气候变化研究进展 ›› 2024, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (4): 440-453.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2024.067
数字经济赋能“双碳”战略研究——影响机理及实现路径
- 1 中国社会科学院大学应用经济学院,北京 102488
2 中国社会科学院生态文明研究所,北京 100710
3 中国社会科学院可持续发展研究中心,北京 100732
-
收稿日期:2024-04-17修回日期:2024-06-09出版日期:2024-07-30发布日期:2024-07-19 -
通讯作者:王谋 -
作者简介:刘莉雯,女,硕士研究生,liuliwen7577@163.com -
基金资助:国家社会科学基金重大项目“碳中和新形势下我国参与国际气候治理总体战略和阶段性策略研究”(22ZDA111)
Digital economy empowers “Dual Carbon” goals: influence mechanism and implementation path
- 1 Faculty of Applied Economics, University of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 102488, China
2 Research Institute for Eco-Civilization, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 100710, China
3 Research Center for Sustainable Development, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing 100732, China
-
Received:2024-04-17Revised:2024-06-09Online:2024-07-30Published:2024-07-19 -
Contact:WANG Mou
摘要:
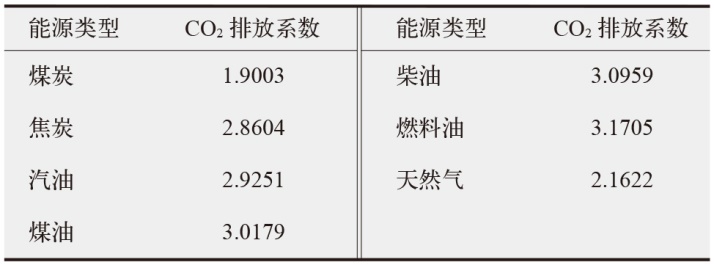
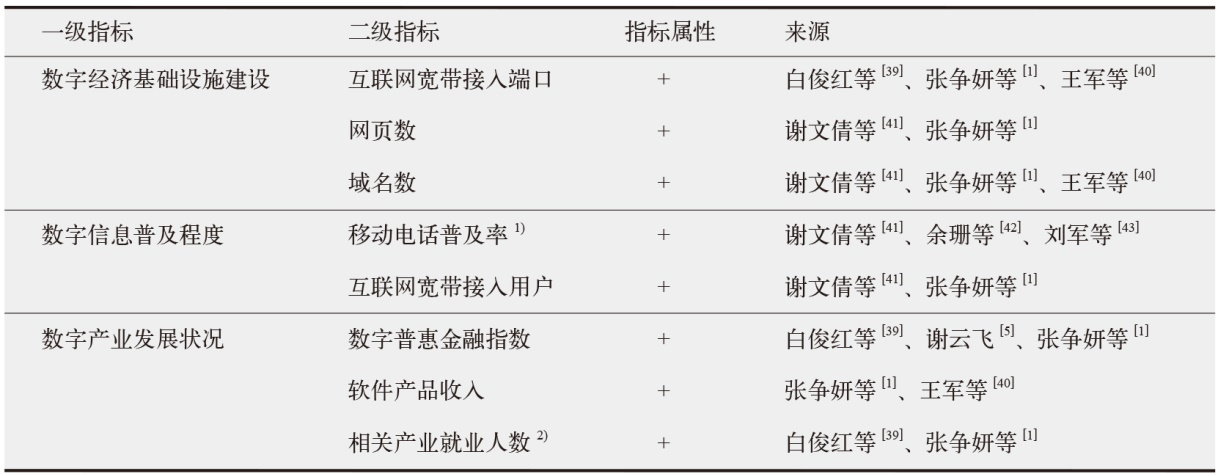
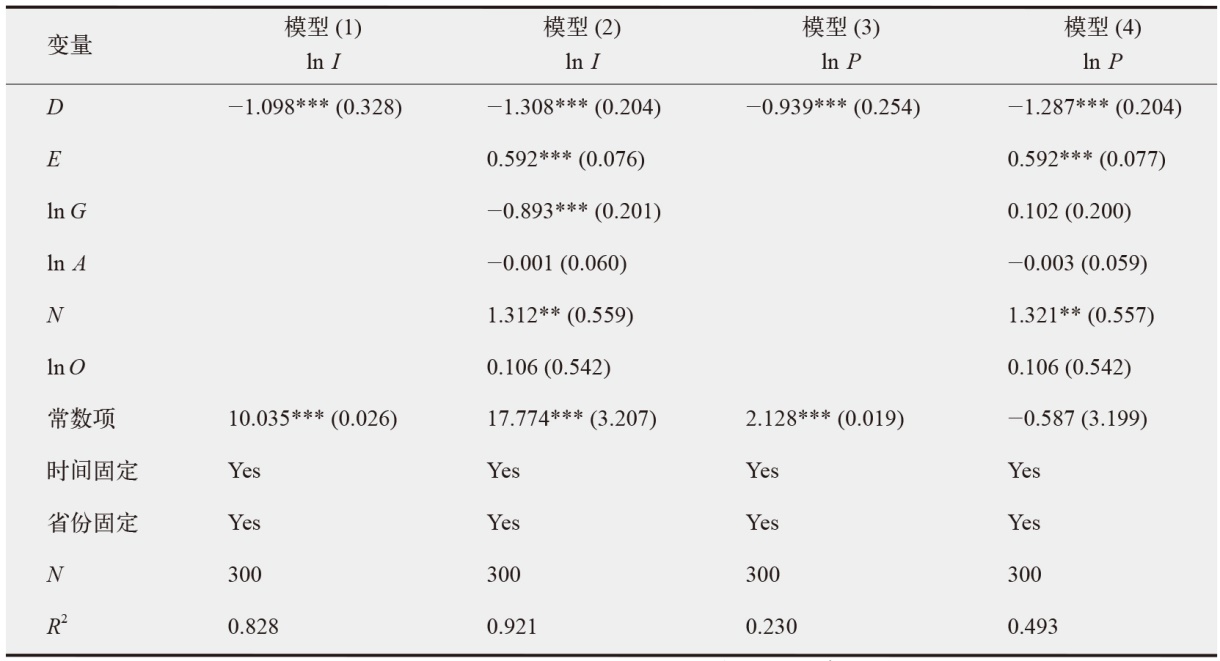
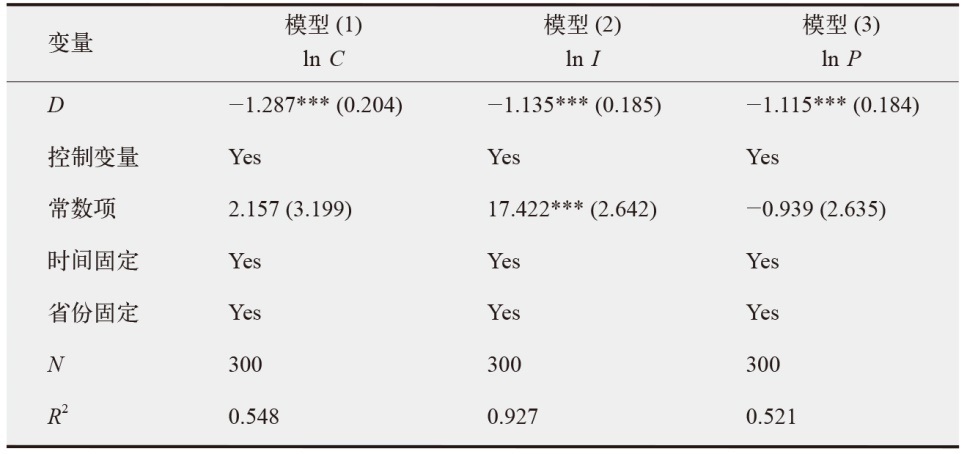
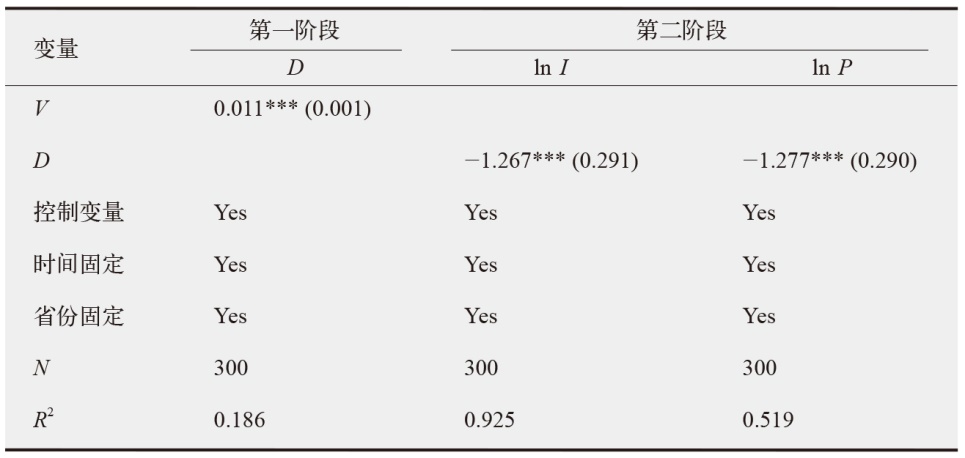
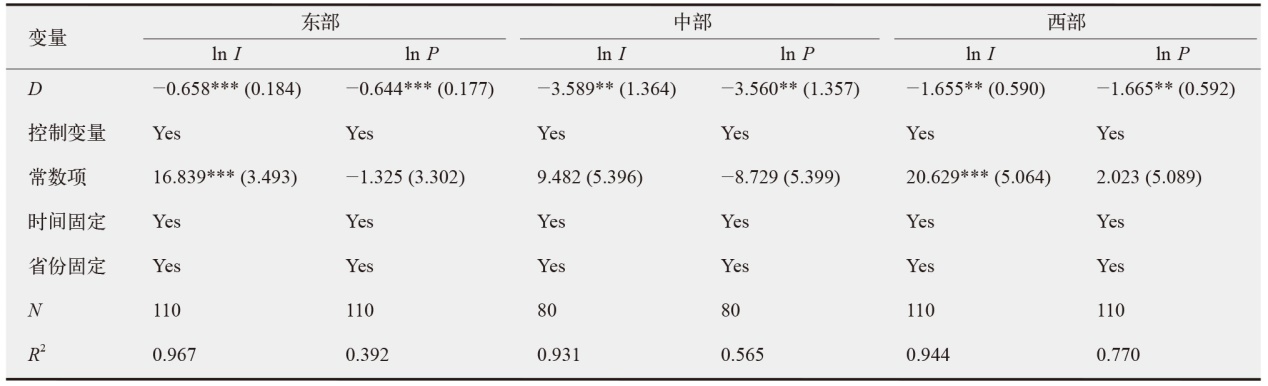
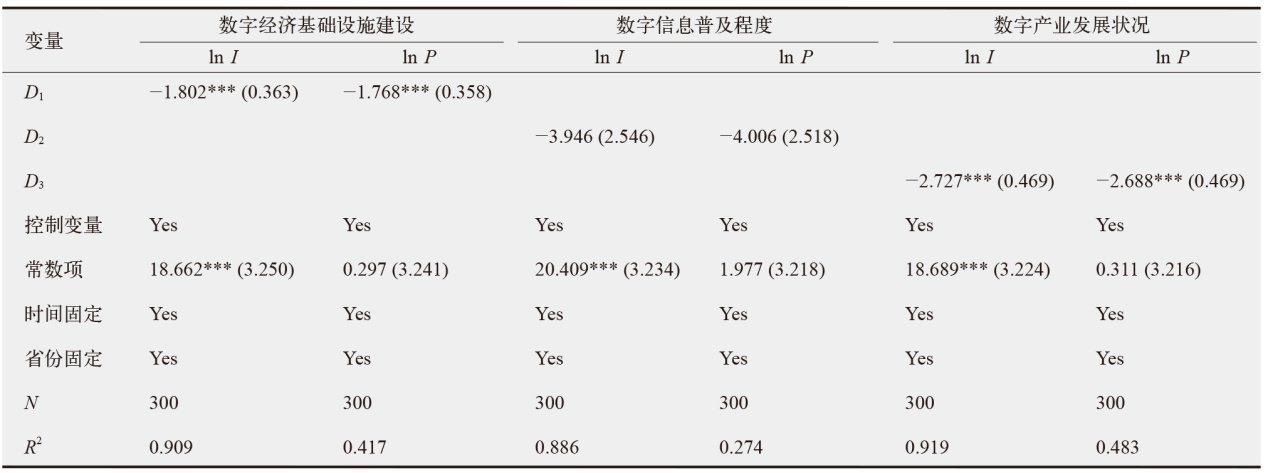
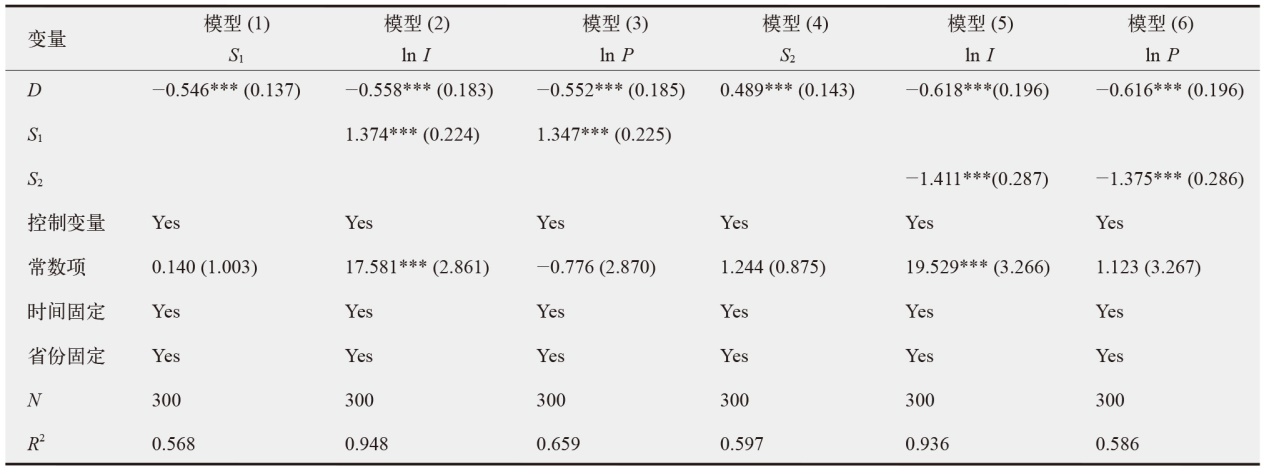
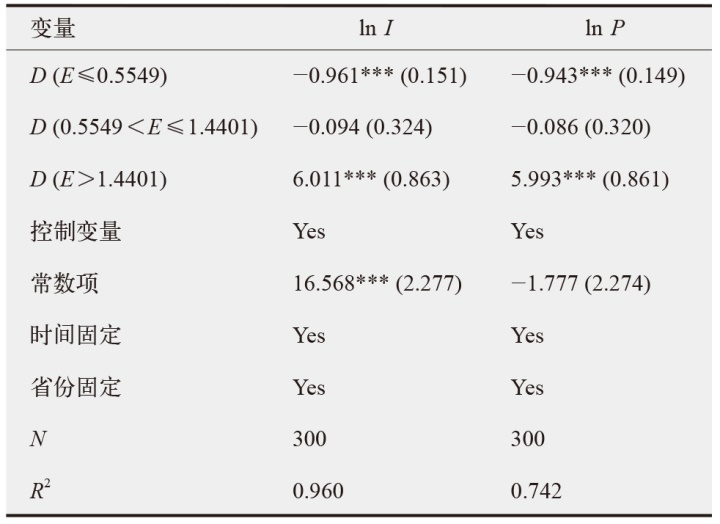
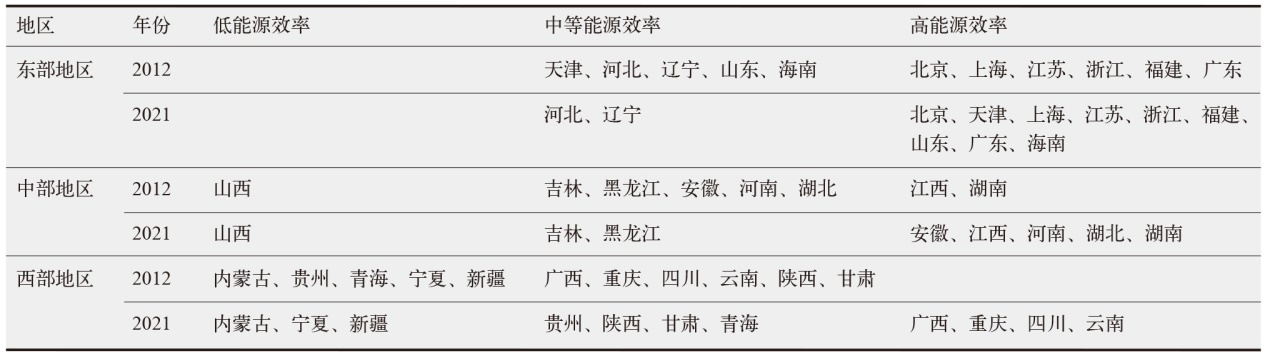
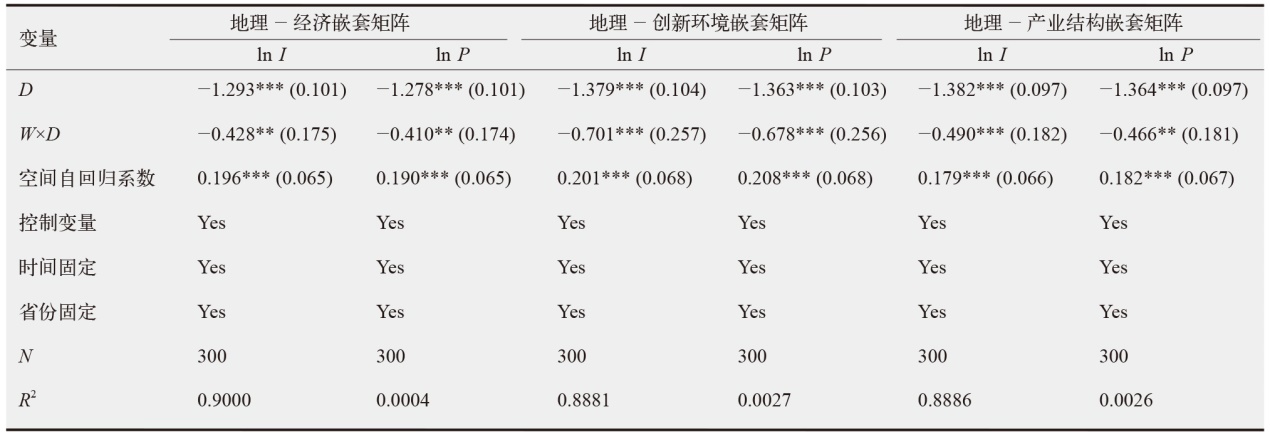
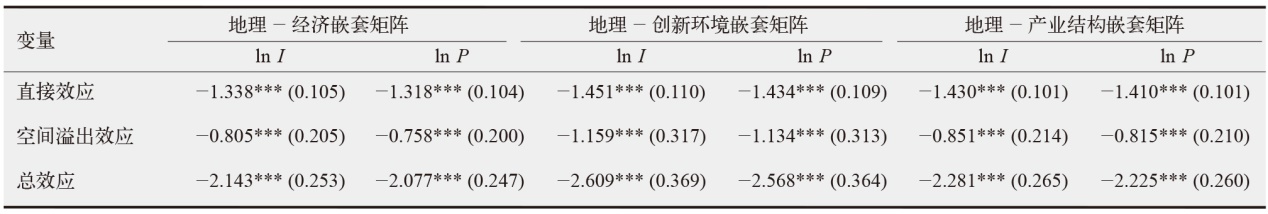
数字经济已成为支撑当前和未来经济发展的重要动力,在“双碳”目标下,探讨数字经济发展能否助力减排对当前经济高质量发展以及生态文明建设都具有重要价值。为验证数字经济与碳排放之间复杂的影响路径,文中采用双向固定效应模型、中介效应模型、门槛效应模型及空间杜宾模型进行实证分析。结果发现:数字经济可以显著抑制碳排放强度和人均碳排放;数字经济可以帮助调整能源结构进而显著减少碳排放;随着能源效率的提高,数字经济与碳排放之间的关系呈现倒“U”型特征;在3种空间距离权重矩阵下,数字经济对碳排放的作用效果展现出空间溢出特征。研究结论为进一步推动数字经济发展、实现“双碳”目标提供了有价值的决策参考。
引用本文
刘莉雯, 王谋. 数字经济赋能“双碳”战略研究——影响机理及实现路径[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2024, 20(4): 440-453.
LIU Li-Wen, WANG Mou. Digital economy empowers “Dual Carbon” goals: influence mechanism and implementation path[J]. Climate Change Research, 2024, 20(4): 440-453.
| [1] | 张争妍, 李豫新. 数字经济对我国碳排放的影响研究[J]. 财经理论与实践, 2022, 43 (5): 146-154. |
| Zhang Z Y, Li Y X. Research on the impact of digital economy on carbon emissions in China[J]. The Theory and Practice of Finance and Economics, 2022, 43 (5): 146-154 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | Gonel F, Akinci A. How does ICT-use improve the environment? The case of Turkey[J]. World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, 2018, 15 (1): 2-12 |
| [3] | Salahuddin M, Alam K, Ozturk I. The effects of internet usage and economic growth on CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a panel investigation[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 62: 1226-1235 |
| [4] | Shahnazi R, Dehghan S Z. The effects of spatial spillover information and communications technology on carbon dioxide emissions in Iran[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26: 24198-24212 |
| [5] | 谢云飞. 数字经济对区域碳排放强度的影响效应及作用机制[J]. 当代经济管理, 2022, 44 (2): 68-78. |
| Xie Y F. The effect and mechanism of digital economy on regional carbon emission intensity[J]. Contemporary Economic Management, 2022, 44 (2): 68-78 (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 张修凡, 范德成. 数字经济发展赋能我国低碳经济转型研究: 基于国家级大数据综合试验区的分析[J]. 科技进步与对策, 2023, 40 (19): 118-128. |
| Zhang X F, Fan D C. The development of digital economy empowering China’s low carbon economy transformation: an analysis of national big data comprehensive pilot zones[J]. Science & Technology Progress and Policy, 2023, 40 (19): 118-128 (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | Zhang L, Mu R, Zhan Y, et al. Digital economy, energy efficiency, and carbon emissions: evidence from provincial panel data in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 852: 158403 |
| [8] | Hao X, Wen S, Li Y, et al. Can the digital economy development curb carbon emissions? Evidence from China[J]. Frontiers in Psychology, 2022, 13: 938918 |
| [9] |
徐维祥, 周建平, 刘程军. 数字经济发展对城市碳排放影响的空间效应[J]. 地理研究, 2022, 41 (1): 111-129.
doi: 10.11821/dlyj020210459 |
| Xu W X, Zhou J P, Liu C J. The impact of digital economy on urban carbon emissions: based on the analysis of spatial effects[J]. Geographical Research, 2022, 41 (1): 111-129 (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | Yang G, Wang F, Deng F, et al. Impact of digital transformation on enterprise carbon intensity: the moderating role of digital information resources[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2023, 20 (3): 2178 |
| [11] | Pouri M J, Hilty L M. ICT-enabled sharing economy and environmental sustainability: a resource-oriented approach[C]// Advances and new trends in environmental informatics: managing disruption, big data and open science. Springer International Publishing, 2018: 53-65 |
| [12] | Hilty L M, Aebischer B. ICT for sustainability: an emerging research field[J]. ICT Innovations for Sustainability, 2015: 3-36 |
| [13] | 陈晓东, 杨晓霞. 数字经济发展对产业结构升级的影响: 基于灰关联熵与耗散结构理论的研究[J]. 改革, 2021, 325 (3): 26-39. |
| Chen X D, Yang X X. The impact of digital economic development on the upgrading of industrial structure: based on the research of grey relational entropy and dissipative structure theory[J]. Reform, 2021, 325 (3): 26-39 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | Lyu Y, Ji Z, Liang H, et al. Has information infrastructure reduced carbon emissions? Evidence from panel data analysis of Chinese cities[J]. Buildings, 2022, 12 (5): 619 |
| [15] | He J K. China’s INDC and non-fossil energy development[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2015, 6 (3-4): 210-215 |
| [16] | Jiao J, Song J, Ding T. The impact of synergistic development of renewable energy and digital economy on energy intensity: evidence from 33 countries[J]. Energy, 2024, 295: 130997 |
| [17] | Lee C C, Fang Y, Quan S, et al. Leveraging the power of artificial intelligence toward the energy transition: the key role of the digital economy[J]. Energy Economics, 2024: 107654 |
| [18] | Thanh T T, Ha L T, Dung H P, et al. Impacts of digitalization on energy security: evidence from European countries[J]. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 2023, 25 (10): 11599-11644 |
| [19] | Shahbaz M, Wang J, Dong K, et al. The impact of digital economy on energy transition across the globe: the mediating role of government governance[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 166: 112620 |
| [20] | Bhatt J G, Jani O K. E-governance for smart cities[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2015: 177-230 |
| [21] | Miskiewicz R. Clean and affordable energy within sustainable development goals: the role of governance digitalization[J]. Energies, 2022, 15 (24): 9571 |
| [22] | 曾鸣, 杨雍琦, 刘敦楠, 等. 能源互联网“源-网-荷-储”协调优化运营模式及关键技术[J]. 电网技术, 2016, 40 (1): 114-124. |
| Zeng M, Yang Y Q, Liu D N, et al. “Generation-Grid-Load-Storage” coordinative optimal operation mode of energy internet and key technologies[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40 (1): 114-124 (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | Takase K, Murota Y. The impact of IT investment on energy: Japan and US comparison in 2010[J]. Energy Policy, 2004, 32 (11): 1291-1301 |
| [24] | Lange S, Pohl J, Santarius T. Digitalization and energy consumption. Does ICT reduce energy demand?[J]. Ecological Economics, 2020, 176: 106760 |
| [25] | Allan G, Gilmartin M, McGregor P, et al. Economics of energy efficiency[M]// International Handbook on the Economics of Energy. UK: Edward Elgar Publishing, 2009 |
| [26] | Zheng R, Wu G, Cheng Y, et al. How does digitalization drive carbon emissions? The inverted U-shaped effect in China[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 2023, 102: 107203 |
| [27] | Stern D I. The role of energy in economic growth[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2011, 1219 (1): 26-51 |
| [28] | Nel W P, Cooper C J. Implications of fossil fuel constraints on economic growth and global warming[J]. Energy Policy, 2009, 37 (1): 166-180 |
| [29] | 史丹. 我国经济增长过程中能源利用效率的改进[J]. 经济研究, 2002 (9): 49-56, 94. |
| Shi D. The improvement of energy consumption efficiency in China’s economic growth[J]. Economic Research Journal, 2002 (9): 49-56, 94 | |
| [30] | 陈堂, 陈光. 数字化转型对产业融合发展的空间效应: 基于省域空间面板数据[J]. 科技管理研究, 2021, 41 (4): 124-132. |
| Chen T, Chen G. Spatial effect of digital transformation innovation on industrial convergence: based on interprovincial spatial panel data[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2021, 41 (4): 124-132 (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | Luo S, Yimamu N, Li Y, et al. Digitalization and sustainable development: how could digital economy development improve green innovation in China?[J]. Business Strategy and the Environment, 2023, 32 (4): 1847-1871 |
| [32] | Liu L, Ding T, Wang H. Digital economy, technological innovation and green high-quality development of industry: a study case of China[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14 (17): 11078 |
| [33] |
温忠麟, 叶宝娟. 中介效应分析: 方法和模型发展[J]. 心理科学进展, 2014, 22 (5): 731-745.
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731 |
|
Wen Z L, Ye B J. Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models[J]. Advances in Psychological Science, 2014, 22 (5): 731-745 (in Chinese)
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731 |
|
| [34] | Jaffe A B. Technology opportunity and spillovers of R&D: evidence from firms patents, profits, and market value[J]. Economics, Engineering Corporate Finance: Valuation, 1986, 76: 984-1001 |
| [35] | Paci R, Usai S. Knowledge flows across European regions[J]. The Annals of Regional Science, 2009, 43: 669-690 |
| [36] | 杨海生, 陈少凌, 周永章. 地方政府竞争与环境政策: 来自中国省份数据的证据[J]. 南方经济, 2008 (6): 15-30. |
| Yang H S, Chen S L, Zhou Y Z. Local government competition and environmental policy empirical: evidence from province governments in China[J]. South China Journal of Economics, 2008 (6): 15-30 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | 黄亮雄, 王贤彬, 刘淑琳. 经济增长目标与激进城镇化: 来自夜间灯光数据的证据[J]. 世界经济, 2021, 44 (6): 97-122. |
| Huang L X, Wang X B, Liu S L. Economic growth target and radical urbanization: evidence from satellite night-light data[J]. The Journal of World Economy, 2021, 44 (6): 97-122 (in Chinese) | |
| [38] | 王雅晴, 谭德明, 张佳田, 等. 我国城市发展与能源碳排放关系的面板数据分析[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40 (21): 7897-7907. |
| Wang Y Q, Tan D M, Zhang J T, et al. The impact of urbanization on carbon emissions: analysis of panel data from 158 cities in China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40 (21): 7897-7907 (in Chinese) | |
| [39] | 白俊红, 陈新. 数字经济、空间溢出效应与区域创新效率[J]. 研究与发展管理, 2022, 34 (6): 67-78. |
| Bai J H, Chen X. Digital economy, spatial spillover effect and regional innovation efficiency[J]. R&D Management, 2022, 34 (6): 67-78 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 王军, 朱杰, 罗茜. 中国数字经济发展水平及演变测度[J]. 数量经济技术经济研究, 2021, 38 (7): 26-42. |
| Wang J, Zhu J, Luo Q. Research on the measurement of China’s digital economy development and the characteristics[J]. Journal of Quantitative & Technological Economics, 2021, 38 (7): 26-42 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 谢文倩, 高康, 余家凤. 数字经济、产业结构升级与碳排放[J]. 统计与决策, 2022, 38 (17): 114-118. |
| Xie W Q, Gao K, Yu J F. Digital economy, industrial structure upgrading, and carbon emissions[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2022, 38 (17): 114-118 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 余姗, 樊秀峰, 蒋皓文. 数字经济发展对碳生产率提升的影响研究[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2022, 37 (7): 26-35. |
| Yu S, Fan X F, Jiang H W. Research on the impact of digital economy development on carbon productivity improvement[J]. Journal of Statistics and Information, 2022, 37 (7): 26-35 (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 刘军, 杨渊鋆, 张三峰. 中国数字经济测度与驱动因素研究[J]. 上海经济研究, 2020 (6): 81-96. |
| Liu J, Yang Y Y, Zhang S F. Research on the measurement and driving factors of China’s digital economy[J]. Shanghai Journal of Economics, 2020 (6): 81-96 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 邵帅, 李欣, 曹建华, 等. 中国雾霾污染治理的经济政策选择: 基于空间溢出效应的视角[J]. 经济研究, 2016, 51 (9): 73-88. |
| Shao S, Li X, Cao J H, et al. China’s economic policy choices for governing smog pollution based on spatial spillover effects[J]. Economic Research Journal, 2016, 51 (9): 73-88 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | Zhang D, Zhao M, Wang Y, et al. Technological innovation and its influence on energy risk management: unpacking China’s energy consumption structure optimization amidst climate change[J]. Energy Economics, 2024, 131: 107321. |
| [46] | 刘传明, 孙喆, 张瑾. 中国碳排放权交易试点的碳减排政策效应研究[J]. 中国人口?资源与环境, 2019, 29 (11): 49-58. |
| Liu C M, Sun Z, Zhang J. Research on the effect of carbon emission reduction policy in China’s carbon emissions trading pilot[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2019, 29 (11): 49-58 (in Chinese) | |
| [47] | 赵涛, 张智, 梁上坤. 数字经济、创业活跃度与高质量发展: 来自中国城市的经验证据[J]. 管理世界, 2020, 36 (10): 65-76. |
| Zhao T, Zhang Z, Liang S K. Digital economy, entrepreneurship, and high-quality economic development: empirical evidence from urban China[J]. Journal of Management World, 2020, 36 (10): 65-76 (in Chinese) | |
| [48] | Meng Z, Li W B, Chen C, et al. Carbon emission reduction effects of the digital economy: mechanisms and evidence from 282 cities in China[J]. Land, 2023, 12: 773 |
| [49] |
Dong F, Li Y, Qin C, et al. Information infrastructure and greenhouse gas emission performance in urban China: a difference-in-differences analysis[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 316: 11525
doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115252 pmid: 35594820 |
| [1] | 丁丽媛, 王艳华, 王克. 碳排放权交易的减污降碳协同效应及影响机制[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(6): 786-798. |
| [2] | 谭显春, 高瑾昕, 曾桉, 幸绣程. 绿色金融改革创新试验区政策对碳排放的影响评估[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 213-226. |
| [3] | 许光清, 吴静怡. 碳信息披露与资本市场开放——基于沪港通与深港通的实践检验[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2023, 19(2): 227-237. |
| [4] | 宝哲, 周小亮. 数字赋能与城市碳排放——基于下一代互联网示范城市的准自然试验[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2022, 18(4): 503-508. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||