Climate Change Research ›› 2021, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (4): 400-409.doi: 10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.014
Special Issue: 减污降碳协同增效专栏
• Pollutants and GHGs reduction synergy to enhance efficiency • Previous Articles Next Articles
Co-control effect evaluation of the energy saving and emission reduction measures in Chinese cement industry
HE Feng1,2, LIU Zheng-Yan3, XING You-Kai1,4, GAO Yu-Bing1,5, MAO Xian-Qiang1( )
)
- 1 School of Environment, Beijing Normal University, Beijing 100875, China
2 Beijing E20 Environment Co., Ltd, Beijing 100195, China
3 Institute of Spatial Planning and Regional Economy, China Academy of Macroeconomic Research, Beijing 100038, China
4 Transport Planning and Research Institute, Ministry of Transport, Laboratory of Transport Pollution Control and Monitoring Technology, Beijing 100028, China
5 Asia-Pacific Consulting Center for Environment and Development, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2021-03-08Revised:2021-04-20Online:2021-07-30Published:2021-08-11 -
Contact:MAO Xian-Qiang E-mail:maoxq@bnu.edu.cn
Cite this article
HE Feng, LIU Zheng-Yan, XING You-Kai, GAO Yu-Bing, MAO Xian-Qiang. Co-control effect evaluation of the energy saving and emission reduction measures in Chinese cement industry[J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(4): 400-409.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.climatechange.cn/EN/10.12006/j.issn.1673-1719.2021.014
| [1] | 高长明. 我国水泥工业低碳转型的技术途径: 兼评联合国新发布的《水泥工业低碳转型技术路线图》[J]. 水泥, 2019 (1):4-8. |
| Gao C M. The technical path of my country’s cement industry’s low-carbon transformation: comment on the “technical roadmap for low-carbon transformation of cement industry” newly released by the United Nations[J]. Cement, 2019 (1):4-8 (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 中国煤炭消费总量控制方案和政策研究项目. 水泥行业“十三五”煤控中期评估及后期展望 [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-01-01]. http://coalcap.nrdc.cn/datum/info?id=92&type=1. |
| China Coal Cap Project Cement Partner. China cement industry Thirteenth Five Year coal cap mid-term evaluation and later-term outlook [R/OL]. 2019 [2021-01-01]. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | Hu T, He J W, Vennomo H, et al. USEPA IES China country study phase IV report: China’s co-control policy study[R]. US: Policy Research Center of SEPA, Development Research Center of State Council, ECON Center for Economic Analysis, 2007 |
| [4] | IPCC. Climate change 2001: mitigation [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001 |
| [5] |
Schwanitz V J, Longden T, Knopf B, et al. The implications of initiating immediate climate change mitigation: a potential for co-benefits?[J]. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2015, 90:166-177
doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2014.01.003 URL |
| [6] |
Shih Y H, Tseng C H. Cost-benefit analysis of sustainable energy development using life-cycle co-benefits assessment and the system dynamics approach[J]. Applied Energy, 2014, 119:57-66
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.031 URL |
| [7] |
Muller N Z. The design of optimal climate policy with air pollution co-benefits[J]. Resource and Energy Economics, 2012, 34(4):696-722
doi: 10.1016/j.reseneeco.2012.07.002 URL |
| [8] |
Wagner F, Amann M, Borken-Kleefeld J, et al. Sectoral marginal abatement cost curves: implications for mitigation pledges and air pollution co-benefits for annex I countries[J]. Sustainability Science, 2012, 7(2):169-184
doi: 10.1007/s11625-012-0167-3 URL |
| [9] |
Shrestha R M, Pradhan S. Co-benefits of CO2 emission reduction in a developing country[J]. Energy Policy, 2010, 38(5):2586-2597
doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2010.01.003 URL |
| [10] |
Markandya A, Armstrong B J, Hales S, et al. Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: overview and implications for policy makers[J]. The Lancet, 2009, 374(9706):2006-2015
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61715-3 URL |
| [11] |
Groosman B, Muller N Z, O’Neill-Toy E. The ancillary benefits from climate policy in the United States[J]. Environmental and Resource Economics, 2011, 50(4):585-603
doi: 10.1007/s10640-011-9483-9 URL |
| [12] |
Zeng A, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Regional co-control plan for local air pollutants and CO2 reduction: method and practice[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 140:1226-1235
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.037 URL |
| [13] | 邢有凯, 毛显强, 冯相昭, 等. 城市蓝天保卫战行动协同控制局地大气污染物和温室气体效果评估: 以唐山市为例[J]. 中国环境管理, 2020, 12(4):20-28. |
| Xing Y K, Mao X Q, Feng X Z, et al. Assessment of co-control effectiveness of implementing blue sky defense action plan at city level: a case study of Tangshan city[J]. China Environmental Management, 2020, 12(4):20-28 (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 李丽平, 姜苹红, 李雨青, 等. 湘潭市“十一五”总量减排措施对温室气体减排协同效应评价研究[J]. 环境与可持续发展, 2012, 37(1):36-40. |
| Li L P, Jiang P H, Li Y Q, et al. Study of co-benefits assessment of pollution reduction on greenhouse gas reduction in Xiangtan during 11th Five-Year Plan[J]. Environment and Sustainable Development, 2012, 37(1):36-40 (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 李丽平, 周国梅, 季浩宇. 污染减排的协同效应评价研究: 以攀枝花市为例[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2010, 20(5):91-95. |
| Li L P, Zhou G M, Ji H Y. Study of co-benefits assessment of pollution reduction: a case study in Panzhihua[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2010, 20(5):91-95 (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 田春秀, 李丽平, 胡涛, 等. 气候变化与环保政策的协同效应[J]. 环境保护, 2009 (12):67-68. |
| Tian C X, Li L P, Hu T, et al. Co-effect between climate change and environmental protection policies[J]. Environmental Protection, 2009 (12):67-68 (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Co-control of local air pollutants and CO2 from the Chinese coal-fired power industry[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2014, 67:220-227
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.12.017 URL |
| [18] |
Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Co-control of local air pollutants and CO2 in the Chinese iron and steel industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(21):12002-12010
doi: 10.1021/es4021316 URL |
| [19] | 刘胜强, 毛显强, 胡涛, 等. 中国钢铁行业大气污染与温室气体协同控制路径研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(7):168-174. |
| Liu S Q, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Roadmap of co-control of air pollutants and GHGs in iron and steel industry in China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 35(7):168-174 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 毛显强, 邢有凯, 胡涛, 等. 中国电力行业硫、氮、碳协同减排的环境经济路径分析[J]. 中国环境科学, 2012, 32(4):748-756. |
| Mao X Q, Xing Y K, Hu T, et al. An environmental-economic analysis of carbon, sulfur and nitrogen co-reduction path for China’s power industry[J]. China Environmental Science, 2012, 32(4):748-756 (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 高玉冰, 毛显强, Gabriel C, 等. 城市交通大气污染物与温室气体协同控制效应评价: 以乌鲁木齐市为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014 (11):2985-2992. |
| Gao Y B, Mao X Q, Gabriel C, et al. Assessment of co-control effects for air pollutants and greenhouse gases in urban transport: a case study in Urumqi[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014 (11):2985-2992 (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
Xue B, Ma Z X, Geng Y, et al. A life cycle co-benefits assessment of wind power in China[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015, 41:338-346
doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.056 URL |
| [23] |
Ma Z X, Xue B, Geng Y, et al. Co-benefits analysis on climate change and environmental effects of wind-power: a case study from Xinjiang, China[J]. Renewable Energy, 2013, 57:35-42
doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2013.01.018 URL |
| [24] | 毛显强, 曾桉, 刘胜强, 等. 钢铁行业技术减排措施硫、氮、碳协同控制效应评价研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012 (5):1253-1260. |
| Mao X Q, Zeng A, Liu S Q, et al. Assessment of SO2, NOx and CO2 co-control effects by technological reduction measures in iron & steel industry[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012 (5):1253-1260 (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 顾阿伦, 滕飞, 冯相昭. 主要部门污染物控制政策的温室气体协同效果分析与评价[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2016, 26(2):10-17. |
| Gu A L, Teng F, Feng X Z. Assessment and analysis on co-benefits of pollution control and greenhouse gases emission reduction in key sectors[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2016, 26(2):10-17 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Lei Y, Zhang Q, Nielsen C, et al. An inventory of primary air pollutants and CO2 emissions from cement production in China, 1990-2020[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2011, 45(1):147-154
doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.09.034 URL |
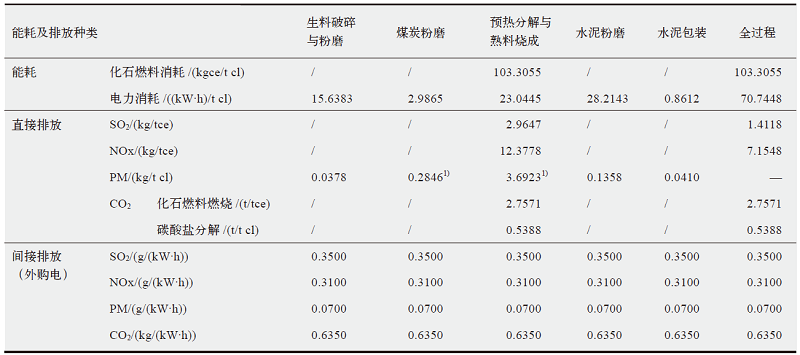
| [27] | 周颖, 张宏伟, 蔡博峰, 等. 水泥行业常规污染物和二氧化碳协同减排研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2013, 36(12):164-168. |
| Zhou Y, Zhang H W, Cai B F, et al. Synergetic reduction of local pollutants and CO2 from cement industry[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 36(12):164-168 (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
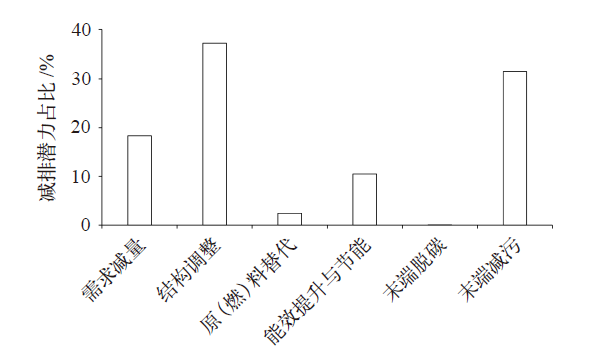
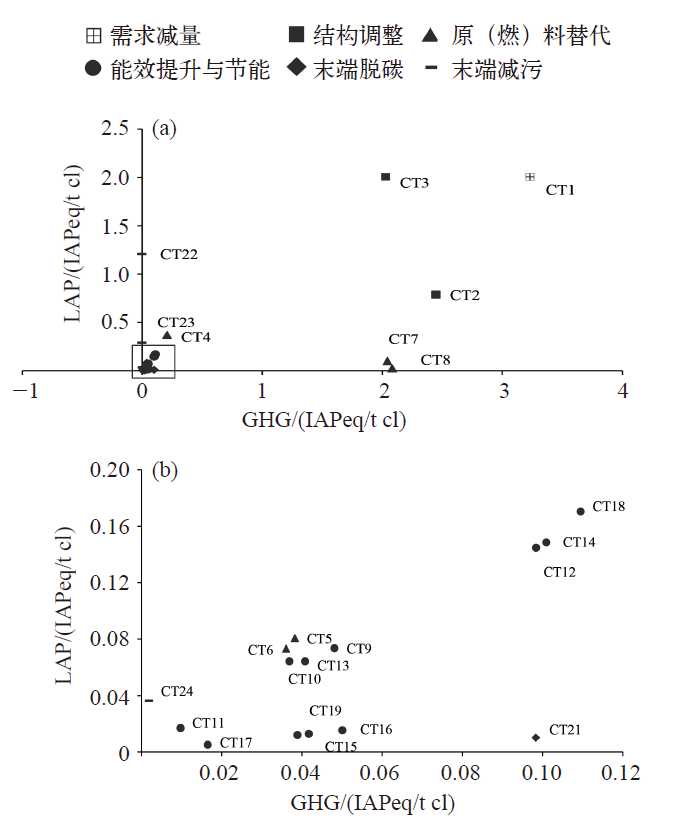
Feng X Z, Oleg L, Qin H. Co-controlling CO2 and NOx emission in China’s cement industry: an optimal development pathway study[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2018, 9(1):34-42
doi: 10.1016/j.accre.2018.02.004 URL |
| [29] |
Pang J, Shi Y C, Feng X Z, et al. Analysis on impacts and co-abatement effects of implementing the low carbon cement standard[J]. Advances in Climate Change Research, 2014, 5(1):41-50
doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2014.041 URL |
| [30] |
Zhang S H, Ren H T, Zhou W J, et al. Assessing air pollution abatement co-benefits of energy efficiency improvement in cement industry: a city level analysis[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 185:761-771
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.293 URL |
| [31] | 王同桂, 吴莉萍, 张灿, 等. 碳减排项目协同效益评价体系构建研究: 以重庆市某水泥厂余热发电项目为例[J]. 环境影响评价, 2019, 41(6):86-90. |
| Wang T G, Wu L P, Zhang C, et al. Study on construction of cooperative benefit evaluation system for carbon emission reduction projects: taking the project of waste heat power generation in a cement plant in Chongqing as an example[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2019, 41(6):86-90 (in Chinese) | |
| [32] |
Yang X, Teng F, Wang G H. Incorporating environmental co-benefits into climate policies: a regional study of the cement industry in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 112:1446-1453
doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.040 URL |
| [33] | Hasanbeigi A, Lobscheid A, Lu H Y, et al. Quantifying the co-benefits of energy-efficiency policies: a case study of the cement industry in Shandong province, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2013, 458:624-636 |
| [34] | 毛显强, 曾桉, 胡涛, 等. 技术减排措施协同控制效应评价研究[J]. 中国人口∙资源与环境, 2011, 21(12):1-7. |
| Mao X Q, Zeng A, Hu T, et al. Study of coordinate control effect assessment of technological measures for emissions reduction[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 2011, 21(12):1-7 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] |
Zeng A, Mao X Q, Hu T, et al. Regional co-control plan for local air pollutants and CO2 reduction: method and practice[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 140:1226-1235
doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.10.037 URL |
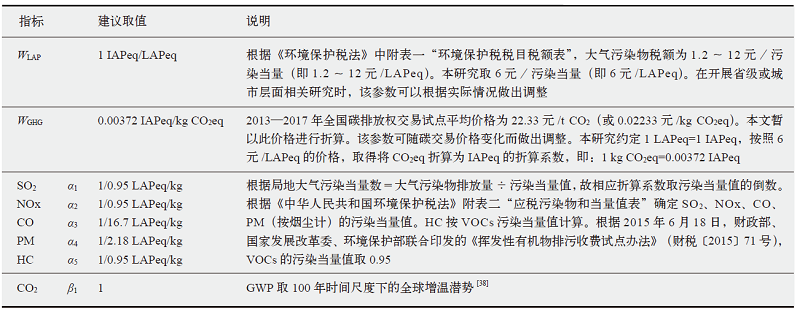
| [36] | 全国人大常委会. 中华人民共和国环境保护税法(2018年修正)[Z]. 北京: 中国法制出版社, 2018. |
| Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress. Environmental protection tax law of the People’s Republic of China (Amended in 2018)[Z]. Beijing: China Legal Publishing House, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [37] | Ministry of Finance, National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Environmental Protection. Pilot measures for volatile organic compound discharge fees (Caishui [2015] No. 71) [EB/OL]. 2015 [2021-02-01]. http://szs.mof.gov.cn/zhengcefabu/201506/t20150625_1261143.htm (in Chinese) |
| [38] | IPCC. Climate change 2014: synthesis report [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014 |
| [39] | 沈飞, 陈寿雨. 人力资本, 物质资本与经济增长关联研究: 基于长三角区域的实证[J]. 科技管理研究, 2014, 34(8):96-98. |
| Shen F, Chen S Y. Empirical study on correlation of human capital and economic growth in Yangze River Delta region based on the production function framework[J]. Science and Technology Management Research, 2014, 34(8):96-98 (in Chinese) | |
| [40] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2015年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2015. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2015, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2015 (in Chinese) | |
| [41] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2016年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2017. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2016, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [42] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2017年本,节能部分)[R]. 北京, 2018. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2017, Energy saving part)[R]. Beijing, 2018 (in Chinese) | |
| [43] | 国家发展和改革委员会. 国家重点节能低碳技术推广目录(2017年本,低碳部分)[R]. 北京, 2017. |
| National Development and Reform Commission. National key energy-saving and low-carbon technology promotion catalog (2017, Low carbon part)[R]. Beijing, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [44] | 熊华文, 符冠云. 重塑能源:面向2050年能源消费和生产革命路线图∙中国∙工业卷[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2017. |
| Xiong H W, Fu G Y. Reshaping energy: a roadmap for the energy consumption and production revolution in 2050∙China∙industry volume [M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2017 (in Chinese) | |
| [45] | 中国水泥协会. 水泥行业煤炭消费总量控制方案及政策研究 [R]. 北京, 2015. |
| China Cement Association. Research on total coal consumption control plan and policy in cement industry[R]. Beijing, 2015 (in Chinese) | |
| [46] | 工业和信息化部. 建材工业十三五规划(2016—2020年)[Z]. 北京, 2016. |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. 13th Five Year Plan for building materials industry (2016-2020)[Z]. Beijing, 2016 (in Chinese) | |
| [47] | 搜狐网. 全国最新电网销售电价汇总(9月1日执行)[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. https://www.sohu.com/a/271827080_146940. |
| Sohu. Summary of the latest nationwide power grid sales price (implemented on September 1)[EB/OL]. 2018 [2021-01-01]. https://www.sohu.com/a/271827080_146940. | |
| [48] | 王庆一. 2019能源数据 [R]. 北京: 绿色创新发展中心, 2019. |
| Wang Q Y. 2019 energy data[R]. Beijing: Innovative Green Development Program, 2019 (in Chinese) |
| [1] | GAO Yu-Bing, XING You-Kai, HE Feng, KUAI Peng, MAO Xian-Qiang. Research on co-control effectiveness evaluation of energy saving and emission reduction measures in China’s iron and steel industry [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(4): 388-399. |
| [2] | XING You-Kai, LIU Zheng-Yan, MAO Xian-Qiang, GAO Yu-Bing, HE Feng, YU Hong. Research on co-control effect of environmental economic policies in China’s transportation sector [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(4): 379-387. |
| [3] | WANG Min, FENG Xiang-Zhao, DU Xiao-Lin, WU Li-Ping, ZHAO Meng-Xue, WANG Peng, AN Qi. Evaluation of co-controlling GHGs from pollutant reduction facilities in the industrial sectors, empirical analysis based on data in Chongqing city [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 296-304. |
| [4] | FENG Xiang-Zhao, ZHAO Meng-Xue, WANG Min, DU Xiao-Lin, TIAN Chun-Xiu, GAO Ji. Simulation research on co-controlling pollutants and greenhouse gases emission in China's transportation sector [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 279-288. |
| [5] | MAO Xian-Qiang, ZENG An, XING You-Kai, GAO Yu-Bing, HE Feng. From concept to action: a review of research on co-benefits and co-control of greenhouse gases and local air pollutants reductions [J]. Climate Change Research, 2021, 17(3): 255-267. |
| [6] | Wang Wenjun, Xie Pengcheng, Hu Jilian, Wang Le, Zhao Daiqing. Analysis of the Relative Mitigation Cost Advantages of Carbon Tax and ETS for the Cement Industry [J]. Climate Change Research, 2016, 12(1): 53-60. |
| [7] | Xu Jinhua Fan Ying. Potential Energy Saving and CO2 Emission Reduction in China’s Cement Industry [J]. Climate Change Research, 2013, 9(5): 341-349. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||