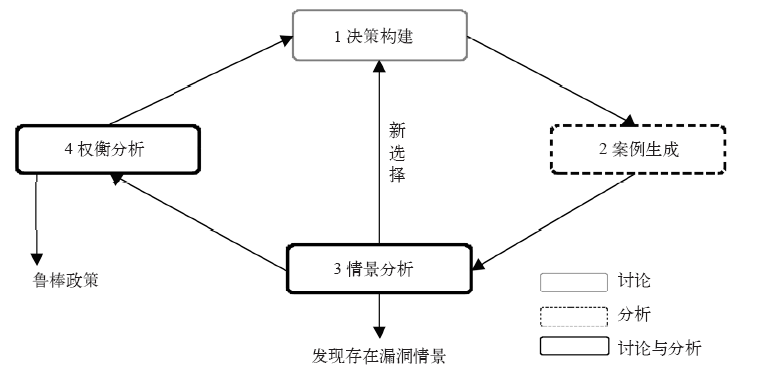
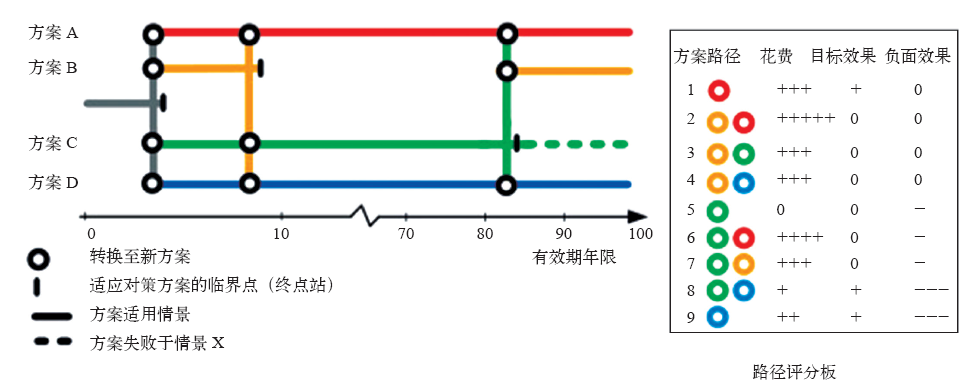
| [1] | 张建云. 气候变化对水的影响研究及科学问题[J]. 中国水利, 2008 (2): 14-18 | | [2] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 | | [3] | 丁一汇, 孙颖. 国际气候变化研究新进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2006, 2(4): 161-167 | | [4] | 程晓陶, 王静, 夏军, 等. 气候变化对淮河防洪与排涝管理项目的影响及适应对策研究[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2008, 4(6): 324-329 | | [5] | Hine D, Hall J W.Information gap analysis of flood model uncertainties and regional frequency analysis[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(19), W01514 | | [6] | Walker W E, Marchau V A W J, Swanson D. Addressing deep uncertainty using adaptive policies: introduction to section 2[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2010, 77(6): 917-923 | | [7] | Bryant B P, Lempert R J.Thinking inside the box: a participatory, computer-assisted approach to scenario discovery[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2010, 77(1): 34-49 | | [8] | Lempert R J, Popper S W, Bankes S C.Shaping the next one hundred years: new methods for quantitative, long-term policy analysis[M]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, MR-1626-RPC, 2003 | | [9] | 胡笑旋, 陈意. 深度不确定环境下的决策分析方法: 研究现状与展望[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(3): 385-394 | | [10] | Popper S W, Lempert R J, Bankes S C.Shaping the future [N]. Scientific American, 2005: 66-71 | | [11] | Dessai S, van der Sluijs J P. Uncertainty and climate change adaptation: a scoping study[M]. Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development and Innovation, Utrecht, 2007 | | [12] | Wilby R L, Keenan R.Adapting to flood risk under climate change[J]. Progress in Physical Geography, 2012: 1-31 | | [13] | Kwakkel J H, Walker W E, Marchau V A.From predictive modeling to exploratory modeling: how to use non-predictive models for decision making under deep uncertainty[C]. Proc of the 25th Mini-EURO Conf on Uncertainty and Robustness in Planning and Decision Making, Portugal, 2010: 1-10 | | [14] | Albrechts L.Strategic (spatial) planning reexamined[J]. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 2008, 31(5): 743-758 | | [15] | Groves D G, Lempert R J.A new analytic method for finding policy-relevant scenarios[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2007, 17(1): 73-85 | | [16] | Regan H M, Ben-Haim Y, Langford B, et al. Robust decision-making under severe uncertainty for conservation management[J]. Ecological Applications, 2005, 15(4): 1471-1477 | | [17] | Dewar J A, Builder C H, Hix W M, et al. Assumption-based planning: a planning tool for very uncertain times[J]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 1993 | | [18] | Lempert R J, Popper S W, Groves D G, et al. Making good decisions without predictions robust decision making for planning under deep uncertainty[J]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2013 | | [19] | 胡恒智, 温家洪. 社区自然灾害风险分析进展综述[C]. 法国: Atlantis出版社, 2011, 308-315 | | [20] | ISO. ISO guide 31000-2009, risk management: principles and guidelines[S]. ISO, 2009 | | [21] | 温家洪, 黄蕙, 陈珂, 等. 基于社区的台风灾害概率风险评估: 以上海市杨浦区富禄里居委地区为例[J]. 地理科学, 2012, 3(23): 348-355 | | [22] | 尹占娥, 许世远, 殷杰, 等. 基于小尺度的城市暴雨内涝灾害情景模拟与风险评估[J]. 地理学报, 2010, 65(5): 553-561 | | [23] | 刘敏, 权瑞松, 许世远, 等. 城市暴雨内涝灾害风险评估: 理论、方法与实践[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 27-28 | | [24] | Lempert R J, Myles T C.Managing the risk of uncertain threshold responses: comparison of robust, optimum, and precautionary approaches[J]. Risk Analysis, 2007, 27(4): 1009-1026 | | [25] | Lempert R J, McKay S. Some thoughts on the role of robust control theory in climate-related decision support[J]. Climatic Change. 2011 (107): 241-246 | | [26] | IISD. Designing policies in a world of uncertainty, change and surprise: adaptive policy-making for agriculture and water resources in the face of climate change: phase I research report[M]. International Institute for Sustainable Development, Winnipeg, 2006 | | [27] | Hallegatte S.Strategies to adapt to an uncertain climate change[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19: 240-247 | | [28] | Gersonius B, Ashley R, Pathirana A, et al. Climate change uncertainty: building flexibility into water and flood risk infrastructure[J]. Climatic Change, 2013, 116: 411-423 | | [29] | van der Brugge R, Rotmans J, Loorbach D. The transition in Dutch water management[J]. Regional Environmental Change, 2005, 5: 164-176 | | [30] | Haasnoot M, Middelkoop H, Offermans A, et al. Exploring pathways for sustainable water management in river deltas in a changing environment[J]. Climatic Change, 2013, 115: 795-819 | | [31] | Lempert R J, Groves D G.Identifying and evaluating robust adaptive policy responses to climate change for water management agencies in the American west[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2010, 77: 960-974 | | [32] | Groves D G, Lempert R J, Knopman D, et al. Preparing for an uncertain future climate in the inland empire: identifying robust water management strategies[J]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2008 | | [33] | Lempert R J.A new decision sciences for complex systems[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2002, 99(3): 7309-7313 | | [34] | Minville M, Brissette F, Leconte R.Uncertainty of the impact of climate change on the hydrology of a nordic watershed[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2008, 358(1): 70-83 | | [35] | Johnson D R, Fischbach J R, et al. Estimating surge-based flood risk with the coastal Louisiana risk assessment model[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2013 (67): 109-126 | | [36] | Fischbach J R, Groves D, Johnson D. Managing New Orleans flood risk in an uncertain future using non-structural risk mitigation [D]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, RGSD-262, 2010 | | [37] | Groves D G, Fischbach J R, Bloom Evan, et al.Adapting to a changing Colorado River: making future water deliveries more reliable through robust management strategies[J]. American Geophysical Union, 2013 | | [38] | Popper S W, Berrebi C, Griffin J, et al. Natural gas and Israel’s energy future: near-term decisions from a strategic perspective[J]. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 2009 | | [39] | Groves D G., Lempert R J.A new analytic method for finding policy-relevant scenarios[J]. Global Environ Change: Human Policy Dimensions, 2007, 17(1): 73-85 | | [40] | Lempert R J, Nidhi K.Managing climate risks in developing countries with robust decision making[M]. Washington DC: World Resources Institute, 2011 | | [41] | Ben-Haim Y.Robust reliability in the mechanical sciences[J]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1996 | | [42] | 刘艳丽, 张建云, 王国庆, 等. 环境变化对流域水文水资源的影响评估及不确定性研究进展[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2015, 11(2): 102-110 | | [43] | Moilanen A, Wintle B A.Uncertainty analysis favours selection of spatially aggregated reserve networks[J]. Biological Conservation, 2006, 129(3): 427-434 | | [44] | Duncan S J.Including severe uncertainty into environmentally benign life cycle design using information gap-decision theory [D]. Atlanta: School of Mechanical Engineering,Georgia Institute of Technology, 2008 | | [45] | Hall J W, Harvey H.Decision making under severe uncertainties for flood risk management: a case study of info-gap robustness analysis [R]. Hydro informatics Conference, Concepcion, Chili, 2009. | | [46] | Ben Haim Y.Info-gap decision theory: decisions under severe uncertainty, 2nd edition [M]. London: Academic Press, 2006. | | [47] | Hallegatte S.Strategies to adapt to an uncertain climate change[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19(2): 240-247 | | [48] | Sutton and East Surrey Water. Revised water resources management plan [R/OL]. 2014 [2017-09-01]. | | [49] | Kwadijk J C, Haasnoot M, Mulder J P, et al. Using adaptation tipping points to prepare for climate change and sea level rise: a case study in the Netherlands[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Climate Change, 2010, 1(5): 729-740 | | [50] | Walker W E, Haasnoot M, Kwakkel J H.Adapt or perish: a review of planning approaches for adaptation under deep uncertainty[J]. Sustainability, 2013, 5: 955-979 | | [51] | Haasnoot M, Kwakkel J H, Walker W E, et al. Dynamic adaptive policy pathways: a method for crafting robust decisions for a deeply uncertain world[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2013, 23(2): 485-498 | | [52] | Matrosov E, Woods A, Harou J.Robust decision makingand info-gap decision theory for water resource system planning[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 494(7): 43-58 | | [53] | Hall J W, Lempert R J, Keller K, et al. Robust climate policies under uncertainty: a comparison of robust decision making and info-gap methods[J]. Risk Analysis an Official Publication of the Society for Risk Analysis, 2012, 32(10): 1657-1672 | | [54] | Tariq A, Lempert R J, Riverson J, et al. A climate stress test of Los Angeles’ water quality plans[J]. Climatic Change, 2017, 144(2): 625-639 | | [55] | Yan D, Ludwig F, Huang H Q, ,et al. Many-objective robust decision making for water allocation under climate change [J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017: 607-608, 294-303 | | [56] | 王栋, 潘少明, 吴吉春, 等. 洪水风险分析的研究进展与展望[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2006, 15(1): 103-109 | | [57] | Xie J Q, Chen H, Liao Z L, et al. An integrated assessment of urban flooding mitigation strategies for robust decision making[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2017, 95: 143-155 |
|
 ), Ting-Ting GU3, Zhan TIAN1(
), Ting-Ting GU3, Zhan TIAN1( )
)