, Wang Z H, Chen F, et al. Enhancing hydrologic modelling in the coupled weather research and forecasting: urban modelling system[J]. Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 2015, 155(2): 369-369
doi: 10.1007/s10546-015-0020-1 URL |
| [38] |
Sun R, Chen A, Chen L, et al. Cooling effects of wetlands in an urban region: the case of Beijing[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2012, 20: 57-64
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2012.02.006 URL |
| [39] | Zhang M, Cheng C H, Ma H Y. Projection of residential and commercial electricity consumption under SSPs in Jiangsu province, China[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2020. DOI: 10.1016/j.accre.2020.06.005 |
| [40] |
Kuramochi T, Hoehne N, Schaeffer M, et al. Ten key short-term sectoral benchmarks to limit warming to 1.5℃[J]. Climate Policy, 2018, 18(1-5): 287-305
doi: 10.1080/14693062.2017.1397495 URL |
| [1] | 张领雁,张朝,侯斌. 高温热浪致死风险的人群和城市分异及保险费率厘定的研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2018, 14(5): 475-484. |
| [2] | 王怡, 刘冠秋, 齐熙, 潘丹琳, 祁新华. 高温热浪支付意愿人群分异及其影响因素——以福州市为例[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2017, 13(2): 172-180. |
| [3] | 罗晓玲, 杜尧东, 郑璟. 广东高温热浪致人体健康风险区划[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2016, 12(2): 139-146. |
| [4] | 叶殿秀 尹继福 陈正洪 郑有飞 吴荣军. 1961—2010年我国夏季高温热浪的时空变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2013, 9(1): 15-20. |
| [5] | 陈业国 农孟松. 2003-2006年南宁市热岛强度变化特征[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2009, 05(01): 35-38. |
| [6] | 丁淑娟;张继权;刘兴朋;董芳蕾. 哈尔滨市城市发展与热岛效应的定量研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(004): 230-234. |
| [7] | 李明华;龚斐;黄健;杨柳;肖炳坤. 1961-2004年惠州城市与乡村气温变化的对比[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(004): 235-239. |
| [8] | 郑艳 潘家华 吴向阳. 影响北京城市增温的主要社会经济因子分析[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2006, 02(04): 188-192. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||