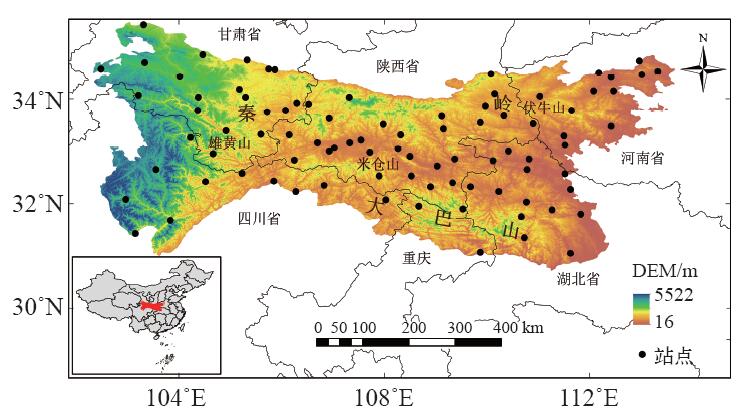
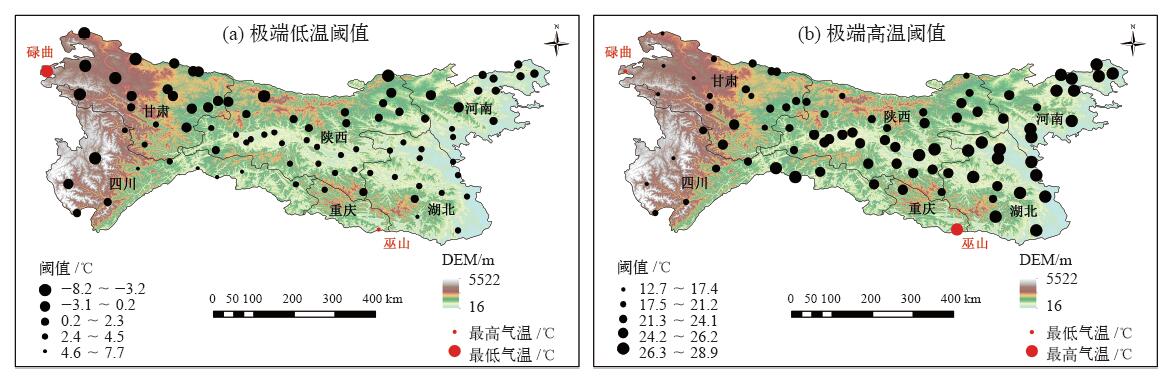
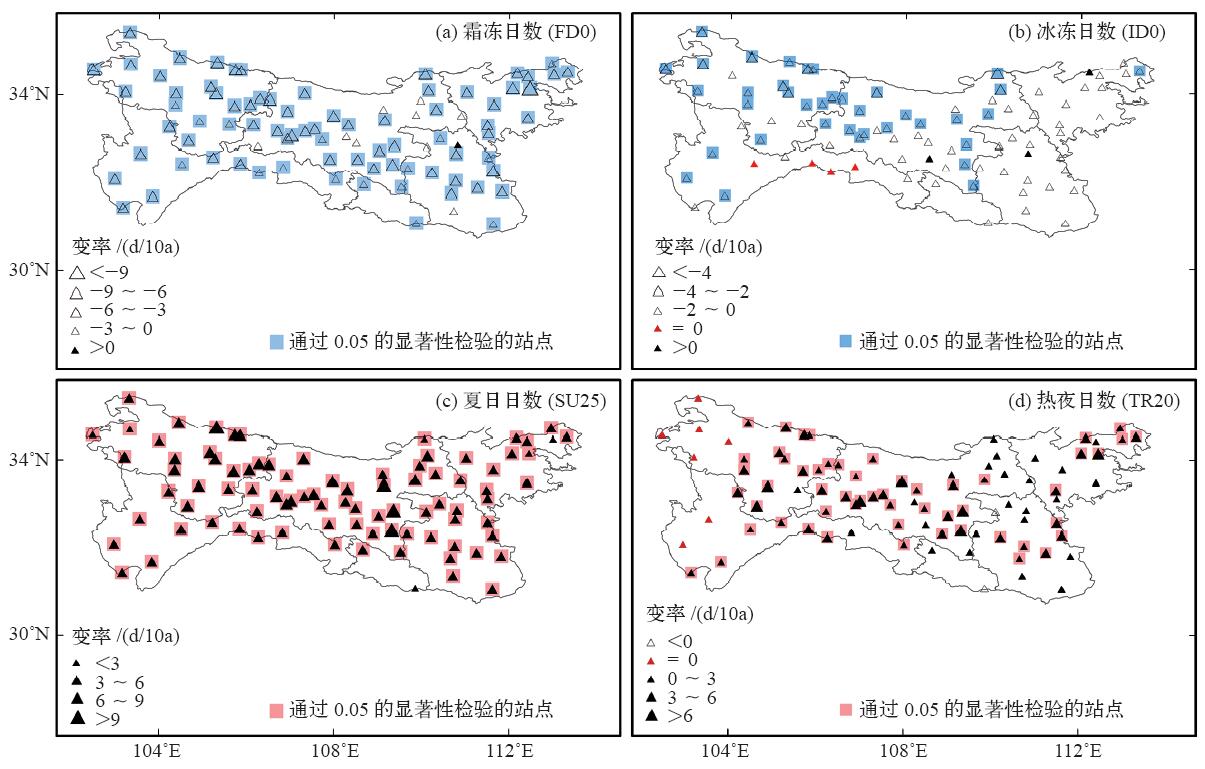
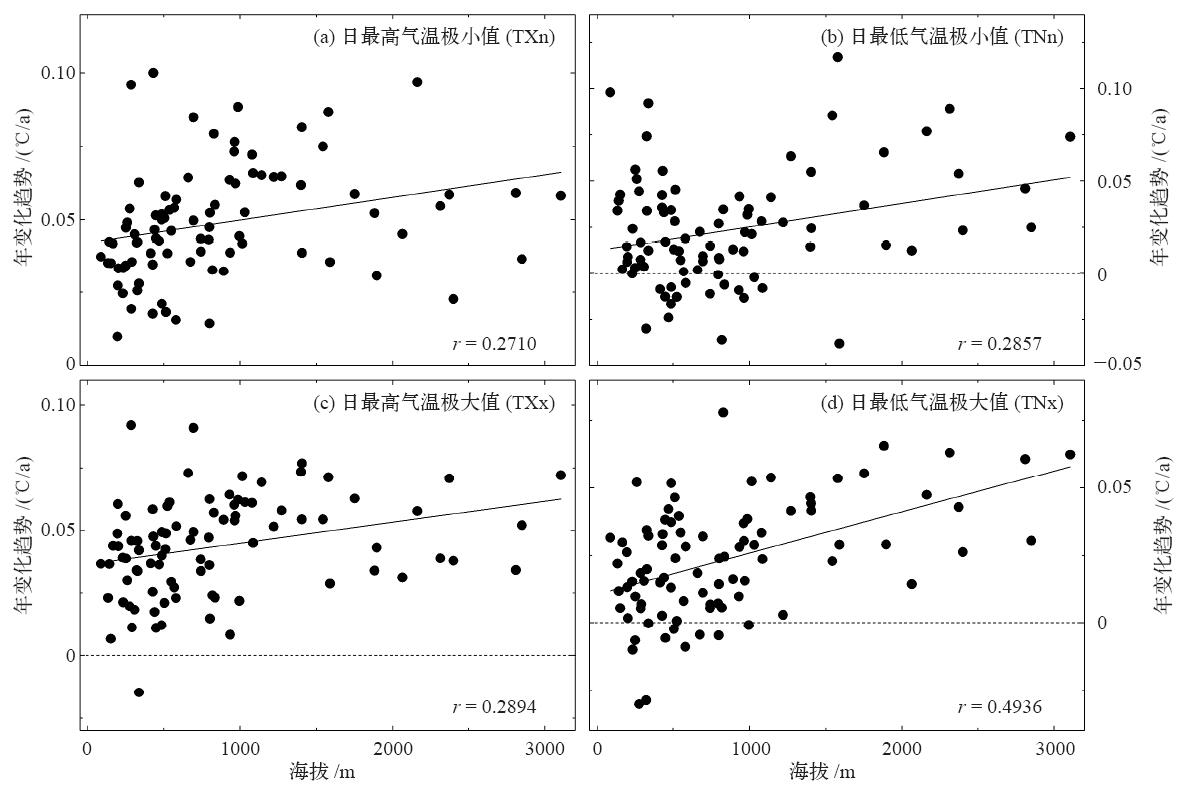
| [1] | IPCC. Climate change 2013: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013 | | [2] | IPCC. Climate change 2007: the physical science basis [M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007 | | [3] | Alexander L V, Zhang X, Peterson T C , et al. Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation[J]. Geophysical Research, 2006,111:1-22 | | [4] | Choi G Y, Collins D, Ren G Y , et al. Changes in means and extreme events of temperature and precipitation in the Asian-Pacific network region 1955-2007[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2009,29(13):1906-1925 | | [5] | Christidis N, Stott P A, Zwiers F W , et al. Fast-track attribution assessments based on pre-computed estimates of changes in the odds of warm extremes[J]. Climate Dynamics, 2015,45:1547-1564 | | [6] | 赵军, 师银芳, 王大为 , 等. 1961—2008年中国大陆极端气温时空变化分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2013,26(3):52-56 | | [7] | 任国玉, 封国林, 严中伟 . 中国极端气候变化观测研究回顾与展望[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2010,15(4):337-353 | | [8] | 王冀, 蒋大凯, 张金玲 , 等. 华北地区极端气候事件的时空变化规律分析[J]. 中国农业气象, 2012,33(2):166-173 | | [9] | Zhang Y J, Gao Z Q, Pan Z T , et al. Spatiotemporal variability of extreme temperature frequency and amplitude in China[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2017,185:131-141 | | [10] | 张立伟, 宋春英, 延军平 . 秦岭南北年极端气温的时空变化趋势研究[J]. 地理科学, 2011,31(8):1007-1011 | | [11] | 史帆, 赵景波 . 1960—2013年陕南地区极端气温指数变化研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2016,28(7):96-104 | | [12] | 王钊, 彭艳, 魏娜 . 近52a秦岭南北极端温度变化及其与区域增暖的关系[J]. 干旱气象, 2016,34(2):269-276 | | [13] | Parmesan C . Ecological and evolutionary responses to recent climate change[J]. Annual Review Ecology, Evolution, and Systematicst, 2006,37:637-699 | | [14] | IPCC. Climate change 2007: synreport report [R]. Geneva, Switzerland, 2007: 104 | | [15] | 王琼, 张明军, 王圣杰 , 等. 1962—2011年长江流域极端气温事件分析[J]. 地理学报, 2013,68(5):611-625 | | [16] | 刘青娥, 吴孝情, 陈晓宏 , 等. 珠江流域1960—2012年极端气温的时空变化特征[J]. 自然资源学报, 2015,30(8):1356-1366 | | [17] | Vincent L A, Peterson T C, Barros V R , et al. Observed trends in indices of daily temperature extremes in South American 1960-2000[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005,23(18):5011-5023 | | [18] | Dong B W, Rowan T S , et al. Abrupt summer warming and changes in temperature extreme over Northeast Asia since the mid-1990s: drivers and physical processes[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2016,33(9):1005-1023 | | [19] | Bonsal B R, Zhang X B, Vineent L A , et al. Characteristics of daily and extreme temperature over Canada[J]. Journal of Climate, 2001,5(14):1959-1976 | | [20] | 周雅清, 任国玉 . 中国大陆1956—2008年极端气温事件变化特征分析[J]. 气候与环境研究, 2010,15(4):405-417 | | [21] | Wang B L, Zhang M J, Wei J L , et al. Change in extreme events of temperature and precipitation over Xinjiang, Northwest China, during 1960-2009[J]. Quaternary International, 2013,298:141-151 |
|
 ),Bo-Tao ZHOU2,3,Xin BIN1,Dong-Lei FENG1,4
),Bo-Tao ZHOU2,3,Xin BIN1,Dong-Lei FENG1,4